BSC 111: Chapter 20, 21, 23, 25 Definitions and Key Concepts
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/175
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:57 AM on 10/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
176 Terms
1
New cards
Virus
noncellular parasitic agent consisting of outer capsid and innercore of nucleic acid
2
New cards
Obligate Intracellular Pathogens
replicate using the metabolic machinery of host cells
3
New cards
Outer layer of a virus
protein capsid contains genetic material that will attach to a host cell through tissue specificity, lock and key fit, or target immune response
4
New cards
Outer Membranous envelope
outer layer of a virus is derived from the host cell's plasma membrane
5
New cards
Attachment Step(Lytic Cycle )
virus gains based on proteins on a cell and virus (must match)
within the cells of specific living Organisms
-> determined by the structure of proteins in the naked capsid in the spikes of an enveloped virus
within the cells of specific living Organisms
-> determined by the structure of proteins in the naked capsid in the spikes of an enveloped virus
6
New cards
Penetration step (Lytic Cycle)
host cell engulfs virus or injects genome into cell
7
New cards
biosynthesis step (lytic cycle)
viral component synthesized using host cell
8
New cards
Released step(Lytic Cycle)
new viruses exit the host cell through lysis or budding to infect new host cells
9
New cards
Lysogenic Cycle
After penetration, bacterial cell is integrated into bacterial DNA and is passed on when bacteria reproduce. Causes the bacteria to go dormant and will be activited with the chnages in the enviroment
10
New cards
lytic cycle starts immediately
in animal viruses reproduction:
11
New cards
Seasonal FLu (RNA Virus)
-Influenza A-virus: host changes, caused epidhous
-Influenza B and C: only in humans
Rapid mutation rate
-Influenza B and C: only in humans
