math 2
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms

A table of values for a function f is given below. Estimate the slope of the tangent line to the curve y = f (x) at x = 1. x 0.9 0.99 1.0 1.01 1.1 f (x) 2.45 2.9405 3.0 3.0605 3.65
6 (use values around 1, don’t actually subtract 1)

if a stone is dropped from a height of 450 meters, its position at time t seconds is given by
s(t) = 450 − 4.9t2.
a. Find the average velocity over the time interval [4, 5].
a. Average velocity on [4,5]: −44.1 m/s.
![<p>a. <strong>Average velocity on [4,5]: </strong>−44.1 m/s.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f36173db-46d7-4a15-a61a-c4434c80a2c6.png)
if a stone is dropped from a height of 450 meters, its position at time t seconds is given by
s(t) = 450 − 4.9t2.
b. Estimate the instantaneous velocity at t = 4 seconds.
-39.2 m/s

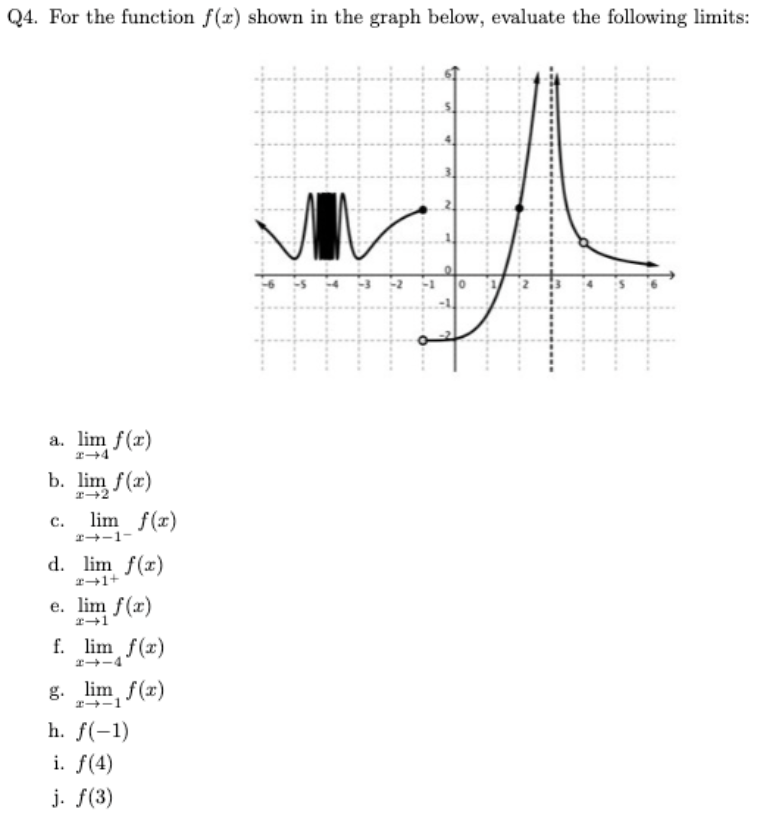
lim
x→4 f (x)
b. lim
x→2 f (x)
c. lim
x→−1−
f (x)
d. lim
x→1+ f (x)
e. lim
x→1 f (x)
f. lim
x→−4 f (x)
g. lim
x→−1 f (x)
h. f (−1)
i. f (4)
j. f (3)
a. limx→4f(x)=1
b. limx→2f(x)=2.
c. limx→−1−f(x)=2.
d. limx→1+f(x)=0.
e. limx→1f(x)=0.
f. limx→−4f(x)does not exist (the function oscillates wildly near x=−4
g. limx→−1f(x)=2.
h. f(−1)=2
i. f(4) does not exist (there is an open circle at (4,1)
j. f(3) does not exist (no value is defined at x=3

Q8. Evaluate the following limits using direct substitution, if possible:
c. lim
x→π(sin x + cos x)
-1
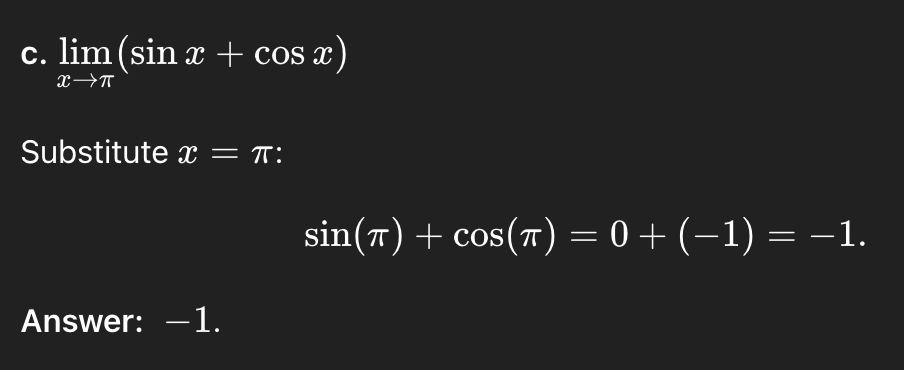

