Bio exam 3 - Mendelian Genetics
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Genetic crosses of peas - generations
P1 - parental generation, F1 - first filial generation (offspring of P1), F2 - second filial generation (offspring of F1)
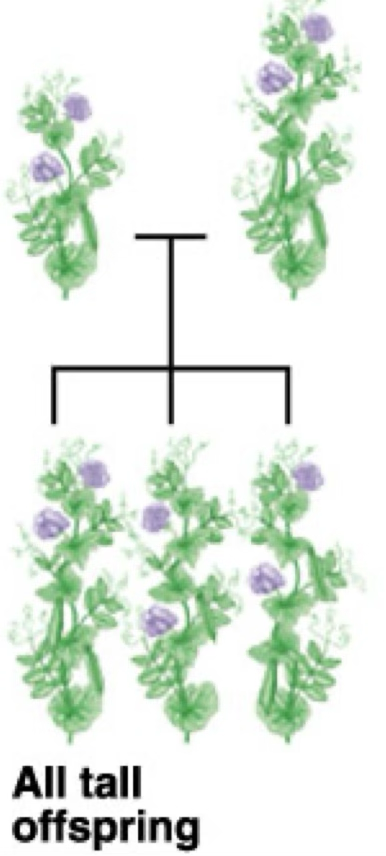
True breeding plants
Plants which consistently have offspring with the same traits as the parents; homozygous dominant or recessive plants
Homozygous
Two of the same allele, can be homozygous recessive - tt or homozygous dominant - TT
Heterozygrous
Two different alleles - Tt
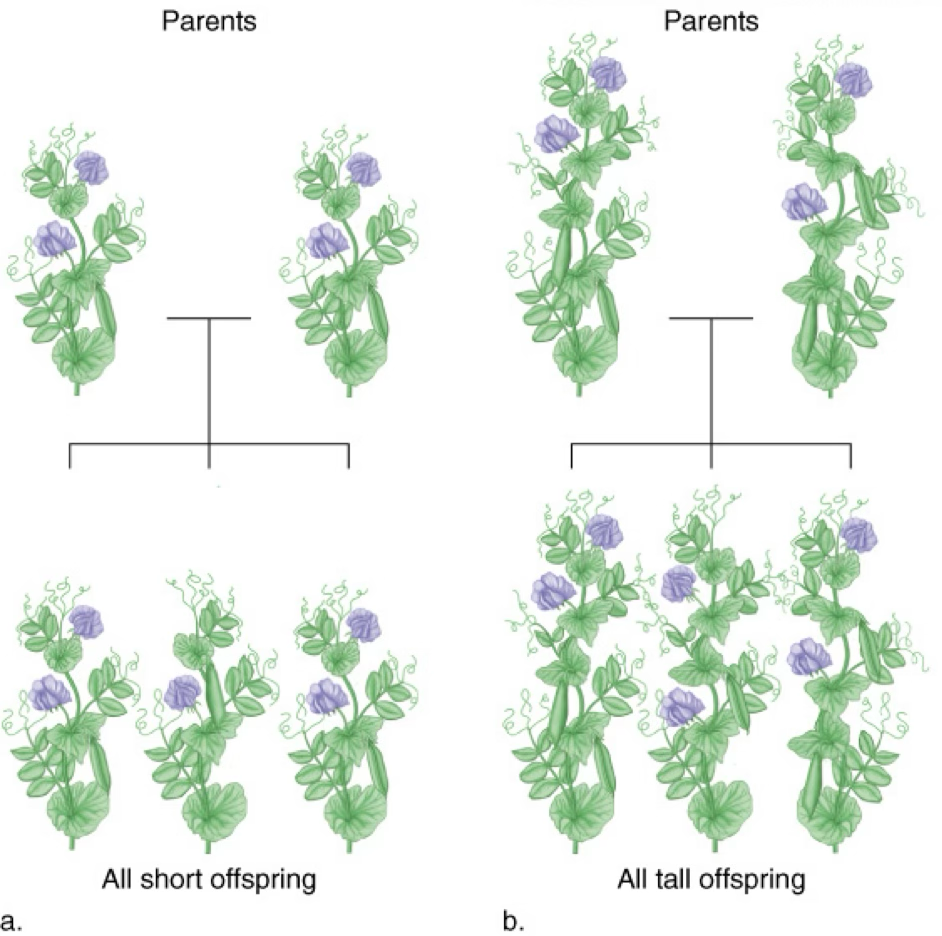
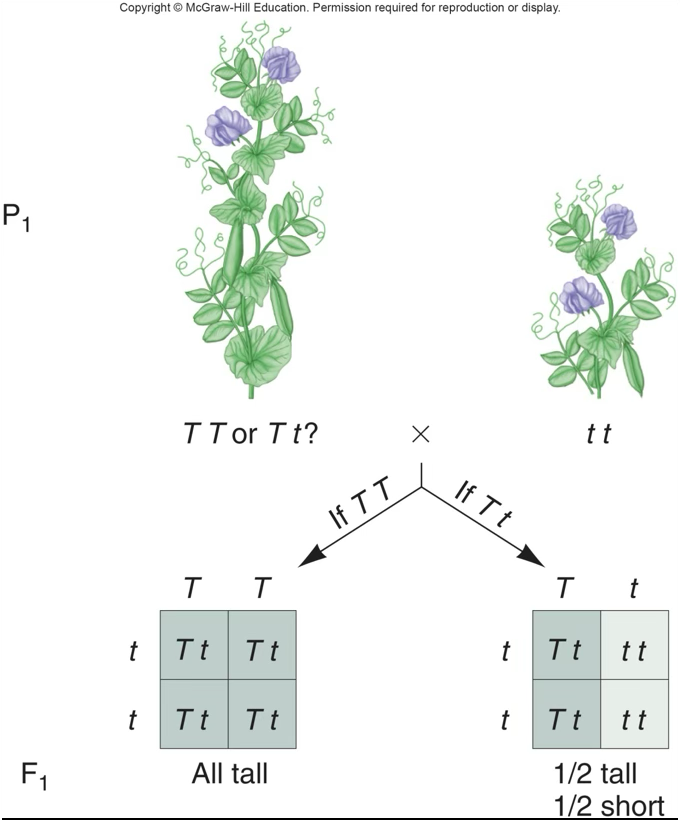
