G Chem Ch 4
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What are nucleons?
Protons and neutrons in nucleus
What are charges of protons, neutrons, electrons?
Protons +
Neutrons 0
Electrons -
How many protons does an atom have?
Its atomic number
What is the mass number of an atom?
Number of protons and neutrons in an atom
What differentiates isotopes?
How many neutrons are present in the atom
What is the atomic weight of an atom?
Weighted average of masses of all naturally occurring isotopes
What is an anion? Cation?
Anion: negatively charged atom
Cation: positively charged atom
What holds the protons and neutrons in the nucleus together?
Nuclear force
What does it mean to be radioactive?
The nucleus is unstable, so it chages the number of protons/neutrons it has via radioactive decay
What is the parent nucleus? Daughter nucleus?
Parent: nucleus that undergoes radioactive decay
Daughter: more stable nucleus after radioactive decay has occurred
What is alpha decay?
When a large nucleus wants to be more stable, it emits 2 protons and 2 neutrons
The lost particles are large, lose energy quickly, and do not travel far
Skin stops them
What are three types of beta decay?
Beta +, beta -, and electron capture
Beta particles are smaller than alpha, have more energy, and travel further
Aluminum foil, 1 cm glass, and 1 cm plastic stop them
What is beta - decay?
Neutron → proton
Atomic number of the daughter is one greater than the parent, but the mass number is the same
Assume “beta decay" is this unless other info given
What is beta + decay?
Positron emission
Proton → neutron
Atomic number of daughter is one less than parent nucleus, but mass numbers are the same
What is electron capture?
Unstable nucleus takes an electron from its closes electron shell and uses it in the conversion of a proton into a neutron
Atomic number of daughter is one less than parent; mass numbers are the same
What is gamma decay?
A nucleus in an excited state (usually it is after undergoing alpha or any beta decay) emits energy in the form of photons of electromagnetic radiation
Penetrate matter most effectively because the photons do not have mass or charge
Neither atomic number nor mass number changes
What is a half life?
Time it takes for one-half of a sample of radioactive substance to decay
What is the equation of exponential decay curve
See image

What is nuclear binding energy?
Energy released when neutrons and protons were bound to form a nucleus
Equal to energy required to break the nucleus
What is the mass defect?
When nucleons bind, some mass is converted to energy, so mass of nucleus is less than nucleons
change in m = (total mass of separate nucleons) - (mass of nucleus)
Always positive
What is the equation for nuclear binding energy E?
E = (change in m)c²
c = 3 × 10^8 m/s
What is an emission spectrum?
When light is passed through gas, then a prism, the colors that show up (component wavelengths)
Different for each element
What is the energy emited by photons?
E photon = h (c/wavelegth)
c/wavelength = frequency
c = 3 × 10^8 m/s
h = 6.6 × 10^-34 J*s (Planck’s constant)
What is a ground state?
Lowest energy level of an electron
What is an excited state?
Electron absorbs a photon and jumps to a higher energy level
What is the Bohr equation?
En = (-2.178 × 10^-18 J)/n²
n = energy level of the electron
What is an orbital?
3d region around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found
What is the shape and number of an s subshell orbital?
Every s subshell has one spherically symmetical subshell
What is the number and shape of p orbitals?
Each p subshell has three dumbell shaped orbitals
One on X axis, one on Y, one on z
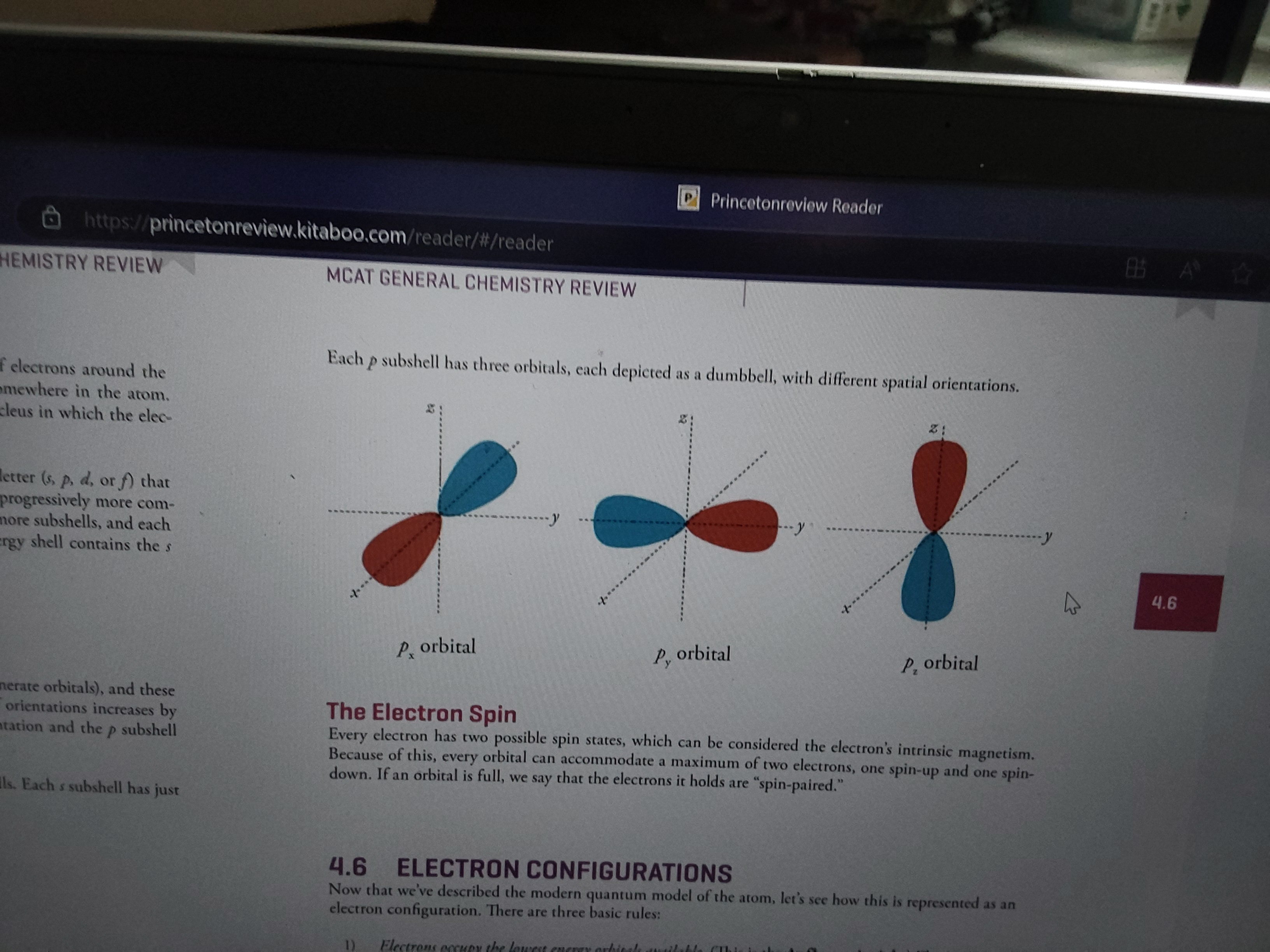
What are the three rules of electron configurations?
Electrons occupy the lowest energy orbital available (Aufbau's principle)
Electrons in the same subshell occupy available orbitals singly before pairing up (Hund's rule)
There can be no more than two electrons per orbital (Pauli's exclusion principle)
How do electron shells progress as you go down the periodic table and left to right?
1s², 2s², 2p^6, 3s², 3p^6
Increase
What is a diamagnetic atom?
One that has all electrons spin-paired
Must have even number of electrons and all subshells filled
Have no net magnetic field; will be repelled by all externally produced magnetic fields
What is a paramagnetic atom?
Atoms with electrons that are not all spin paired
Produce magnetic fields and are attracted to externally produced ones
How do you know how many orbitals something has and which ones?
Look at what block it is in, look how many rows down
How do you tell which orbitals an atom has?
Look at what block it is in (s, p, d, or f)
Look at how many rows down it is