Rapid mutation rate
12
New cards
HIV/AIDS
Retrovirus:
Animal viruses with an RNA genome that is converted into DNA within the host cell by reverse transcriptase
->AIDS
->Human Immuno Deficiency
Animal viruses with an RNA genome that is converted into DNA within the host cell by reverse transcriptase
->AIDS
->Human Immuno Deficiency
13
New cards
Emerging Viruses
Outbreak of previously unknown disease or known disease that increase in occurrence
-Mutated from existing RNA
-Expanded host range
-Antigenic shift
-vector born
-Mutated from existing RNA
-Expanded host range
-Antigenic shift
-vector born
14
New cards
Viral Diseases in Plants
-Can occur due to varroids
> 10,000 known viruses
> 10,000 known viruses
15
New cards
Viroids
RNA with no capsid
16
New cards
Prions
misfolded proteins that can transmit their misfolded shape onto variants of the same protein
17
New cards
Fatal Neurovegetative Brain Disease
TSEs(transmissible spongiform encephalopathies) caused by prions
-Scrapie
-Chronic Waste Disease
-Kuru
-Mad Cow Disease
-Scrapie
-Chronic Waste Disease
-Kuru
-Mad Cow Disease
18
New cards
Prokaryotes
single celled, lacks membrane bound nucleus and the membranous organelles typical of eukaryotes
-> Evolved 3.5 BYA
-> Evolved 3.5 BYA
19
New cards
Cell Wall
Provides support and shapes to a prokaryote cell
20
New cards
Capsule(Slime Layer)
helps parasitic bacteria protect itself from host cell defenses
21
New cards
Fimbriac
hairlike bristles that allow adhesion to surfaces
22
New cards
Flagellum
rotating filament that propels the cell
23
New cards
Conjunction Pilus
elongated, hollow appendage used to transfer DNA to other cells
24
New cards
Ribosome
site of protein synthesis (smaller than eukaryotes)
25
New cards
Nucleoid
single chromosome containing a few thousand genes that codes proteins
26
New cards
Plasmids
accessory rings that contain genes for antibiotic resistance
27
New cards
Binary Fission
