Multicellular Organisms
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
single celled orgainism
can exchange substances directly with their environment
multicellular organism
have cells that don’t interact with the external environment and have a specialised internal environment which allows the exchange of vital substances between cells and the extracellular fluid that surrounds them
specialised cells
what are the 4 types of tissue in animals?
connective tissues, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, nervous tissue
digestive system
the organs that take in food and liquids and break them down into substances that the body can use for energy, growth, and tissue repair
circulatory system
the system that transports blood, nutrients, gases, and waste products throughout the body.
vessels
that carry blood throughout the circulatory system, arteries, veins and capillaries
blood
is a type of connective tissue in animals, which transports nutrients and
oxygen to tissue cells for respiration, metabolism, and growth, as well as
transporting waste products to the excretory organs
erythrocytes
red blood cells
leukoytes
white blood cells
haemoglobin
a protein in red blood cells
platlets
cell fragments
open circulatory system
a type of circulatory system where blood is not always contained within vessels and bathes the organs directly.
what animals have an open circulatory system?
Arthropods including insects, crustaceans and most mollusks
haemolymph
circulates around the organs within the body cavity, reentering the heart through openings called ostia
ostia
openings in the heart that allow haemolymph to reenter after circulating around the organs.
closed circulatory system
there are 2 types the single and the double
single circualtory system
blood passes through the heart once only as it is pumped first through the gill capillaries, then the systemic capillaries in the organs and tissues, before returning to the heart.
double circulatory system
blood passes through the heart twice, as it completes two separate circuits or loops. The first loop carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation, while the second loop distributes oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
what type of animals have a single circulatory system?
fish
what type of animals have a double circulatory system?
amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals
pulmonary circuit
pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs, where oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide expelled, and the blood is then returned directly to the heart.
systematic circuit
pumps the oxygenated blood out to the tissues and organs of the body, before returning the deoxygenated blood to the heart.
what circuit do amphibians have and why is it unique?
pulmocutaneos circulation because it brings deoxygenated blood to the surface for the gas exchange.
in mammals and birds what is the 2 circuits seperated by?
septum, dividing the heart into 2 seprate pumps
what does the septum in the mammalian heart also divide?
atrium and ventricle
atrium
collecting chamber
ventricle
pumping chamber
what does the right atrium do?
collects deoxygenated blood from the body
what does the right ventricle do?
pumps the deoxygenated blood into the lungs
what does the left atrium do?
collect oxygenated blood returning from the lungs
what does the left ventricle do?
pumps the oxygenated blood into the body
tricuspid and bicuspid (mitral) valves
prevent the back flow of blood between the ventricles and atria
pulmonary and aortic valves
prevent backflow between the major arteries and ventricles
pacemaker cells
control the timing within the heart
what do artieries do?
carry blood away from the heart
systole
the hearts contraction, sending blood out of the heart
diastole
when the heart relaxes and refills
what are capillaries?
are small, thin-walled blood vessels that branch out from arteries
capillary beds
maximise the contact between the blood vessels and the cells of the bodily tissues
capillary walls
are leaky and allow plasma to leave and mix with the interstitial fluid
what are in the capillaries?
blood cells and platelets
veins
collect the blood after it has passed through the capillaries and returns it to the heart
why do veins have thinner walls
the blood is under much lower pressure than in the arteries and contain one way valves that prevent back flow
cellular respiration
the process by which cells use oxygen to break down food molecules to create energy for life-sustaining activities
what does the exchange of gases require?
A semi-permeable membrane
A concentration gradient across the membrane
(diffusion occurs from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration)
The membrane must be kept moist at all times
The membrane must have a high surface area relative to the volume of diffusion
insects gas exchange system
through a series of small pores called spiracles, which connect to an internal network of gas exchange surfaces called tracheoles.
