CERTIFIED HEALTHCARE SAFETY PROFESSIONAL (CHSP) OFFICIAL CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION | THE AMERICAN HOSPITAL ASSOCIATION PROCTORED CREDENTIAL ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 2025-2026
1/275
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
276 Terms
Joint Commision core value
Quality of care and safety of patients

The Patient Safety and Quality Improvement Act of 2005
to report events, near misses, unsafe conditions and to decrease medical errors. defined requirements for reporting events that threaten patient safety

Patient Safety
the avoidance and prevention of patient injuries or adverse events resulting from the processes of health care delivery.

Patient safety event
event, incident, or condition that could have resulted or did result in harm to a patient
adverse event
A patient safety event that resulted in harm to a patient
sentinel event
a patient safety event not primarily rekated to the patients illness or underlying condition that leads to death, permanent harm or severe temporary harm.

Reactive risk reduction
Attempts to prevent recurrence of problems that have already caused patient harm.
Proactive risk reduction
Solves problems before patients are harmed
Sentinel event alert
A notification that defines processes and identifies measures that can be used to prevent errors and improve outcomes

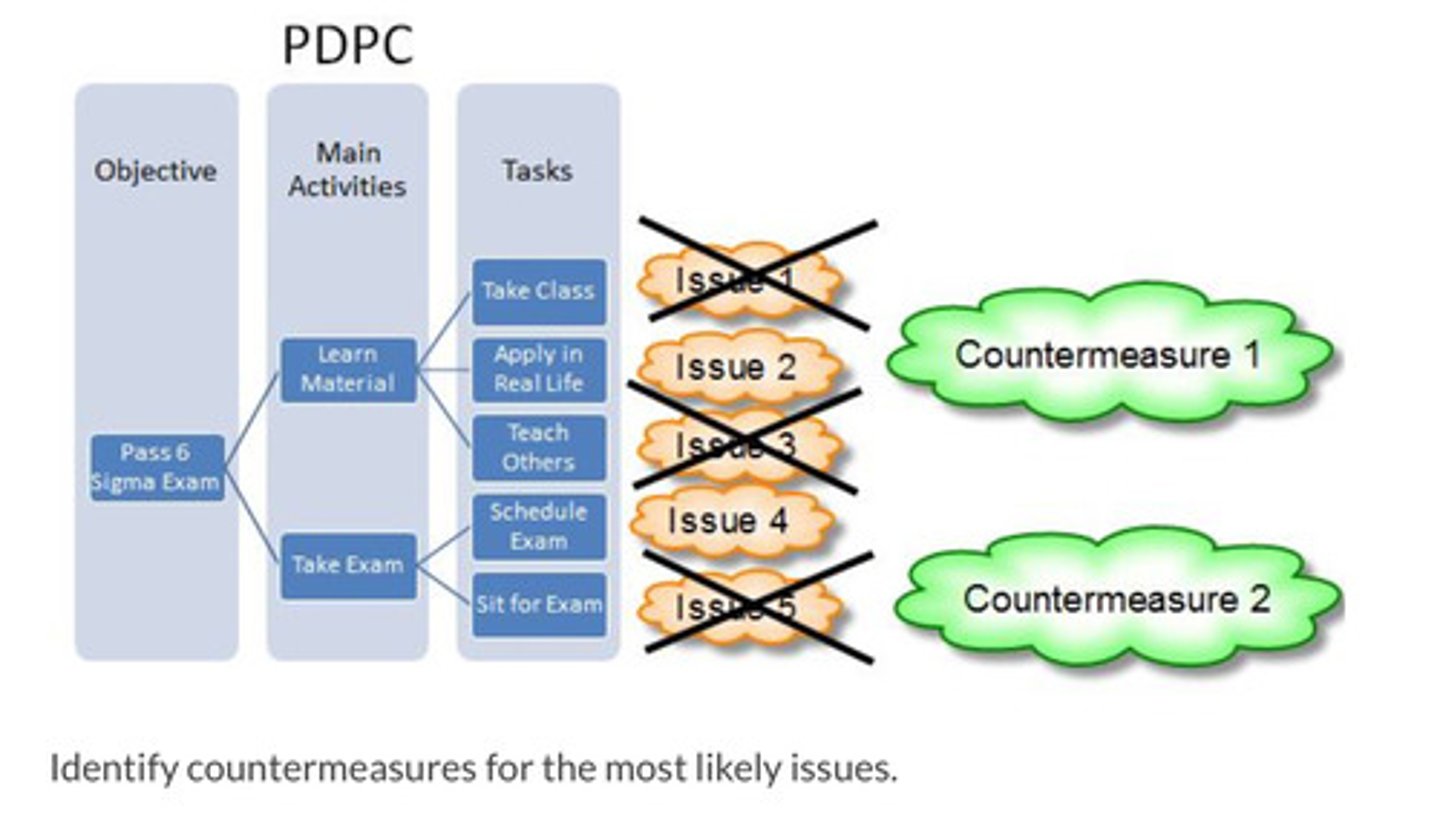
Process Decision Program Charts (PDPC)
Finds errors in plans while it is being created.
American Osteopathic Association (AOA)
inspects and accedidates critical access hospitals

Accreditation canada
Camadian non profit organization that provides health organizations with peer reviews

CARF (Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities)
Focuses on rehabilitation, employment, child and family and aging services.

CAP (College of American Pathologists)
offers laboratory inspection and proficiency testing

NAM (National Academy of Medicine)
Provides guidelines for respirator use in healthcare. Formerly called Institute of Medicine

AHCA / NCAL
American Health Care Association
National centers for assisted living

American Hospital Association (AHA)
advocacy group for health care organizations, particularly hospitals

American Society of Healthcare Risk Management
ASHRM

Association for the health care environment
AHE

NCQA
National Committee for Quality Assurance; an accreditation body that has become the primary group that accredits health plans.

Association of occupational health professionals in healthcare (AOHP)
Advocate for occupational health professionals. Meet with OSHA

ECRI
Has templates for HVAs.

