Vascular Chapter 25 - Multiple Choice
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
a. detailed anatomic information
Which is NOT a limitation of contrast angiography?
a. detailed anatomic information
b. lack of hemodynamic information
c. no identification of functional significance of renal artery disease
d. invasive with possible nephrotoxic contrast
D. All of the above
Which is true regarding duplex US assessment of the renal vasculature?
a. provides anatomic information
b. provides hemodynamic information
c. painless and noninvasive
d. all of the above
b. 9-13
What is the normal length measurement of the kidney?
a. 4-5 cm
b. 9-13 cm
c. 10-15 cm
d. 5-7 cm
c. horseshoe kidneys
Kidneys that are joined at the lower poles by an isthmus of tissue that lies anterior to the aorta?
a. ectopic kidneys
b. cross-fused kidneys
c. horseshoe kidneys
d. junctional kidneys
b. fat and fibrous tissue in the sinus
Why is the renal sinus normally brightly echogenic on a sonographic image?
a. lymphatic vessel location
b. fat and fibrous tissue in the sinus
c. increased blood flow in the area
d. fluid from the collecting system
c. renal pyramids
What are the triangular-shaped structures within the inner portion of the kidney that carry urine from the cortex to the renal sinus?
a. nephrons
b. columns of Bertin
c. renal pyramids
d. renal calyces
d. anterolateral, posterior
The right renal artery initially courses _____ from the aorta, then passes _____ to the IVC.
a. posterolateral, anterior
b. posterior, superior
c. anterolateral, lateral
d. anterolateral, posterior
C. LRV
Which vessel courses anterior to the AO but posterior to the SMA and anterior to both renal arteries?
a. splenic vein
b. RRV
c. LRV
d. IMV
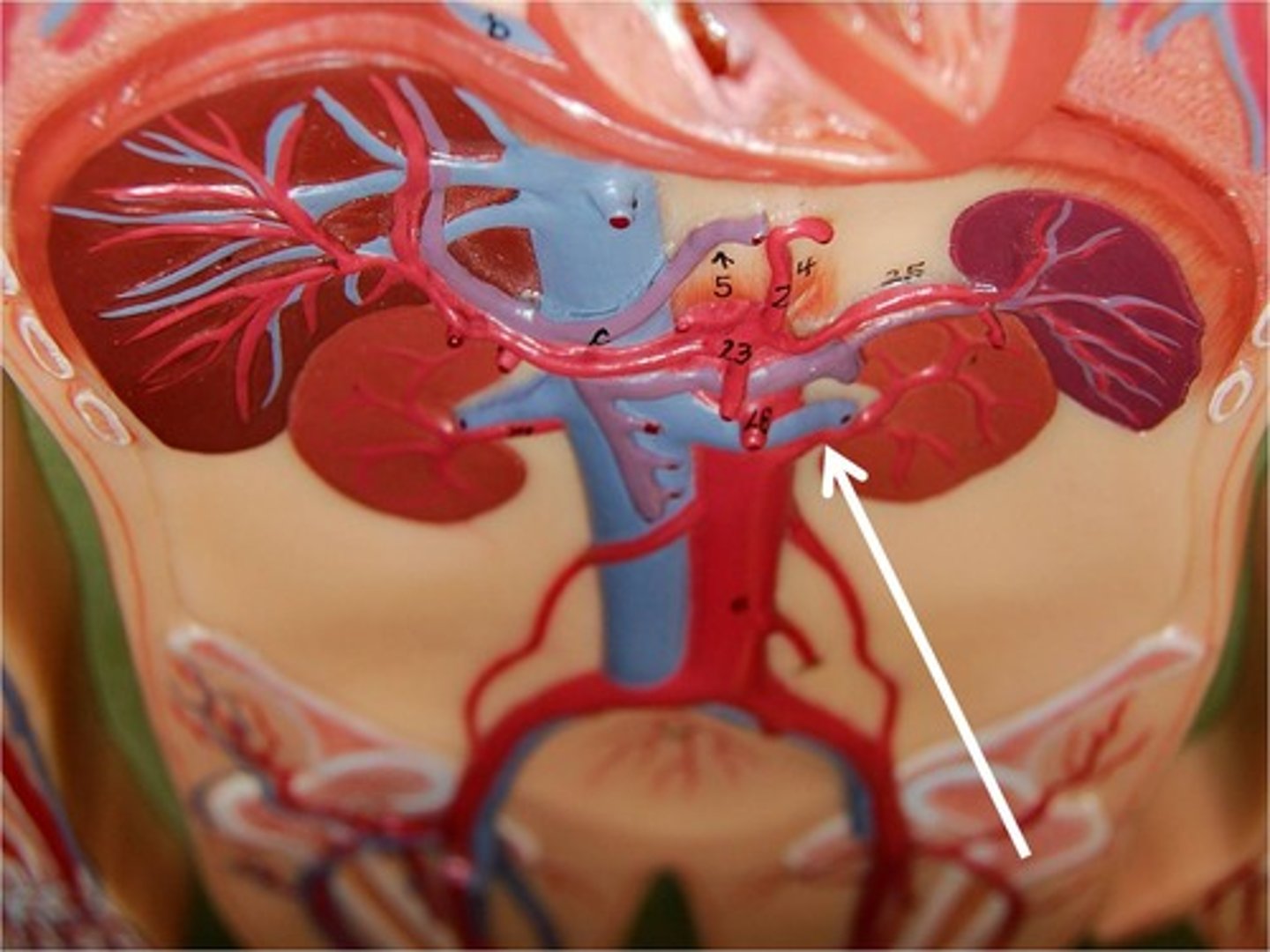
a. origin to proximal 1/3
In which of the renal segments does atherosclerotic disease in the renal artery typically occur?
a. origin to proximal 1/3
b. distal renal artery just before entering the kidney
c. mid-to-distal segment
d. interlobar arteries within the renal parenchyma
d. 32 year-old female with poorly controlled HTN
Which patient would be suspected of fibromuscular dysplasia in the renal artery?
a. 85-year old diabetic male
