module 9
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
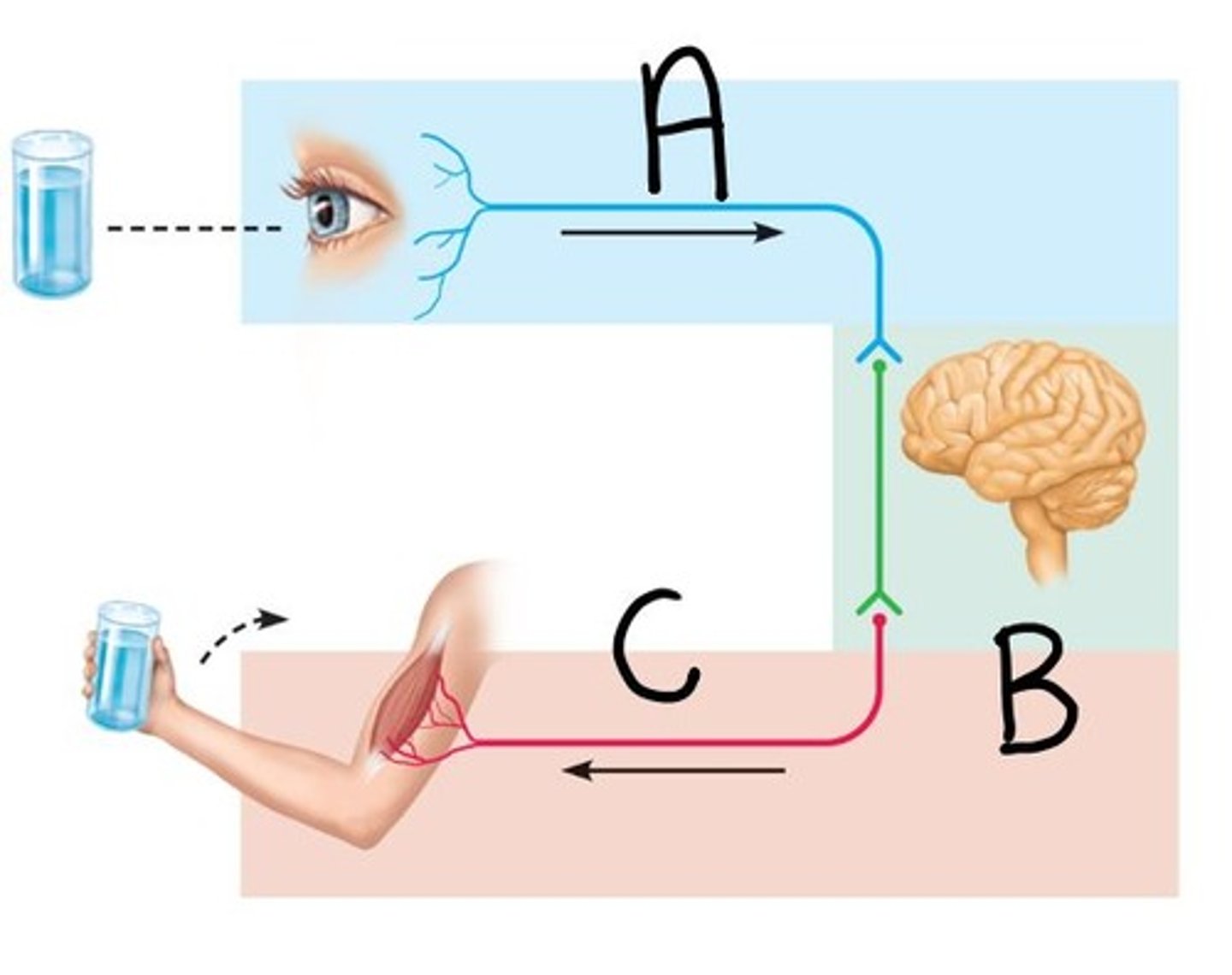
sensory input
vison
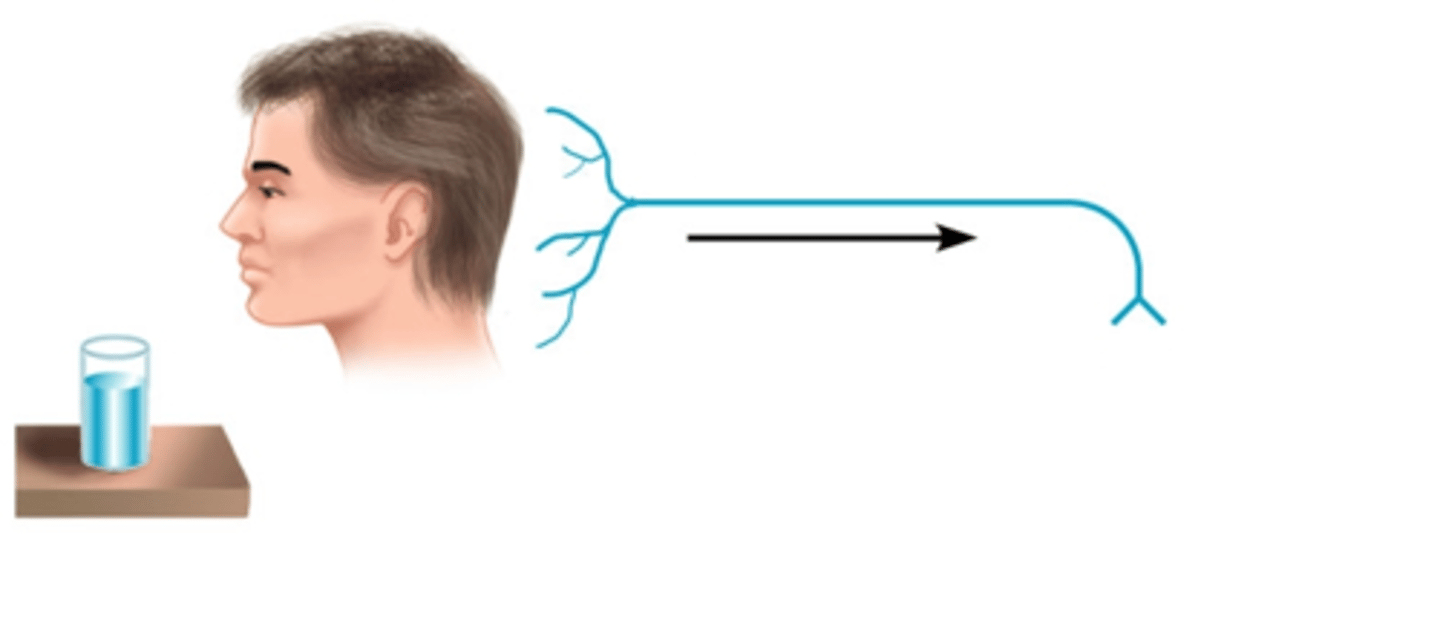
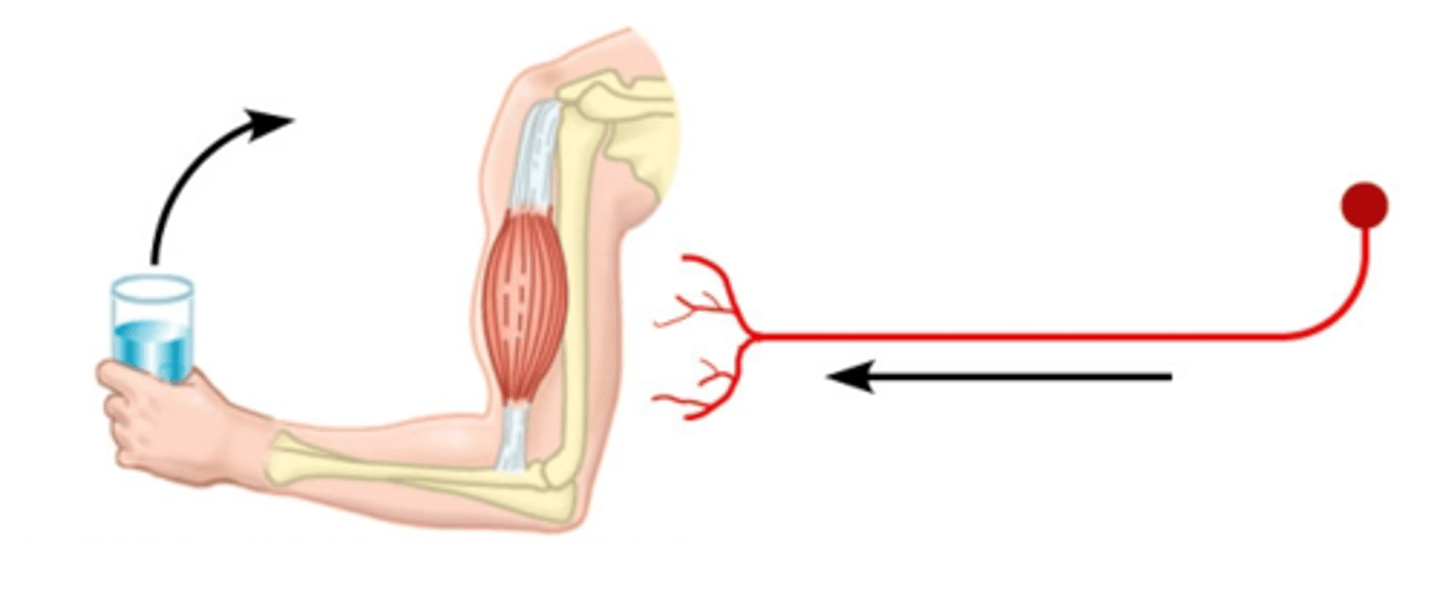
motor input
lifting
integration center
brain
Click on the gray box that where the sensory (afferent) division is described.
-somatic and visceral sensory nerve fibers
-conducts impulse from receptors to the CNS
Click on the gray box that where the central nervous system (CNS) is described.
-brain and spinal cord
-integrative and control center
Click on the gray box that where the autonomic division is described.
-visceral (involuntary) motor never fibers
-conducts impulses from the CNS to cardiac, smooth muscles, and glands
Click on the gray box that where the motor (efferent) division is described.