valuate the following limits by factoring or simplifying algebraically:
c. lim
h→0 (4 + h)2 − 16/h
8
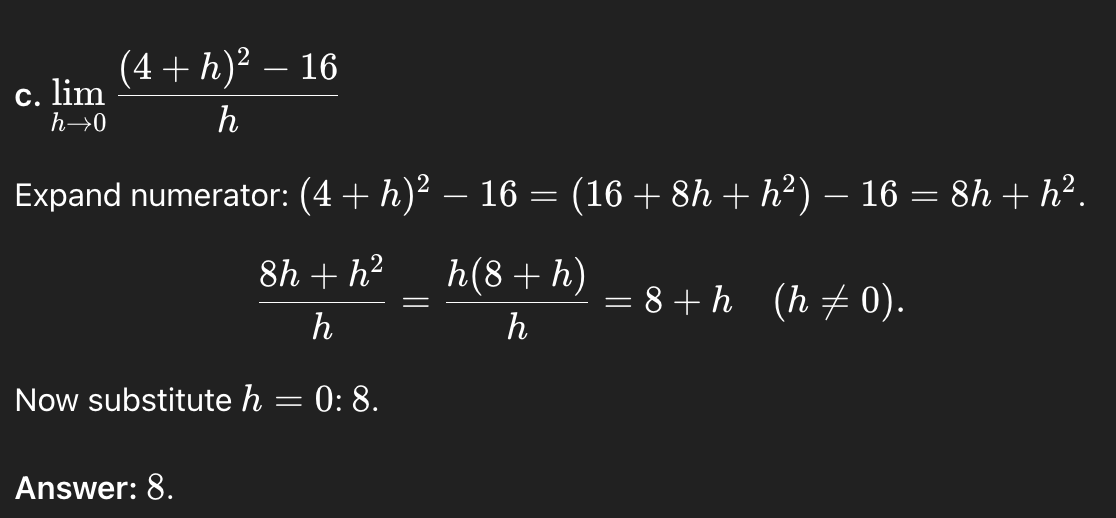

limx→1 x³-1/x²-1
3/2 difference of cubes
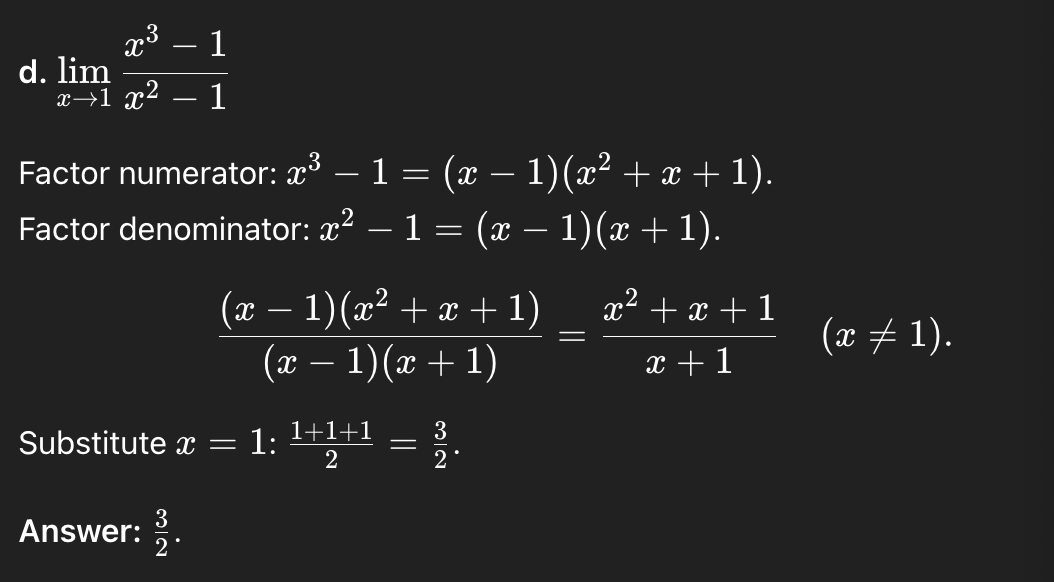