Prokaryote reproduction where the cell splits and genetically identical sister cells
-allows rapid population growth because every individual our reproduce
- disadvantage: less genetic variation
-allows rapid population growth because every individual our reproduce
- disadvantage: less genetic variation
28
New cards
transformation
Source of genetic variation where prokaryotes can absorb and express genetic material from environment
29
New cards
transduction
source of genetic variation where the process of transferring genetic material from one cell to another by a plasmid or bacteriophage
30
New cards
conjugation
source of genetic variation where genetic material transmitted by plasmids
-Cells connect by conjugation pilus
-donor cell passes DNA to recipient in the form of a plasmid
-Cells connect by conjugation pilus
-donor cell passes DNA to recipient in the form of a plasmid
31
New cards
Peptidoglycan
Composition of Domain bacterial cell walls
32
New cards
gram-negative
indicates that a bacteria has a thin peptidoglycan wall and a extra LPS membrane layer
33
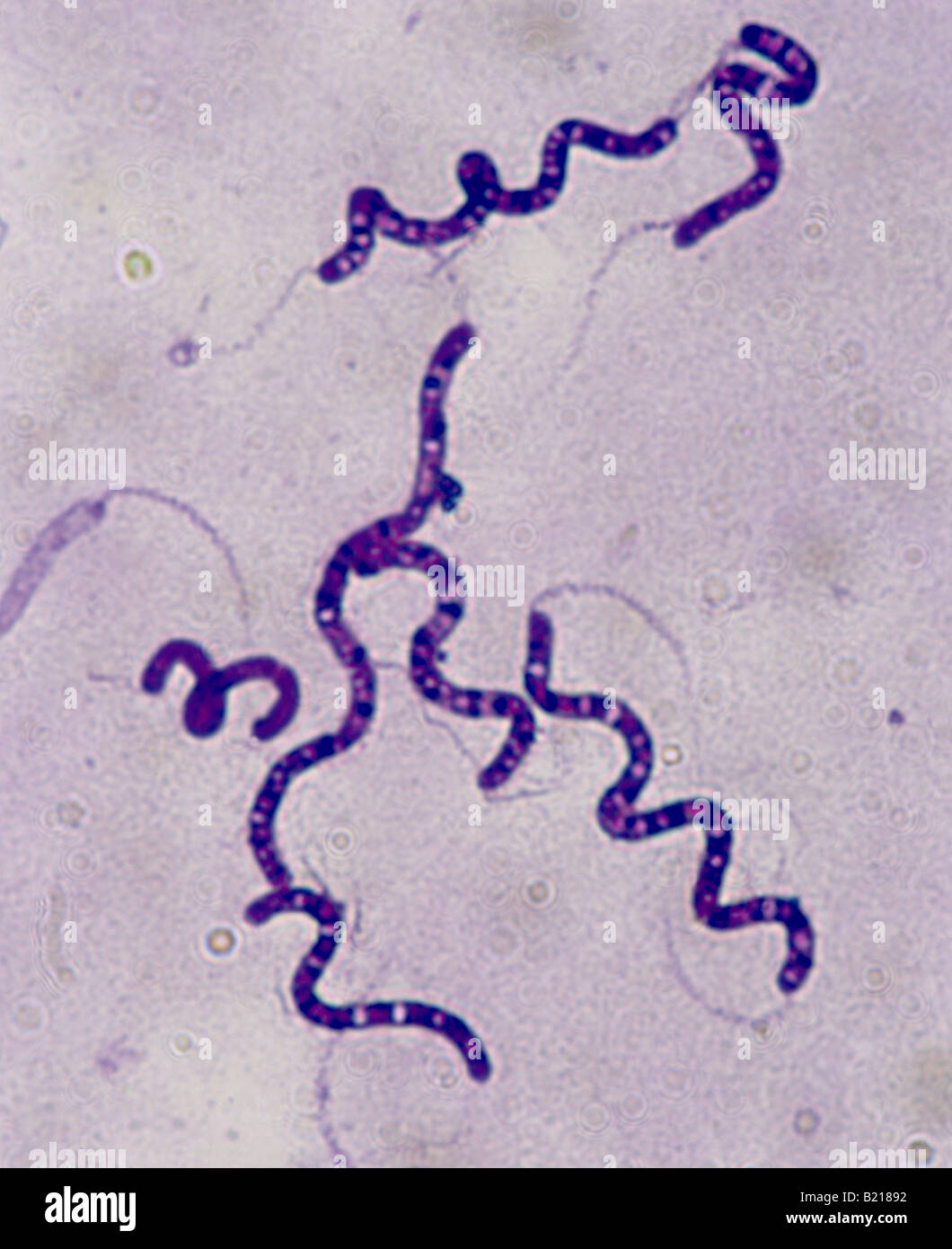
New cards
Spirilla
Spiral
34
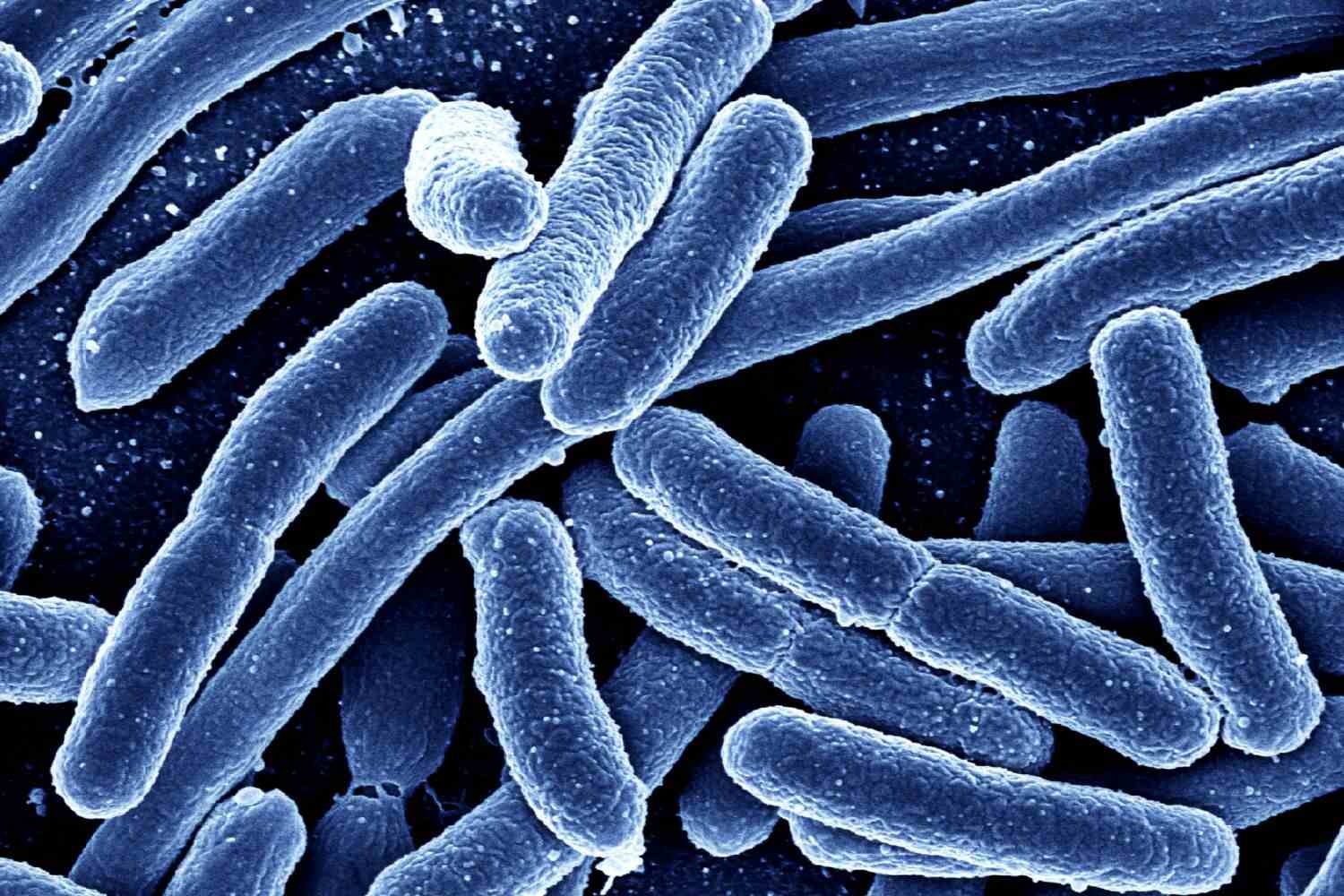
New cards
Bacillus
rod shaped
35
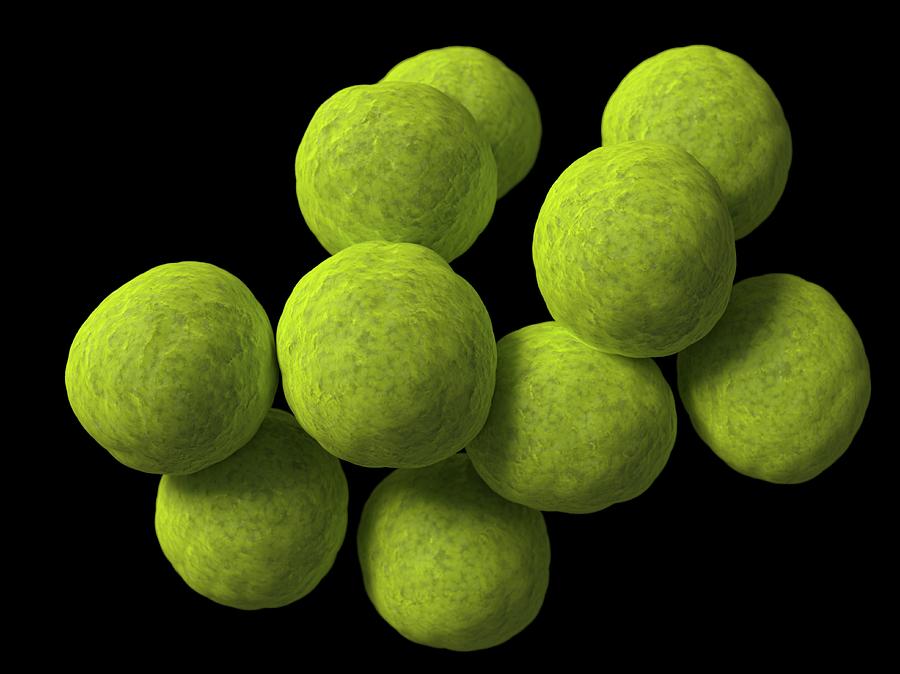
New cards
coccus
circle
36
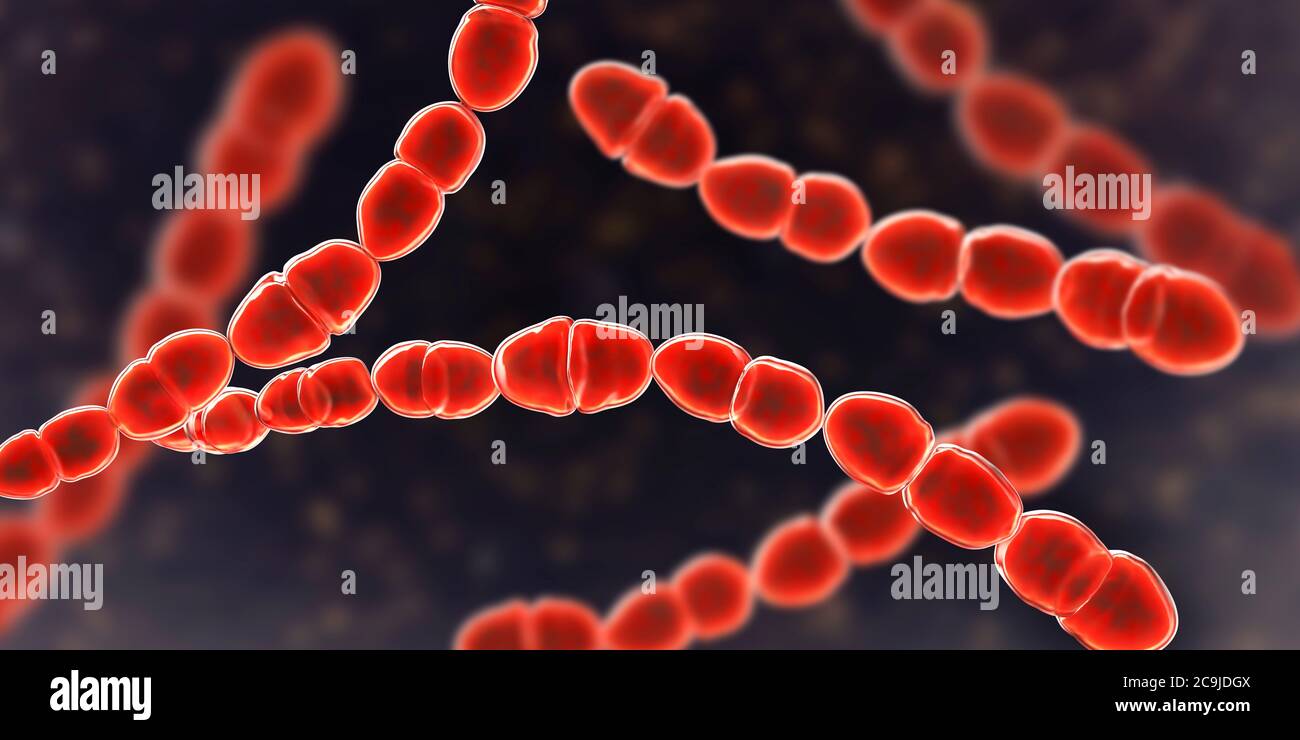
New cards
Strepto
chain
37
New cards
Stapho
clump
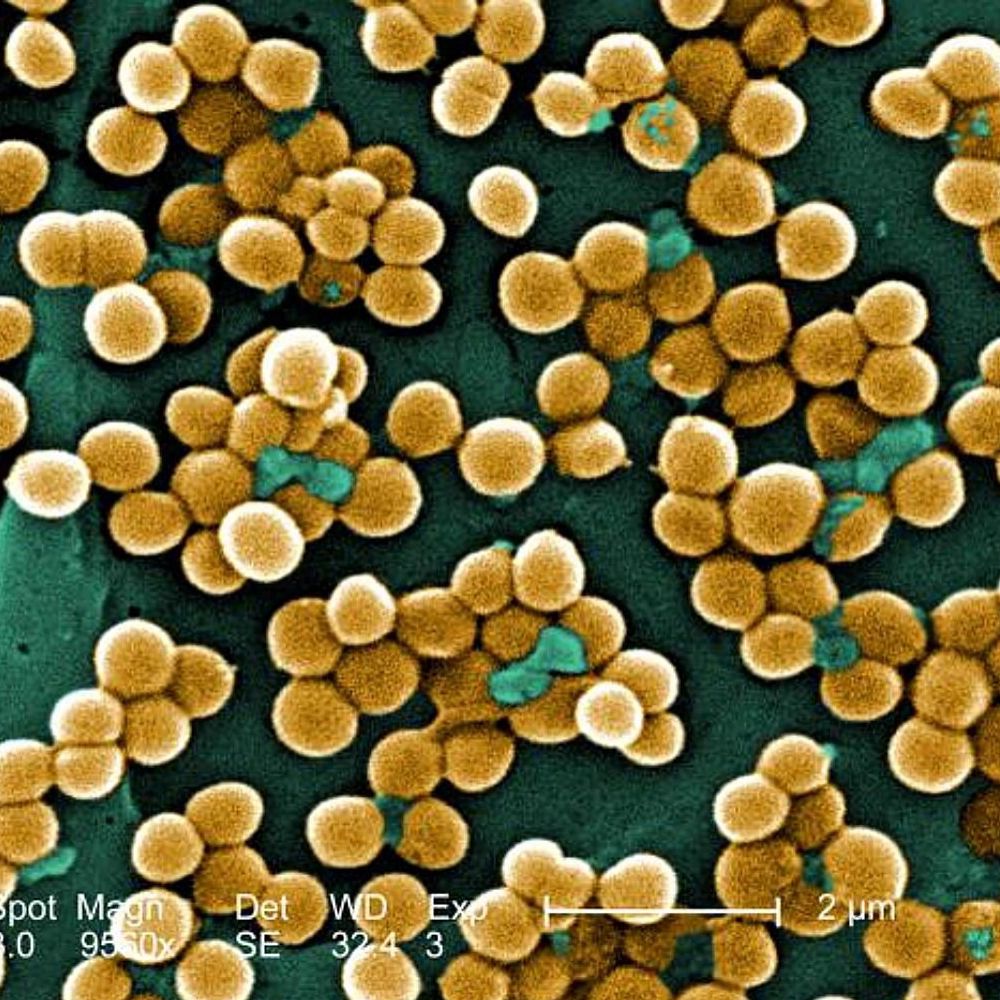
38
New cards
autotrophic
of or relating to organisms that can make complex organic nutritive compounds from simple inorganic sources by photosynthesis
39
New cards
heterotrophic
requiring organic compounds of carbon and nitrogen for nourishment
40
New cards
Bacterial Photoautotrophs
photosynthetic bacteria
41
New cards
Facultative anaerobes
bacteria is able to growing either the presence of absence of gaseous oxygen
42
New cards
Chemoautotrophs
bacteria that carry out chemosynthesis