What does it mean to be isoelectric?
If an ion gains or loses an electron and its configuration matches the configuration of another they are isoelectric
Ex: F- has 1s², 2s², 2p^6 and Neon does too
How do transition metals lose/gain electrons?
They have both ns and (n-1)d orbitals
They will lose valence electrons first, so they lose s electrons before d
What is group 1? Valence configuration?
Alkali metals
ns^1
What is group 2? Valence configuration?
Alkaline earth metals
ns²
What is group VII? Valence configuration?
Halogens
ns²np^5
What is group VIII? Valence configuration?
Noble gases
ns²np^6
What is the d-block?
Transition metals
What are the s and p blocks?
Representative elements
What is the f block?
Rare earth metals
What is the nuclear shielding effect?
Each filled shell between nucleus and valence electrons shields the valence electrons from the full effect of positive protons in the nucleus
What is first ionization energy?
Energy needed to remove the least tightly bound electron
Increases from left to right on table
What is the second ionization energy?
Energy to remove the least tightly bound electron from the cation
Always bigger than the first ionization energy
What is electron affinity?
Energy associated with the addition of an electron to an atom
Positive if energy is released when an electron is bound, negative if energy is gained
How does electronegativity change throughout the table?
Increases from left to right
Decreases as you go down
What is acidity?
Measure of how well a compound donates protons or accepts electrons
Increases from left to right, increases down each family (in relation to size)
What are the periodic trends for atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, and acidity?
Atomic radius: decrease left to right and up
Ionization energy: increase left to right and up
Electron affinity: more negative as you go left to right and up
Electronegativity: increases as you go left to right and up
Acidity: increases left to right and down

How does charge change atomic radius?
Negative ion larger than neutral, which is larger than positive ion
How is energy related to frequency and wavelength?
Directly proportional to frequency
Inversely proportional to wavelength
What are the waves of the electromagnetic spectrum from lowest to highest frequency?
Radio → mu → IR → ROYGBV → UV → X → gamma
What are the waves of the electromagnetic spectrum from lowest to highest wavelength?
Gamma → X → UV → VIBGYOR → IR → mu → radio
What is an absorption spectrum?
Emits all colors except those that are absorbed (where electron transitions occur)
What is an emission spectrum?
All dark with bright bands where energy levels are (where electron transitions occur)
How do transition metals lose electrons?
They first lose them from the highest subshell
Either lose from s or p before d
What is a period?
Horizontal