Ch 23 Pt 1: Protists
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
protists background
eukaryotes
most are microscopic and unicellular
abundant in soil, freshwater, brackish, and marine environments
some have macroscopics cells
some are multicellular
some are parasites
the complexity and diversity of protists makes it difficult to classify
cannot be classified as plants
gametes and zygotes are not protected from drying out nor do they have roots, stems, etc
cannot be classified as fungi
do not have chitin in their cell wall
cannot be classified as animals
do not undergo embryonic development
who was the first scientist to observe protists?
antonie van leeuwenhoek, 1674
eukaryote characteristics
cells w/ nuclei surrounded by a nuclear envelope w/ nuclear pores
mitochondria
cytoskeleton of microtubules and microfilaments
flagella and cilia
chromosomes organized by histones
mitosis
sexual reproduction
cell walls (absent in animal cells)
protist structure
most are unicellular
some are colonial and multicellular
some are composed of enormous, multinucleate, single cells
unicellular protists carry out essential functions using subcellular organelles
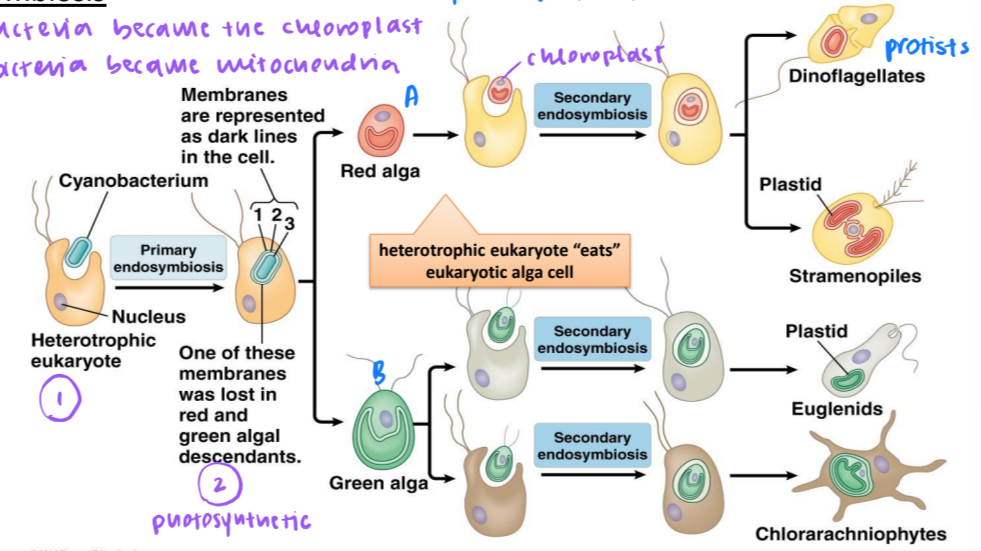
unique plastids came from eukaryotic, symbiotic alga cells through secondary endosymbiosis
cyanobacteria became the chloroplast, proteobacteria became mitochondria
protist cell structure
nucleus
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi apparatus
lysosomes (hydrolytic digestive enzymes)
contractile vacuoles (pumps excess water from protist cell)
endoplasmic reticulum
if ribosome is attached: protein synthesis
if ribosome is not attached: lipid synthesis
true or false. protist cells may be enveloped by animal-like cell membrane or plant-like cell walls
true
protist metabolism
exhibit many forms of nutrition
may be aerobic or anaerobic
photoautotrophs
heterotrophic protists
amoebas and some other heterotrophic protist species ingest particles by phagocytosis
saprobes
mixotrophs
photoautotrophs
characterized by the presence of chloroplasts and perform photosynthesis
heterotrophic protists
consume organic materials (such as other organisms) to obtain nutrition
saprobes
subtypes of heterotrophs absorb nutrients from dead organisms or their organic wastes
mixotrophs
combine photosynthesis and heterotrophic nutrition
protist motility
majority are motile
some have one or more flagella, which they rotate or whip
others are covered in cilia that they beat in a coordinated manner to swim
others from cytoplasmic extensions called pseudopodia anywhere on the cell, anchor the pseudopodia to a substrate, and pull themselves forward
some can move toward or away from a stimulus, called taxis
phototaxis
phototaxis
movement toward light, accomplished by coupling their locomotion strategy w a light sensing organ
protist reproduction
asexual reproduction
binary fission
multiple fission
budding
sexual reproduction
protist life-cycles
binary fission
asexual
produces 2 daughter cells
can be divided into transverse or longitudinal
longitudinal binary fission
the plane of division passes along the longitudinal axis of the organism (Euglena)
transverse binary fission
the plane of division is through the transverse axis of the organism (Paramecium)
