Chapter 3
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Cephalocaudal Pattern
the sequence in which the fastest growth in the human body occurs at the top, with the head
Physical growth in size, weight, and feature differentiation gradually works its way down from the top to the bottom (for example, neck, shoulders, middle trunk, and so on). T
Proximodistal Pattern
the growth sequence that starts at the center of the body and moves toward the extremities
An example is the early maturation of muscular control of the trunk and arms, compared with that of the hands and fingers.
Further, infants use the whole hand as a unit before they can control several fingers
Growth Patterns
it often is not smooth and continuous but rather is episodic, occurring in spurts
In infancy, growth spurts may occur in a single day and alternate with long time frames characterized by little or no growth for days and weeks
Growth Trends in Infancy
20 inches long and weighs 7.5 lbs
the fastest rate of growth
Growth Trends in Early Childhood
slimmer stature
lengthening of trunk
decline in body fat
growth here may vary a lot bc of genetics
Growth Trends in Middle and Late Childhood
slow, constant growth
average 2-3 inch growth, 5-7 lbs weight gain a year
the calm before you hit puberty
Puberty
a brain-neuroendocrine process occurring primarily in early adolescence that provides stimulation for the rapid physical changes that take place during this period of development (Nguyen, 2019)
Order of Puberty Changes in Men
increase in penis and testicle size
appearance of straight pubic hair
minor voice change
first ejaculation (which usually occurs through masturbation or a wet dream)
appearance of curly pubic hair, onset of maximum growth in height and weight, growth of hair in armpits,
more detectable voice changes
growth of facial hair
Order of Puberty Changes in Women
breasts enlarge or pubic hair appears
hair appears in the armpits
the female grows in height and her hips become wider than her shoulders
Menarche
Menarche
a girl’s first menstruation
comes rather late in the pubertal cycle
cycles initially may be irregular
Horomones
powerful chemical substances secreted by the endocrine glands and carried through the body by the bloodstream
Endocrine System
role in puberty involves the interaction of the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, and the gonads
Hypothalamus
a structure in the brain, is involved with eating and sexual behavior
Pituitary Gland
controls growth and regulates other glands such as the gonads
sends a signal via gonadotropins to the appropriate gland to manufacture hormones
through interaction with the hypothalamus the pituitary gland also secretes hormones that either directly lead to growth and skeletal maturation or produce growth effects through interaction with the thyroid gland, located at the base of the throat
Gonads
the testes in males, the ovaries in females
Gonadotropins
hormones that stimulate the testes or ovaries (the gonads)
Testosterone
a hormone associated in boys with the development of genitals, increased height, and deepening of the voice
present in pubescent boys and girls, just more in boys
Males – development of genitals, increase in
height, facial hairFemales – body hair, oil production, muscle
development, sex drive
Estradiol
a type of estrogen associated in girls with breast, uterine, and skeletal development
Estrogen
Females – development of breasts, uterus, and
skeletal changesMales – bone growth, body fat, libido, voice
change
Timing of Puberty
affected by nutrition, health, family stress, and other environmental factors
some studies say ppl w higher BMI’s start puberty earlier
For most boys, the pubertal sequence may begin as early as age 10 or as late as 13½, and it may end as early as age 13 or as late as 17
For girls, menarche is considered within the normal range if it appears between the ages of 9 and 15
Gender Differences in the Timing of Puberty
Girls tend to mature faster
Girls who mature early suffer negative
social/psychological effectsBoys who mature early tend to benefit socially, while
“late bloomers” suffer
Growth Trends in Early Adulthood
age 18-39
height remains mostly constant
peak functioning of the body is the twenties (19-26)
can begin to see signs of aging
wrinkles
joint pain
weight gain in abdomen
sagging chin and skin
Growth Trends in Middle Adulthood
increased, but still gradual decline
Physical Appearance:
start to lose height and many start to gain weight
skin loses plasticity (from loss of fat and collagen in underlying tissues)
Middle Adulthood Change in Strength, Joints, and Bones
sarcopenia - age-related loss of lean muscle mass and strength
sarcopenic obesity - reference to individuals who have sarcopenia and are obese
Middle Adulthood Change in Cardiovascular System
Cardiovascular disease increases considerably in middle age
Cholesterol comes in two forms: LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and HDL (high-density lipoprotein)
LDL is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol because when the level of LDL is too high, it sticks to the lining of blood vessels, a condition that can lead to arteriosclerosis
HDL is often referred to as “good” cholesterol because when it is high and LDL is low, the risk of cardiovascular disease decreases
Middle Adulthood Change in Lungs
at about the age of 55, the proteins in lung tissue become less elastic
This change, combined with a gradual stiffening of the chest wall, decreases the lungs’ capacity to shuttle oxygen from the air people breathe to the blood in their veins
Middle Adulthood Change in Sexuality
Climacteric - the midlife transition when fertility declines
Menopause - the time in middle age, usually in the late forties or early fifties, when a woman has not had a menstrual period for a full year
Testosterone production begins to decline about 1 percent a year during middle adulthood, and this decline can reduce sexual drive (Hyde & others, 2012). Sperm count usually shows a slow decline, but men do not lose their fertility altogether.