b. 66 year-old female with hx of controlled HTN and smoking
c. 25 year-old male with chronic asthma
d. 32 year-old female with poorly controlled HTN
b. b. 2-5 MHz curved linear
What is the most appropriate transducer for evaluation of kidneys?
a. 7-10 MHz straight linear
b. 2-5 MHz curved linear
c. 1-2 MHz vector array
d. 5-8 MHz phased sector array
a. proximal, at the level of the celiac artery and SMA
At what level is spectral Doppler waveform with PSV needed from the AO for use in the renal-aortic ratio (RAR)?
a. proximal, at the level of the celiac artery and SMA
b. mid, at the level of the kidneys
c. distal, at the level of the IMA
d. distal, at the level of the common iliac bifurcation
c. transverse, slightly inferior to the SMA
To identify the renal Ostia from a ML approach, an image is obtained from what location?
a. transverse, at the level of the CA
b. sagittal, at the level of the CA
c. transverse, slightly inferior to the SMA
d. sagittal, slightly superior to the left renal vein
b. power Doppler
Which US modality has a low-angle dependence that may be helpful in IDing duplicate renal arteries?
a. color-flow Doppler
b. power Doppler
c. spectral Doppler
d. pulse inversion Doppler
c. 0
Using which angle insonation are flow patterns within the kidney parenchyma typically obtained with a spectral Doppler?
a. 60
b. 90
c. 0
d. 45
a. 1 cm
When comparing renal length from side to side, how much of a difference suggests compromised flow in the smaller kidney?
a. 1 cm
b. 2 mm
c. 3 mm
d. 3 cm
b. low resistance, high diastolic flow with velocities between 90-120 cm/s
Which describes normal spectral Doppler waveform characteristics in the renal artery?
a. high resistance, minimal diastolic flow with velocities between 90-120 cm/s
b. low resistance, high diastolic flow with velocities between 90-120 cm/s
c. low resistance, minimal diastolic flow with velocities between 10-120 cm/s
d. high resistance, high diastolic flow with velocities between 50-70 cm/s
A. RRA stenosis <60%
A patient presents to the vascular lab for a renal duplex evaluation. Velocities in the RRA origin reach 175 cm/s with no evidence of poststenotic turbulence. Velocities on the left are 100 cm/s. What is suggested?