-oxidize compounds to obtain the necessary energy to reproduce CO2 to an organic compound
-oxidize compounds to obtain the necessary energy to reproduce CO2 to an organic compound
43
New cards
Chemoheterotrophic
bacteria that obtain carbon and energy in the form of organic nutrients produced by other living things
44
New cards
Symbiotic relationship
close relationship between two different species
45
New cards
Mutualistic Symbiosis
both species benefit from the association
46
New cards
Parasitic Symbiosis
one species benefit, the other is harmed
47
New cards
Commensalism symbiosis
one species benefits whereas the other is unaffeced
48
New cards
Endospores
formed by pathogens within a cell wall
a copy of chromosome and cytoplasm shriveled into a dormant state, are encased by a heavy coat
a copy of chromosome and cytoplasm shriveled into a dormant state, are encased by a heavy coat
49
New cards
Antibiotics
treatment that targets prokaryotes cell wall production in humans
50
New cards
cyanobacteria
Gram-negative bacteria that photosynthesize-> produces oxygen
Contains chlorophyll
Common in fresh and marine waters, soil, and on moist surfaces
Form lichens that can grow on rocks
Contains chlorophyll
Common in fresh and marine waters, soil, and on moist surfaces
Form lichens that can grow on rocks
51
New cards
Roles of Bacteria
Producers:
Responsible for the oxygen revolution
An important part of marine phytoplankton (food and oxygen production)
Responsible for the oxygen revolution
An important part of marine phytoplankton (food and oxygen production)
52
New cards
Domain Archaea
bacterial cells with pseudopeptidoglycan cell walls
Extremophiles: live in conditions of acidity, pressure, temp, salinity that would kill most other cells
Extremophiles: live in conditions of acidity, pressure, temp, salinity that would kill most other cells
53
New cards
Extreme Halophiles
archaea that live in extreme salt conditions
54
New cards
