9) Microevolution pt A.
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
2 types of evolutionary processes
Microevolution
Macroevolution
Microevolution
Small scale genetic changes within a population in response to environmental changes
Macroveloution
Large scale evolutionary pattern in history like speciation and the origin of higher taxonomic groups
Taxonomy
The scientific study of naming, defining, and classifying biological groups based on shared characteristics
Plastic traits
An organisms ability to change its phenotype in repose to the environment
Flamingo Skin and Hydrangea color
Classifying Evolution
The changes must be genetic, populational, and generational.
Qualitative variation
Less common
Polymorphism
A trait that exist in 2 or more discrete states in the same species
Blue and White now geese
Panama frogs coloration

Quantitative Variation
More common
Continuous
A traits that usually vary continuously across a population
Humans height variation
Horses variation in running speed
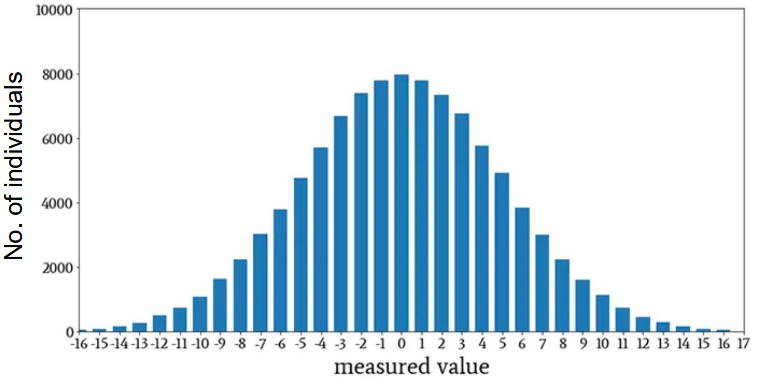
Variation in Variation
Some snails species have more shell size variation than other species.
A low-wide histogram = large variation
A tall-thin histogram = small variation

Genotype
An organisms genetic information
Phenotype
The set of observable physical traits
Reflect an interaction between genotype and the environment
Nature + nurture
How to test if variation in a trait is caused by genetics or the environment (flower height)
Grow the organisms in different environments
Breed like individuals
Then observe if differences persist or disappear.
Persistent vs disappearing traits after manipulation
Persistent = probably determined by genetics
Disappear = probably determined by environment
Mice genetic basis of wheel behavior
Artificial selection enhanced wheel running speed and distance
Chromosomal locus
The position of a gene or other DNA sequence on a chromosome
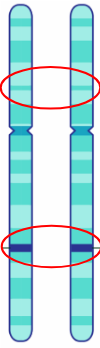
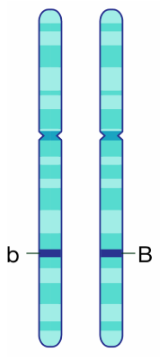
Allele
The differences in genes that determines a specific trait
B = the dominant traits
b = the recessive trait
One from each parent
Population genetics
A field of biology that studies the genetic composition of population and what alters this genetic composition
Genotype frequency
How common a certain pair of alleles is in a population
How common is each genotype in the population
The proportion of individuals with each genotype (BB, bb, or Bb)
Allele frequency
How common each allele is in a population compared to the total number of alleles for the gene
a change in allele frequencies = evolution
Hardy -Weinberg Equilibrium model
Calculates allele frequencies
When at equilibrium frequency doesn’t change across successive generations
Allele and Diploid equation
Alleles: p+q = 1
Diploid: p² + 2pq + q² = 1

What is the frequency of dominant and recessive alleles
What is the frequency of individuals with the 3 different genotypes in the population
Answers

