Unit 2: #6 Genetics: Operons (copy)
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Operon
Regulatory sequence used to regulate genes and their products
Only prokaryotes use operons to regulate genes and their products
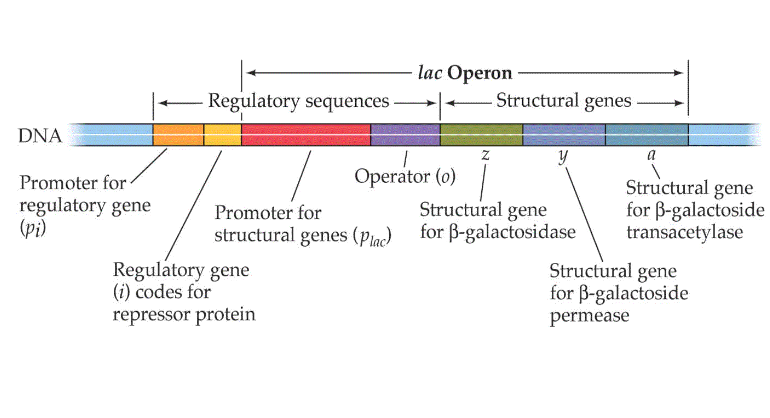
What does an Operon Include?
A cluster of structural genes
Promoter: Binding site for RNA polymerase
Operator: Short sequence of bases controls access of RNA Polymerase to gene
Operator switched off by protein called repressor
Repressor Protein
Binds to operator
Blocks attachment of RNA Polymerase to promoter, preventing transcription
Lac Operon
Consists of 3 genes that code for proteins involved in metabolism of lactose (lacZ, lacY and lacA)
These genes are only required to be transcribed when lactose is present
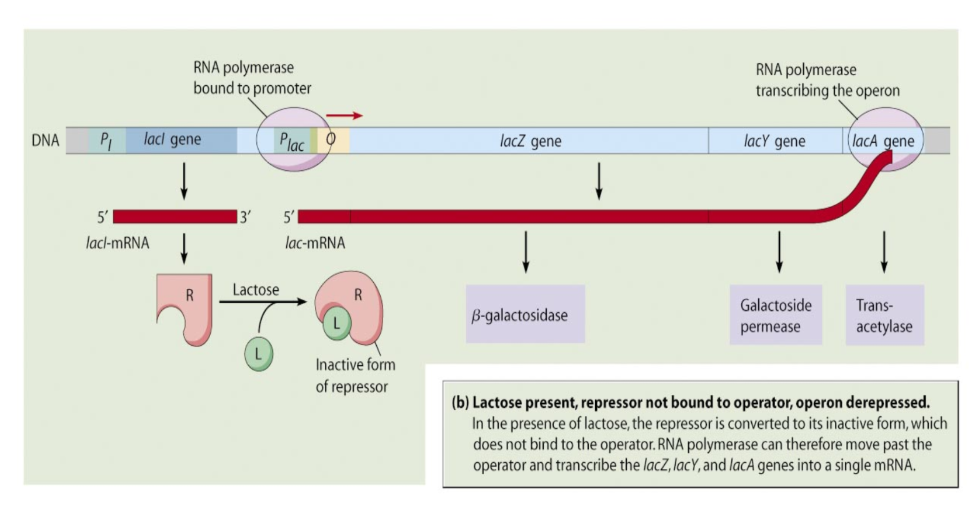
Lac Operons (How it works)
Inducible operon (to start something)
Presence of lactose signals the cell when to synthesize the lactose-metabolizing enzymes
Inducer (lactose) inactivates repressor by changing its shape and allows genes to be transcribed
Transcription proceeds and enzyme Ƃ-galactosidase (needed to break down lactose) is made
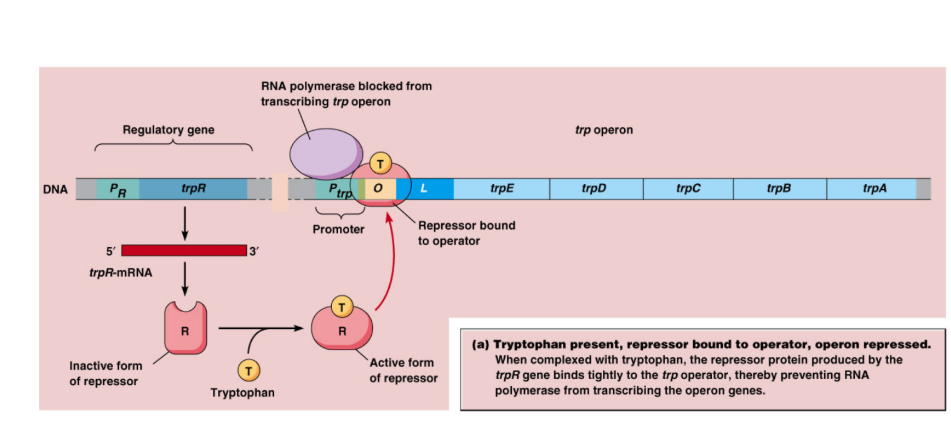
trp Operons
Tryptophan is an amino acid used by E.coli to produce proteins
May need to make their own
If enough tryptophan, it can stop producing it by inhibiting genes
trp Operons (How it works)
Repressible operon
Presence of tryptophan causes transcription to stop
Tryptophan known as co-repressor
When trp levels are high - Tryptophan binds to trp repressor protein, activating it, thus stopping transcription
When trp levels low - Does not bind to operator