American Society of Healthcare Engineering
ASHE

Tenosynovitis
inflammation of the tendon and synovial membrane
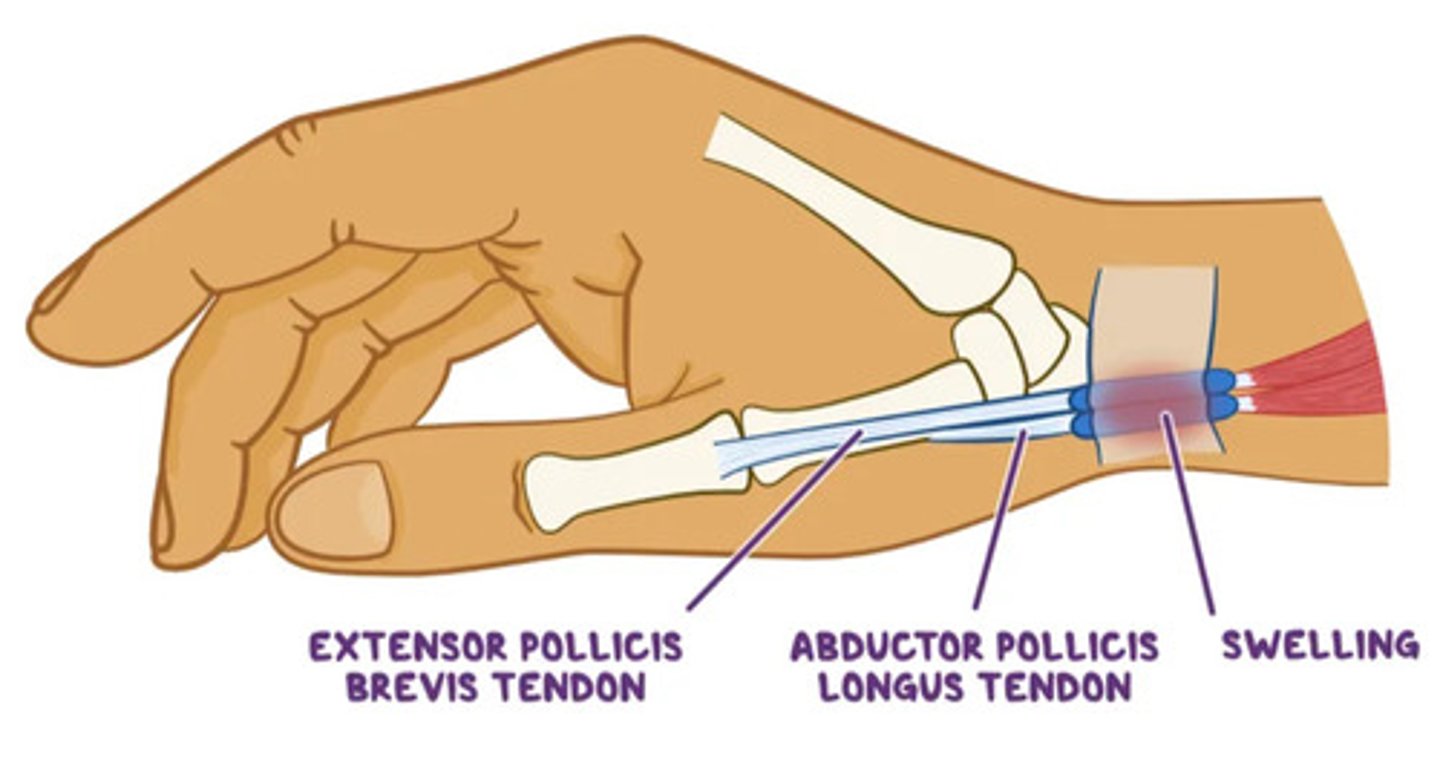
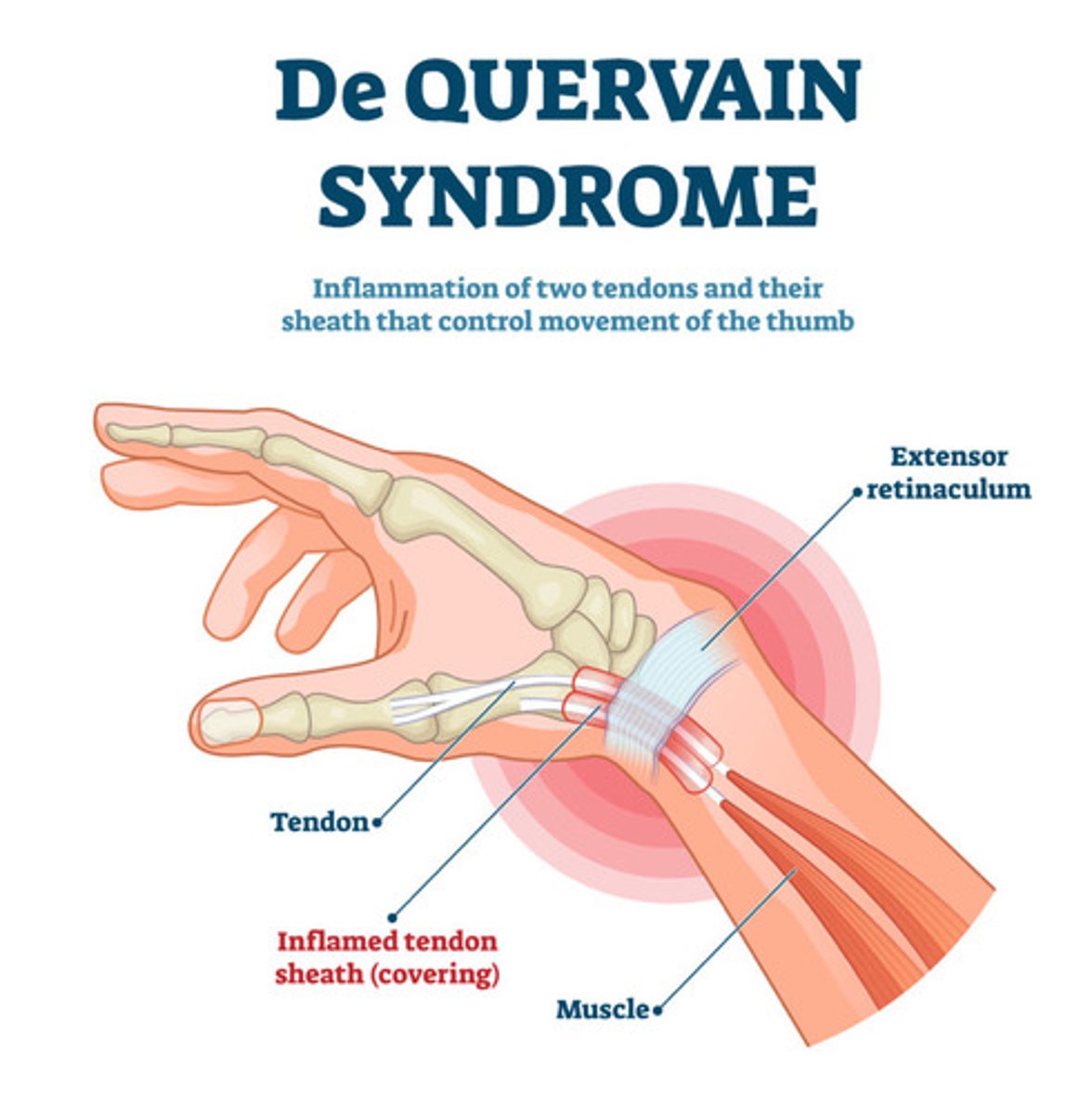
DeQuervain's Disease
tenosynovitis of abductor pollicus longus and extensor pollicus brevus
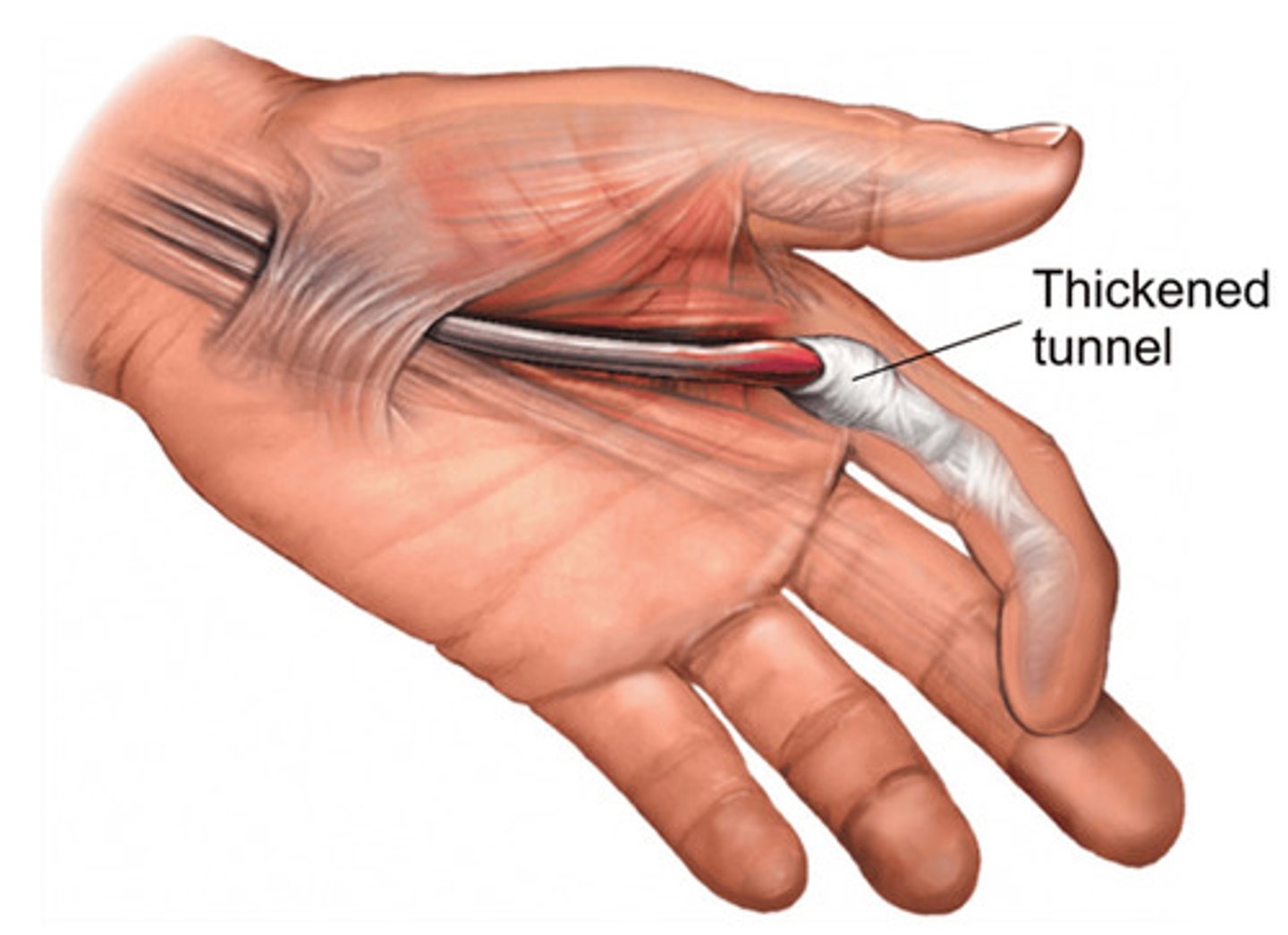
Trigger Finger
A condition whereby the finger flexors contract but are unable to reextend because of a nodule within the tendon sheath or due to the sheath being too constricted to allow for free motion.
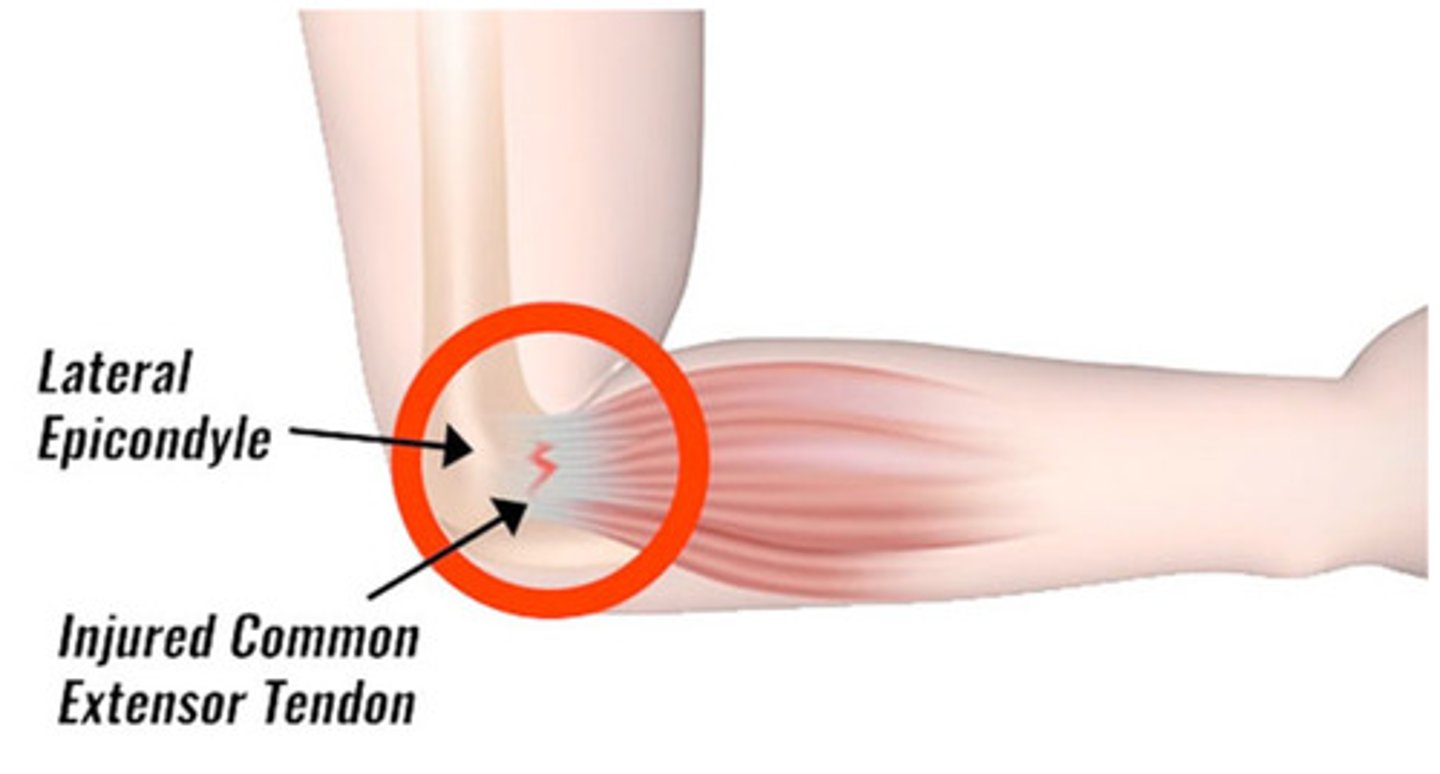
Tennis elbow
painful inflammation of the tendon at the outer border of the elbow resulting from overuse of lower arm muscles (as in twisting of the hand)
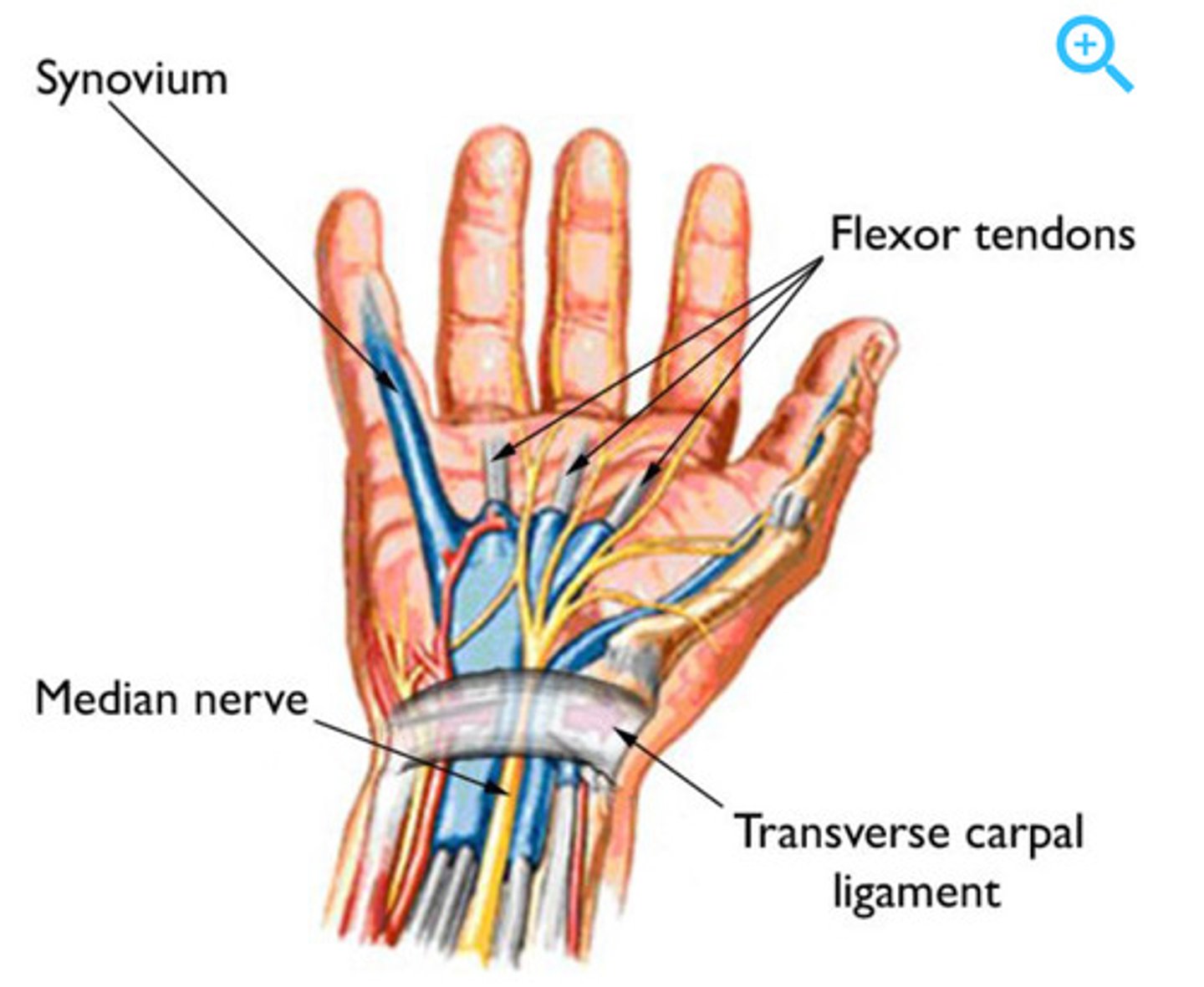
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