5 factors that can push a population out of HW equilibrium
Mutation
Gene Flow
Non-random mating
Genetic drift
Natural selection
Mutation
UV lighting and chemicals can cause random heritable changes to DNA
Mutations create new DNA sequences resulting in new alleles
In most multicellular organisms, only mutations in germ cells are transmitted to offspring
Most mutations are harmful and decrease reproductive success
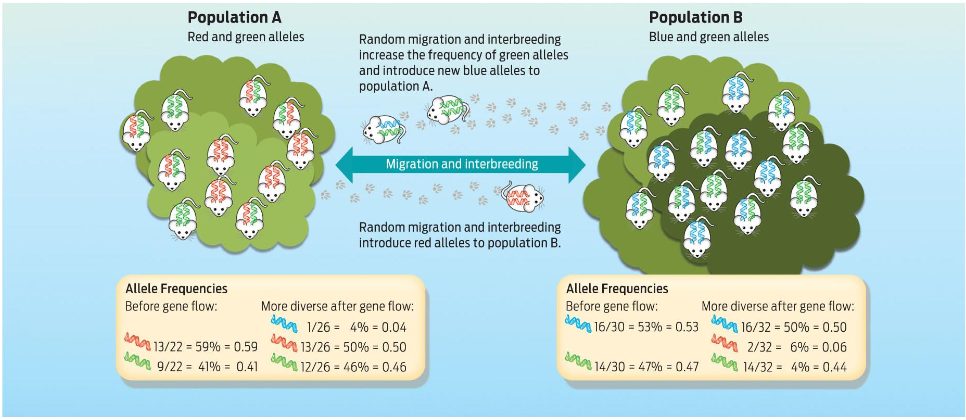
Gene flow
Individuals immigrate to existing populations and bring their alleles with them
This caused different populations to become more similar
It may introduce +, -, or ± alleles to a population
No-random mating (sexual selection)
Selection of mates based on their phenotype
Effects on reproductive success
It often increases success of individuals with unusual traits
It could increase the frequency of alleles with + , -, or ± impacts on survival
Genetic drift
A change in frequency of alleles in a population sue to chance events
Small populations are more vulnerable
loss of a few individuals can drastically change allele frequencies and genetic diversity
Often harmful because of the loss in genetic diversity
Formation of small population
Founder effect
Bottleneck effect
Chance events
Founder effect
When a few individuals start a new population
They carry only a small sample of the original population’s genetic variation
Bottleneck effect
A catastrophic event dramatically reduces the size of a population
The surviving subset population only passes on some of the original populations alleles.
Cheetah
Chance events
Natural disasters eliminate rare alleles making the new population genetically distinct from the original population
Brown beetles getting stepped on more because of bad luck :(
Natural Selection
When individuals have a between chance at survival and reproduction die to heritable traits and live to pass them on.
It can cause one allele to replace another or increase allele variation
The positively effect reproduction success
Three types of natural selection
Directional selection: Favor increase or decrease
Stabilizing selection: Favor mean
Disruptive selection: Favor only Extremes
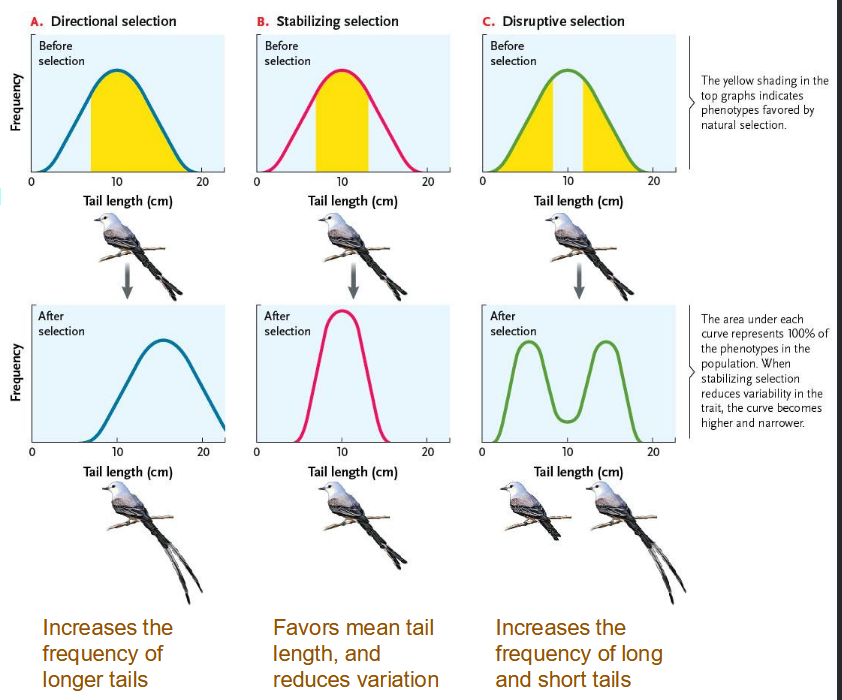
According to Darwin’s theory what drives the process of natural selection
Competition for limited resources
Is competition for limited resources necessary for evolution to operate
NO!!!!
Can happen though gene drift, gene flow, sexual selection, and mutation
In an isolated population of fruit flies, 4% of the individuals have pink eyes, a homozygous recessive condition, and 96% have the dominant black eye phenotype. What percentage of the population are heterozygotes?
32%
Learning Objective
Define evolution as descent with modification in heritable characters within a population.
Distinguish evolution from other forms of biological change such as plasticity, individual development, and ecological succession
Describe the differences between quantitative and qualitative phenotypic variation.
Distinguish between genotype and phenotype.
Discuss the role of the environment in shaping phenotype.
Design experiments that test for a critical role of genetics in the development of a phenotypic response.
Solve problems using the H-W equilibrium equation to determine the frequency and number of (a) the dominant and recessive alleles, and (b) the homozygous dominant, heterozygous and homozygous recessive genotypes in a population.
Use the H-W equilibrium equation to determine whether a population has evolved.
Distinguish between the five agents of evolutionary change.
Distinguish between directional, stabilizing and disruptive selection.
Indicate conditions that would resist evolutionary change in a population.