8. Transition metal catalysts
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
transition metals and their compounds make good catalysts
because they can change oxidation states gaging or losing electrons within their d orbitals
transition metals can transfer electrons
to speed up reactions

other elements aren’t used to catalyse redox reactions
because they dont have an incomplete 3d subshell and dont have variable oxidation states
heterogeneous catalyst
a catalyst that’s a different physical phase from the reactants
when heterogeneous catalysts are used
the reaction occurs on the surface of the catalyst
increasing the surface area of the catalyst
increases the number of molecules that can react at the same time, thus increasing the rate of reaction
support medium
often used to make the area of the catalyst as large as possible

during a reaction
reactants are adsorbed onto active sites on the surface of heterogeneous catalyst
impurities in the reaction mixture may also bind to the surface of a catalyst
this blocks reactants from being adsorbed
the process of impurities blocking reactants from being adsorbed
catalyst poisoning
catalyst poisoning reduces the surface area of the catalyst available to reactants
slowing down the reaction
catalyst poisoning increases the cost of chemical process
because less product can be made in a certain time or w certain amount of energy
catalysts may even need replacing or regenerating
which also costs money

catalyst poisoning can be reduced by purifying the reactants
this removes many impurities which would otherwise poison the catalyst
homogeneous catalyst
catalysts in the same physical state as reactants
usually homogeneous catalysts are aqueous catalysts
for reactions between 2 aqueous solutions
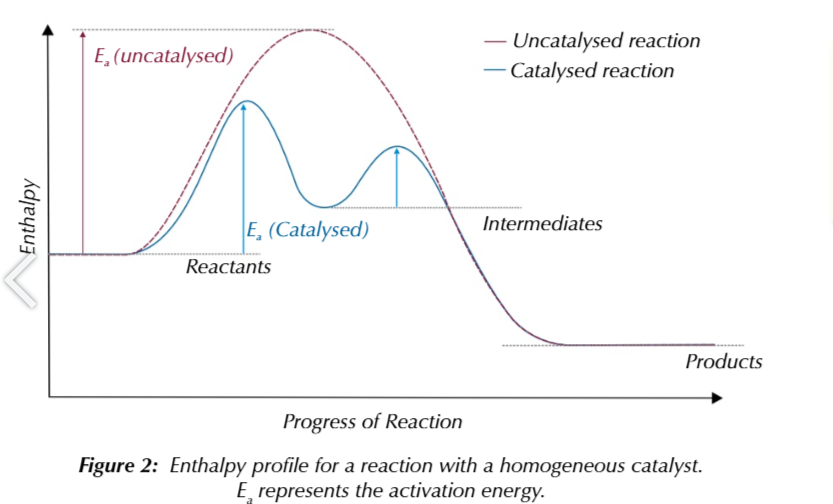
homogeneous catalysts work
by forming intermediate species
the reactants combine with the catalyst to make an intermediate species
which then reacts to form the products and reform the catalyst
this causes an enthalpy profile for a homogeneously catalysed reaction to have 2 peaks
corresponding the 2 reactions
the activation energy required to form the intermediate and product from it
is lower than the activation energy needed to make the products directly from the reactans
catalysts are always reformed
so it can carry on catalysing the reaction
Fe2+ catalysing the reaction between
S2O82- and I-
redox reaction between iodide ions and peroxodisulfate S2O82- Ions
S2O82- + 2I- → I2 + 2SO42-
The reaction occurs annoyingly slowly because both ions are negatively charged
the ions repel each other so it sunlikely they;ll collide and react
is Fe2+ ions are added, things are really sped up
because each stage of the reaction involves a positive and negative ion so there’s no repulsion
Fe2+ ions are oxidised to Fe3+ ions by S2O82- ions
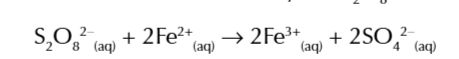
the newly formed Fe3+ ions now easily oxidises I- ions getting reduced in the process and reforming as Fe2+
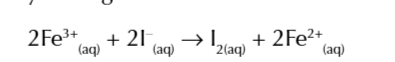
you can test for iodine by adding start solution
the solution turning blue-black indicates iodine is present
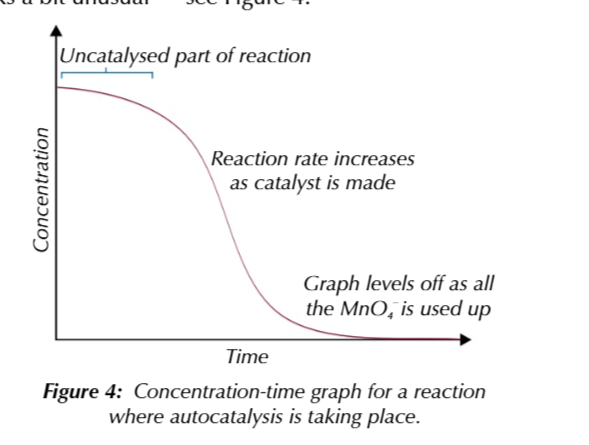
Mn2+ autocatalysing the reaction
between MnO4- and C2O42-
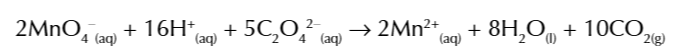
is it an autocatalysing reaction
because the Mn2+ is a product of the reaction and acts as a catalyst for the reaction
this means that as the reaction progresses and the amount of the product increases
the reaction speeds up
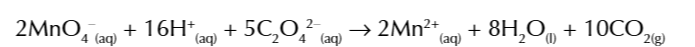
there isnt many Mn2+ present at the beginning of the reaction to catalyse it
so at first the reaction rate is slow
during the uncatalysed part of the reaction
the activation energy is very high
because the reaction proceeds via the collision of negative ions
which require alot of energy to achive
once alittle Mn2+ catalyst has been made it reacts with the MnO4- ions
to make Mn3+ ions
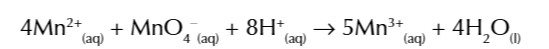
Mn3+ ions are intermediate and react w C2O42- ions
to make CO2 and reform Mn2+ catalyst
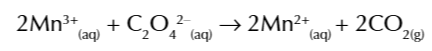
because Mn2+ autocatalyse the reaction
the reaction rate increases with time as more catalyst is made
this means a concentration time graph of the reaction looks a lil funny