Dominant and recessive traits: What happens when true breeding plants with two distinct forms of a trait are crossed?
When true breeding plants, one tall and one short, are crossed, all the offspring are tall
Genotype
An organism’s alleles; homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive, or heterozygous
Phenotype
Outward expression of an allele combination; what you see - tall plant or short plant
Monohybrid cross
Looking at just one trait/gene/genotype
Monohybrid cross - first slide
F1 is all tall, F2 is ¼ short and ¾ tall
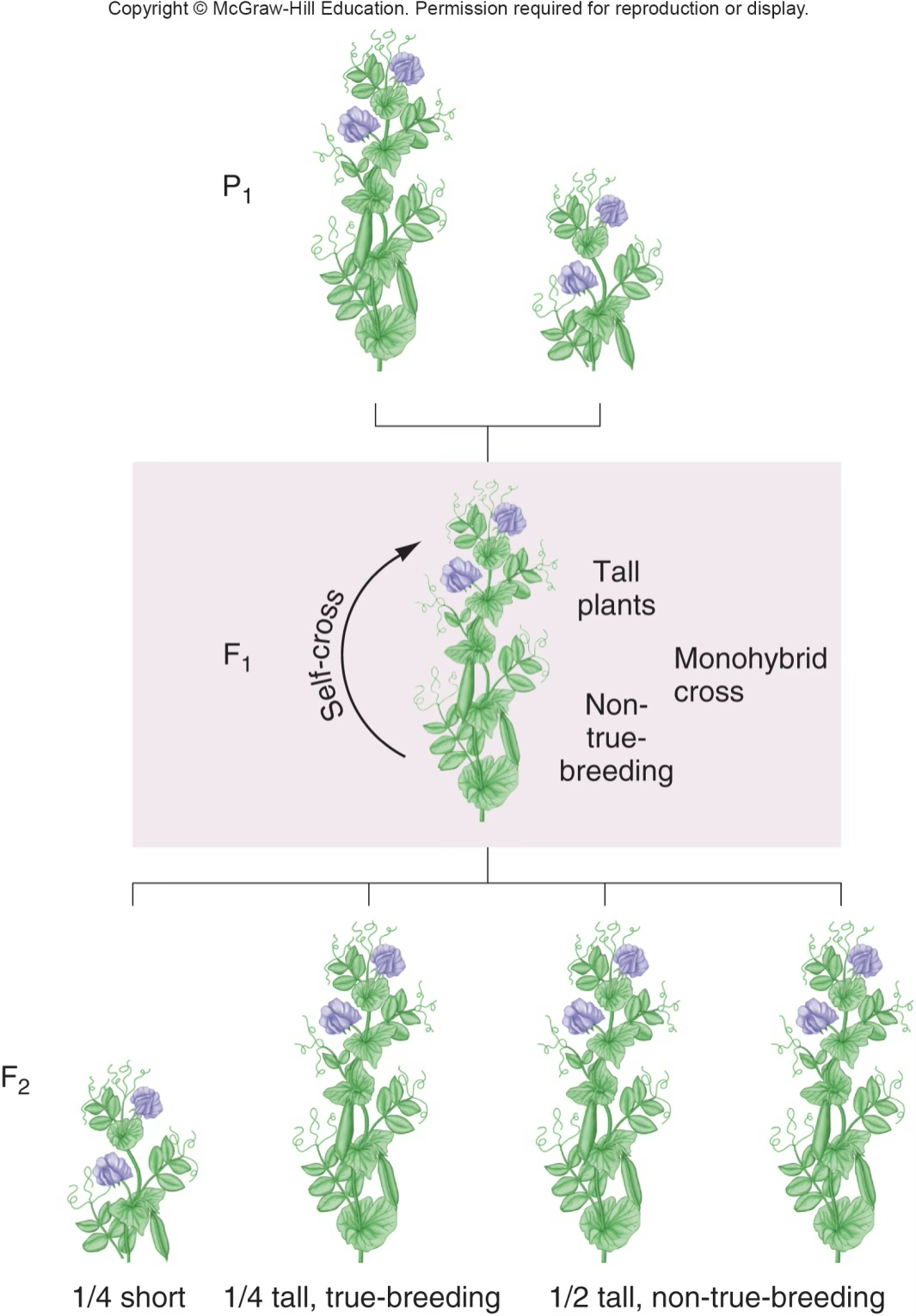
Monohybrid cross Tt x Tt - 2nd slide
Offspring genotypes - ¼ TT, ½ Tt, ¼ tt; Offspring phenotypes - ¾ tall, ¼ short