Late Adulthood Change in Physical Appearance
Increased changes
Weight drops after 60 due to muscle
lossHealthy lifestyle can prevent this
Late Adulthood Change in Circulatory Appearance
increase in hypertension rates
heart attack
stroke
kidney disease
Frontal Lobe
voluntary movement, thinking, personality, emotion, memory, sustained attention, intentionality or purpose, self-control
Occipital Lobe
Vision
Temporal Lobe
hearing, language processing and production, and memory
Parietal Lobes
registering spatial location, special ability, focusing attention, and maintaining motor control
Neurons
nerve cells
that transmit and
process information
How Neurons Process Infromation
Basically, an axon sends electrical signals away from the central part of the neuron. At tiny gaps called synapses, the axon communicates with the dendrites of other neurons, which then pass the signals on. The communication in the synapse occurs through the release of chemical substances known as neurotransmitters
Myelination
encasing a neuron in fat to increase
speed and efficiency with which information travelsimportant for brain functioning
Myelin Sheath
the fatty substance that insulates the axon of the neuron
controls how fast a neuron communicates
Synapse
gap between a sending and receiving neuron
Lateralization
left
Speech and grammar
controls right side of the body, analytic reasoning, and language
Right
humor and the use of metaphors depend
attention and emotion
ontrols left side of the
body, special reasoning, emotional reasoning
This is called lateralization - specialization of function in one hemisphere of the cerebral cortex or the other
The Infant Brain
Sensitive Period
Synaptogenesis: growth of synapses in the
brainSynaptic Pruning: removal of unnecessary
synapsesPromote efficient processing
Environmentally influenced
Plasticity: the brain can is changes by our
experiencesTrauma and plasticity
Greatest plasticity during early development
Brain Development in Infancy and Childhood
Brain triples in weight first two years of life
Large degree of myelination
Development of neural pathways
As we experience and learn
Stimulating environment
Growth depends on what is being learned
The Brain and Neglect
causes depressed brain activity
some damage can be reversed if caught early
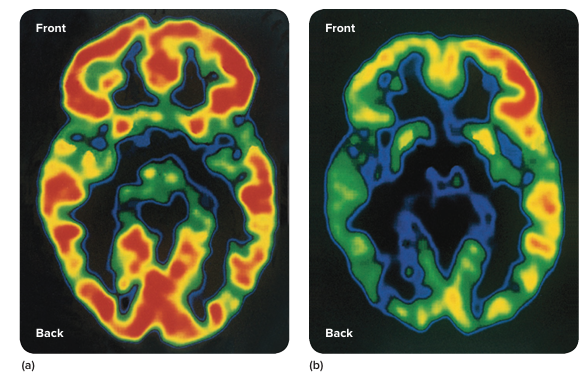
Brain Development in Adolescence
Growth focused on efficiency
corpus callosum thickens
connects hemisphere
Some areas have reached maturity
limbic system - emotions and rewards
amygdala
Dopamine
increased levels contribute to ward seeking
Brain isn’t done yet:
prefrontal cortex - controls decision making and emotion
Corpus Callosum
where fibers connect the brain’s left and right hemispheres, thickens in adolescence, which improves adolescents’ ability to process information
Limbic System
which is the seat of emotions and where rewards are experienced, matures much earlier than the prefrontal cortex and is almost completely developed by early adolescence
Amygdala
A part of the brain’s limbic system that is the seat of emotions such as anger
Aging in the Adult Brain
On average, the brain loses 5 to 10 percent of its weight between the ages of 20 and 90
number of synapses decreases, neurons shrink
increased decline in late adulthood
slower processing speed and memory
decline
prefrontal cortex - working memory
acetycholine - memory, alzheimer’s
dopamine - parkinsons
exercise, diet, and continued stimulation through challenging the brain can slow this
Free-Radical Theory
build up of toxins and chemicals over time
metabolic processes produce unstable oxygen
oxygens pair inefficiently in the body
Cellular Clock Theory
Leonard Hayflick’s theory that the number of times human cells can divide is about 75 to 80. As we age, our cells become less able to divide
Mitochondrial Theory
The theory that aging is caused by the decay of the mitochondria, which are tiny cellular bodies that supply energy for cell function, growth, and repair.