limt→0 t³-4t²/t²-2t
0
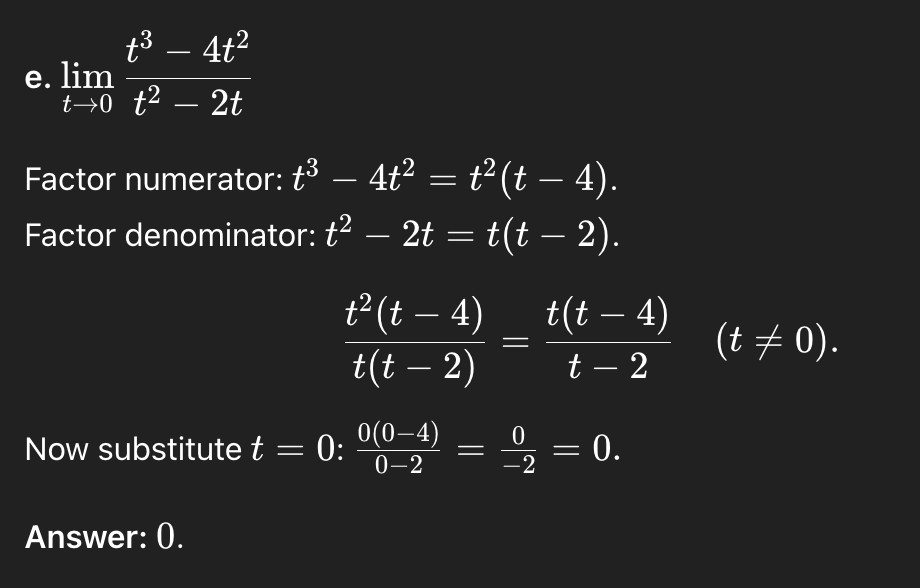

y³+8/y+2 y→-2
12 difference of cubes

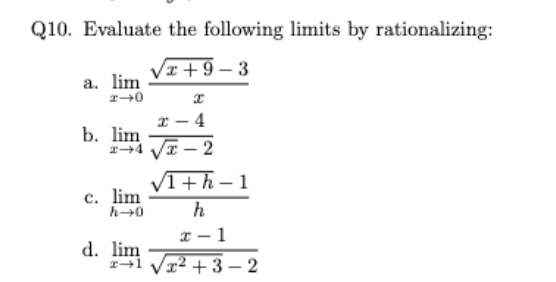
lim
x→0
√x + 9 − 3/
x
1/6 (conjugate)
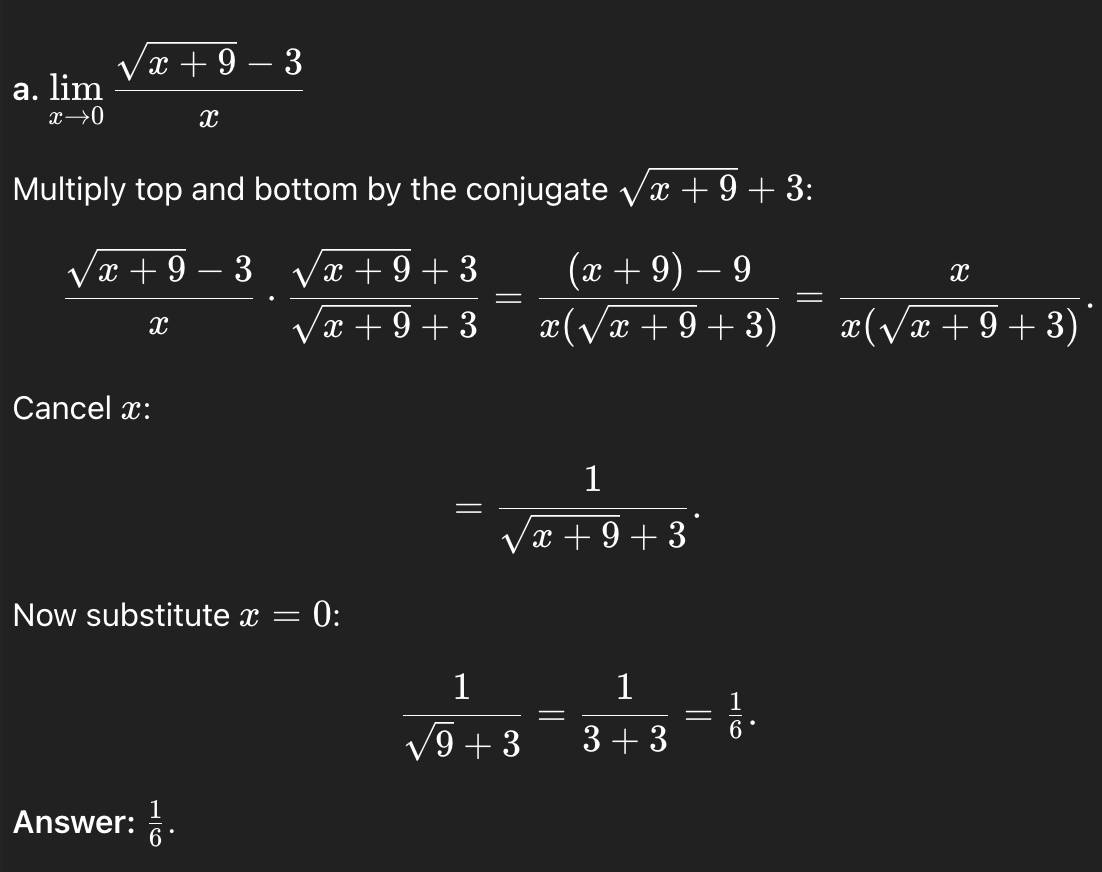
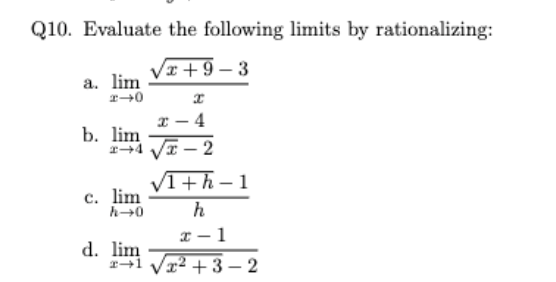
lim
x→4
x − 4/
√x − 2
4 (factor)

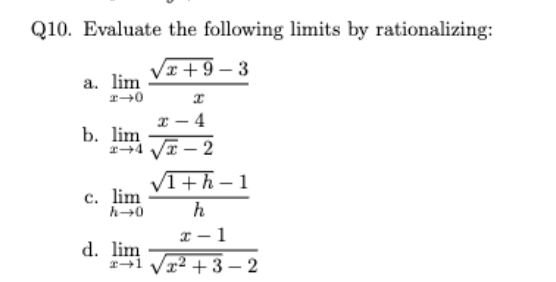
lim x→1
x − 1/
√x2 + 3 − 2
2 (conjugate)