-motor nerve fibers
-conducts impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles and glands)
Click on the gray box that where the parasympathetic division is described.
-conserves energy
-promotes house keeping functions during rest
Click on the gray box that where the sympathetic division is described.
-mobilizes body systems during activity
Schwann cells
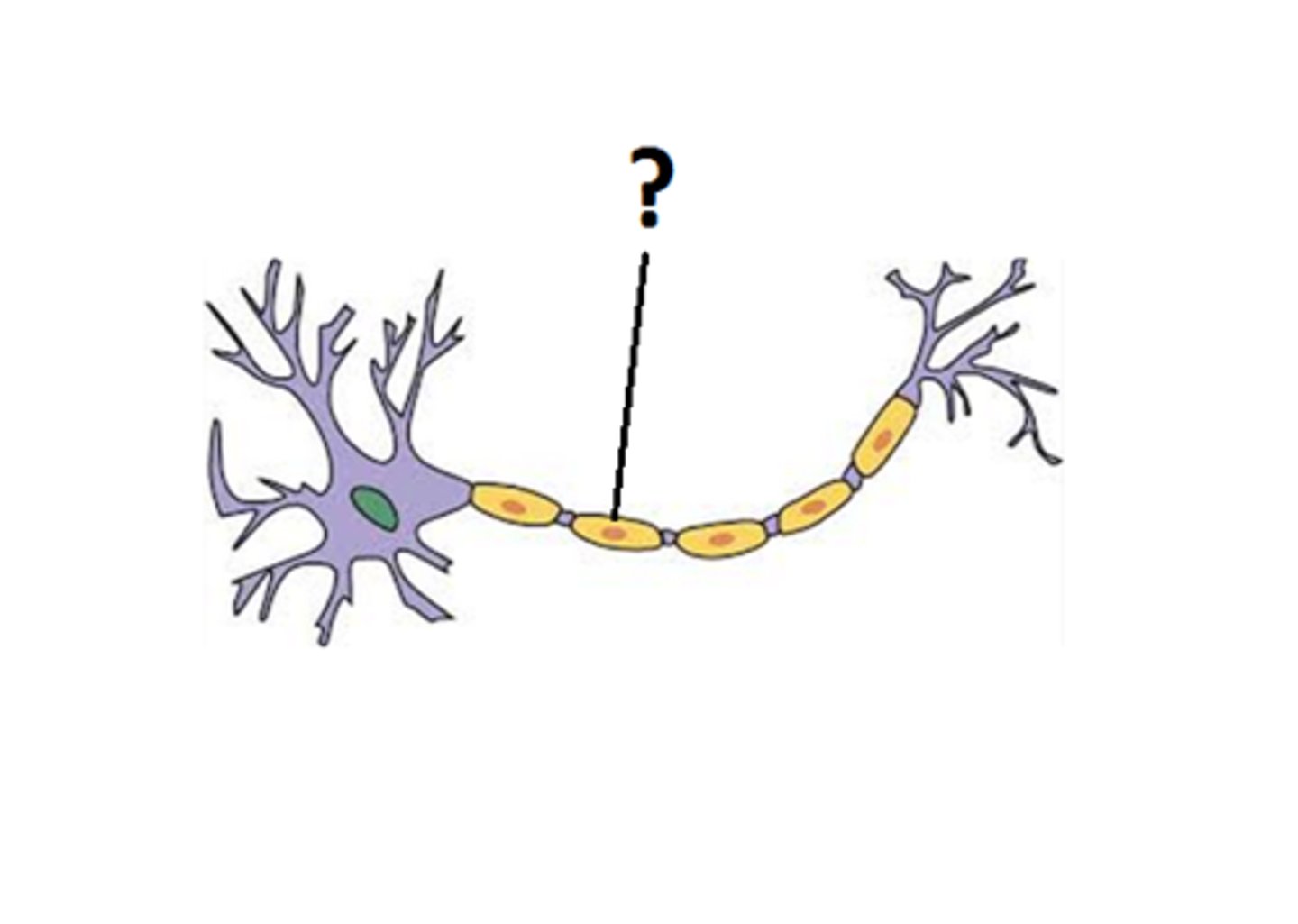
chromatophilic substance
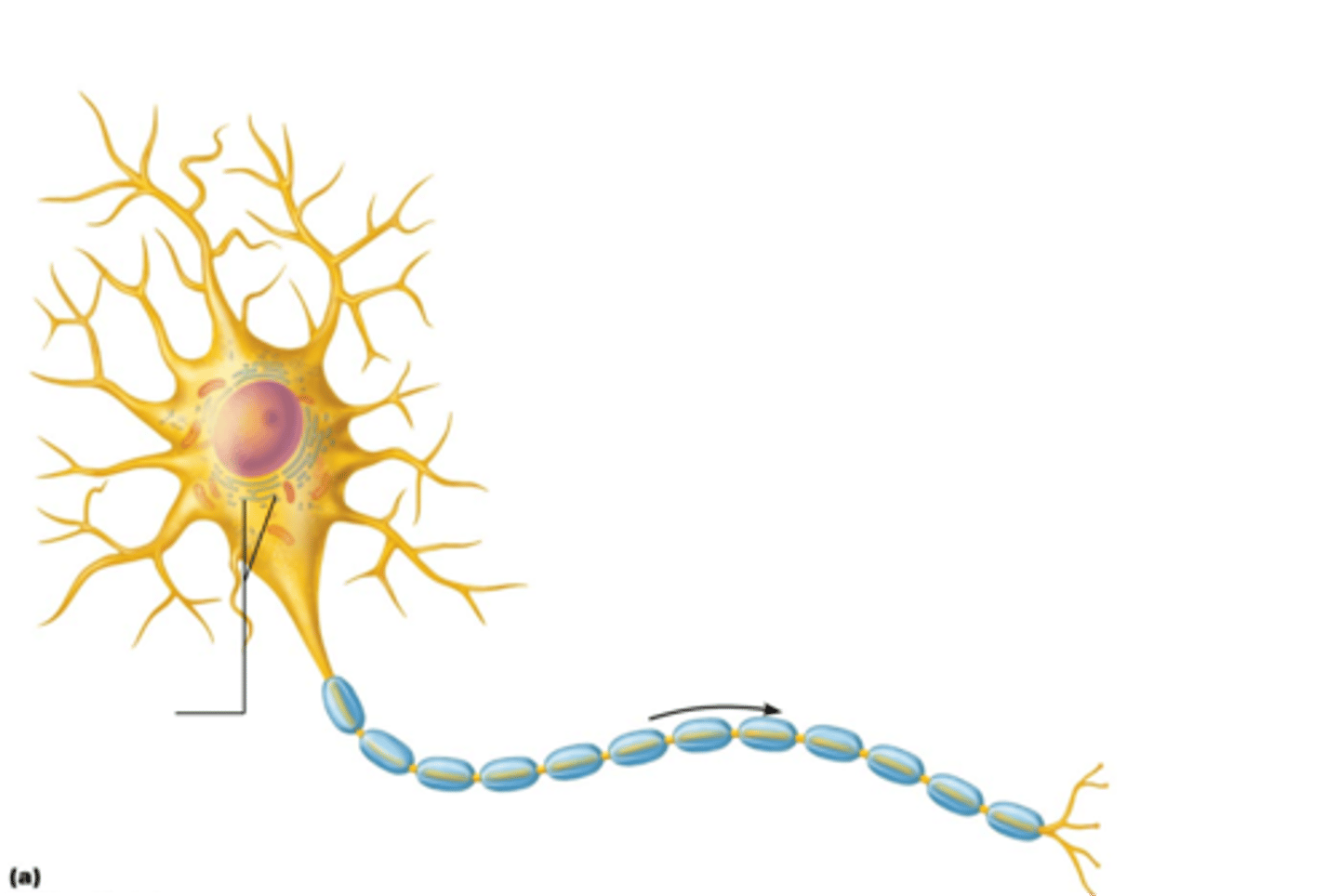
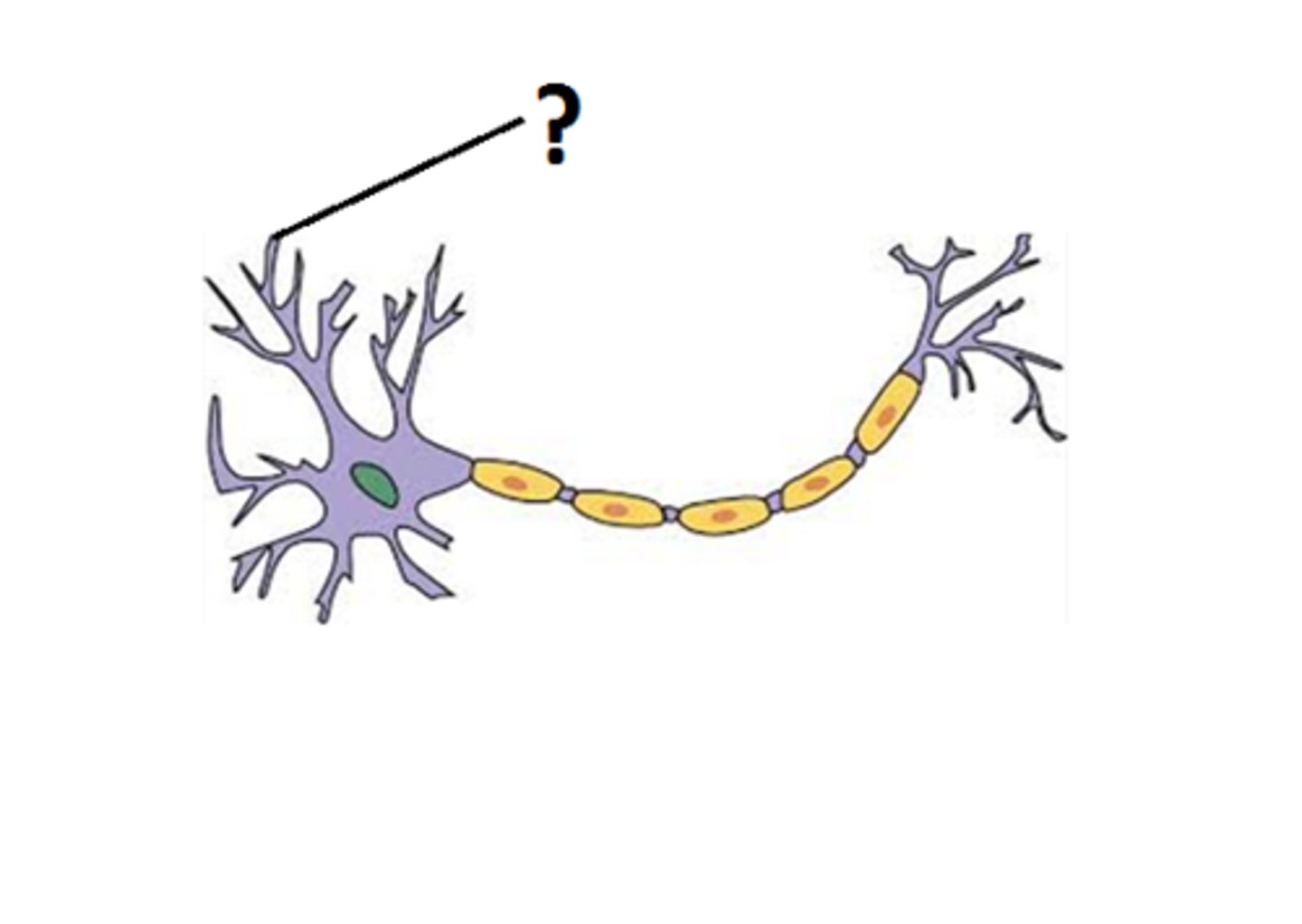
Dendrites
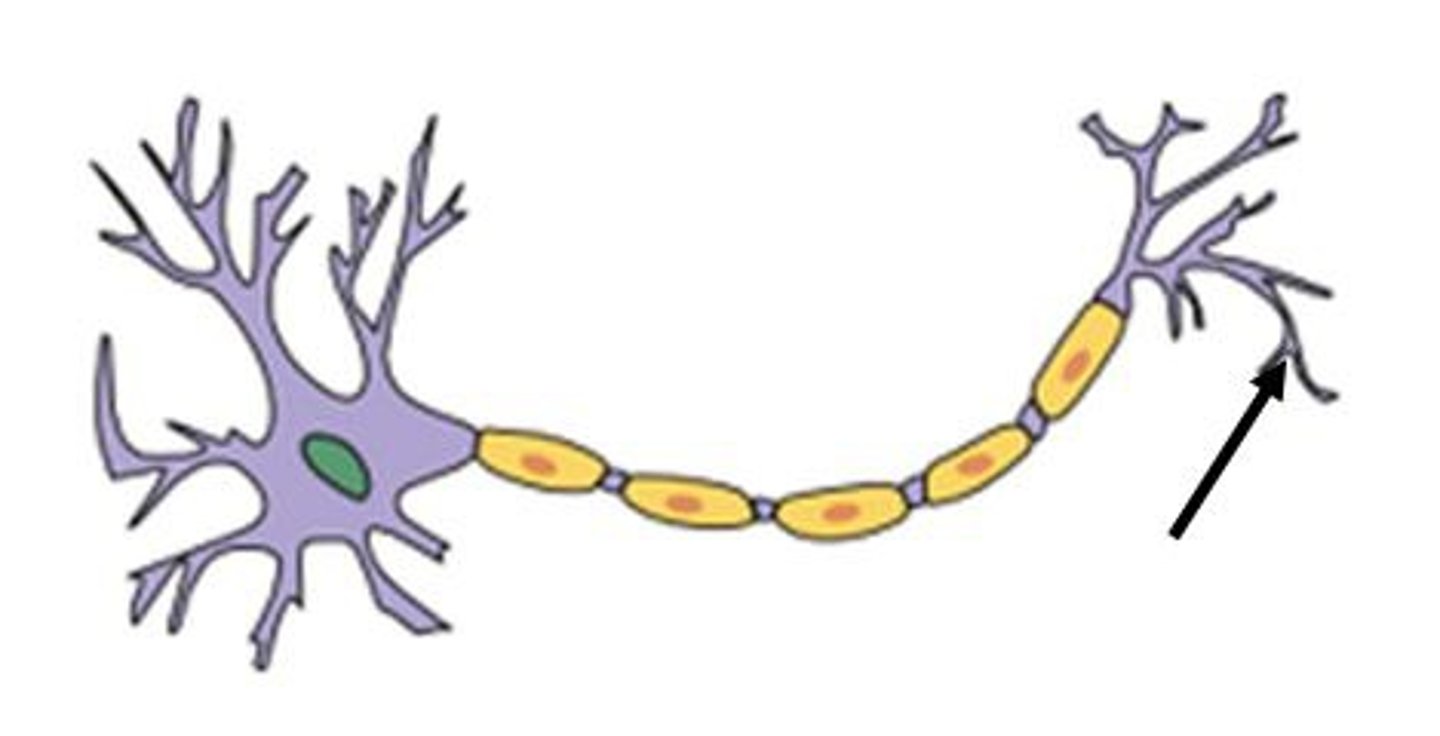
axon terminal
initial segment of the axon
number 7
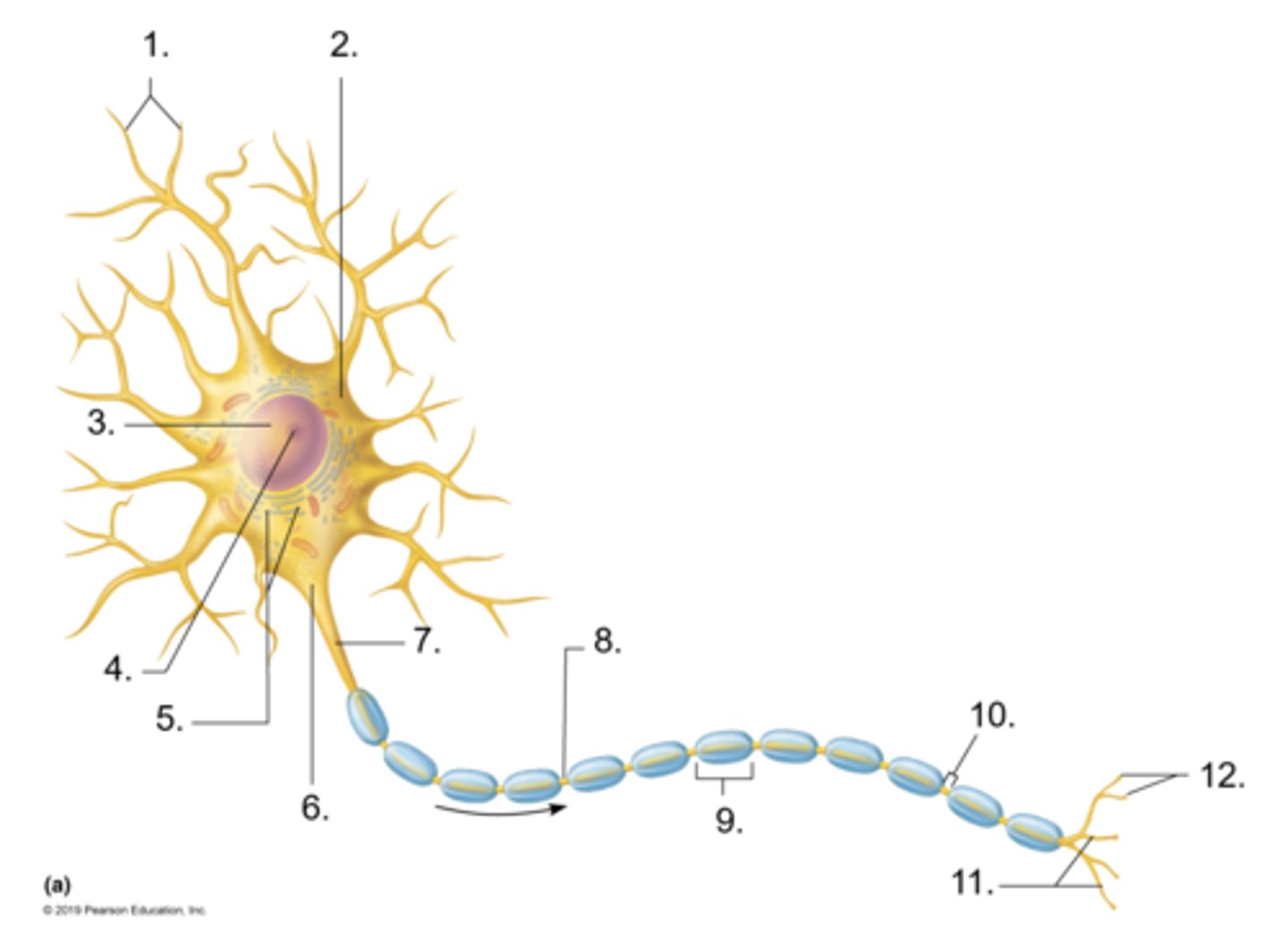
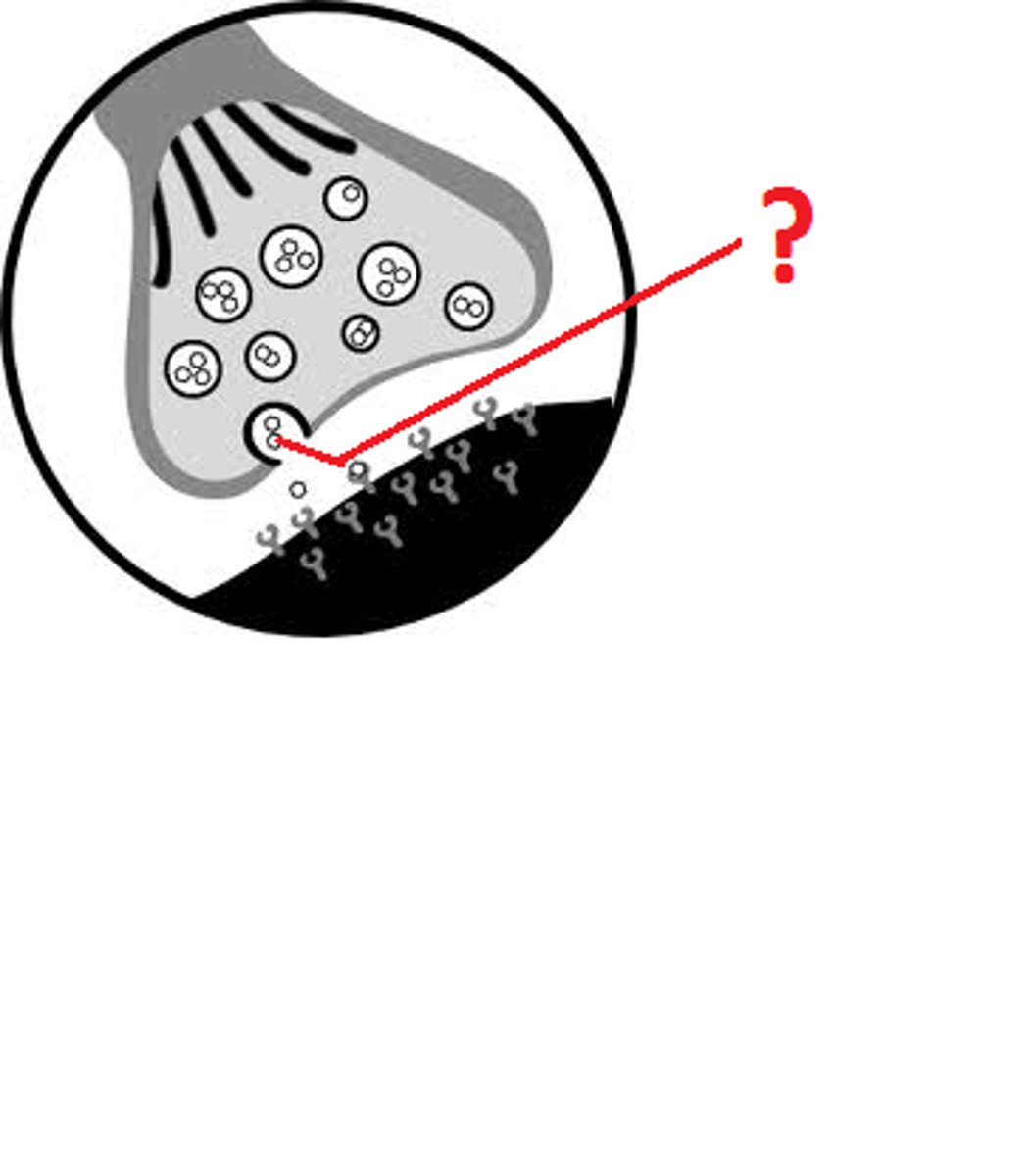
Click on the blue box that shows the synaptic cleft.