Mendel’s Law of Segregation
During meiosis, homologous pairs of chromosomes (and the genes they carry) separate from each other and are packaged into separate gametes. Alleles therefore separate from each other. At fertilization, gametes combine at random.
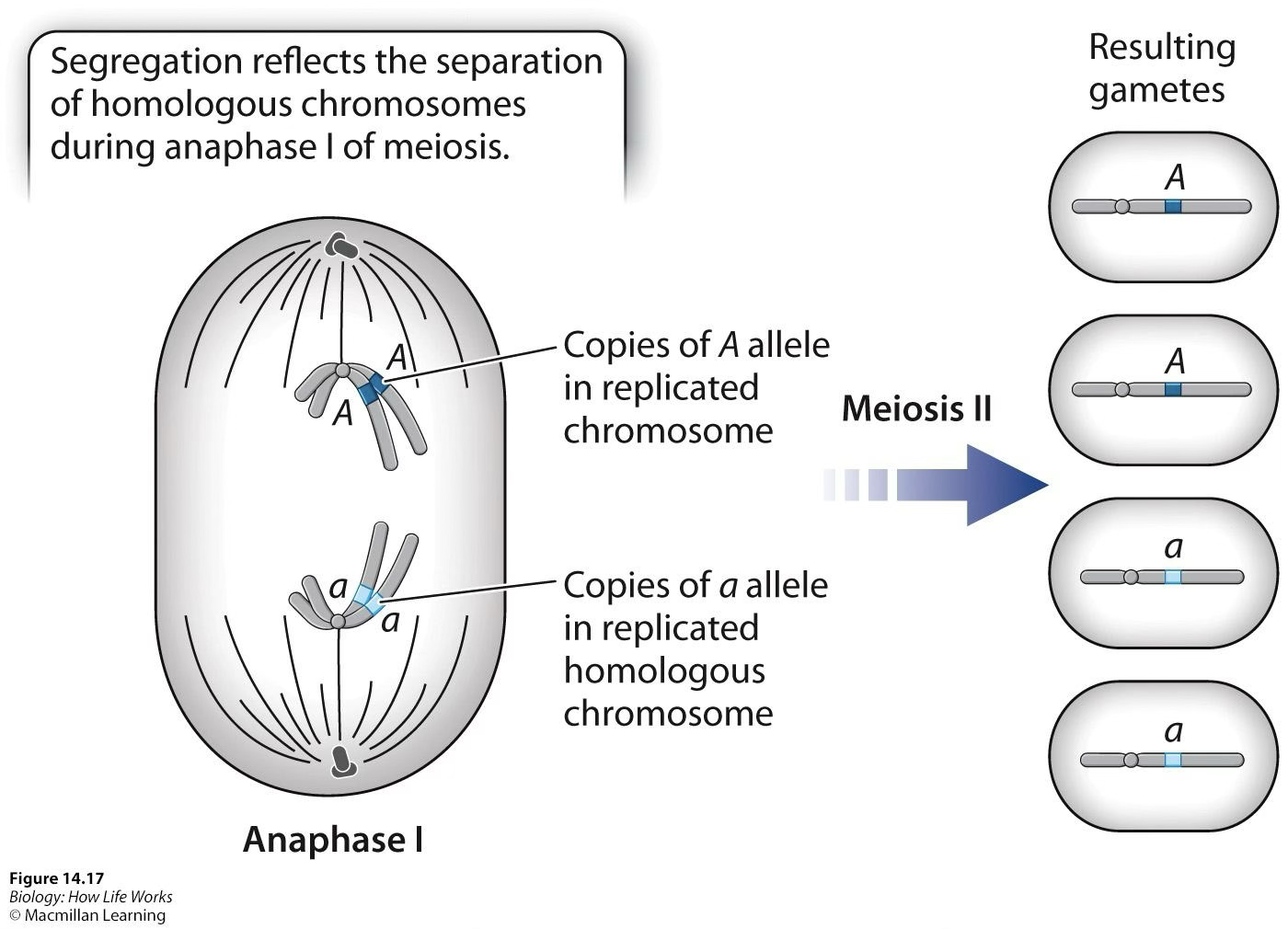
Which phase of meiosis corresponds to segregation?
Separation of homologs in anaphase 1
Test cross
Crossing an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual
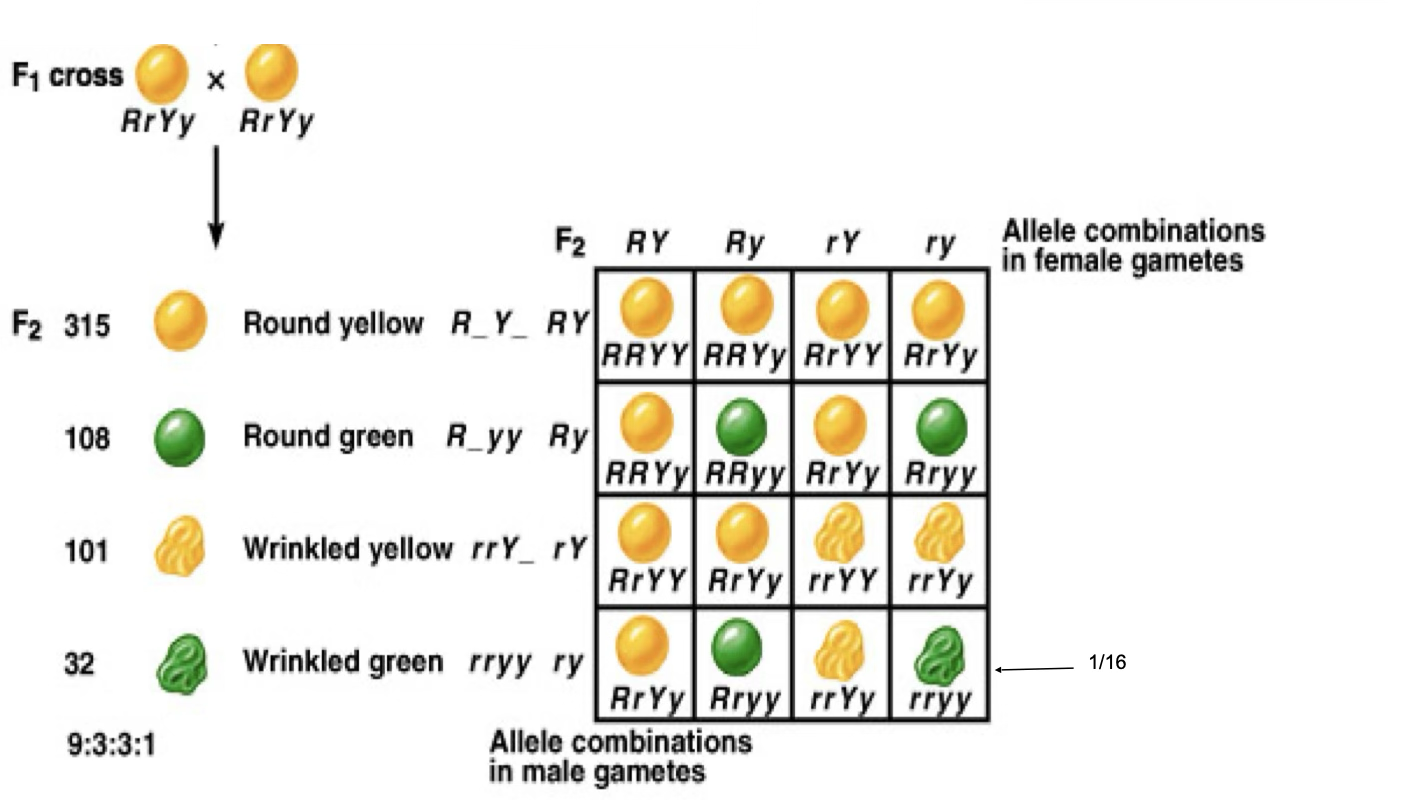
Dihybrid cross
Looking at 2 traits/genes/genotypes at the same time
Independent assortment alignments
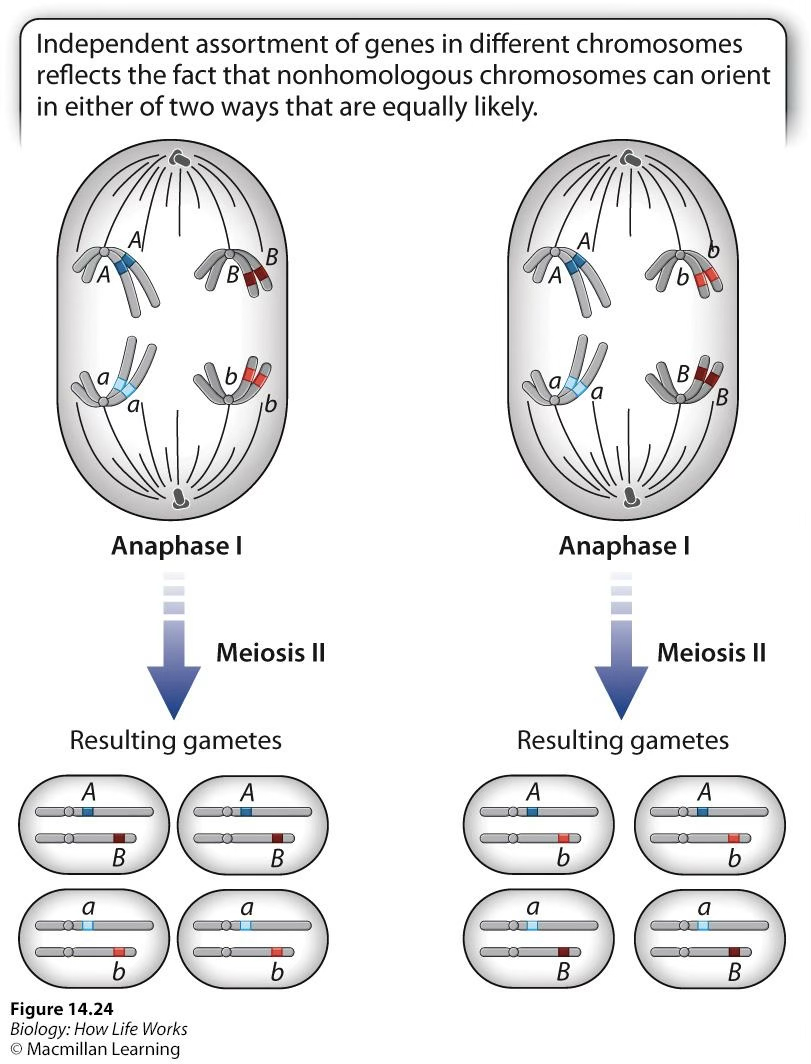
Which phase corresponds to independent assortment?
Random alignment of homologs on the metaphase plate during metaphase 1
Probability
The likelihood that an event will occur; probability = # of chances of event/total possible events
Product rule
Probability of simultaneous independent events equals the product of their individual probabilities; predicts the chance of parents with known genotypes to produce offspring of a particular genotype
How to do the product rule
Find the individual probability for each gene/letter, then multiply them together
When to do the product rule
Use the product rule when there are two different genes/traits (ex what is the chance that a seed is both wrinkled and green) or two different events (ex what is the chance that the first seed is round and the second seek is wrinkled)
Mendel’s Laws: Principle of Segregation
Individuals inherit two copies of each gene, one from the mother and one from the father, and when individuals form reproductive cells, the two copies separate equally in the eggs and sperm.
Short definition of segregation
Every single allele of a gene will separate into a different gamete
Mendel’s Laws: Principle of Independent Assortment
The two copies of each gene segregate into gametes independently of the two copies of another gene.