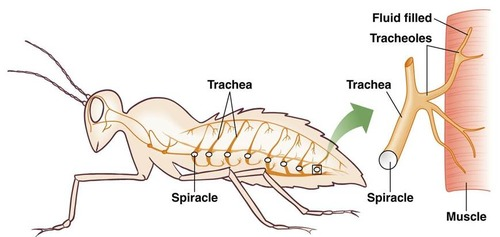
fish gas exchange
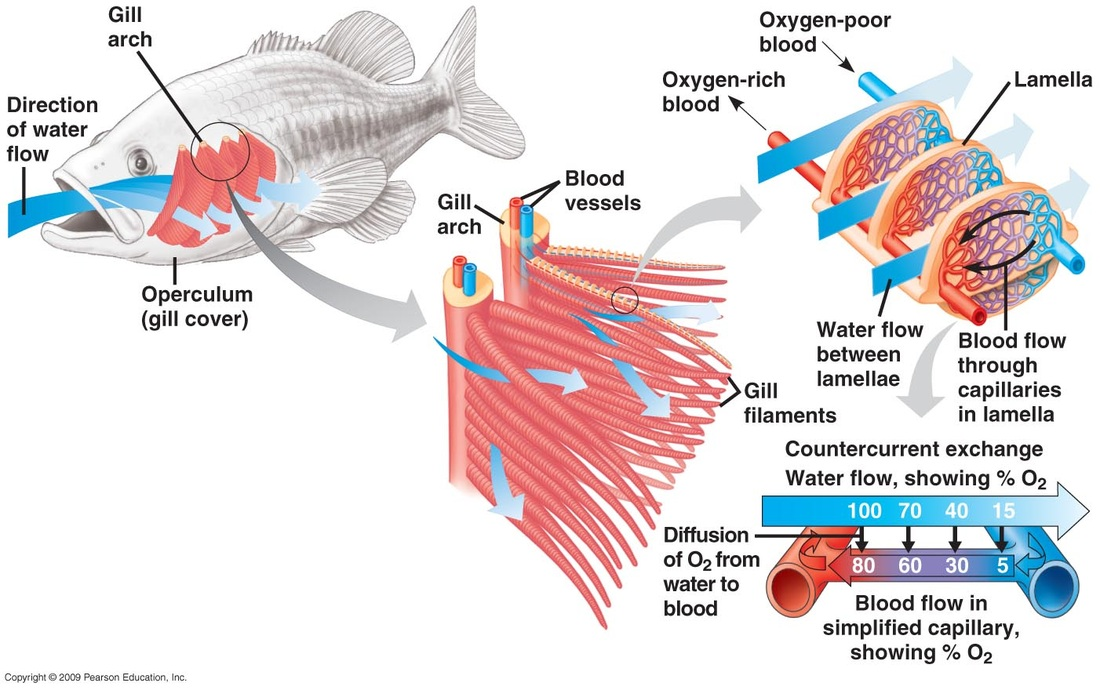
are vertebrate animals that use gills to exchange gases with their water environment.
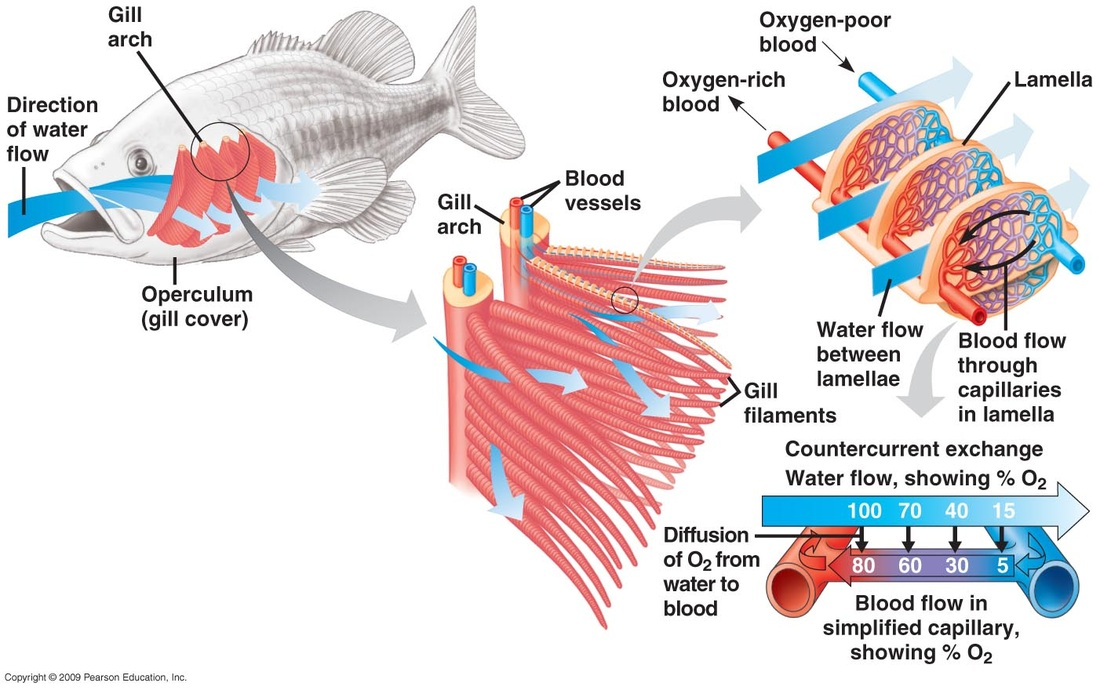
gills
have many folds and individual filaments which provide a large surface area for the exchange of gases.
