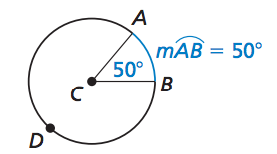
Unit 1 Basics of Geometry
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Midpoint Property
If (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of the endpoints of a segment, then the coordinates of the midpoint are: (X plus X divided by 2, and, Y plus Y divided by 2) Labeled as a coordinate pair (X, Y).
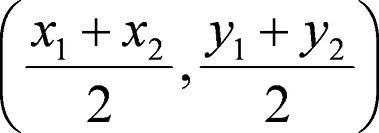
Undefined terms of Geometry
point, line, plane
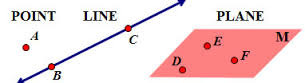
Collinear Points
points that lie on the same line
Coplanar Points
points that lie on the same plane
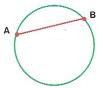
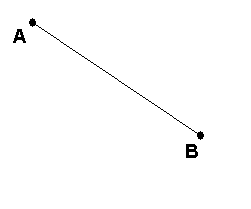
Line Segment
consists of two points called the endpoints and all the points in between them that are collinear with the two points
Congruent segments
segments that have the same measure or length
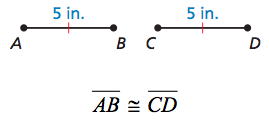
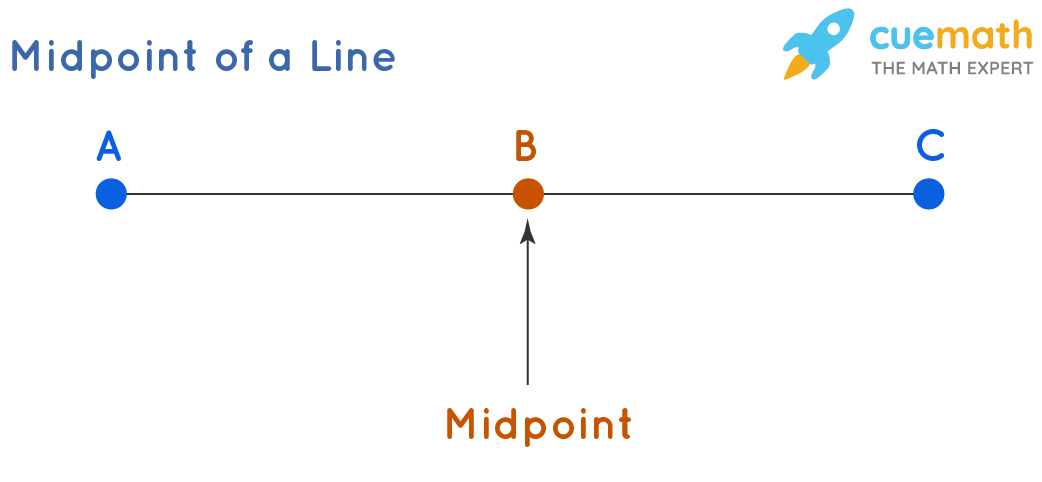
Midpoint of a segment
the point on the segment that is same distance from both endpoints, midpoint bisects the segment
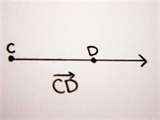
Ray
Portion of a line that contains all the points on the line that are on the same side of the first letter as the second letter
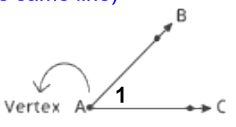
Angle
Two noncollinear rays having a common endpoint.
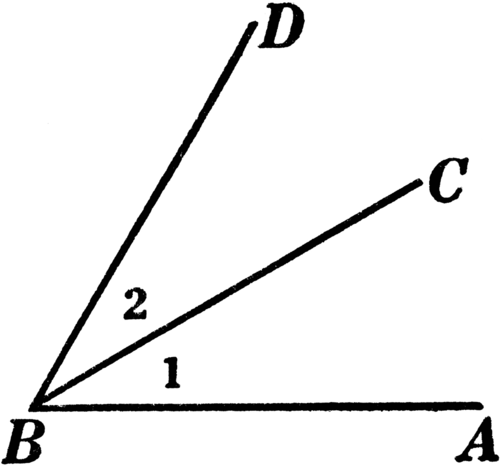
Adjacent Angles
two angles that share a common vertex and side, but have no common interior points
the smallest amount of rotation about the vertex from one ray to the other.