Telomerase-Injection Theory
the ends of DNA unravel as cells reproduce
eventually, new cells are unstable
cells cannot replicate and die
Sirtuins
A family of proteins that have been proposed as having important influences on longevity, mitochondrial functioning in energy, calorie restriction benefits, stress resistance, and cardiovascular functioning
mTOR Pathway
A cellular pathway that involves the regulation of growth and metabolism and has been proposed as a key aspect of longevity
Hormonal Stress Theory
The theory that aging in the body’s hormonal system can lower resistance to stress and increase the likelihood of disease.
Life Span maximum numbers of years an individual can live
about 120-125 years
Why do We Sleep?
evolutionary - needed to protect themselves at night
replenishes and rebuilds the brain and body, increases the production of proteins
clears out waste in neural tissues
essential to waste plasticity
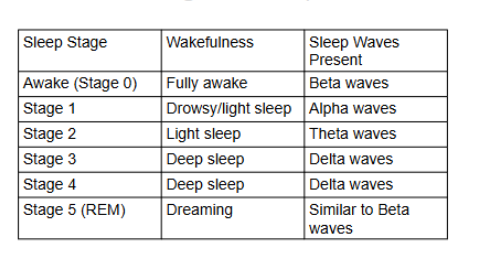
Stages of Sleep
Sleep in Infancy
ages 0-2 sleep 12.8 hours a day
newborns sleep 16-17 hours
REM Sleep
rapid eye movement
take up more time in infancy than any other point in the life span
for adults, (and maybe babies, we don’t know) this is when they dream
SIDS (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome)
a condition that occurs when infants stop breathing, usually during the night, and die suddenly without an apparent cause
remains the highest cause of infant death in the United States
highest around 2-4 months
Causes of SIDS
Many causes: Arrhythmias, low birth weight, temporary sleep
apnea, abnormal brain stem functioning, exposure to
cigarette smokeBiggest risk: sleeping on stomach and sleeping with parents
Sleep During Childhood
2-6: 11-13 hrs w a daytime nap
7-12: 10-11
routine w good sleep hygiene probes brain to wind down and fall asleep quicker
Childhood Sleep Habits
Good habits:
better attention, language abilities, social skills, peer acceptance, school performance
Bad habits:
can contribute to ADHD
Sleep in Adolescence and Emerging Adulthood
Most need 7-8 hours, but very few get this
Poor sleep can lead to:
obesity
poor school performance
attention problems
caffeine use
anxiety
depression
Sleep in Adulthood
7 to 8 hours
Chronic sleep deprivation
Cardiovascular disease
Shortened life span
Impaired cognitive abilities
Can be counted by:
Less caffeine, sleep aids
healthy weight
healthy diet
stay active!
The Effect of Marijuana on the Brain
Impact on teenagers
Drug dependency (marijuana and other!)
Schizophrenia
Self-control
Decision making
Neurotransmitter disruption
Impact on developing fetus
Emotional regulation
Susceptibility to addiction
Climateric
the midlife transition when fertility declines.