histology: methods of study
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
first lecture tissue prep tissue strain artifacts plane of section useful tip
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
what is histology
study of microscope structure and organization of tissues of the body relative to their function
methodology of histology
examine slide, recognize components
assess if normal
if abnormal, identify what is different
before tissue stain what must you do
tissue prep: collect and fix immediately
paraffin for thin sectioning
then you stain, visualize, and view under electron microscope: transmission or scanning EM
what three light microscopes do not require tissue staining?
dark field (DF)
phase contrast (PC)
differential interference contrast (DIC)
what is the light microscope type that typically requires tissue staining?
bright-field (BF) 95% of what we will see
positive/cationic/basic stains will bind to negative or positive molecules?
negative and stain purple
negative tissues are basophilic and have an affinity for hematoxylin; lots of proteins
negative/anionic/acidic stain will bind to negative or positive molecules?
positive and stain pink
positive tissues are acidophilic and have an affinity for eosin
why would other stains be used?
cytoplasmic and ECM proteins cannot be distinguished with H&E staining
some specific cells/inclusions are not preserved with fixation- appear empty
ex: lipid stains for steatosis (fatty liver disease) to see adipocytes are full of lipids
mucus stains
periodic-acid schiff (PAS) stains molecules rich in carbs (glycoproteins and proteoglycans)
silver stains
bind reticular fibers and nerve cell processes
Masson’s trichrome
three-colored stain that distinguishes cells from surrounding ECM
blue=collagen (connective tissue)
purple/dark= nuclei(-)
cytoplasm/keratin= red
elastic fiber stain
aorta and elastic cartilage
metachromasia
change in color within cell/tissue due to interaction with basic dye and polyanions
basic dye=toluidine blue, for mast cells the nuclei is dark but lighter than the outside which is super negative due to mast cell granules which hold heparin
explain a fluorescent tag
anti-tubulin antibody has a fluorescent tag. it binds to tubulin which is the component of cilia.
ground section
take a cut and grind small enough for light to pass through
no organic tissue; this is mineralized bone
air spaces are dark (previous organic)
fine detail visible
non-mineralized bone viewing
no mineralized tissue
soft flexible tissue stains well with H&E
fine detail less visible
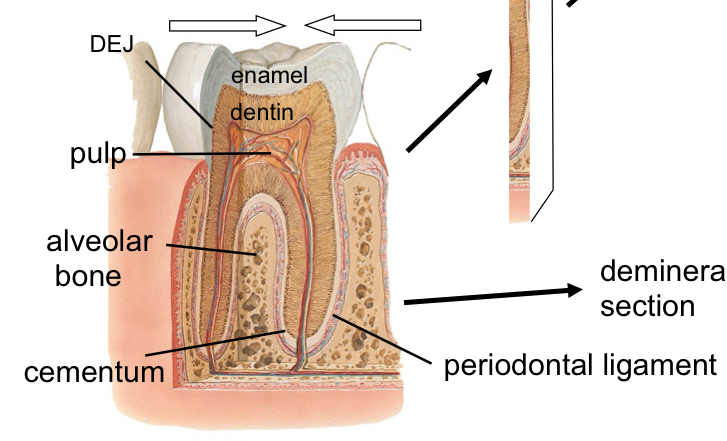
three tissues of the teeth
dentin (70%) and cementum (60%) have mix of collagen and mineralized tissue and resemble bone
enamel (95%) : little protein and no collagen
%=inorganic
tooth composition
pulp (100% organic), periodontal ligament and the three tissues
helpful tips
look at entire field of view
notice scale (compare to nuclei or RBCs)
note nuclear and cytoplasmic characteristics
ratio between cell and non-cell
diagnose epithelium when present: nuclei, type, homo or hetero, unique features: cilia or microvili