compression of the median nerve as it passes between the ligament and the bones and tendons of the wrist
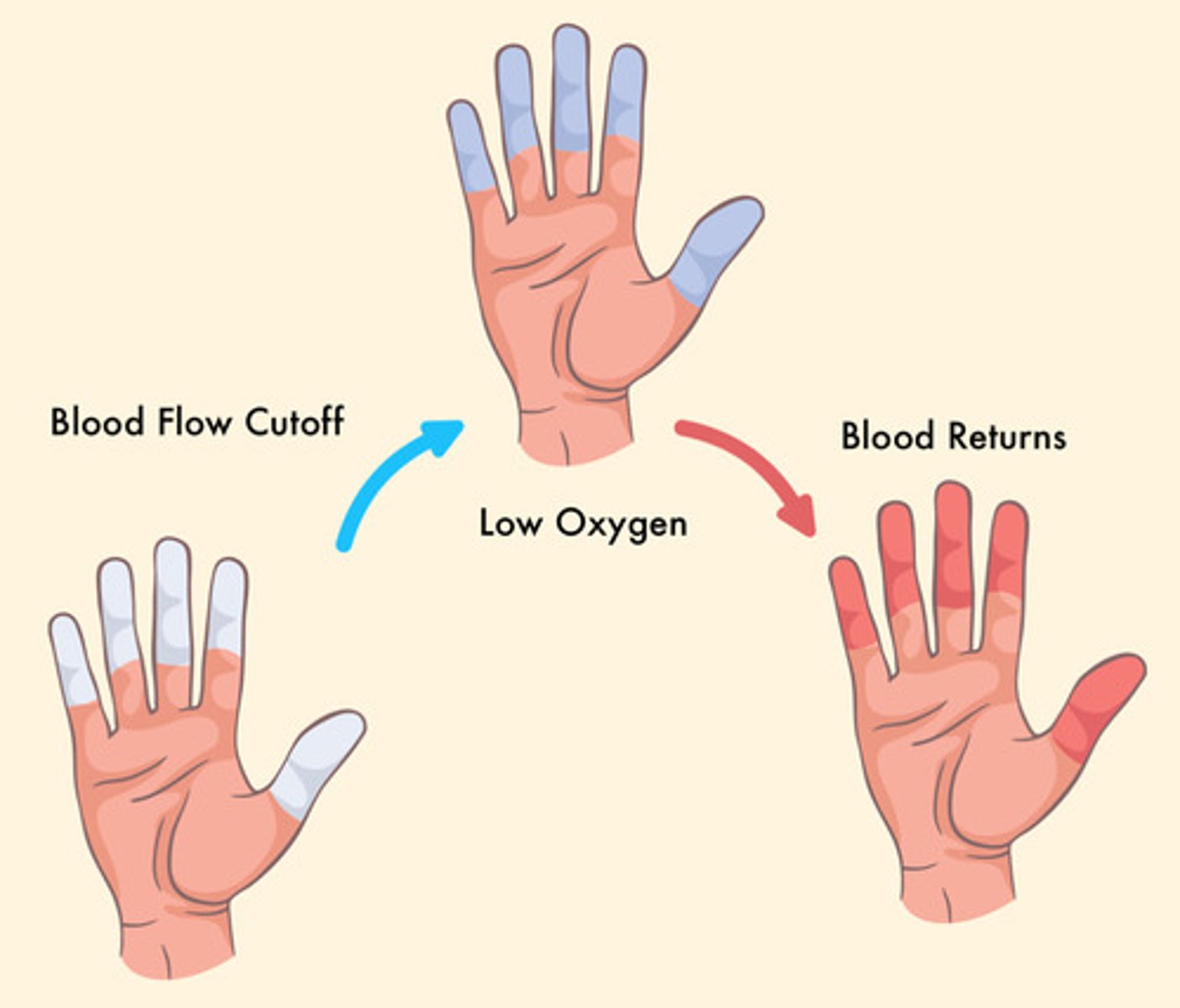
Raynaud's syndrome
a peripheral arterial occlusive disease in which intermittent attacks are triggered by cold or stress
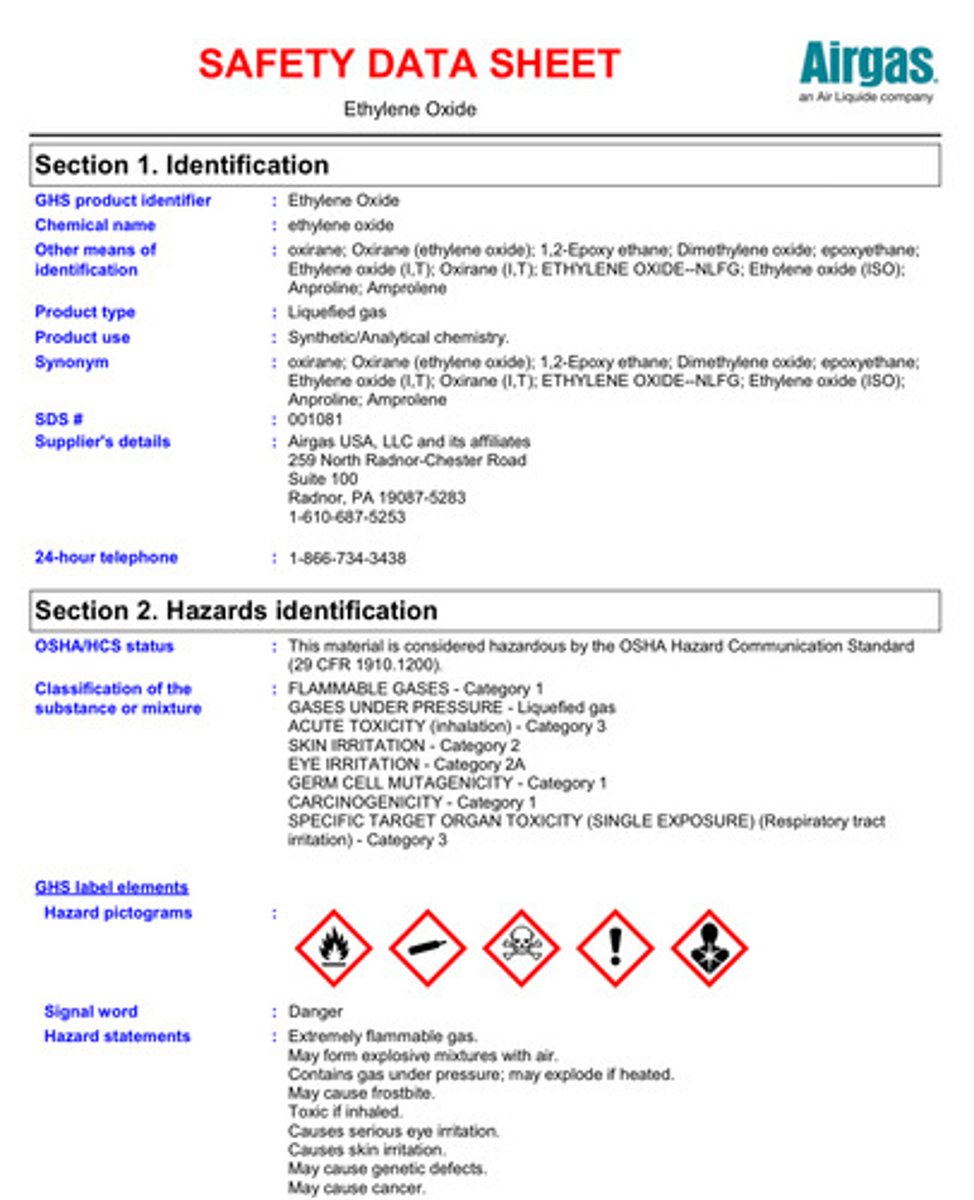
Ethylene oxide
gas used to sterilize surgical instruments and other supplies
1910,1047
AL = 0.5 ppm
PEL = 1 ppm
STEL = 5 ppm
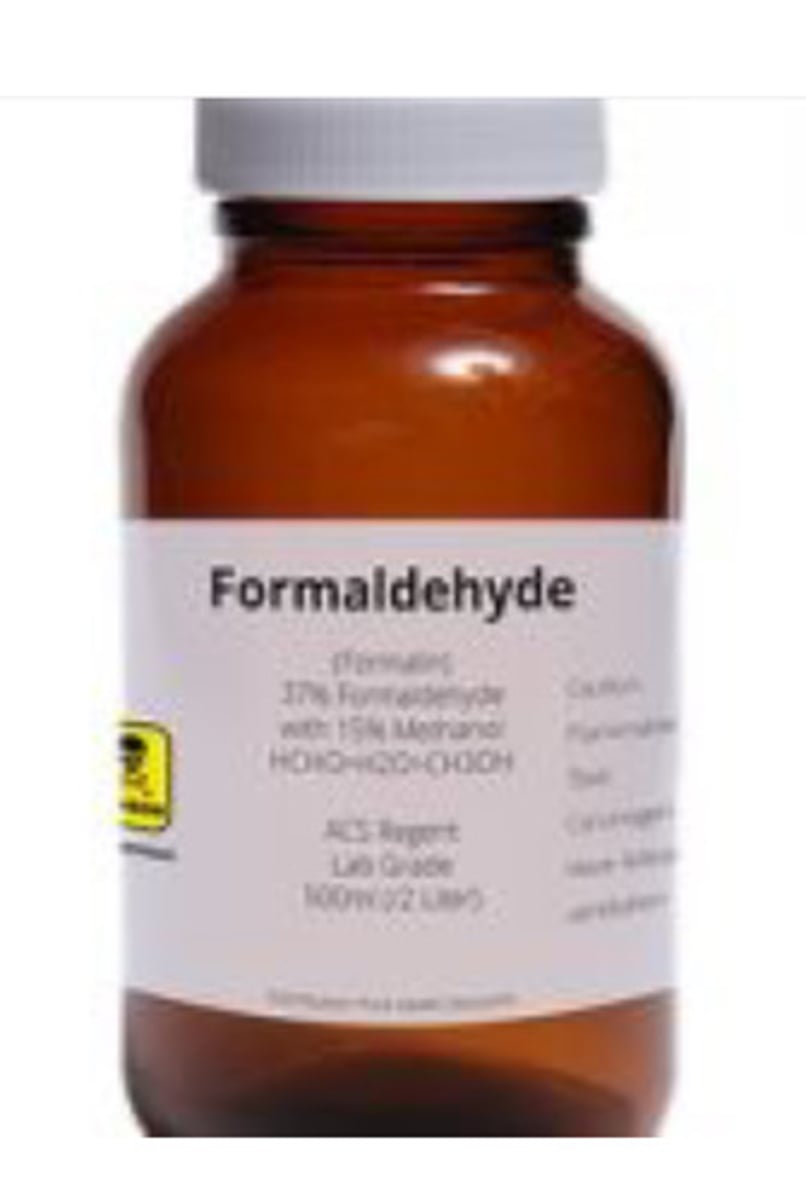
Formaldehyde
1910.1048
Action level = 0.5 ppm
PEL = 0.75 ppm
Glutaraldehyde (Cidex)
Liquid disinfectant and sterilizing agent but can require long submersion times to be effective. a cheaper and effective alternative is a 1:10 bleach solution. Chemical disinfectants cannot be used on patients skin.