a
5
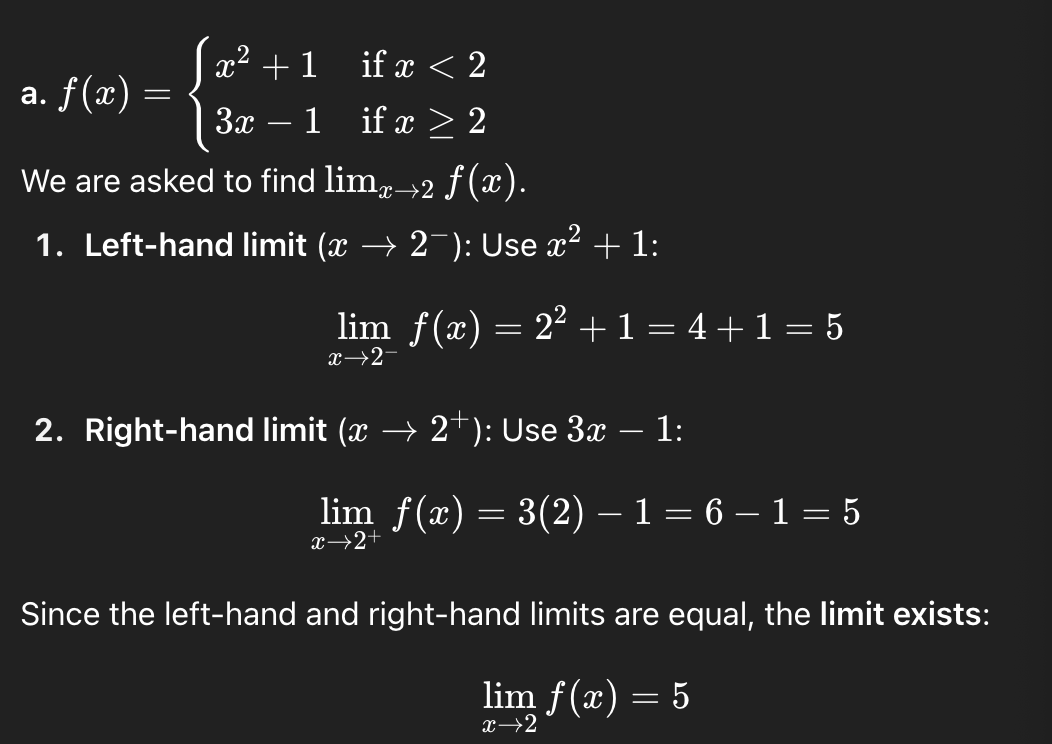

c
6
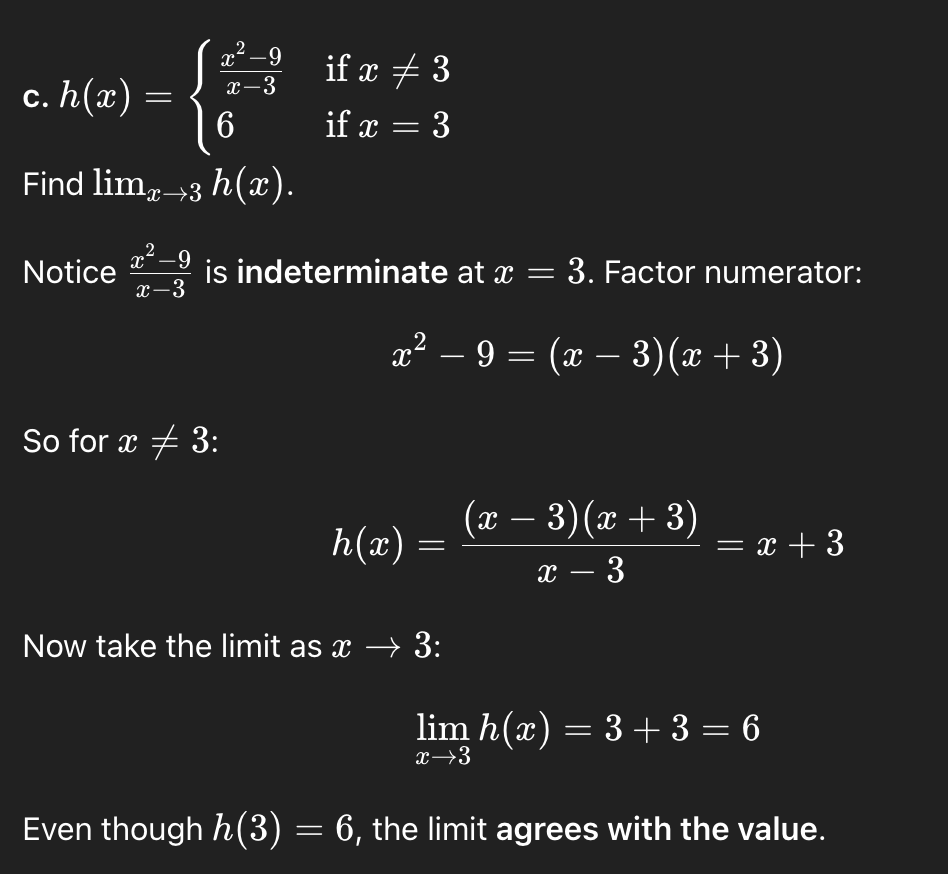

ab
+infinity. -infinity


cd
+infinity, -infinity
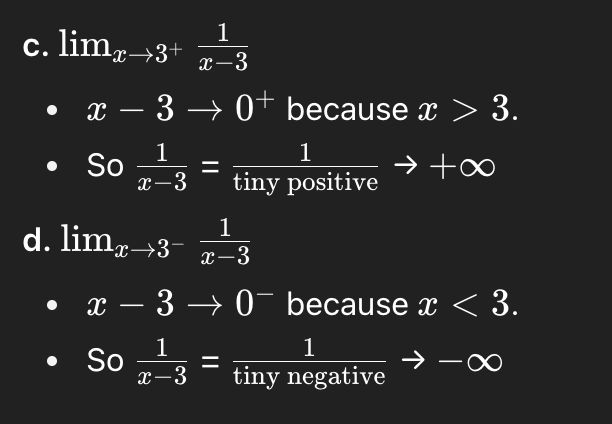

ef
+infinity, +infinity

15
continuous everywehere

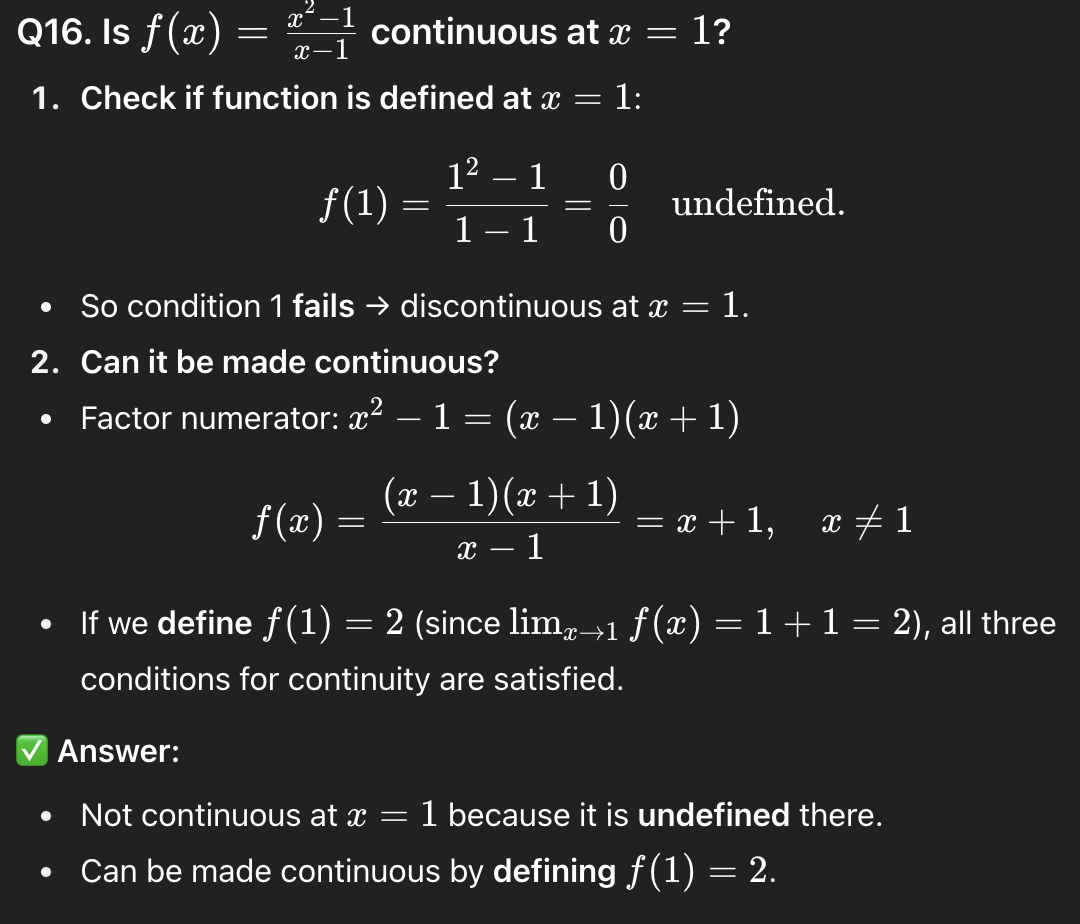