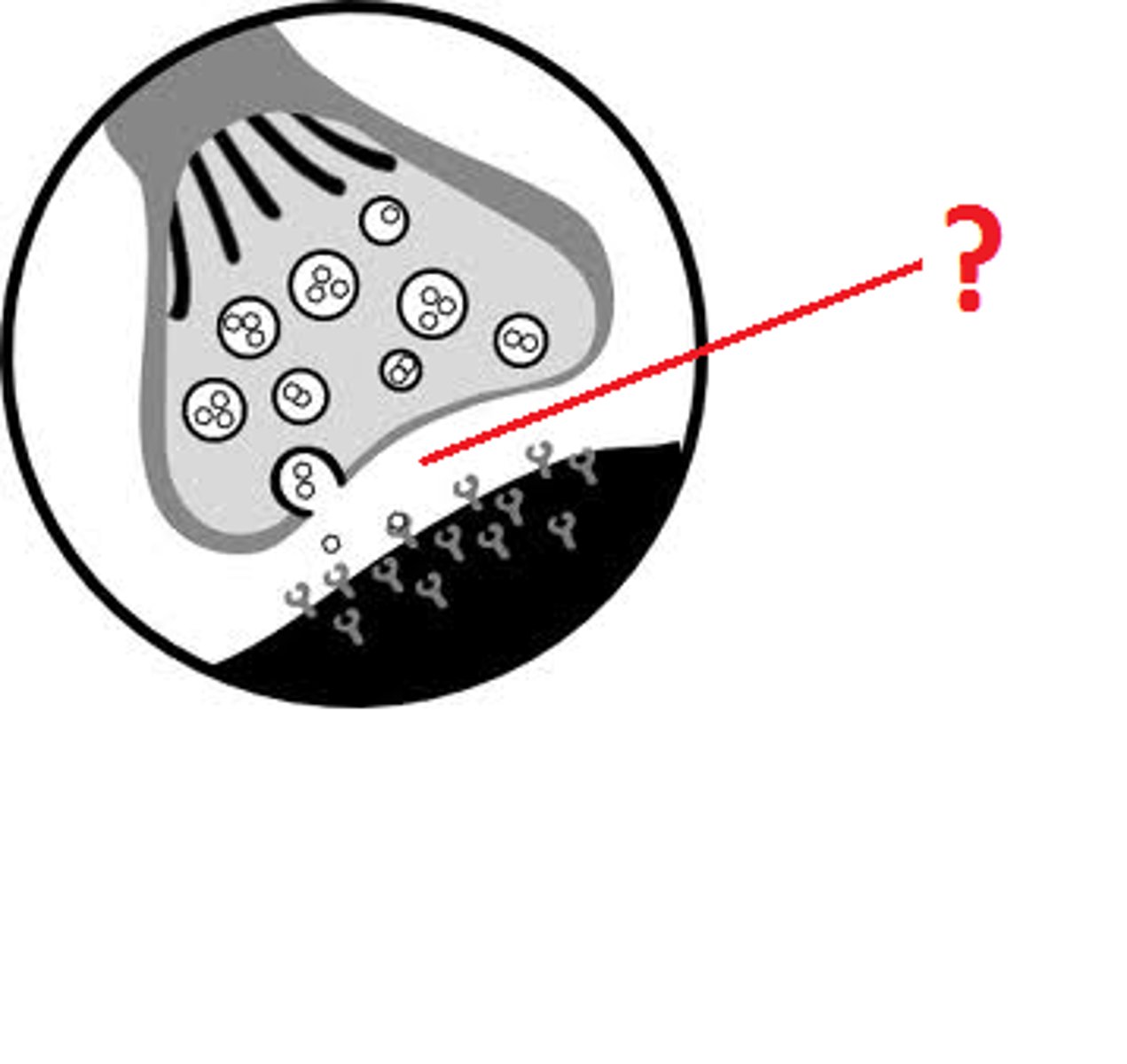
Click on the blue box that shows a receptor for the neurotransmitter.
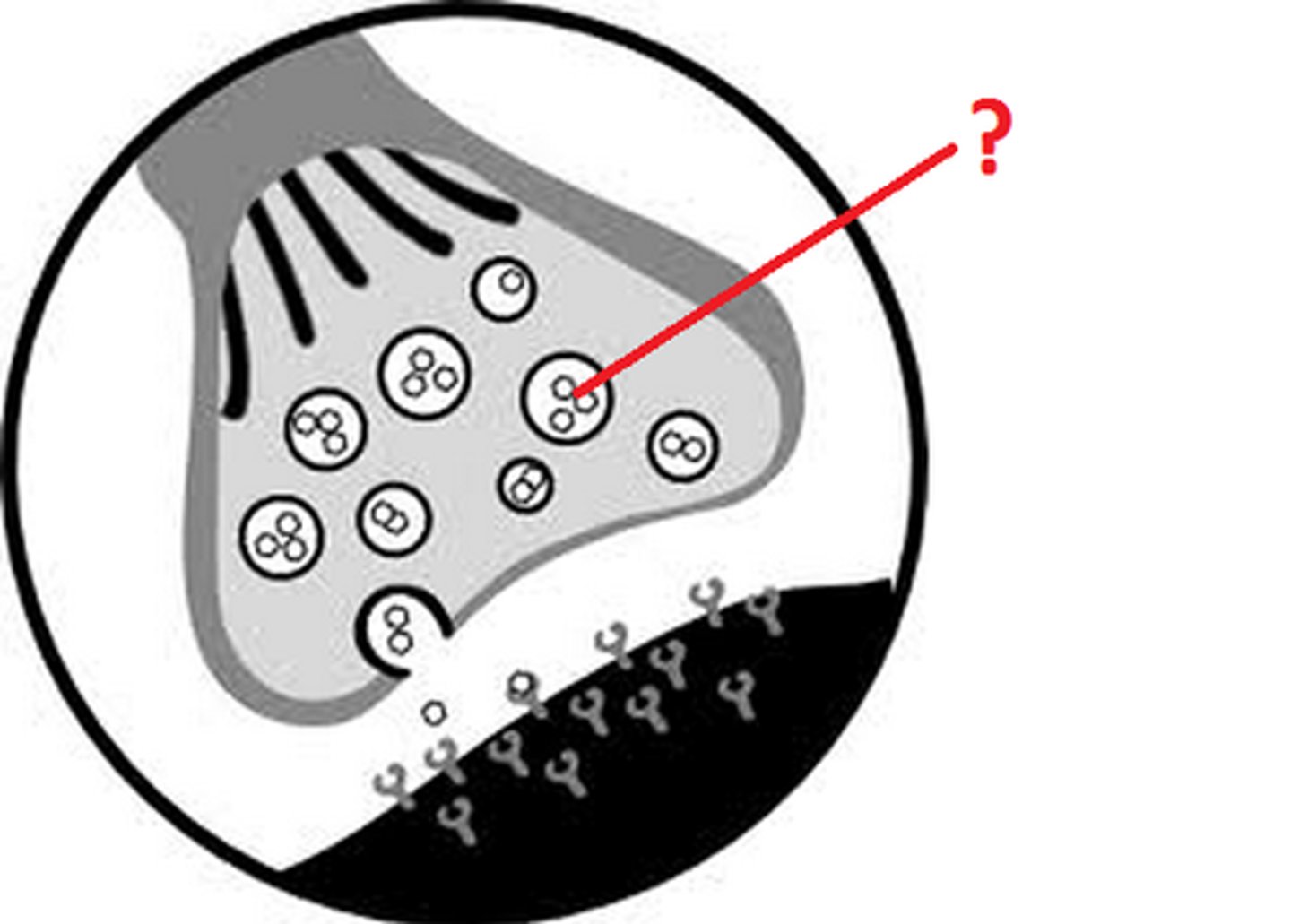
vesicle
motor neuron
number 4
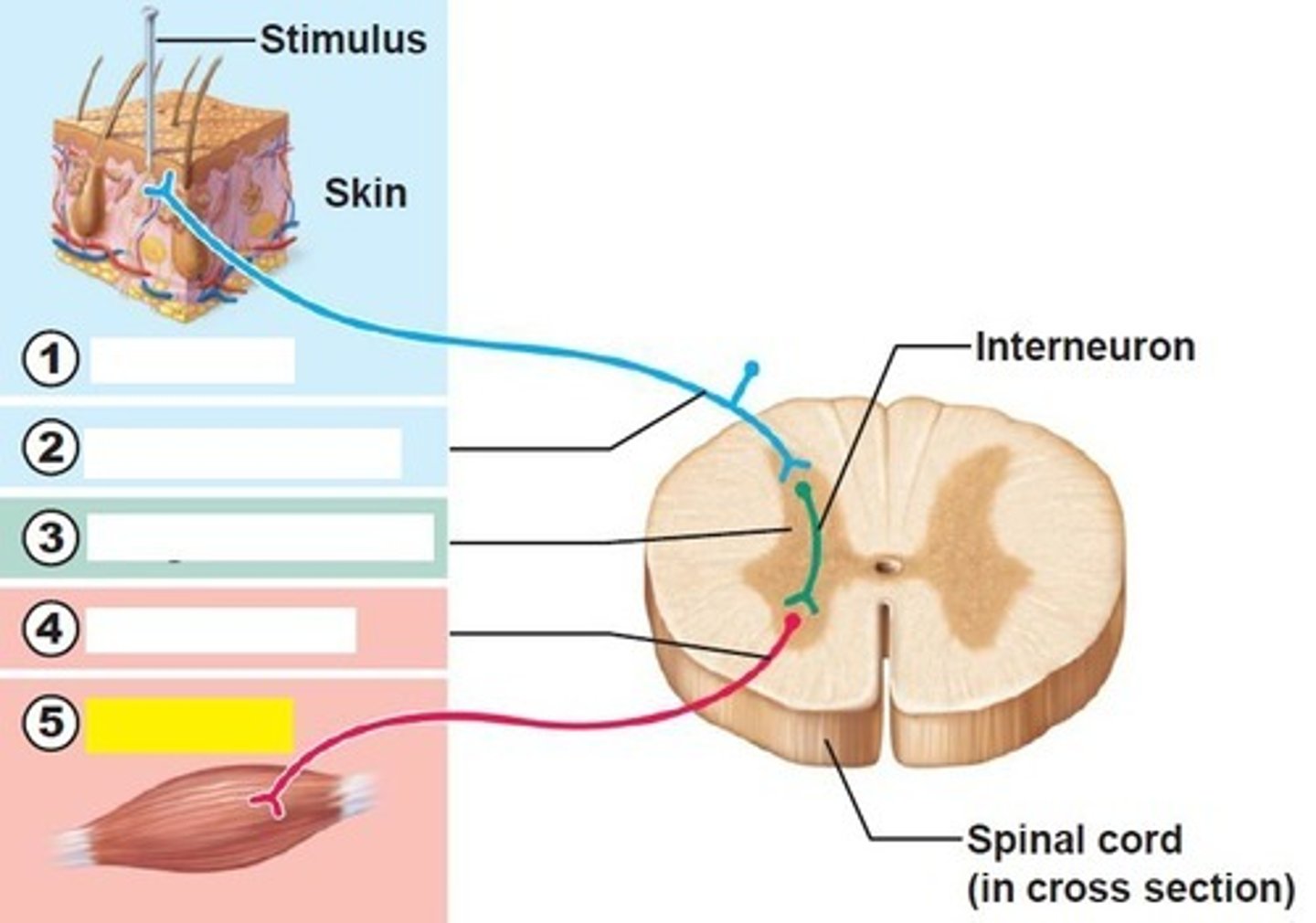
Effector
number 5
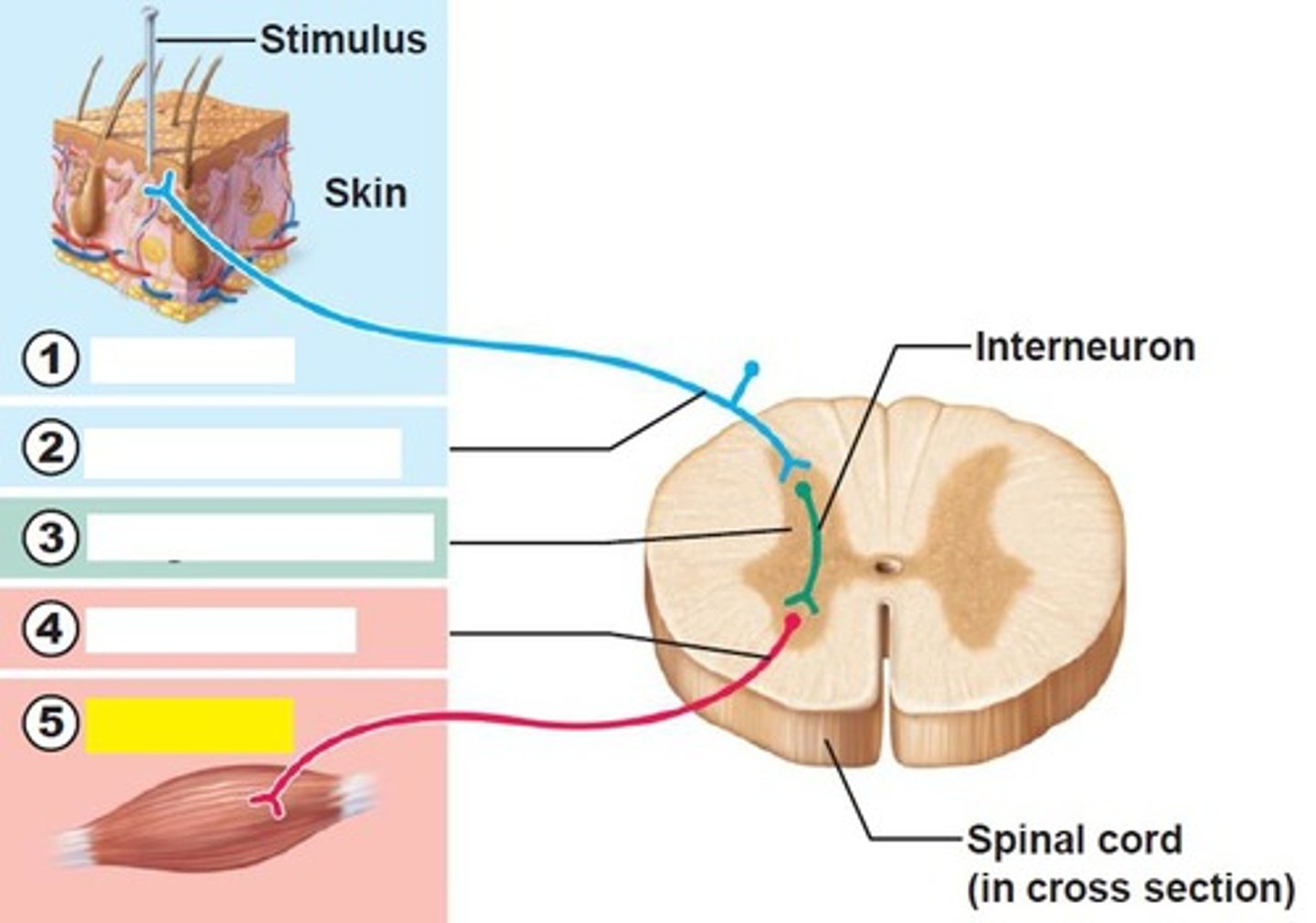
sensory neuron
number 2
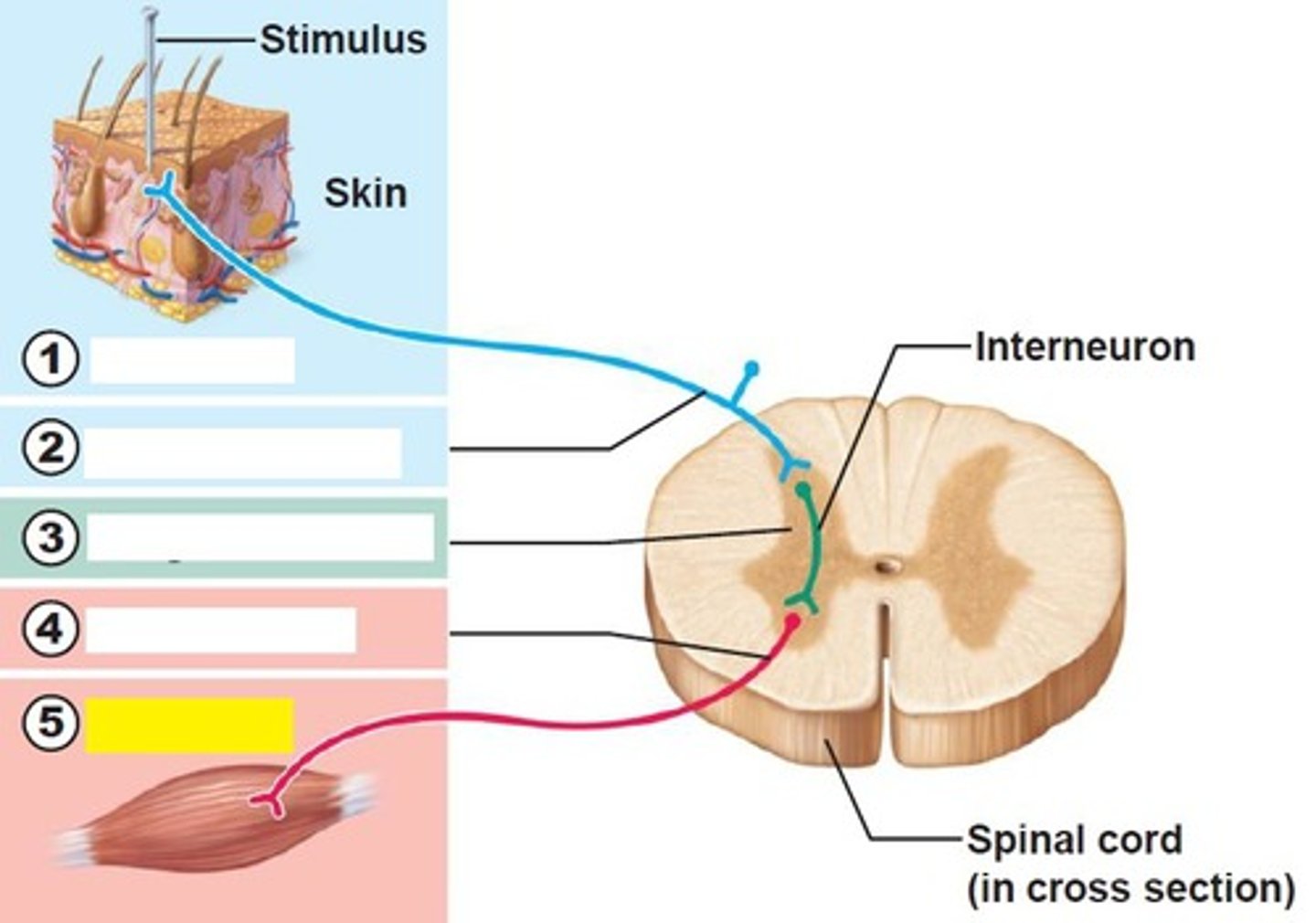
Integration center
number 3