Cytotoxic agents
Drugs used to kill cancer cells that are actively growing or dividing.

Pentamidine isethionate
interferes with nuclear metabolism by inhibition of DNA, RNA, phospholipids and protein synthesis
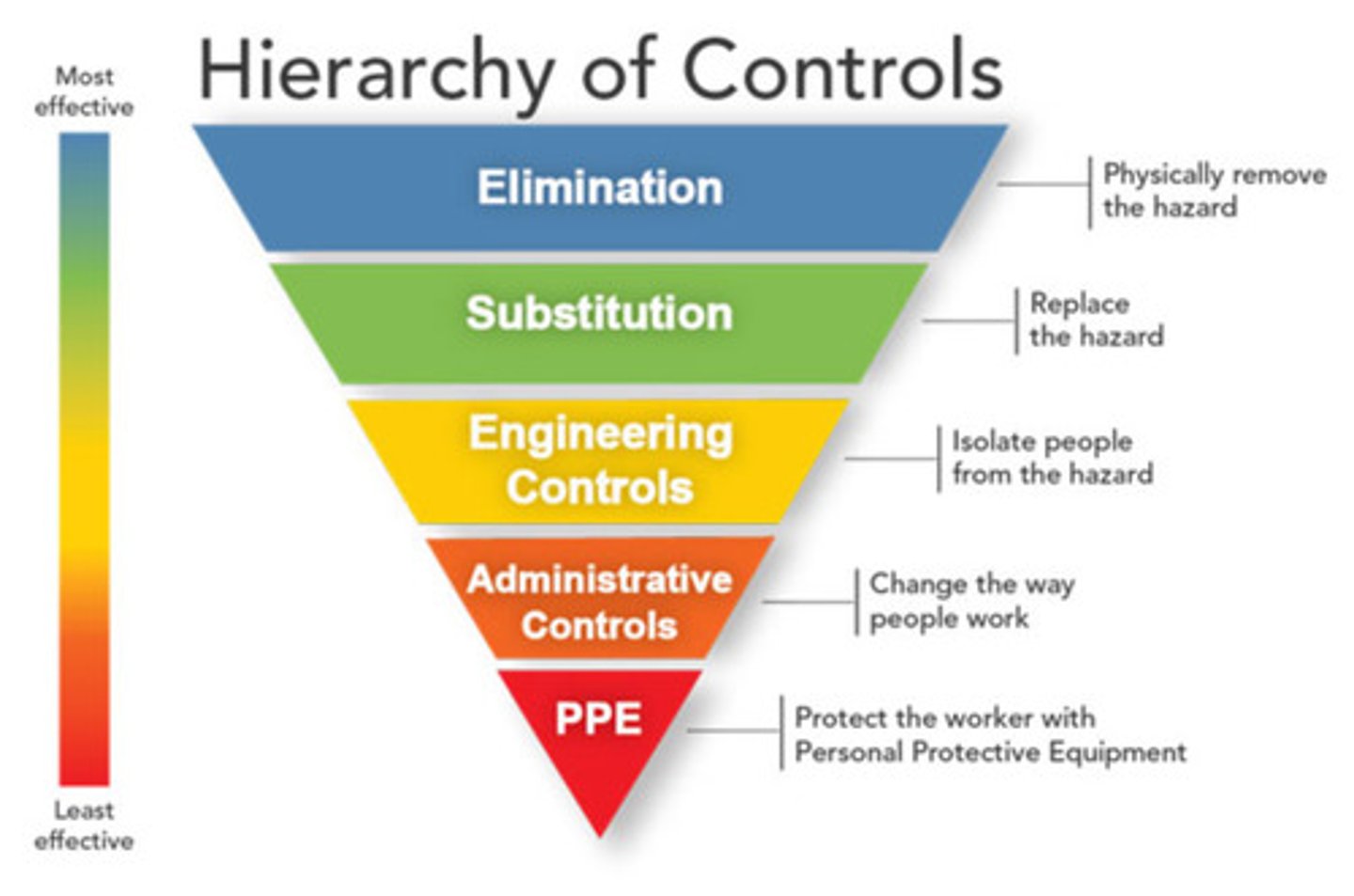
Hierachy of controls
Elimination
Substitution
Engineering controls
Administrative controls
PPE
Hazard vulnerability analysis (HVA)
An assessment to help an organization identify potential hazards, threats, and adverse events and their impact on the care, treatment, and services that must be sustained during an emergency
Drills
Tabletop
Walk through
Functional drill
Full emergency drill
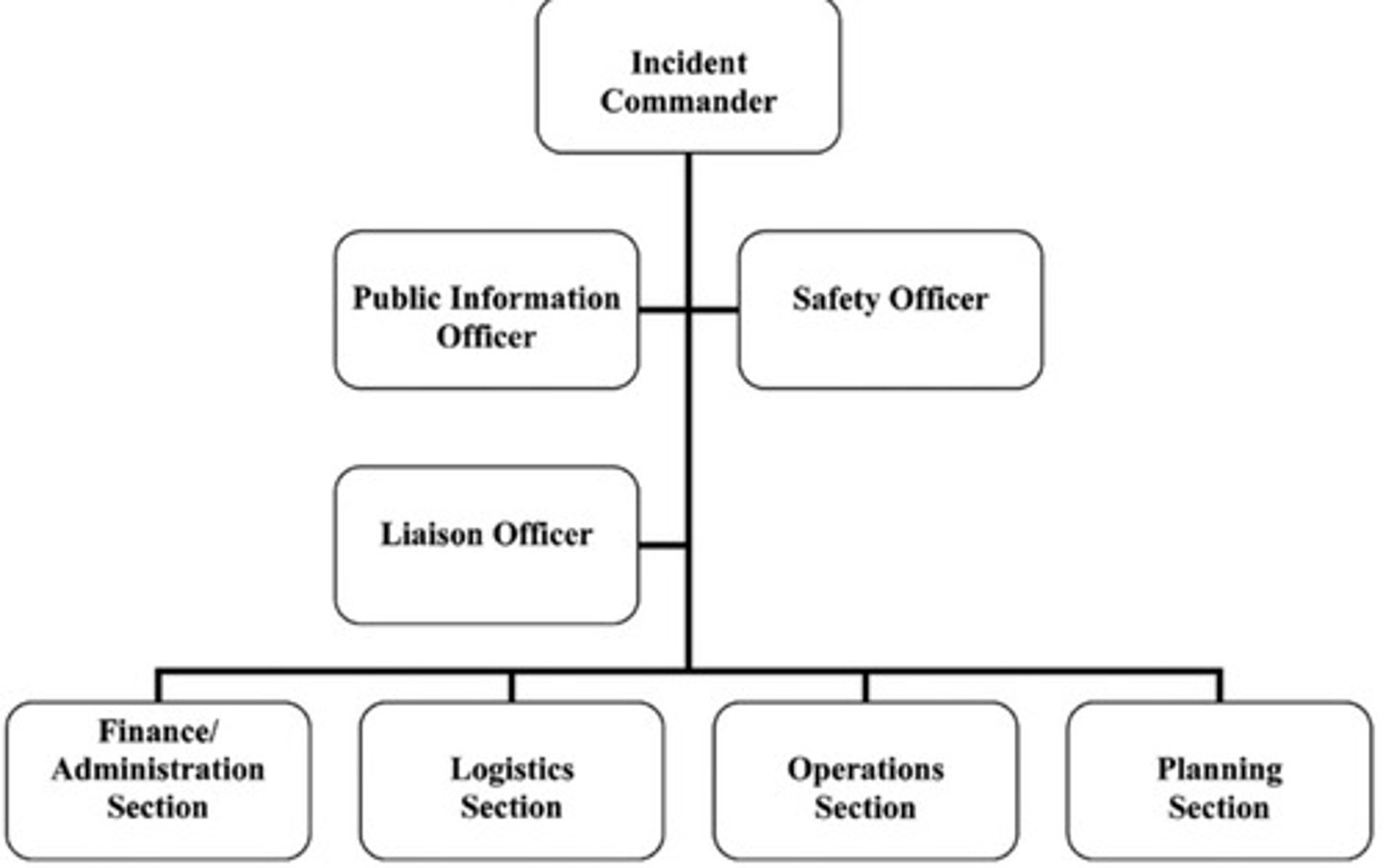
Incident Command System (ICS)
a subset of the National Incident Management System (NIMS) designed specifically for management of multiple-casualty incidents.
EPCRA (Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act)
created to help communities plan for chemical emergencies. It also requires industry to report on the storage, use and releases of hazardous substances to federal, state, and local governments.