Congruent Angles
two angles that have the same measure
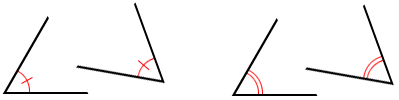
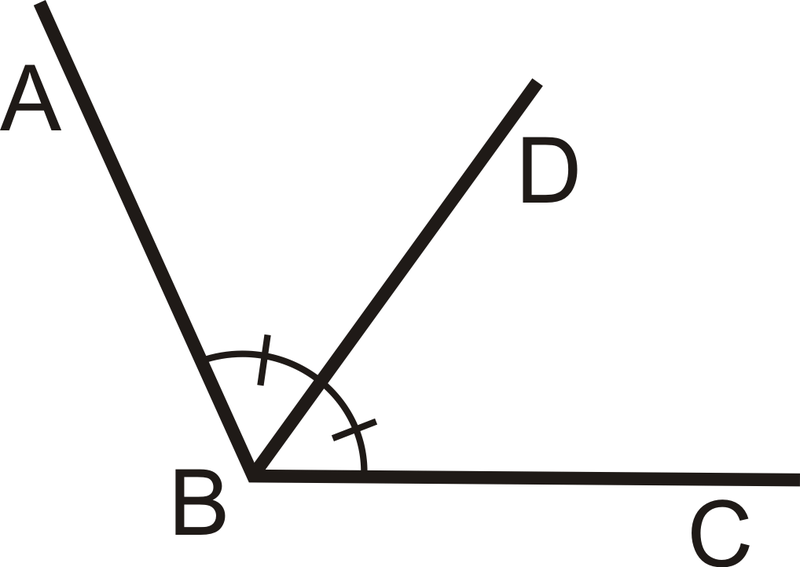
Angle Bisector
a ray that contains the vertex and divides the angle into two congruent angles
Parallel Lines
lines in the same plane that never intersect
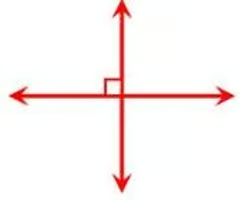
Perpendicular Lines
lines that intersect at right angles (90 degrees)
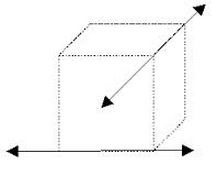
Skew Lines
lines that are not in the same plane and do not intersect
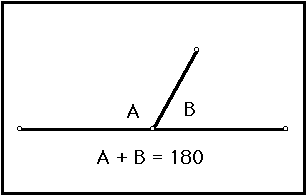
Linear Pair
two adjacent angles whose noncommon sides are opposite rays
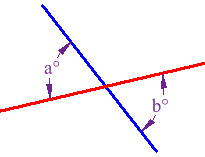
Vertical Angles
angles formed by 2 intersecting lines; they share a common vertex not a side
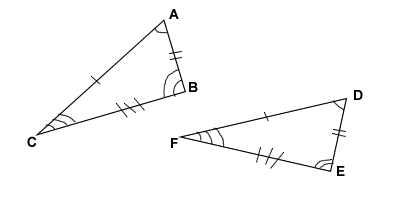
congruent polygons
two polygons whose corresponding sides and angles are congruent
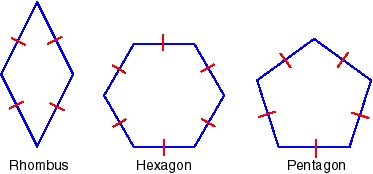
equilateral polygon
a polygon in which all sides are congruent
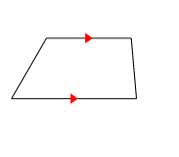
Trapezoid
A quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides
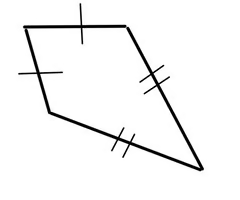
Kite
a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive congruent sides
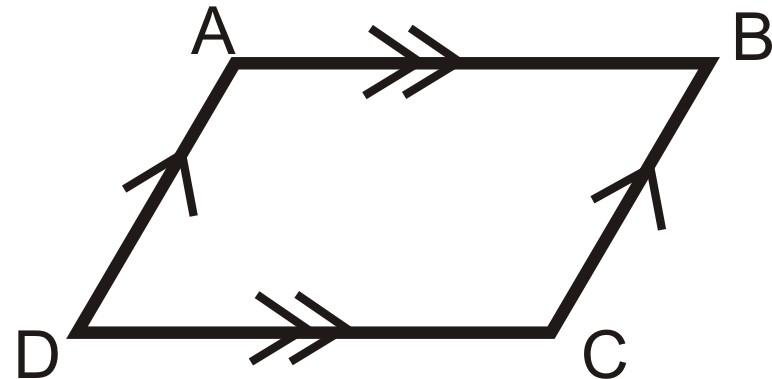
Parallelogram
A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides
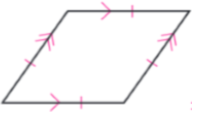
Rhombus
an equilateral parallelogram (all congruent sides, 2 pairs of parallel sides)

Rectangle
an equiangular parallelogram (all congruent angles, 2 pairs of parallel sides)
Square
an equilateral rectangle or an equiangular rhombus or a regular quadrilateral