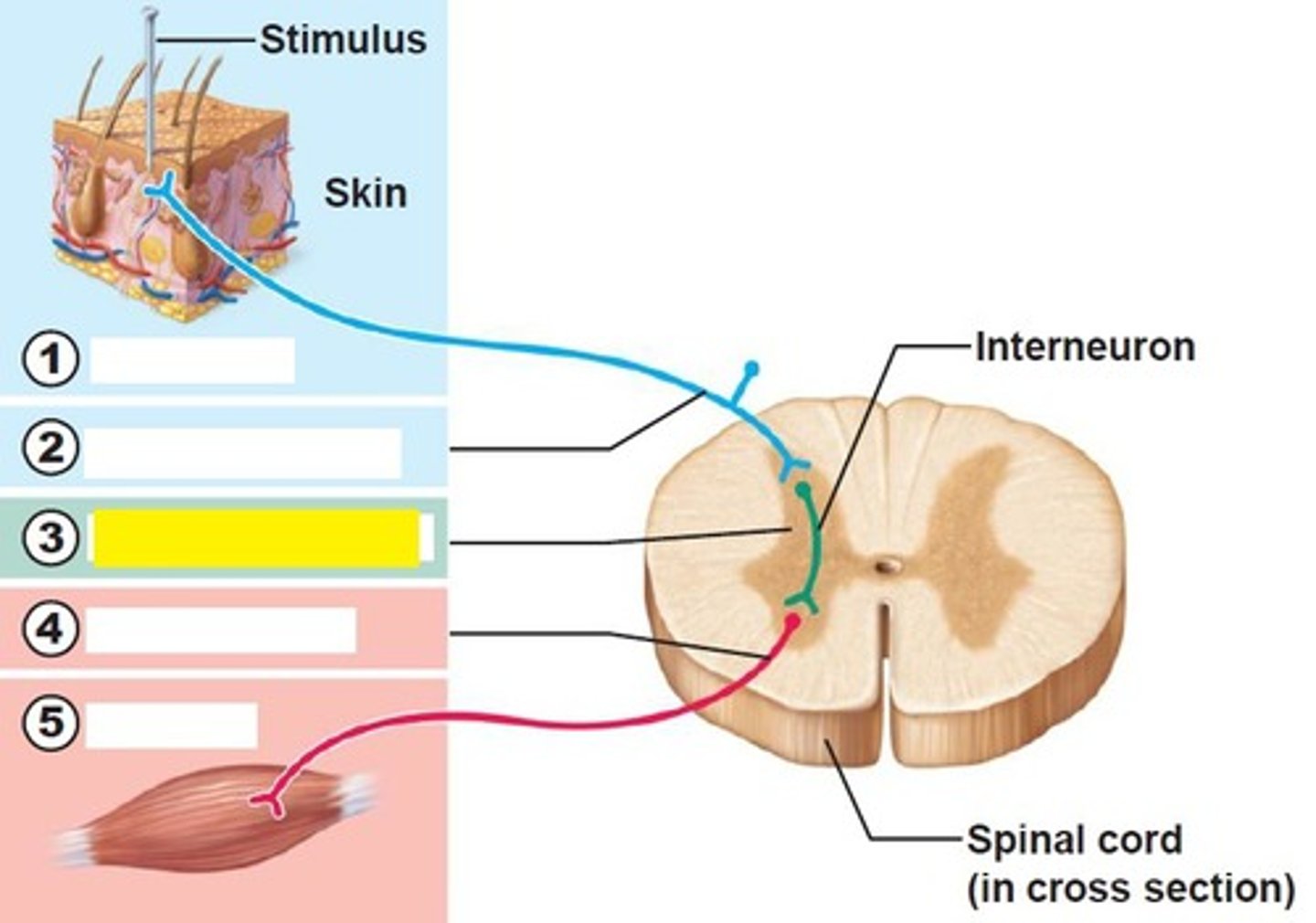
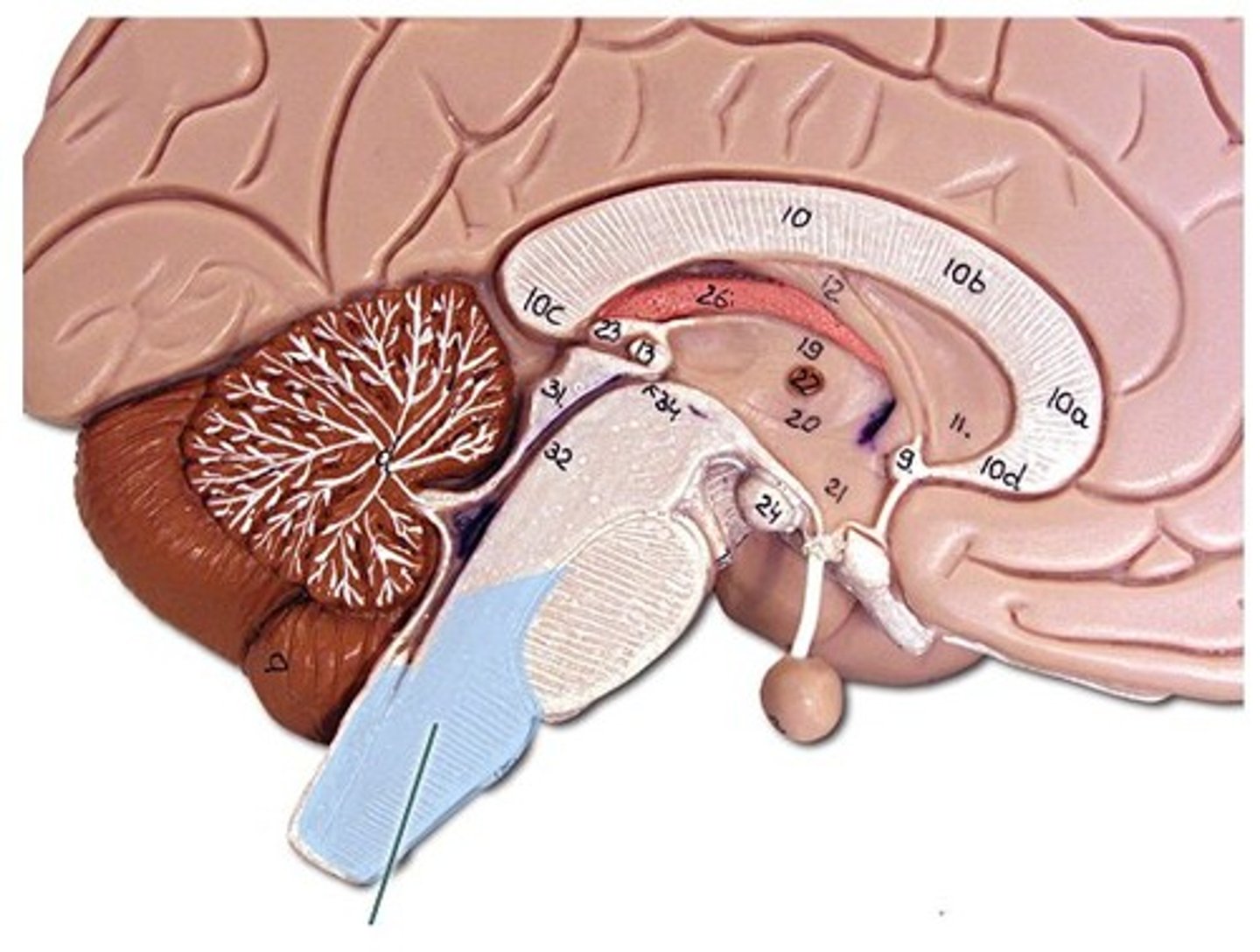
third ventricle
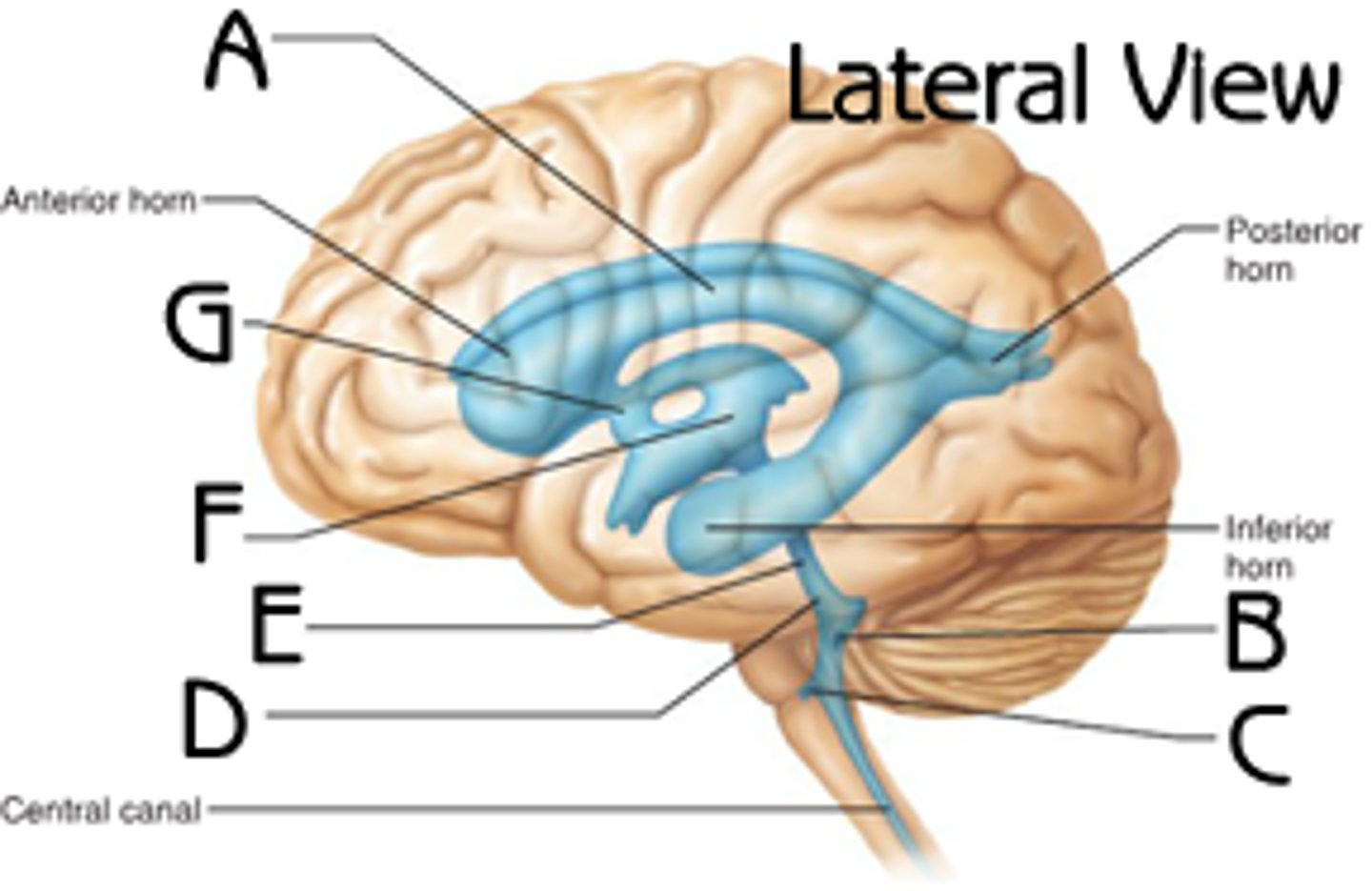
letter F
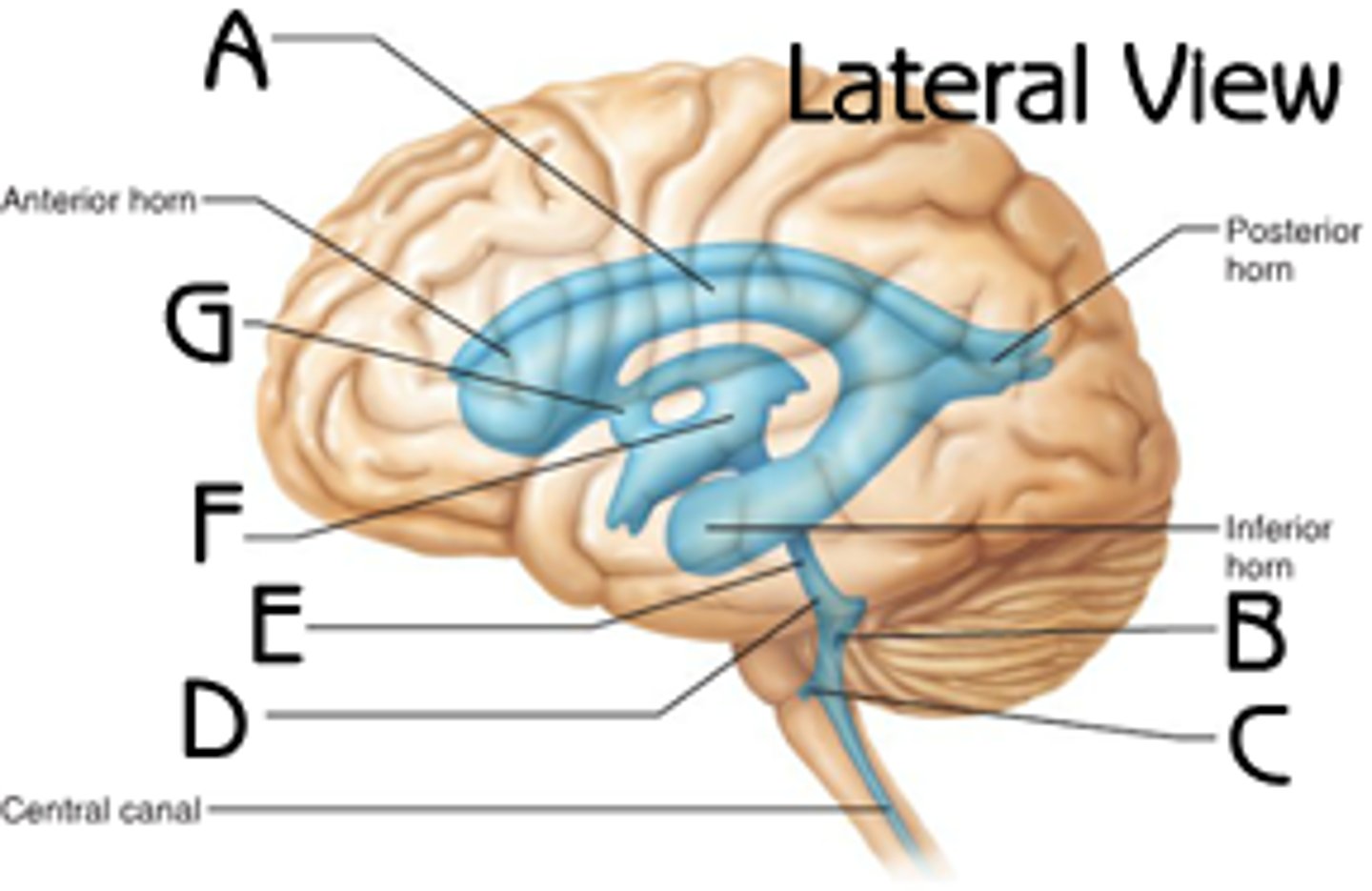
fourth ventricle
letter B
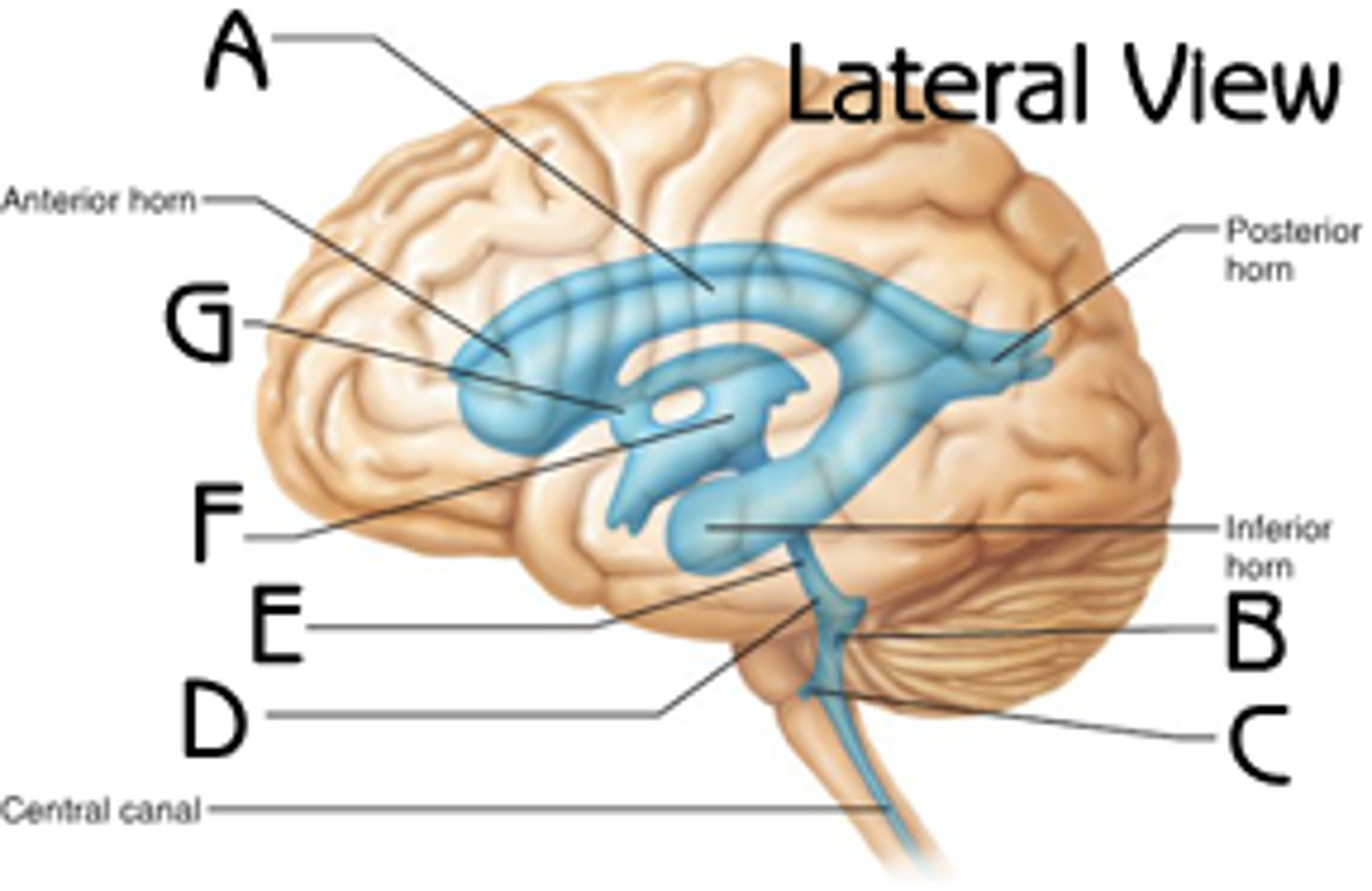
lateral ventricle
letter A
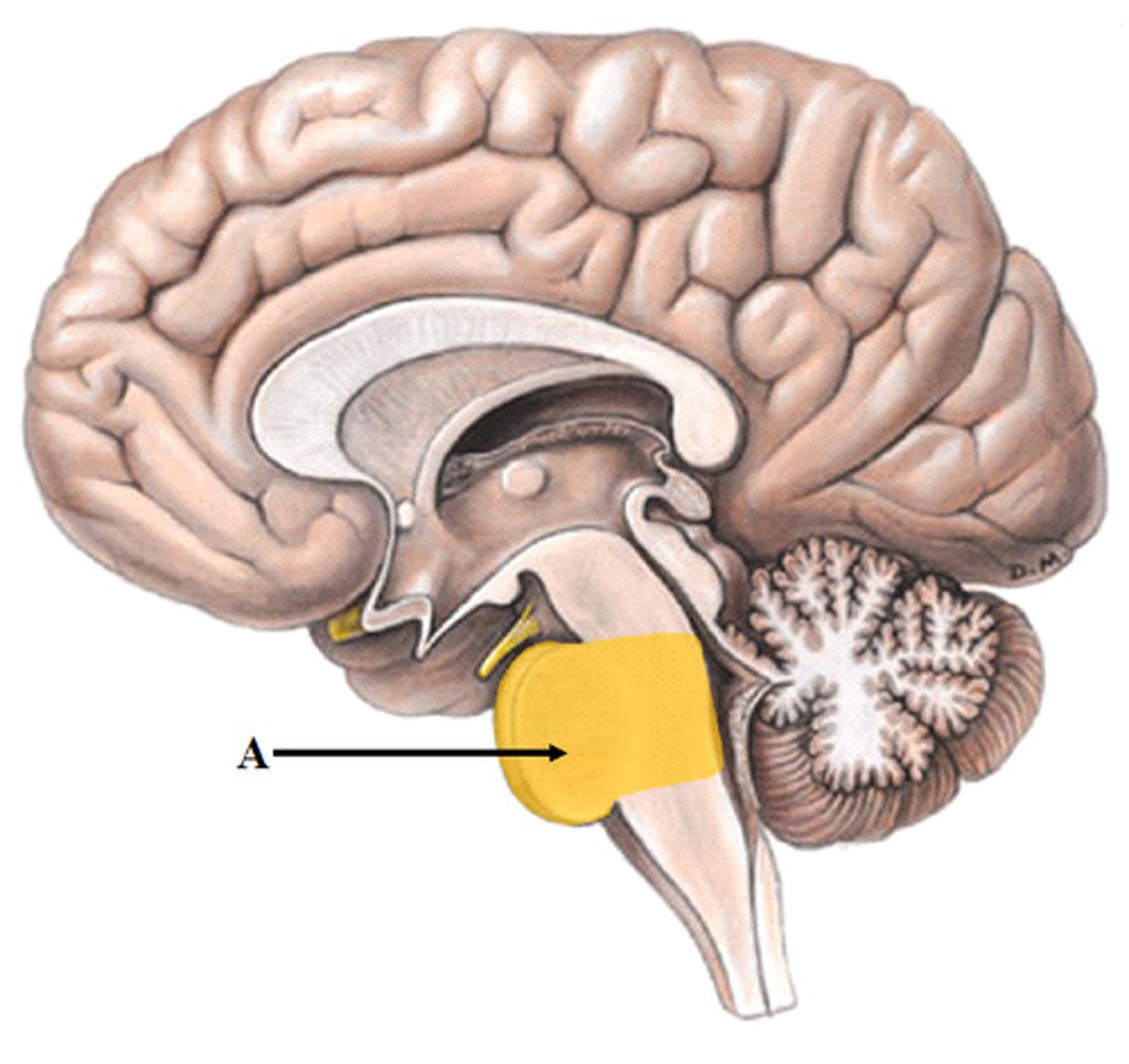
pons
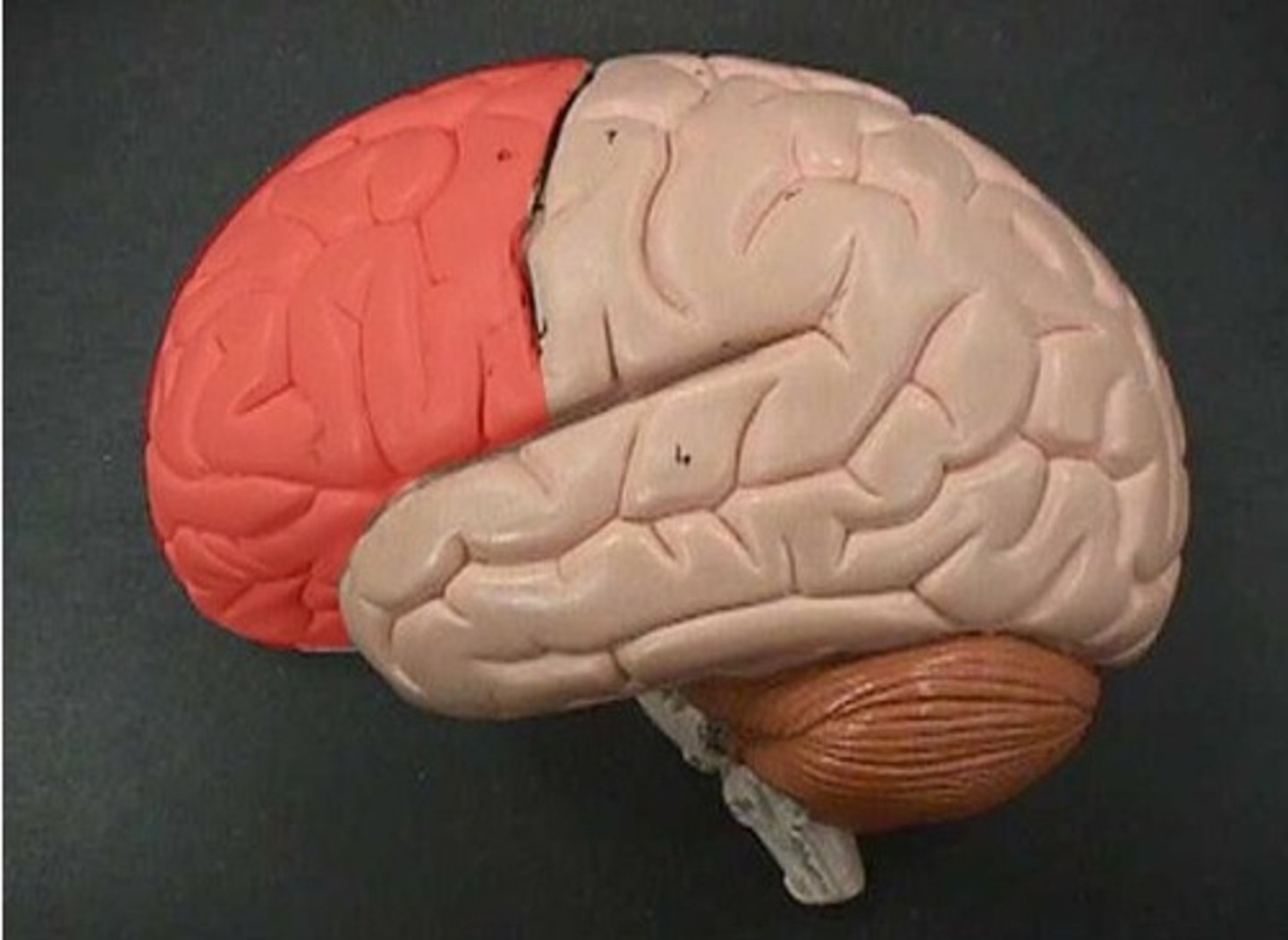