Contaminated Sharps
Any contaminated object that can penetrate the skin including, but not limited to, needles, scalpels, broken glass, and exposed ends of wires.

Decontamination
The removal of blood or other potentially infectious materials on an item's surface and the removal of visible debris or residue such as dust, hair, and skin.

Exposure incident
specific eye, mouth, other mucous membrane, non-intact skin, or parenteral contact with blood or other potentially infectious materials that results from the performance of an employee's duties

Other Potentially Infectious Materials (OPIM)
any materials or bodily fluids other than blood; precautions should be taken to avoid contact

Parenteral
taken into the body or administered in a manner other than through the digestive tract
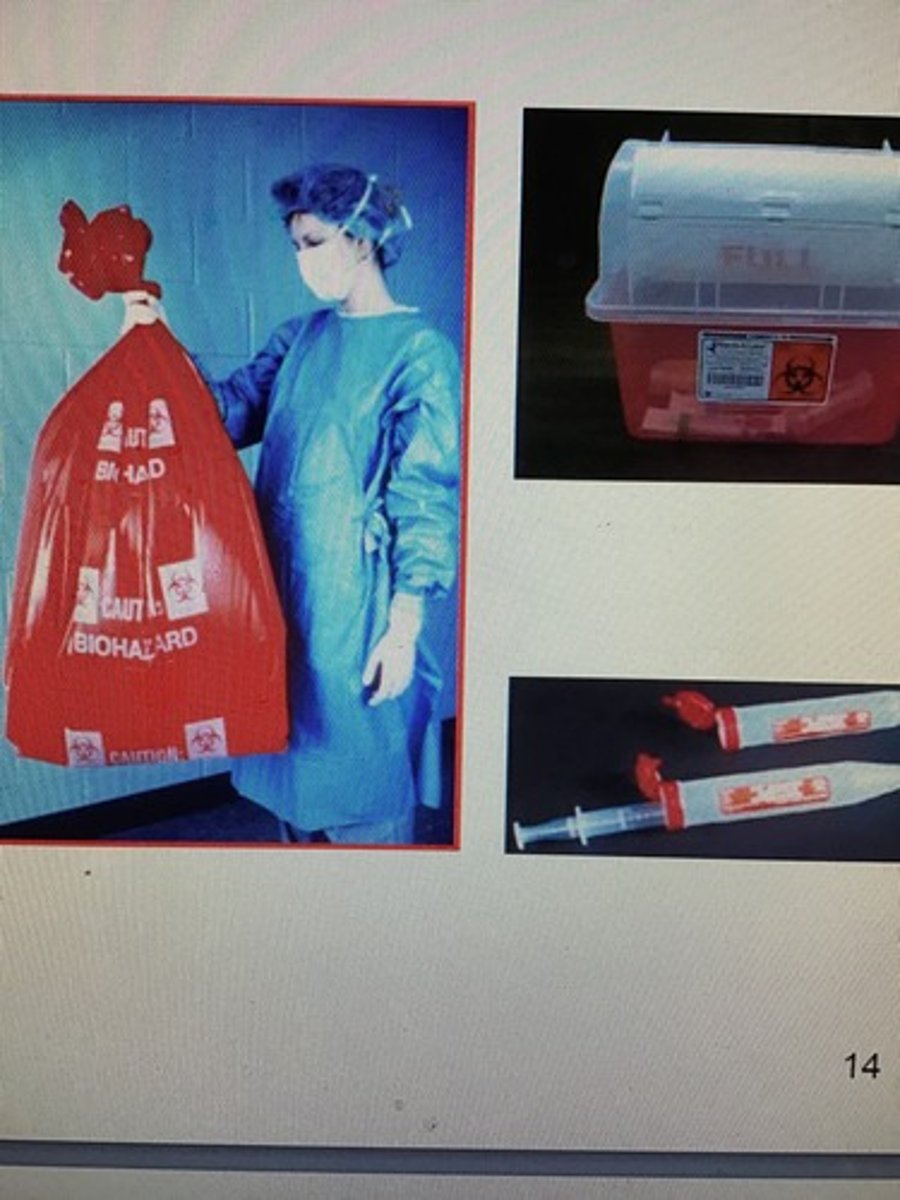
Infectious waste
Waste that is capable of transmitting an infectious disease
Medical Waste Tracking Act
Expired in 1991. Set the stage for future regulatory requirements.

Radioactive waste
Need to be separated into subcategories

Incinerator
a furnace for destroying things by burning them, especially waste

Autoclave
Piece of equipment used to sterilize articles by way of steam under pressure and/or dry heat

Not medical waste
-unused medical products
- iv bags
- Urine and stool containers
- Diapers
Hospital, medical and infectious waste incinerators (HMIWI)
Regulated under CAA

Medical waste
- infectious
- hazardous
- radioactive
- general
ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry)
protects communities from harmful health effects related to exposure to natural and man-made hazardous substances

MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
a technique that uses a magnetic field to create a computerized image of internal bodily structures
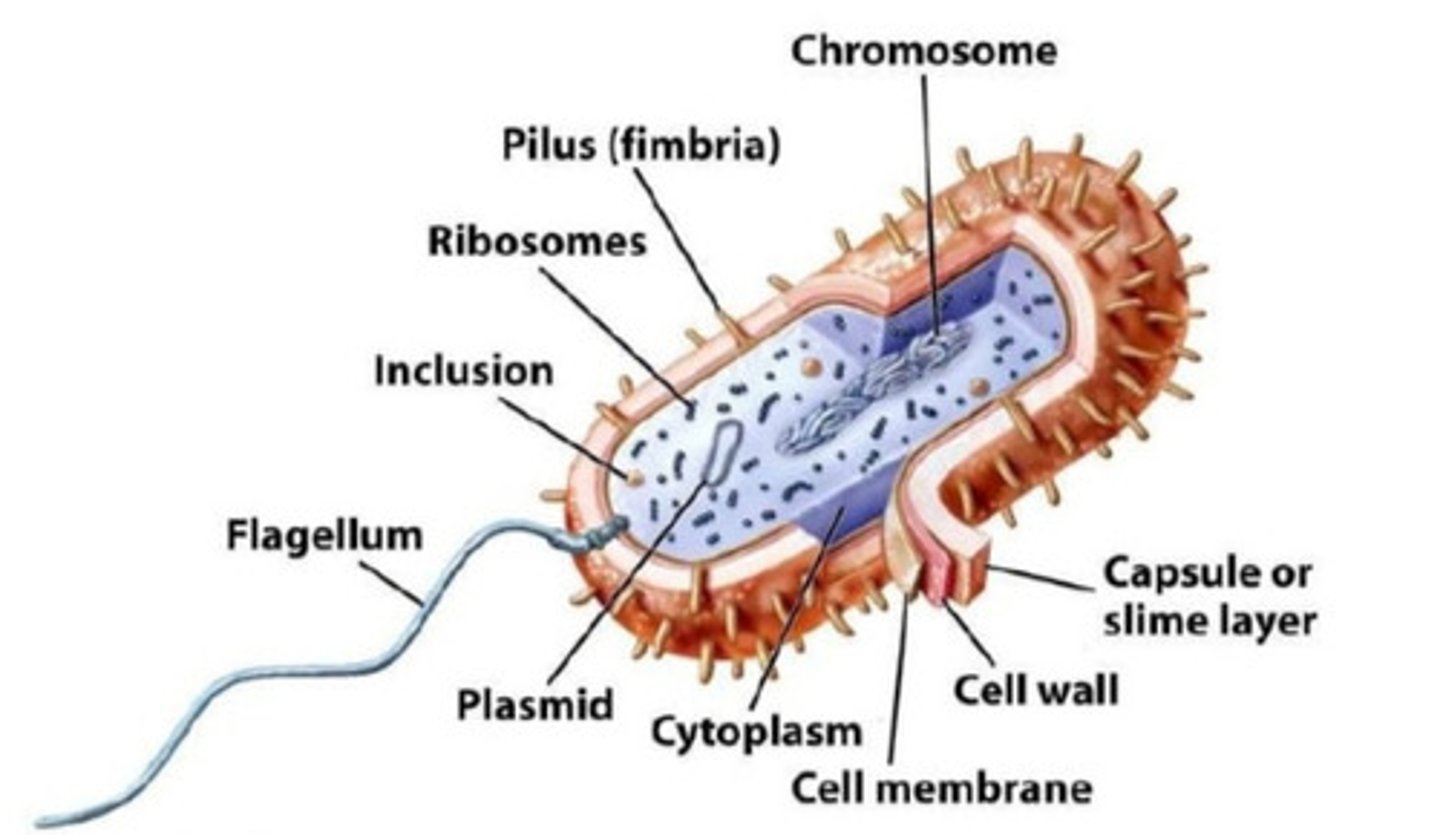
Bacteria
single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus; prokaryotes
Viruses
tiny particles, smaller than bacteria and other pathogens, which must invade living cells in order to reproduce; when they invade, the cells are damaged or destroyed in the process releasing new particles to infect other cells
Biological Toxins
Poisons produced by pathogens, plants, or animals. They can also occur in animals as a result of their diet.