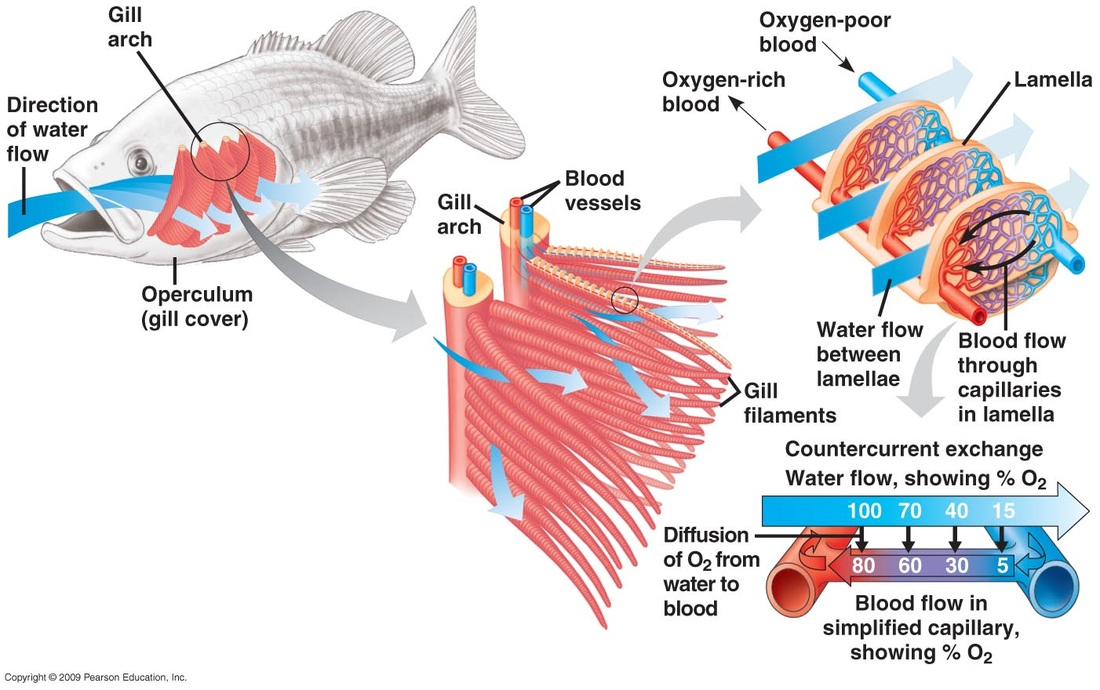
how is the concentration gradient maintained in a fish?
is maintained by the flow of water in through the mouth and out through the gill slits, as well as the flow of blood through capillaries surrounding the gill filaments which carry oxygen to the body and return carbon dioxide to the water
mammals gas exchange
use lungs for the extraction of oxygen from air and the removal of carbon dioxide from the body
alveoli
greatly increase the surface area of the lungs and are composed of a thin layer of epithelial cells that are lined with a fluid that enables the rapid passive diffusion of gases into and out of the blood. Constant blood flow through the surrounding capillaries maintains a strong concentration gradient.
difference between fish and mammals gas exchange
Unlike in fish where water passes in one direction across the exchange surface, air must be constantly pulled in to the lungs, then pushed out again through a process called ventilation (breathing).
what are the 2 main stages of ventilation?
inspiration and expiration
inspiration
is the movement of air into the lungs
The intercostal muscles move the ribcage upwards and outwards causing the chest to expand.
The diaphragm contracts and flattens which increases the volume and decreases pressure inside the lungs
Air flows from the higher pressure of the environment into the lower pressure of the lungs.
expiration
is the movement of air out of the lungs
The intercostal muscles move the ribcage downwards and inwards causing the chest to contract.
The diaphragm relaxes and moves upwards which decreases volume and increases pressure inside the lungs
Air flows from the high pressure inside the lungs to the lower pressure of the external environment.