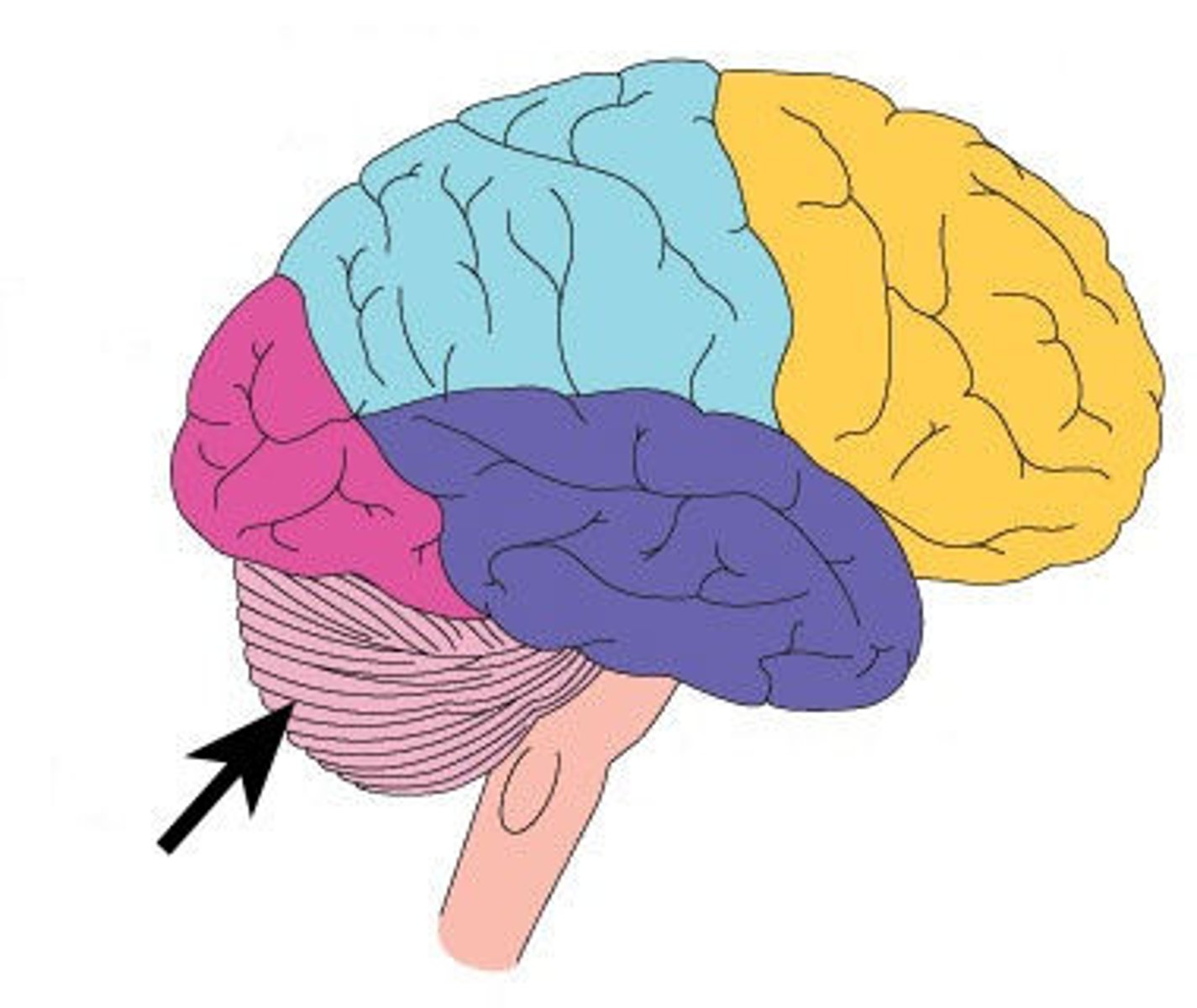
frontal lobe
spinal cord
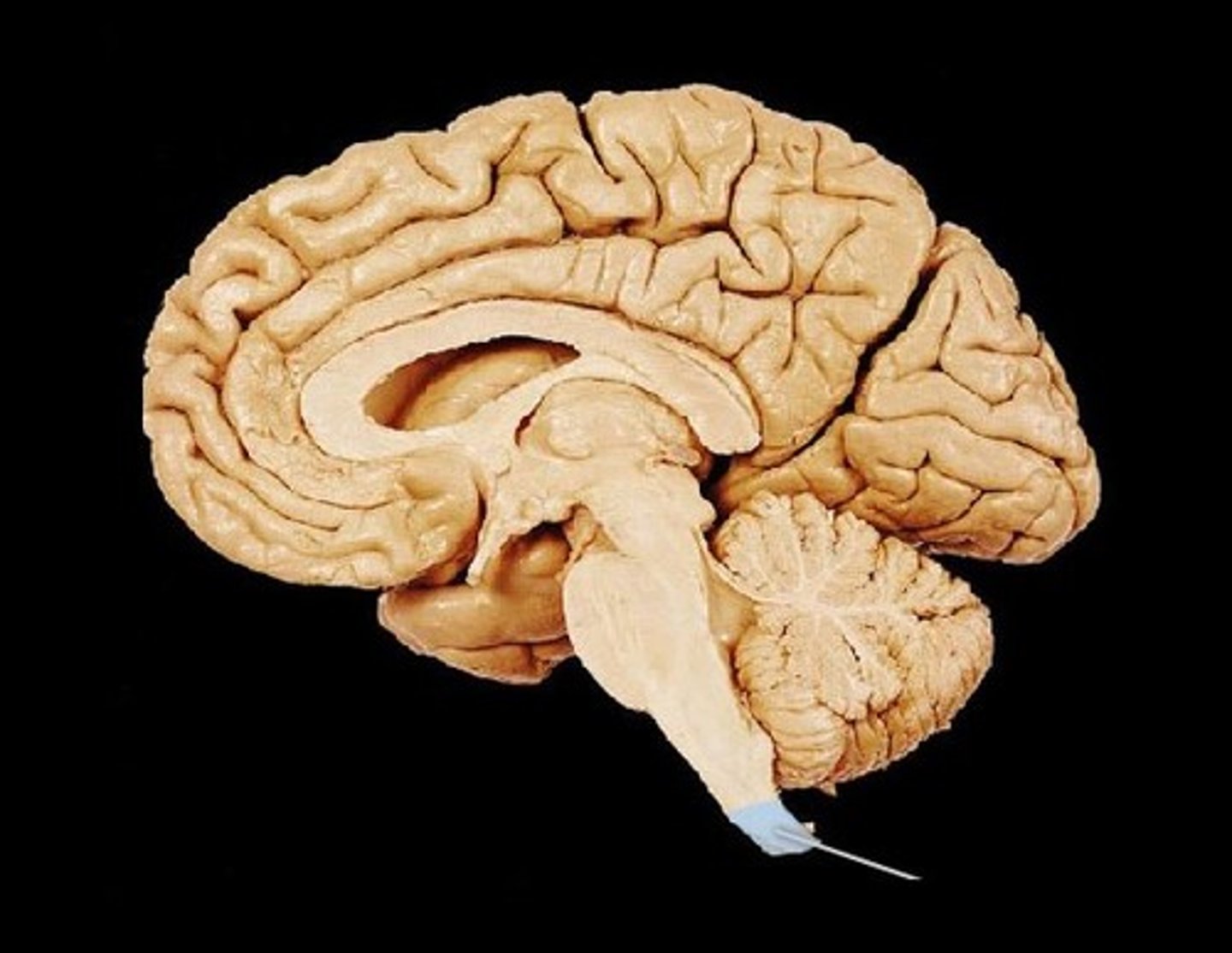
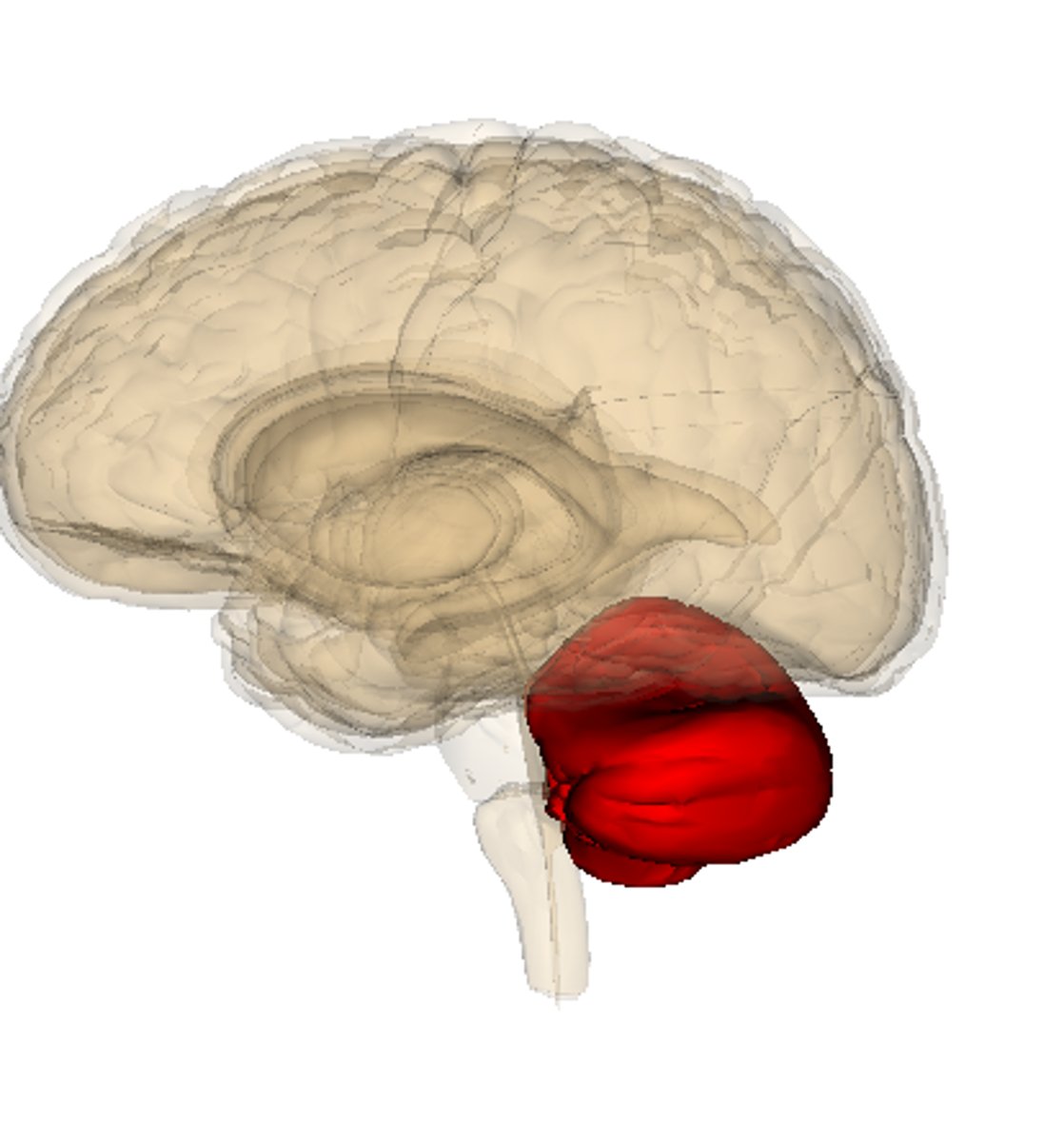
Cerebellum
medulla oblongata
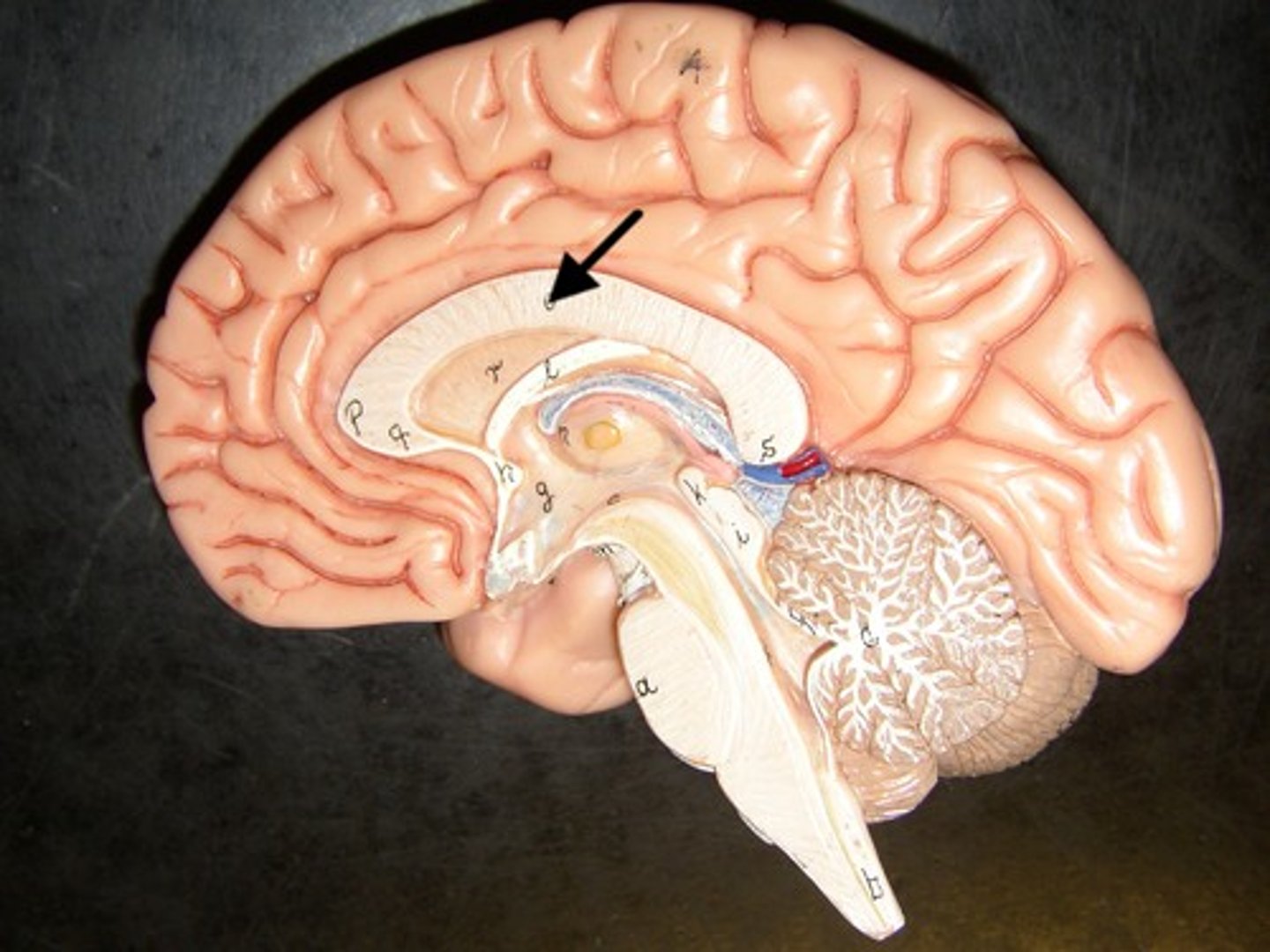
corpus callosum
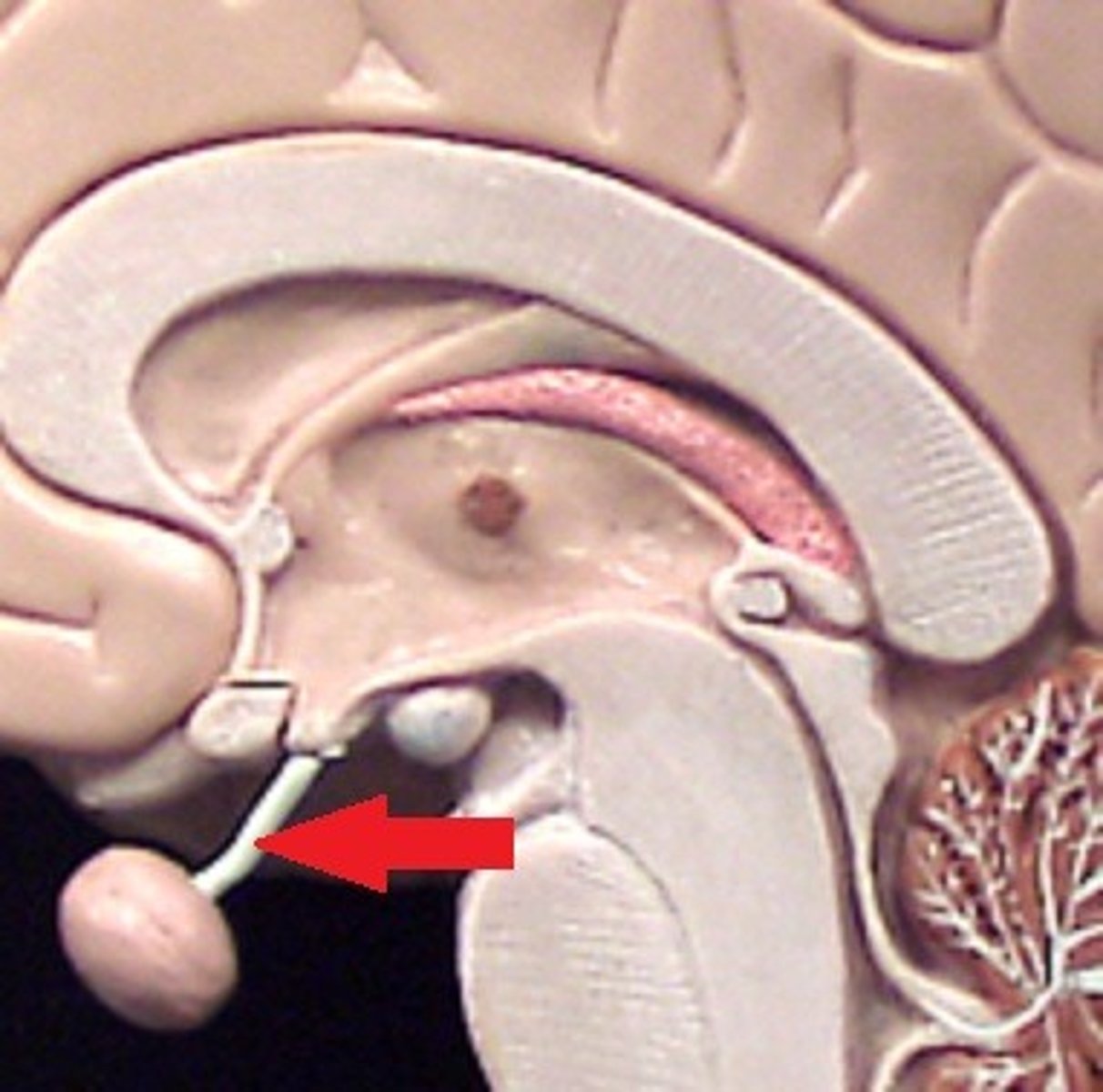
pituitary gland
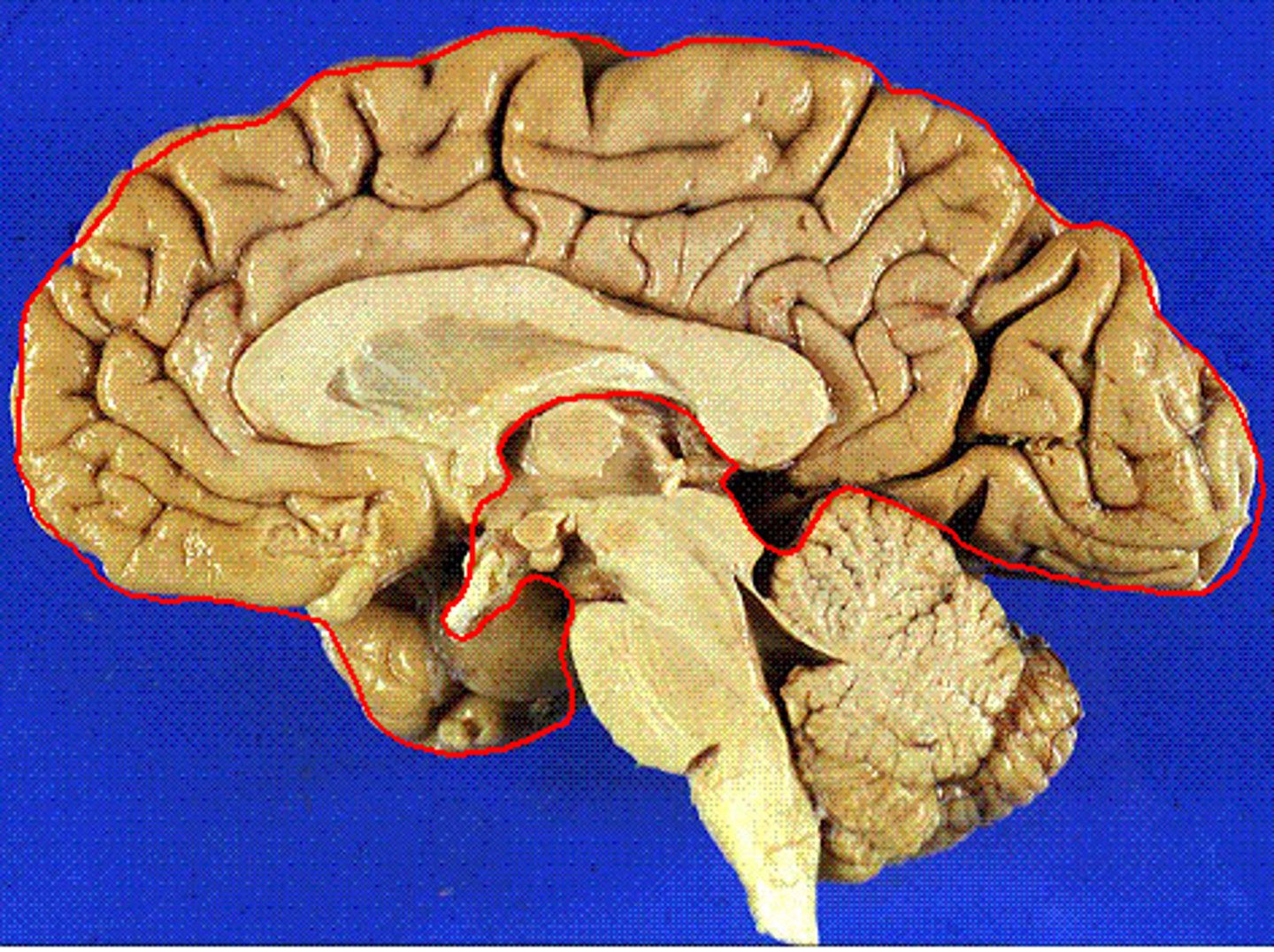
cerebral hemispheres
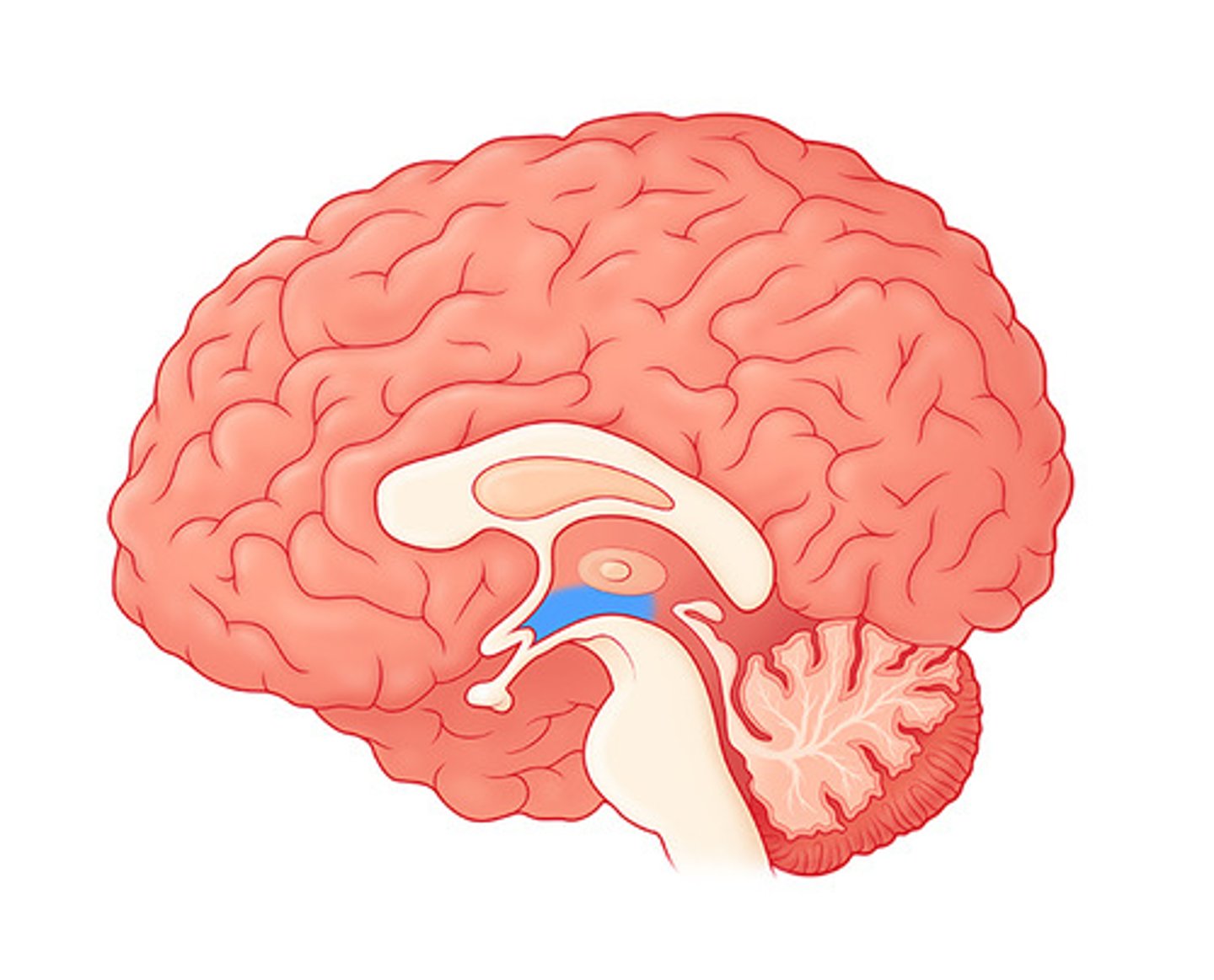