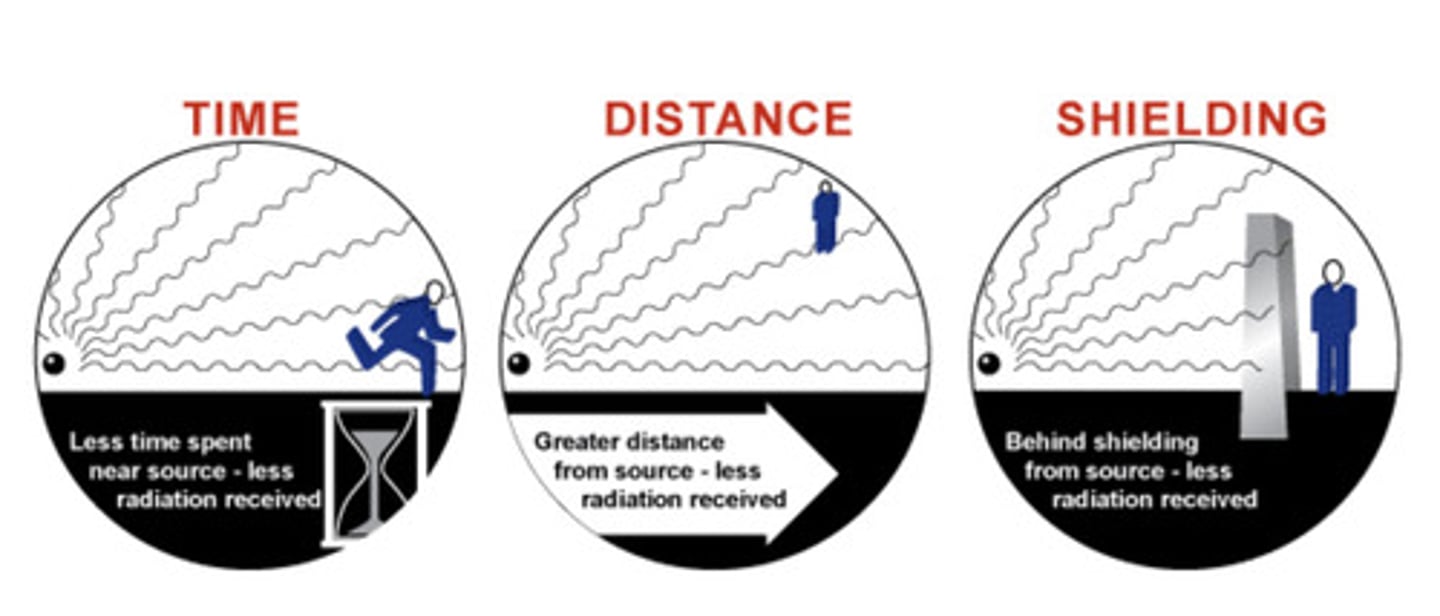
Radiation Controls
Time, distance, shielding
Healthcare occupancies (NFPA 101)
Healthcare
Ambulatory healthcare
Business
Residential

NFPA 72
The National Fire Alarm and signaling code, the standard to which fire alarm systems are to be installed

NFPA 80
Standard for Fire Doors and Other Opening Protectives

Combustible Liquid
Liquid having a flash point at or above 100°F.
Class II - flash below 140ºF
Class III

Flammable liquid (NFPA 30)
a liquid that has a flash point that is below 100ºF and a maximum vapor pressure of 2068 mmHg at 100ºF