extreme thermoacidophiles
archaea that thrive in hot acidic environment
55
New cards
Methagenes
archaea that generate methane
-> exist in swamps and animal intestinal tracts
-> exist in swamps and animal intestinal tracts
56
New cards
Protists
eukaryotes that are not animals, fungi, or plants
Single-celled, but some exist as colonies of cells or are multicellular
Single-celled, but some exist as colonies of cells or are multicellular
57
New cards
Endosymbiotic theory
proposes that eukaryotic cells acquired mitochondria and plastics(including chloroplasts) by engulfing a free-living bacterium that developed a symbiotic relationship within the host cell
-Mitochondria derived first from the endosymbiosis of an aerobic bacterium
-Mitochondria derived first from the endosymbiosis of an aerobic bacterium
58
New cards
mitosis
protists will reproduce asexually by
59
New cards
sexually
protists reproduce how when environmental conditions are unfit
60
New cards
giardia
protist parasite causing serious disease
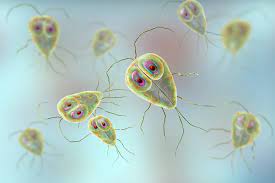
61
New cards
dinoflagellate
Single celled phototrophs
important component phytoplankton
Cellulose plates surround two flagella
Causes Algae blooms: population explosion cause tides
-water turns red or brown due to pigments
important component phytoplankton
Cellulose plates surround two flagella
Causes Algae blooms: population explosion cause tides
-water turns red or brown due to pigments

62
New cards
plasmodium
protist that causes malaria
performs antigen switching
performs antigen switching
63
New cards
inside the insect vector
the sexual stage of plasmodium occurs
64
New cards
in human blood cells
the asexual stage of plasmodium occurs
65
New cards
Diatoms
A type of algae
Single-celled phototrophs
Part of phytoplankton as a source of oxygen and food in aquatic ecosystems
Single-celled phototrophs
Part of phytoplankton as a source of oxygen and food in aquatic ecosystems