Hypothalamus
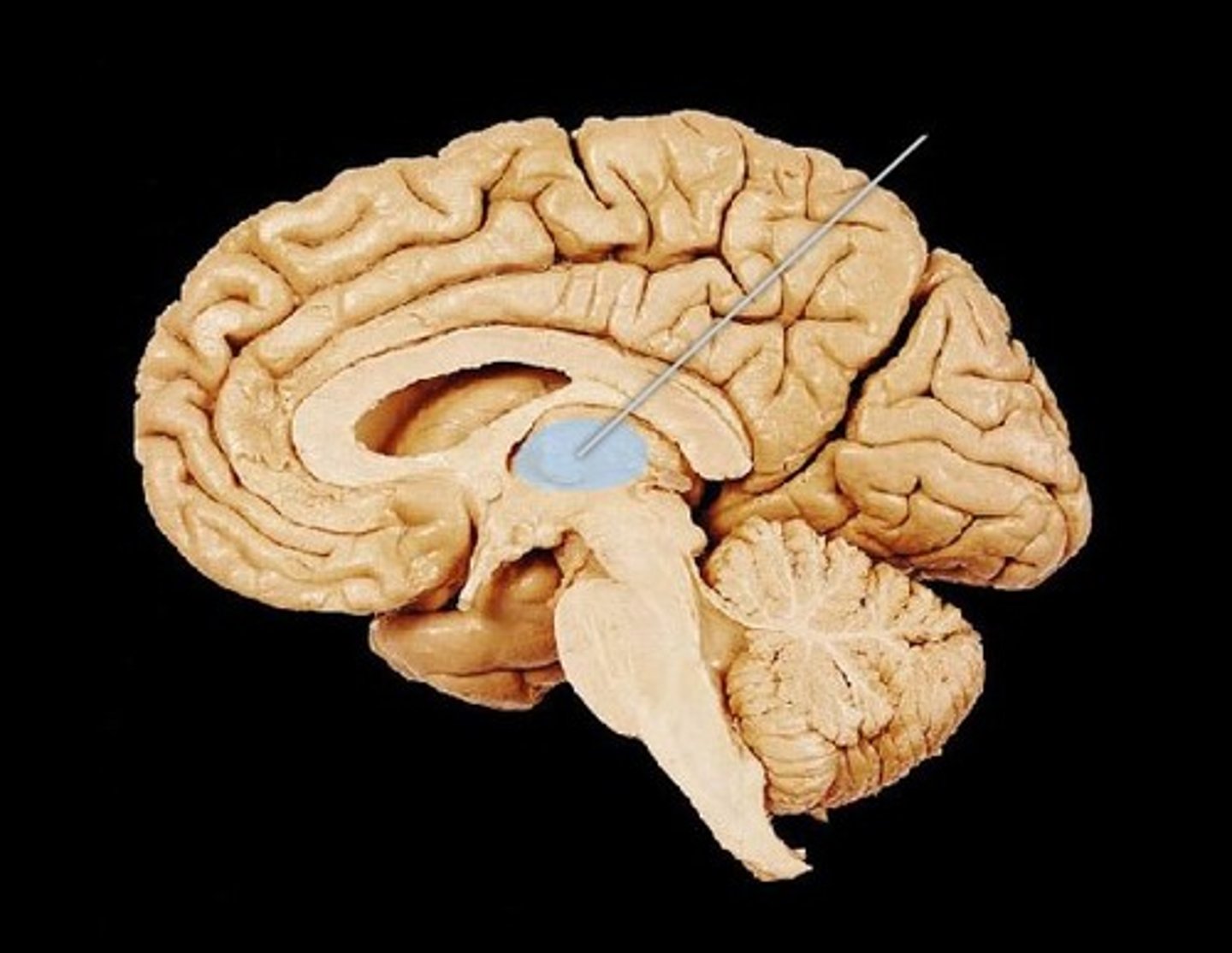
Thalamus
Cerebellum
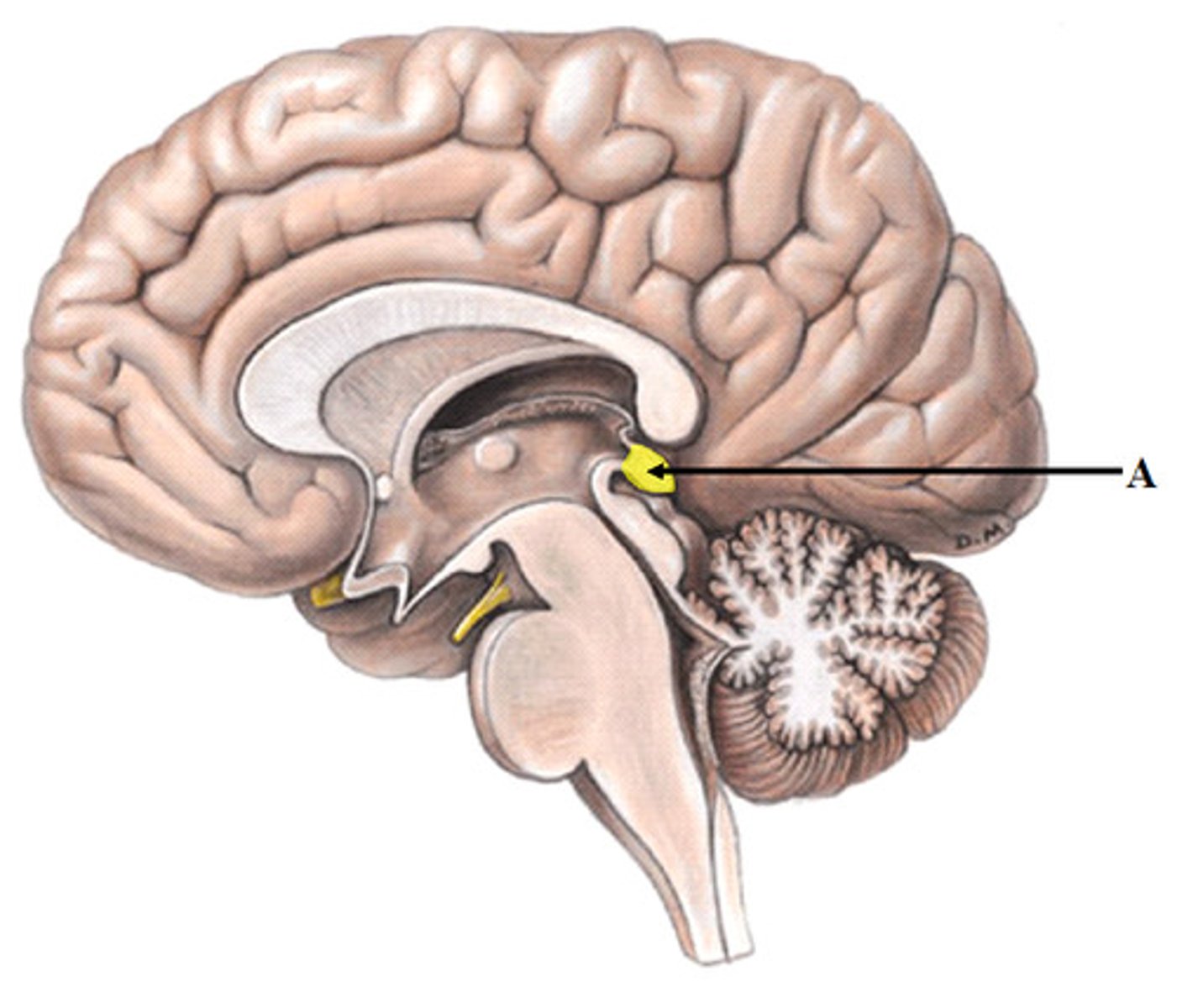
pineal gland
sensory receptor
number 1
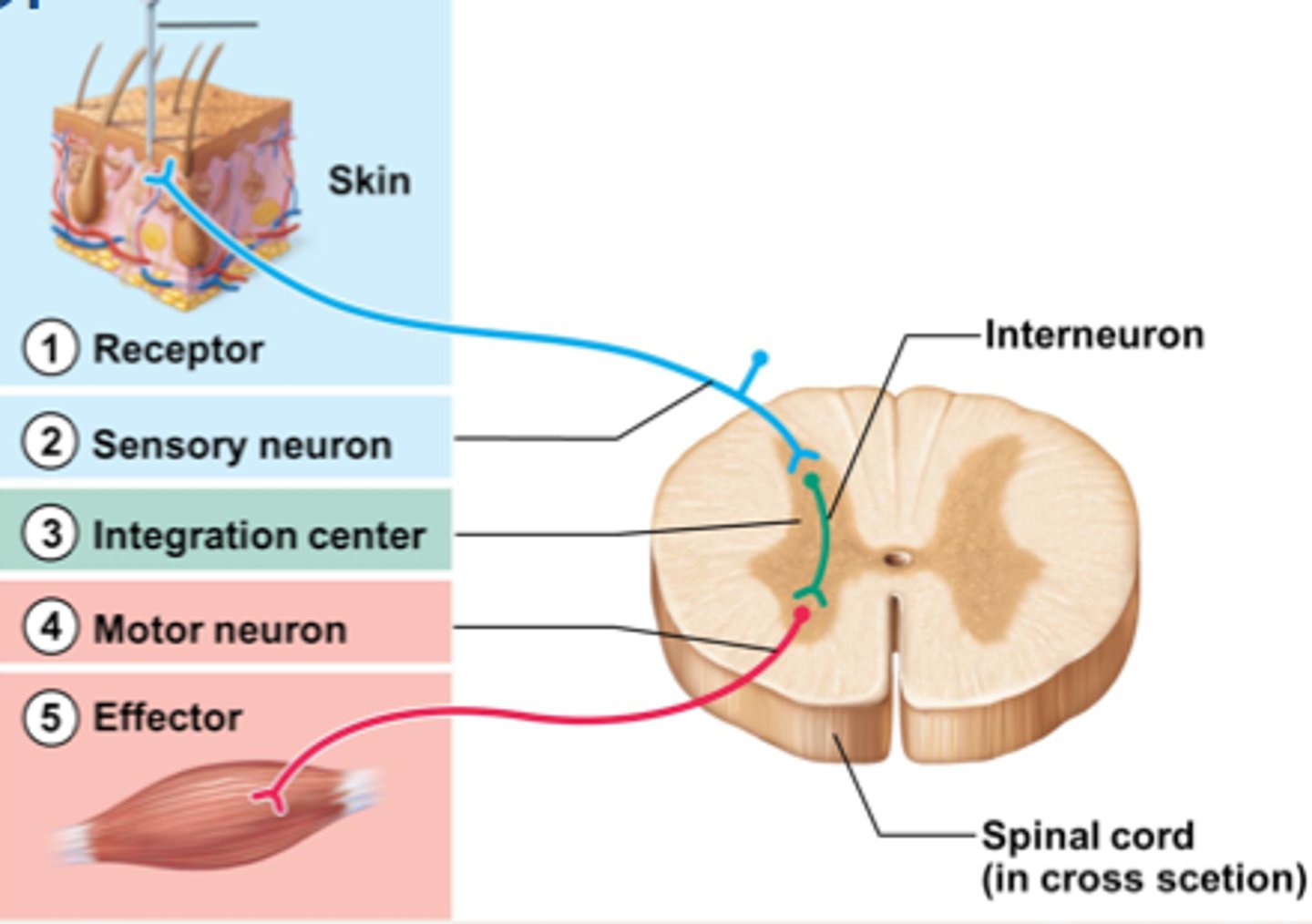
visceral effector
Norepinephrine (NE)
it is an excitatory neurotransmitter. It causes pleasant mood and increased attentiveness in the brain. It causes blood vessels vasoconstriction to increase blood pleasure.
Dopamine
it is an excitatory neurotransmitter. It helps with learning. Associated with pleasant sensation and desire. Often nicknamed the "addiction" neurotransmitter due to its association with addictions. It increases heart rate and force of contraction.
Serotonin
This neurotransmitter increases mood (decreased levels are associated with depression). It stimulates sleep and inhibits appetite.
Endorphin
A type of peptide that decreases sensation of pain. Known as the body's "natural opiates"
GABA
It is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter. Individuals prone to anxiety prone to anxiety may have reduced levels.
Glutamate
It is the main excitatory neurotransmitter and it important in memory and learning.