multiple fission
asexual
some protists such as the true slime molds exhibit multiple fission and simultaneously divide into many daughter cells
budding
asexual
some protists produce tiny buds that go on to divide and grow to the size of the parental protist
true or false. many protist species can switch from asexual to sexual reproduction when necessary
true
sexual reproduction
involves meiosis and fertilization, common among protists
often associated w periods when nutrients are depleted or environmental changes occur
may allow the protist to recombine genes and produce new variations of progeny
protist life-cycles
range from simple to extremely elaborate
certain parasitic protists have complicated life cycles
must infect different host species at different developmental stages to complete their life cycle (ex. Plasmodium → malaria)
some protists are unicellular in the haploid (n) form and multicellular in the diploid (2n) form
alternation of generations
alternation of generations
strategy where protists have multicellular stages in both haploid and diploid forms
ex. Laminaria (brown alga)
cysts
a protective, resting stage
endospores
depending on habitat of the species, the cysts may be particularly resistant to temp extremes, desiccation, or low pH
allows certain protists to “wait out” stressors until their environment becomes more favorable for survival or until they are carried (such as by wind, water, or transport on a larger organism) to a different environment
cysts exhibit virtually no cellular metabolism
endospores
an adaptive strategy against adverse environmental conditions
Giardia lamblia
a flagellate protozoan which is capable of forming cysts
eukaryotic supergroups
Archaeplastida
Amoebozoa
Opisthokonta
Rhizaria
Chromalveolata
Excavata
true or false. protists are not in all 6 eukaryotic supergroups
false
true or false. protists share common ancestors w plants, animals, and fungi
true
Red Algae
archaeplastida
mostly marine, multicellular seaweeds
chloroplasts include unique red phycoerythrin accessory pigment
helps absorb light in deeper water
humans eat it (seaweed)
cellulose + unique cell wall polysaccharides
carrageenan thickener (ice cream)
agar (for petri dish cultures, food, nori)
Chlorophytes
archaeplastida
green algae (along w Charophytes)
chloroplasts same as in plants
most are freshwater; many marine
many w bi-flagellated cells
unicellular forms:
colonial forms
colonial forms of Chlorophytes
Scenedesmus: a simple colony of four cells
Gonium: a small colony
Volvox: a large colony w/ some specialization
Chlorophyte: unicellular form
phytoplankton (ex. Chlamydomonas)
Chlorophytes: colonial form
Volvox
Chlorophytes: multinucleate single cells, large body form
Caulerpa, an intertidal chlorophyte

Chlorophytes: multicellular forms
freshwater algae (ex. Cladophora)
seaweeds (ex. Ulva: edible sea lettuce)
vitamin C, D, and iodine
flattened boy, showing up w no differentiation between stem and leaves
Amoebozoans
slime molds
gymnamoebas
entamoebas
Amoebozoans do amoeboid ________ (cell crawling) and ___________ using lobe-like pseudopodia (false feet) (no cell walls)
movements, phagocytosis
slime molds
Amoebozoans
live in moist terrestrial habitats (rotting wood, etc.)