66
New cards
Diamtaxous earth
fossilized diatoms used in abrasives
67
New cards
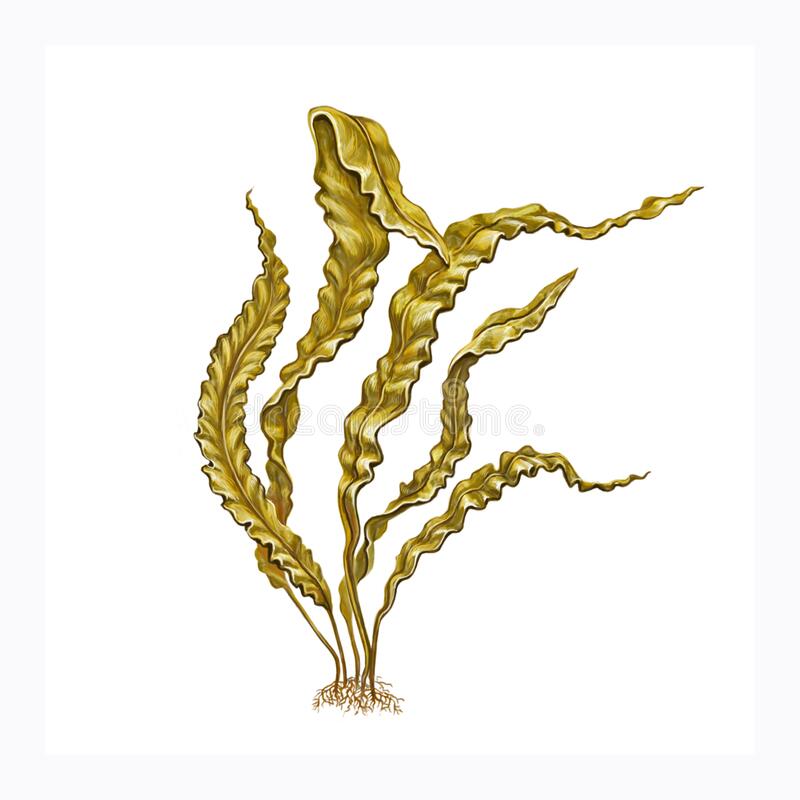
brown algae
true algae
-Multicellular phototrophic
-Kelp
-Homoplastic with plants due to convergent evolution
-Multicellular phototrophic
-Kelp
-Homoplastic with plants due to convergent evolution

68
New cards
oomycetes
fungus like protists
water molds with a filamentous body, chitin cell walls instead of cellulose
water molds with a filamentous body, chitin cell walls instead of cellulose
69
New cards
Entamoebas
-parasite
Used pseudopods to ingest cells-> uses a temporary arm like projection of a cell to move organisms
Acquired through contained water and soil
Causes amoebic dysentery
Used pseudopods to ingest cells-> uses a temporary arm like projection of a cell to move organisms
Acquired through contained water and soil
Causes amoebic dysentery
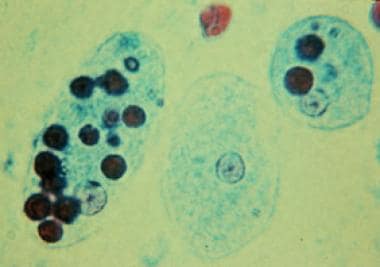
70
New cards
Slime molds
Important decomposer of dead plant material, fungi, and bacterial
Reduce spores but homoplasy with fungi is due to convergent evolution
Amoeboid movement using cytoplasmic streaming
Reduce spores but homoplasy with fungi is due to convergent evolution
Amoeboid movement using cytoplasmic streaming
71
New cards
red algae
Multicellular photoautotrophs (seaweed)
Red and blue accessory pigments in addition to photosynthetic chlorophyll
Pigments allow for us of the wavelength of light present in deep water
Red and blue accessory pigments in addition to photosynthetic chlorophyll
Pigments allow for us of the wavelength of light present in deep water
72
New cards
green algae
algae
Phototrophs
Most are multicellular, but some are unicellular
Contain chlorophyll, scratch, and a cell wall with cellulose
Charophytes: first closet relatives to modern land plants
Phototrophs
Most are multicellular, but some are unicellular
Contain chlorophyll, scratch, and a cell wall with cellulose