16
not continuous but can be by f(1)=2

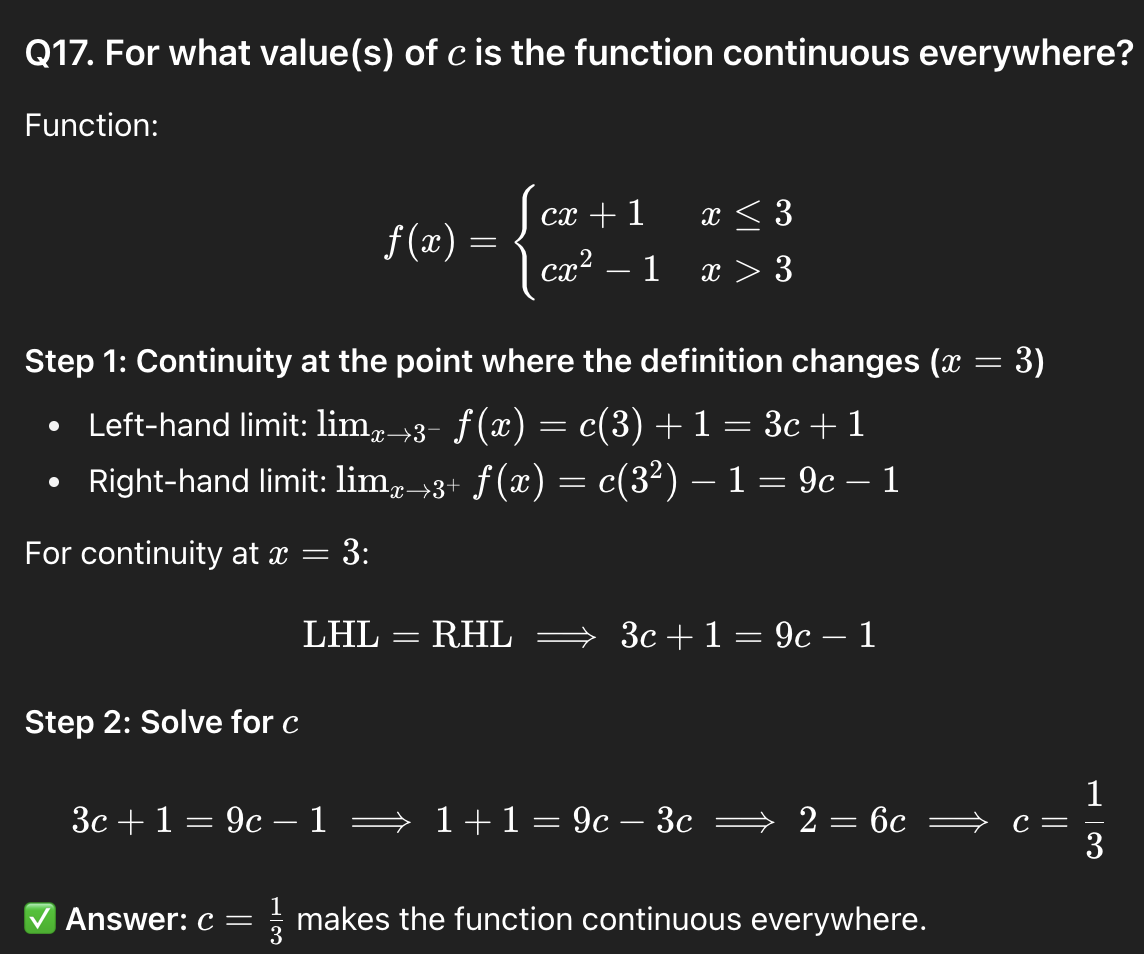
17
1/3
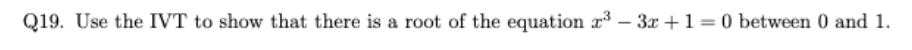
use the IVT to show that there is a root of the equation x3 − 3x + 1 = 0 between 0 and 1.
there is at least one root in the interval (0,1).