use pseudopodia to move and ingest bacteria
move and live up to ingest
ex plasmodial slime mold and cellular slime mold
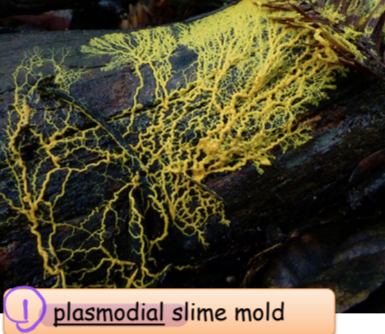
plasmodial slime mold
no cytokinesis → multinucleate, single cell
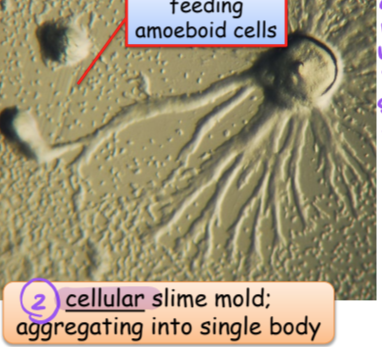
cellular slime mold
aggregating into single body/mass when starving (survival structure)
independent cells when lacking nutrients
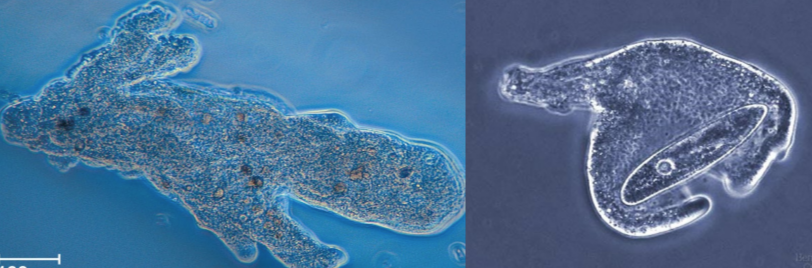
Gymnamoebas
Amoebozoans
found in soil, freshwater, and marine habitats
moves w/ fat pseudopodia, feeding on bacteria, other protists, detritus
ex. Amoeba proteus
entamoebas
Amoebozoans
unicellular parasites of animals
kills and feeds on host cells
spreads by durable cyst form (endospores)
ex. Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica
causes amebic dysentery
kill and digest intestinal lining → bloody diarrhea, fever, abcesses intestinal perforation
Excavata
diplomonads
parabasalids
euglenozoans
unifying features of excavata
unicellular, flagellated, and have no cell wall
diplomonads
Excavata
unicellular, multiple flagella, no cell wall
anaerobic, reduced mitochondria
most are parasitic
ex. Giardia intestinalis
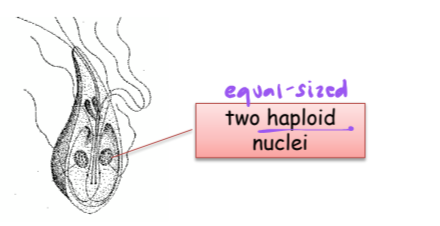
Giardia intestinalis
intestinal paraiste
durable cysts consumed in water
parabasalids
Excavata
unicellular, multiple flagella, no cell wall
anaerobic, reduced mitochondria, asexual reproduction
most are symbiotic
ex. Trichomonas vaginalis
parabasalids in termites contain symbiotic bacteria that help w termites digest wood
Trichomonas vaginalis
human vaginal parasite (STD)
more likely to get HIV and cervical cancer
Euglenozoans
Excavata
unicellular, no cell wall, flagella w crystalline rod
ex. Euglenas
ex. Trypanosoma
Euglenas
free living, aquatic
autotroph w green chloroplasts (2o) (acquired during secondary endosymbiosis of a green algae or heterotroph or mixotroph (switches nutrition - dependent on amt of light)
Trypanosoma
blood parasite
“sleeping sickness” carried by tse-tse fly)
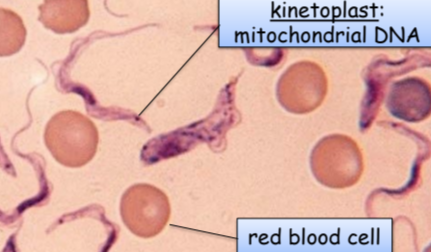
kinetoplastids
kinetoplast mitochondrial DNA: DNA molecules interlocked together
not photosynthetic
not plasmids