Charophytes: first closet relatives to modern land plants
73
New cards
Algae
photosynthetic organisms in freshwater habitats that re most closely related to land plants
Transition between protist and landplants
Transition between protist and landplants
74
New cards
Aquatic
the vast majority of green algae are
75
New cards
green plants (virdiplantae)
green algae + land plants
76
New cards
-water cuticle
-stromata
-Vascularity
-stromata
-Vascularity
Land Plant adaptions to water loss
77
New cards
Stromata
pores in land plants that open and close to regular water and gas exchange
78
New cards
vascular tissue
tissue that conducts water and nutrients through the plant body in higher plants
79
New cards
tracheid
long tubular cell peculiar to xylem, conduct water upward from roots
80
New cards
Flavonoids
An adaption land plants made through pigments that absorb UV rays
81
New cards
Dominate diploid generation
Shift to this minimizes the effect of genetic mutation in plants due to UV rays by having two copies of the same gene
82
New cards
Haplodiplontic life cycle
multicellular haploid and diploid life stages
83
New cards
alternation of generations
a life cycle that alternates between two distinct multicellular haploid and diploid stages
84
New cards
Haploid (n)
cell condition in which only one of each type of chromosome is present,
85
New cards
gametophyte generation
haploid generation of the alternation of generations that produces gametes that unite to form a diploid zygote
->al spores divide by mitosis to produce the gametophyte
-> produces gametes by mitosis
->al spores divide by mitosis to produce the gametophyte
-> produces gametes by mitosis
86
New cards
Diploid (2n)
cell condition in whcih two of each type of of chromosome are present
87
New cards
sporophyte generation
diploid generation that produces haploid spores that develop into the haploid generation
->produces 4 haploid spores