bc
∞, 0


ef
−∞, 1


gh
-1,0


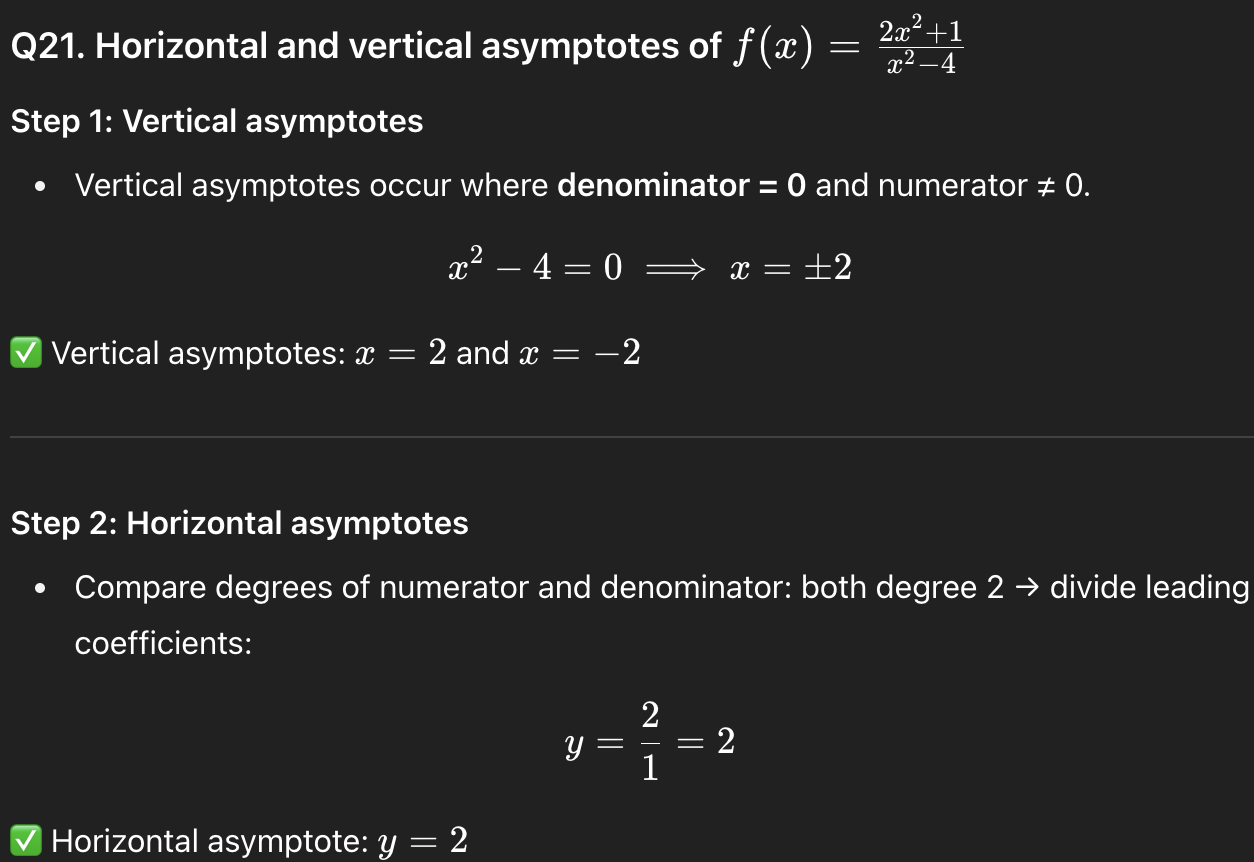
21
2,-2,2

24
-1/a²


25
4x-1


26


28


31


32


33


34


35
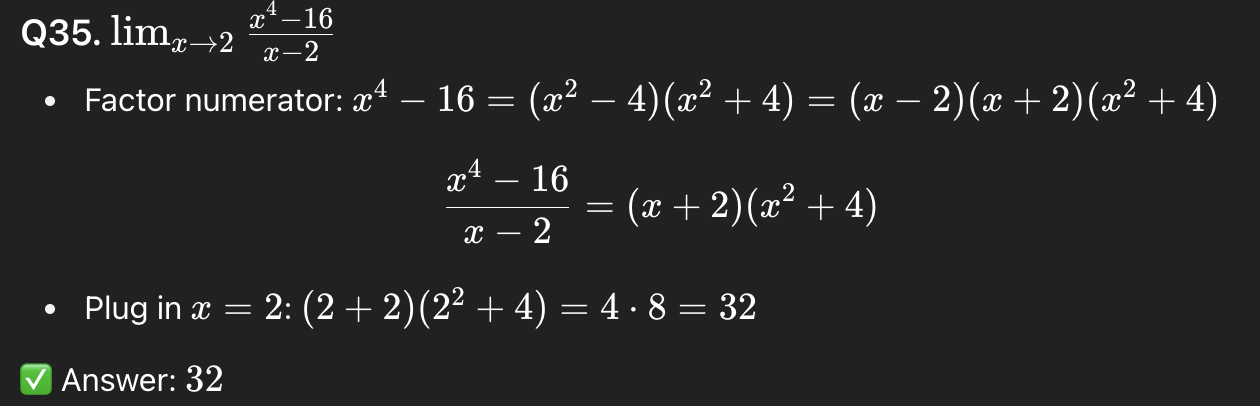

37


38