Elimination
Physically remove the hazard
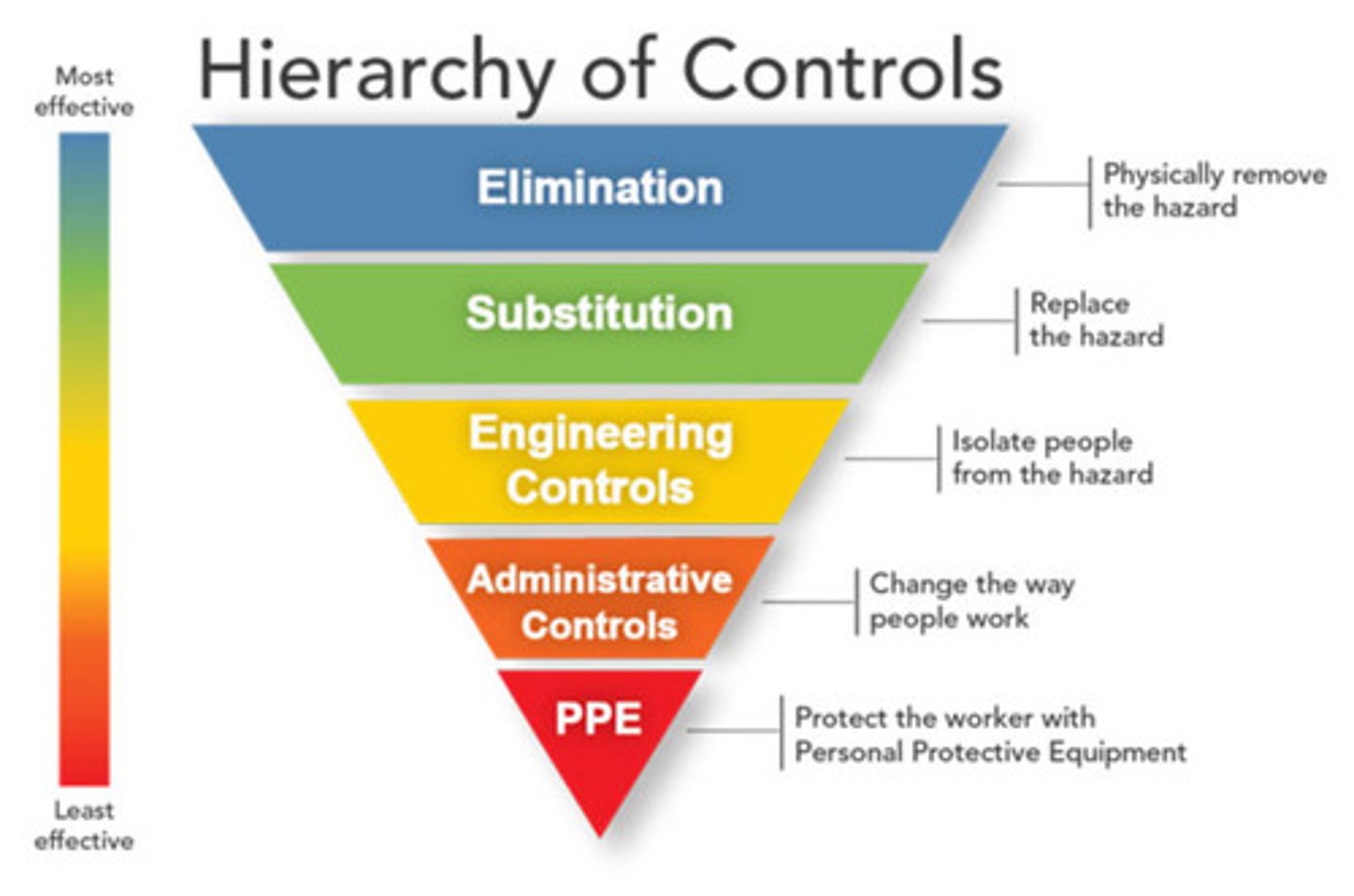
Substitution
Replace the hazard
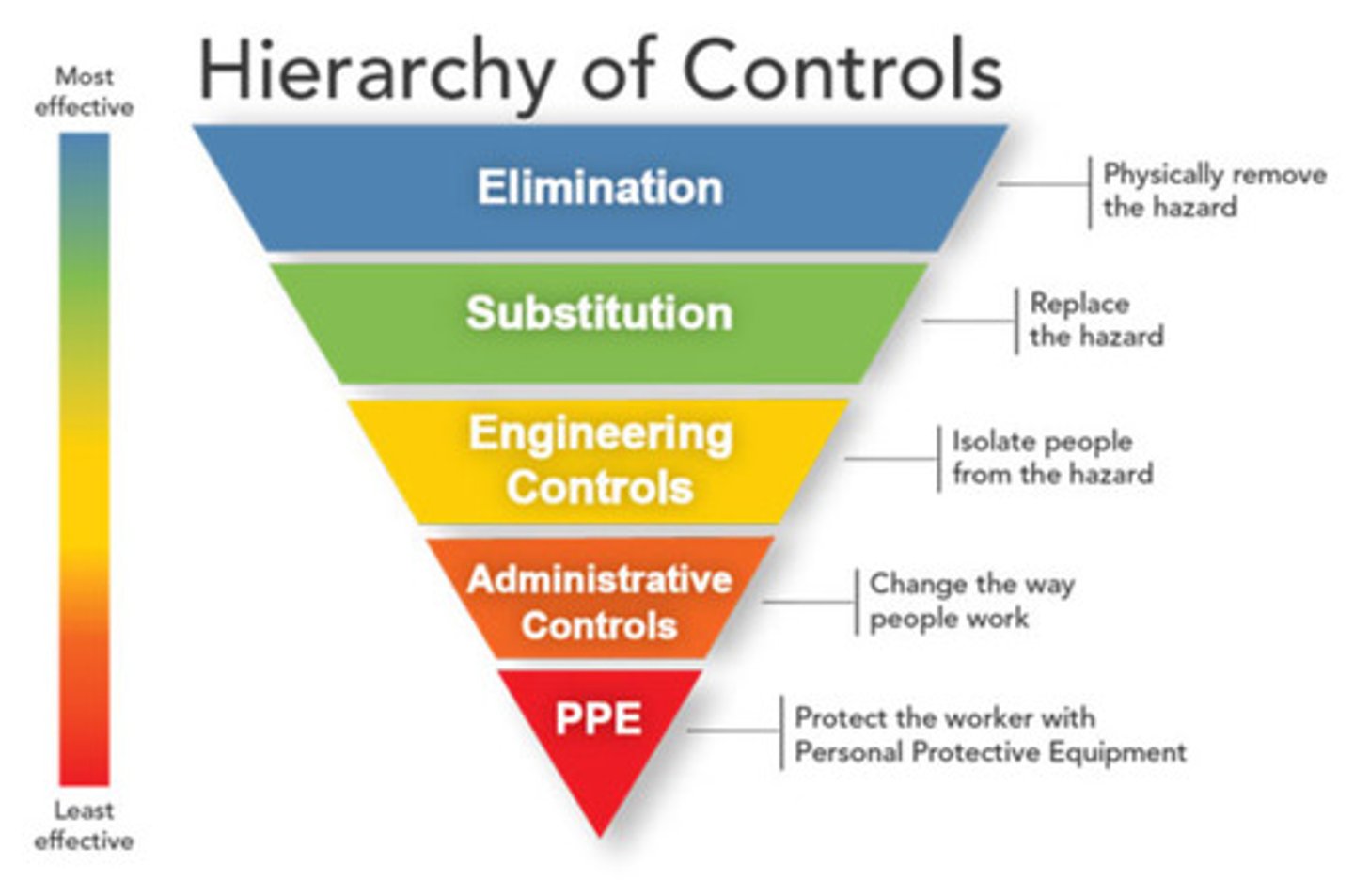
Engineering controls
Isolate people from the hazard
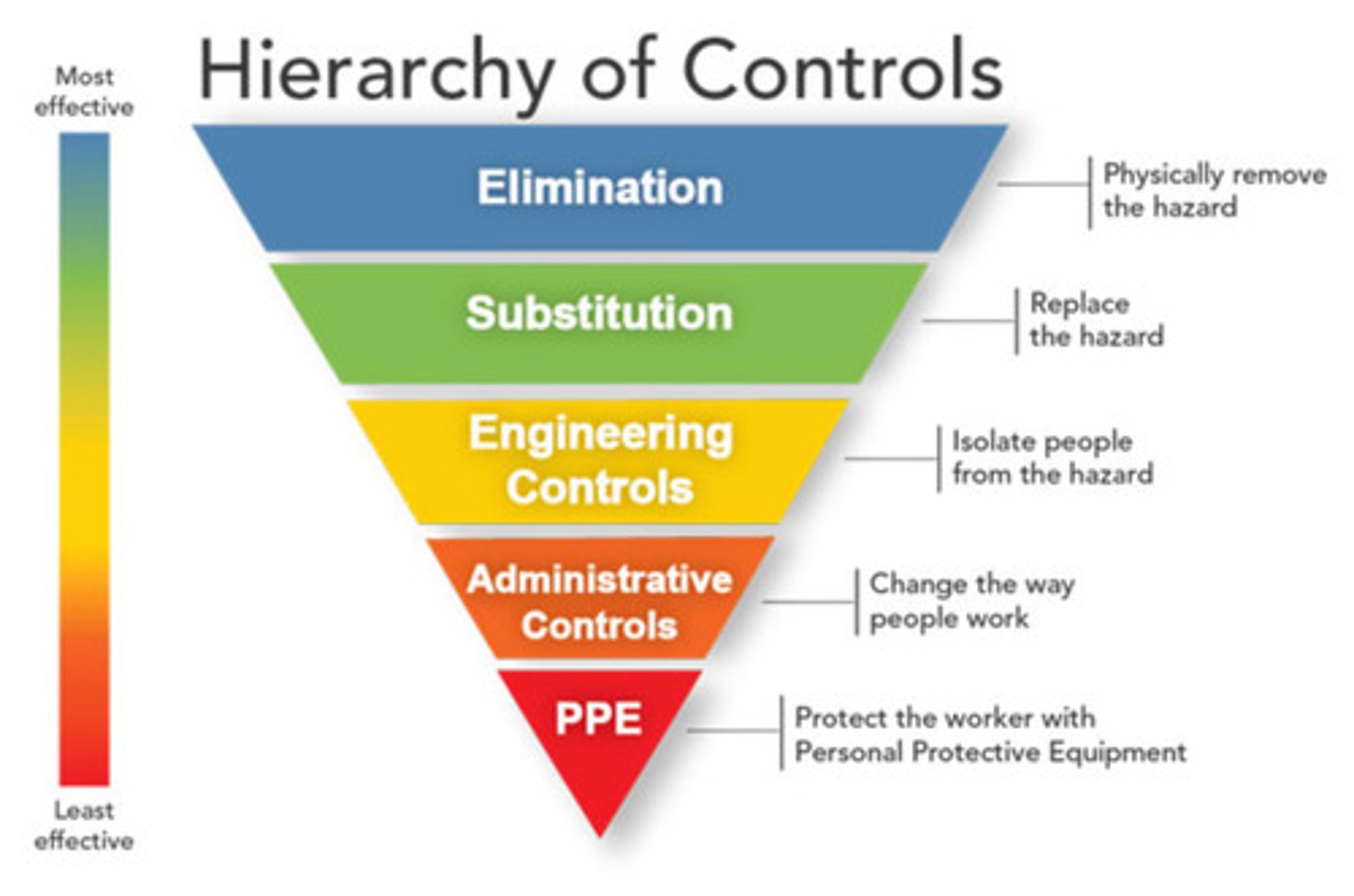
Administrative controls
Change the way people work
PPE
Least effective hazard control
NFPA 1600
focuses on disaster and emergency management and business continuity. Ties back to NFPA 99 for healthcare

Ergonomic risk factors
forceful exertions, repetition, awkward or static posturing, contact stress, excessive vibration, cold temperatures

ANSI Z535.1
Color codes and signs

ASME A13.1
Identification of piping systems

NFPA 37
Standard for the Installation and Use of Stationary Combustion Engines and Gas Turbines

NFPA 110
Emergency and standby power systems
Emergency power supply system (EPSS)
Level 1 = human life
Level 2 = not as critical

CGA
Compressed Gas Association

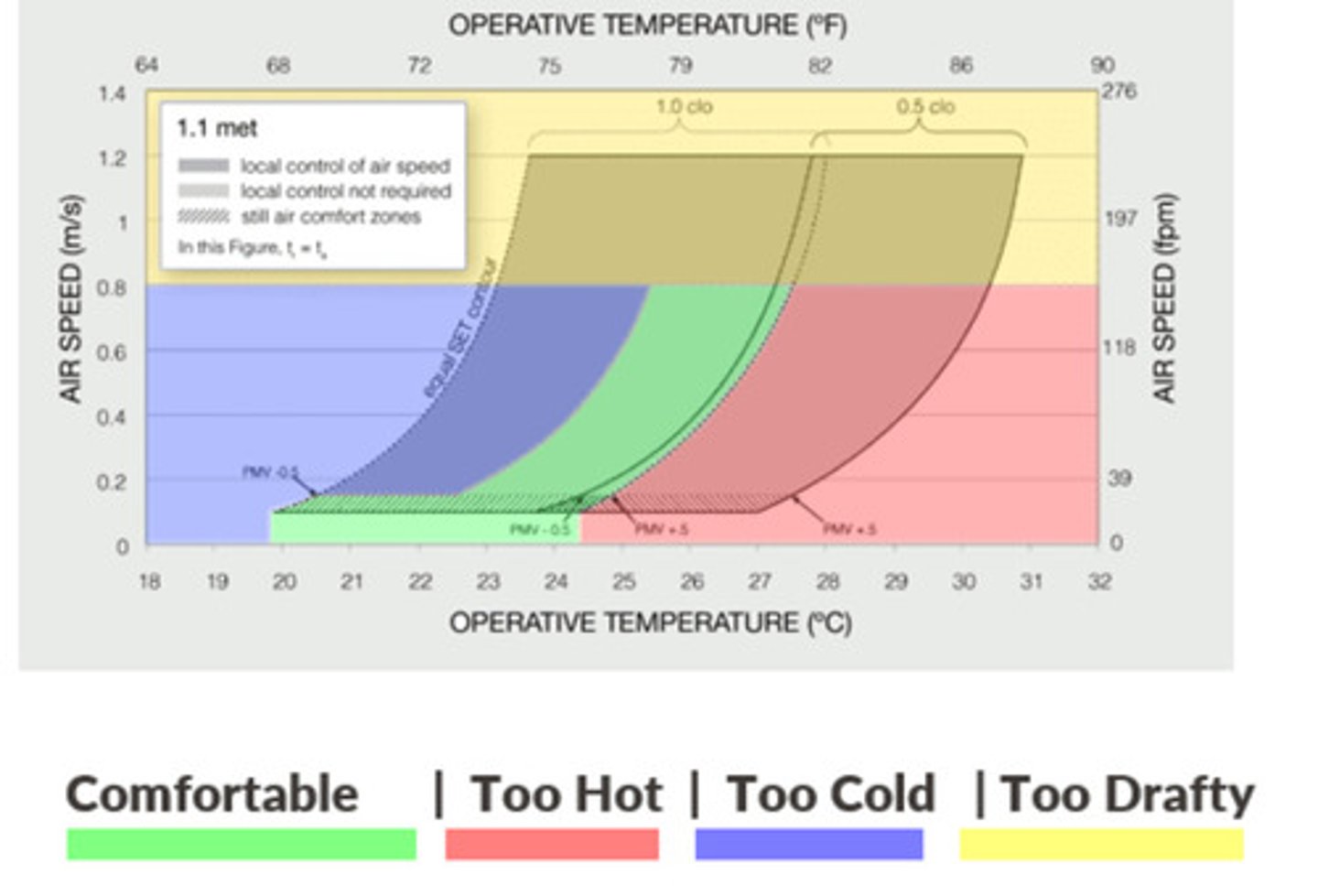
ASHRAE 55
Thermal Environmental Condition for Human Occupancy specifies the combinations of indoor space environment and personal factors that will produce thermal environmental conditions acceptable to 80% or more of the occupants within a space.
Health Care Occupancy
An occupancy used for purposes of medical or other treatment or care of four or more persons where such occupants are mostly incapable of self preservation due to age, physical or mental disability or because of security measures not under the occupants control.