->produces 4 haploid spores
88
New cards
sporangium(2n)
organ containing or producing spores
89
New cards
spore(n)
asexual reproductive cell capable of developing into a new organism without union with another cell. Within the gametocyte part of alteration of generation
90
New cards
gametangia
male and female gamete producing regions
91
New cards
Antheridia
male gametangia; produce sperm
92
New cards
archegonia
female gametangia; produces eggs
93
New cards
Gametophyte Dominant
What generation is dominnst in mosses
94
New cards
microscopic
When a sporophyte gains dominance the gametophyte is
95
New cards
Sporophyte dominance
In Vascular plants, what is the dominate generation
96
New cards
non-tracheophytes
all non-vascular plants
-> Dominant gametophyte generation
-> restricted to living in a wet environment
-> Dominant gametophyte generation
-> restricted to living in a wet environment
97
New cards
Phlyum Bryophyta(non-tracheophytes)
Mosses
-> typically low laying
-> superficial leaves, roots, and stems
-> multicellular gametangia form at the tips of gametophytes
-> typically low laying
-> superficial leaves, roots, and stems
-> multicellular gametangia form at the tips of gametophytes
98
New cards
Phlyum Marchantiophyta (non-tracheophytes)
Liverworts
-> flattened gametophytes with liver like lobes
-> microscopic sporophyte
-> can produce sexually or asexually
-> flattened gametophytes with liver like lobes
-> microscopic sporophyte
-> can produce sexually or asexually

99
New cards
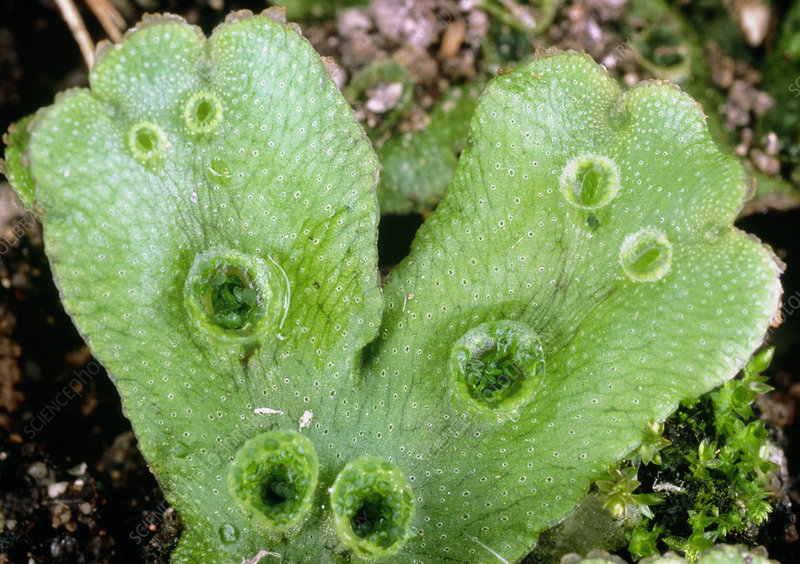
Gemma cups
Asexual reproduction done by liverworts; contain a fragment of parent plant. When water fills the cup, the fragments spread tne reproduction occurs

100
New cards
Phylum Anthocerotophyta(non-tracheophytes)
Hornworts
-> Sporophytes are photosynthetic and embedded in the gametophyte tissue
-> Sporophytes are photosynthetic and embedded in the gametophyte tissue