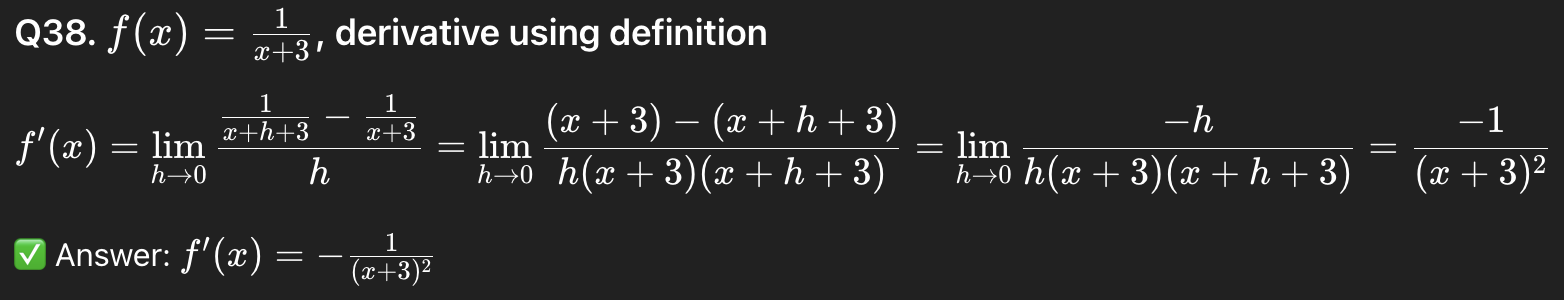

43


44


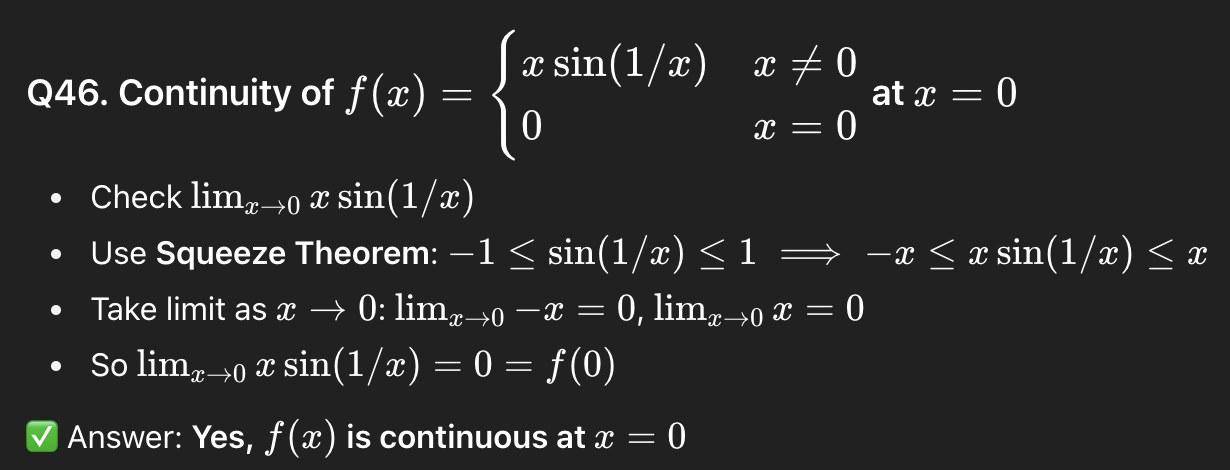
46
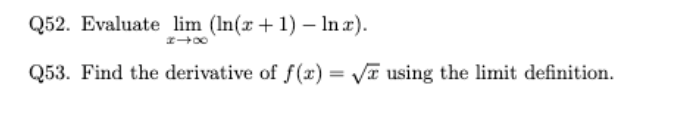
52
53
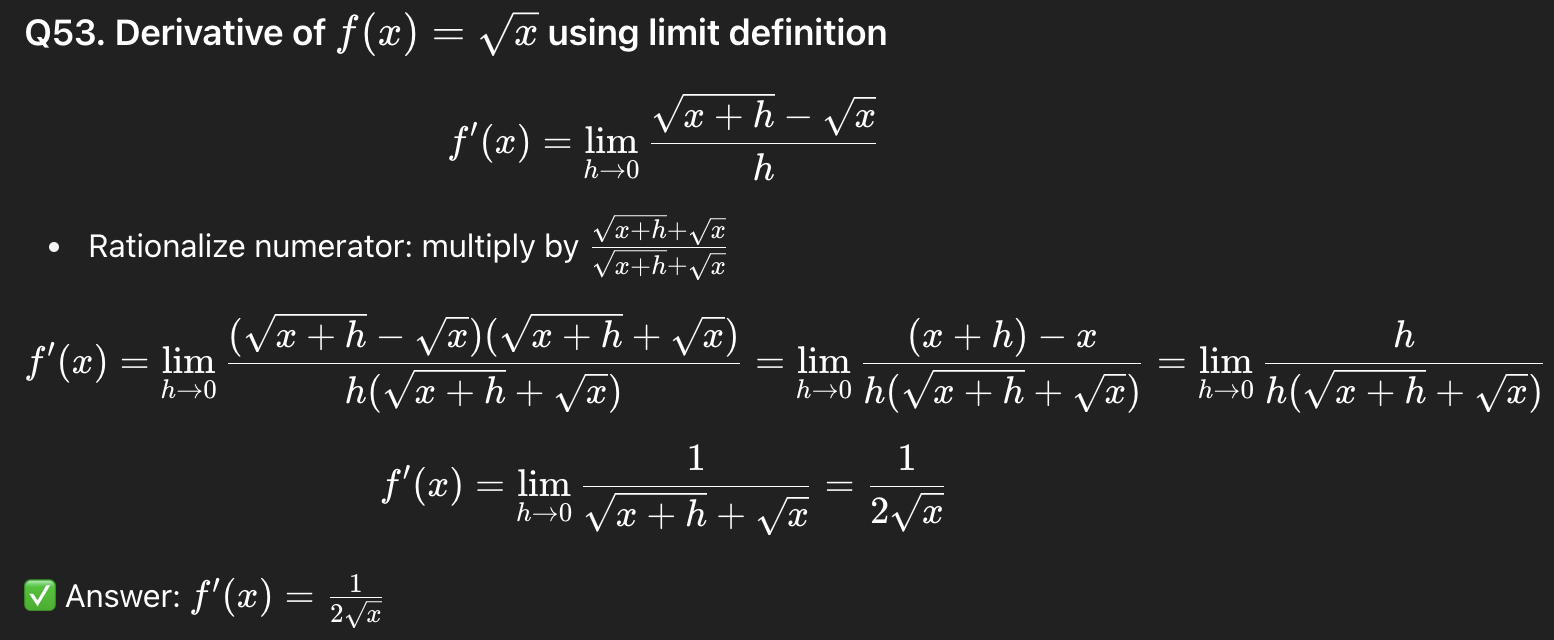