Ambulatory Health Care Occupancy
An occupancy used to provide services or treatment simultaneously to four or more patients, that provides treatment, anesthesia, or urgent care on an outpatient basis which renders the patients incapable of taking action under emergency conditions without the assistance of others.

ASHRAE 62.1-2010
A standard that specifies minimum ventilation rates and other measures intended to provide indoor air quality that is acceptable to human occupants and that minimizes adverse health effects, and is the recognized standard for ventilation system design and acceptable indoor air quality.

ASHRAE SP91
HVAC design manual for hospitals and clinics

ASHRAE 52.2-2017
Air filter standards

Liquid oxygen
Are meant for patients who receive long-term oxygen therapy, generally need to be kept upright and have special requirements fro filling, large-volume storage, and cylinder transfer.

Building system categories (NFPA 99)
Category 1 = work or be available at all times
Category 2 = limited short durations of downtime
Category 3 = normal building system reliability
Category 4 = no impact in patient care

NFPA 551
Guide for the Evaluation of Fire Risk Assessments

Infectious substances (49 CFR 173.134)
Substances that are known or are reasonably expected to contain pathogens.

Patient Specimen
Human or animal material collected directly from humans or animals and transported for research, diagnosis, investigational activities, or disease treatment or prevention. Includes excreta, secreta, blood and its components, tissue and tissue swabs, body parts, and specimens in transport media (e/g transwabs, culture media, and blood culture bottles)

Category A (Shipping name)
Infectious substance, affecting humans (UN2814) and infectious substance, affecting animals

Anemometer
An instrument used to measure wind speed

Category B shipping (49 CFR 173.134)
Not category A.
Biological Substance, Category B (UN3373)

Radioactive materials (49 CFR 173.403)
Contain radionuclides at concentrations above tables in DOT reg.

BEI
Biological exposure indices

Static Pressure
the pressure of air at rest, or that portion in moving air, if the air stream were to stop

Manometer
instrument to measure pressure

Dilution Ventilation
Adding clean air to dilute the contaminant concentration
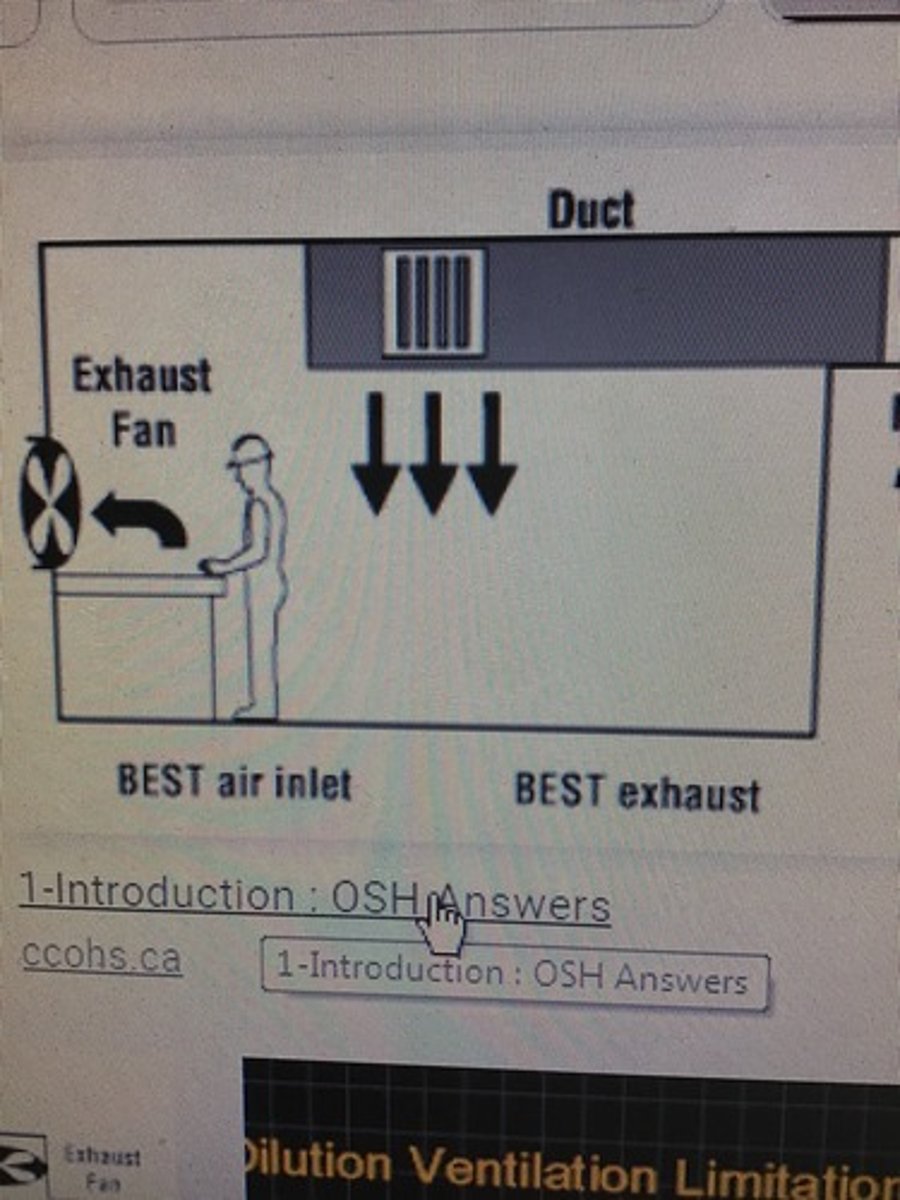
NFPA 90A
Installation of air conditioning and ventilating systems

Legionella
Genus of bacteria responsible for the disease legionellosis
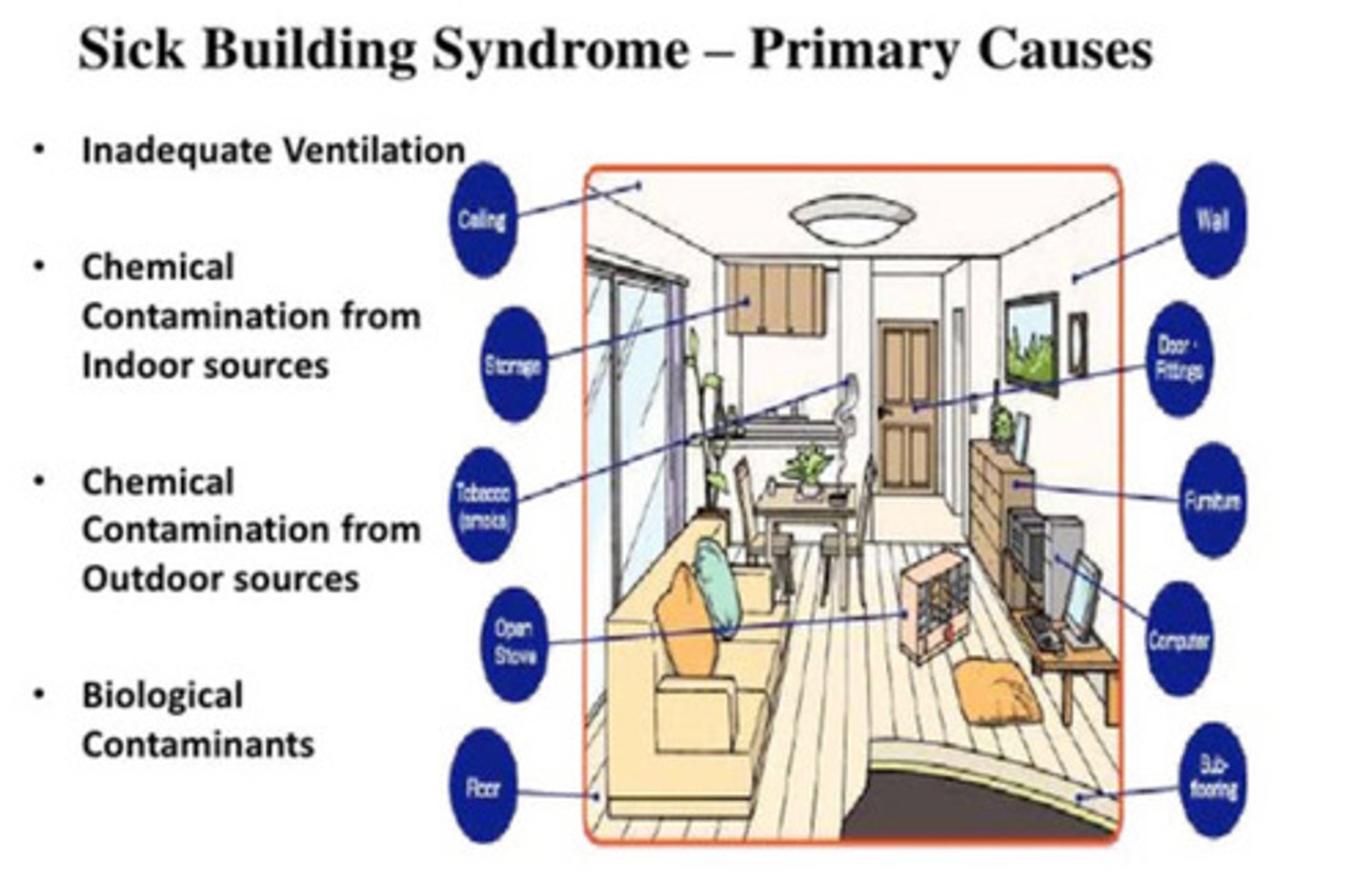
Sick Building Syndrome (SBS)
a condition associated with a particular indoor environment that appears to be unhealthy for the human occupants
Building-related illness
A term used when symptoms of a diagnosable illness are identified and attributed directly to an airborne building contaminant.

Multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS)
Also known as "environmental illness," a condition whereby individuals experience adverse reactions when exposed to low levels of chemicals found in everyday substances.

Biocide
substance that destroys living microorganisms