a. RRA stenosis <60%
b. LRA stenosis <60%
c. RRA stenosis >60%
d. LRA stenosis >60%
d. increased PSV
Which spectral Doppler waveform will NOT occur distal to a hemodynamically significant stenosis of the renal artery?
a. delayed systolic upstroke
b. loss of compliance
c. decreased PSV
d. increased PSV
b. kidney length >9 cm, velocities less than 10 cm/s in the renal cortex
Which finding within the kidney is consistent with renal artery occlusion?
a. kidney length >10 cm, velocities less than 10 cm/s in the renal cortex
b. kidney length >9 cm, velocities less than 10 cm/s in the renal cortex
c. kidney length >13 cm with no detectable flow within the renal parenchyma
d. kidney length <9 cm, velocities greater than 20 cm/s in the renal cortex
c. renal artery velocities 70 cm/s, EDR of 0.19
Acute Tubular Necrosis
which finding on renal artery dup[lex exam is consistent with this finding?
a. renal artery velocities >180 cm/s, EDR of 0.35
b. renal artery velocities >180 cm/s, RI of 0.6
c. renal artery velocities 70 cm/s, EDR of 0.19
d. renal artery velocities 70 cm/s, RI of 0.5
a. onset of systole to the early systolic peak
What is measured to determine acceleration time?
a. onset of systole to the early systolic peak
b. onset of systole to the end of diastole
c. onset of diastole to early systolic peak
d. end diastole to end systole
1. C. right RAR = 2.0, ,<60% stenosis; left RAR = 4.0, >60% stenosis, 2. left renal artery
1. During a renal arterial duplex exam, proximal aortic velocities of 100 cm/s, proximal RRA velocity of 200 cm/s, and proximal LRA velocities of 400 cm/s were found. Which describes the findings?
a. right RAR = 2.0, ,<60% stenosis; left RAR = 0.4, <60% stenosis
b. right RAR = 0.2, ,>60% stenosis; left RAR = 0.4, >60% stenosis
c. right RAR = 2.0, ,<60% stenosis; left RAR = 4.0, >60% stenosis
d. right RAR = 0.2, ,>60% stenosis; left RAR = 4.0, <60% stenosis
2. In which kidney would you see poststenotic turbulence? _____
D. All of these
Which may result in misinterpretation of the hilarity acceleration time?
a. elevated renovascular resistance
b. systemic arterial stiffness
c. renal artery stenosis in the 60-79% range
d. all of these
b. abdominal aorta velocities are over 100 cm/s or under 40 cm/s
Under which conditions is the renal to aortic ratio likely inaccurate?
a. abdominal aorta velocities are between 75-90 cm/s
b. abdominal aorta velocities are over 100 cm/s or under 40 cm/s
c. renal artery velocities are exceed 300 cm/s
d. renal artery velocities are below 100 cm/s
c. proximal renal vein thrombosis
The left renal vein near the hilum is noted to have continuous, non-phasic low-velocity flow. What is suggested?
a. renal artery stenosis
b. normal renal vein findings
c. proximal renal vein thrombosis
d. distal renal vein thrombosis
a. increased velocity because of mismatched sizes of stent to native vessel
After renal artery stent placement, velocities within the distal segment of the stent reach 250 cm/s. At other follow-ups at 6 and 12 months, velocities in the distal stent remain 250 cm/s. These findings are consistent with?
a. increased velocity because of mismatched sizes of stent to native vessel
b. fixed stenosis at the distal end of the stent
c. kinking of the stent, creating artificially elevated velocities
d. stent collapse and failure
b. renal artery PSV >400 cm/s and cortical EDV <5cm/s
Which represents renal duplex findings that demonstrate high risk for renal atrophy and likely unsuccessful renal revascularization?
a. renal artery PSV <400 cm/s and cortical EDV >10 cm/s
b. renal artery PSV >400 cm/s and cortical EDV <5cm/s
c. renal artery PSV >160 cm/s and cortical EDV <10 cm/s
d. renal artery PSV >200 cm/s and cortical EDV <5 cm/s
A. Duplication of the renal collecting system
What is the most common congenital anomaly of the urinary tract?
A. Duplication of the renal collecting system
B. Absence of one or both kidney
C. Junctional kidneys
D. Ureteropelvic junction malformation