54
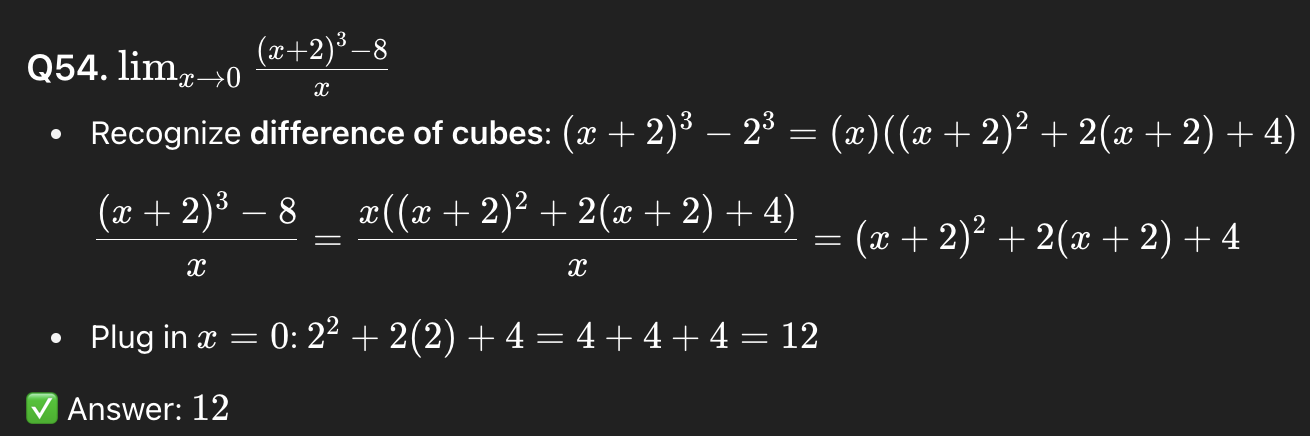

57
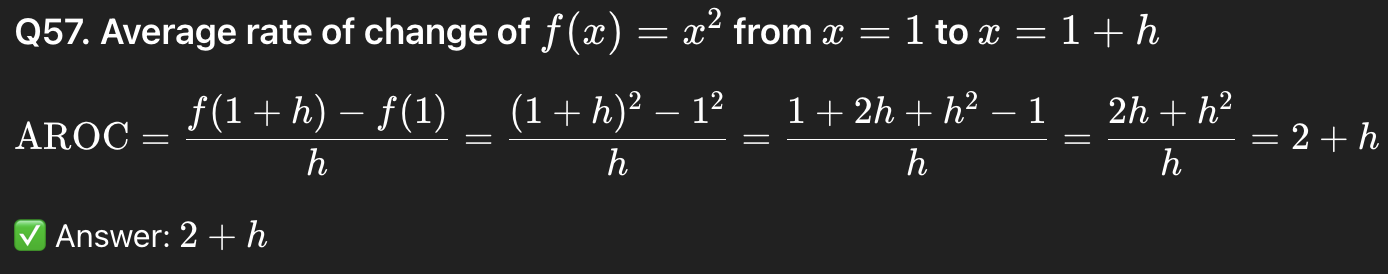

58
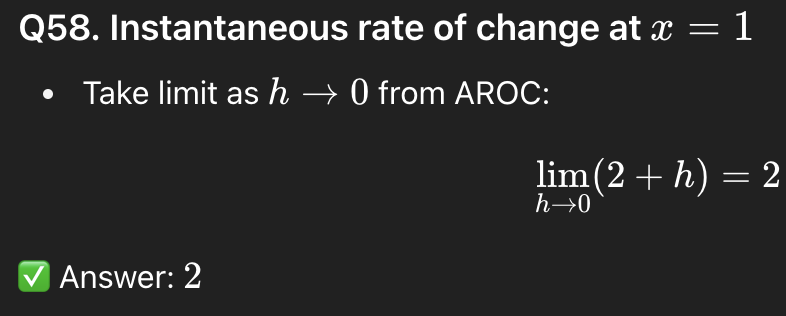

61
