Unit 2: Reformation & Wars of Religion Vocab (ID's)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Teresa of Ávila
Carmelite nun and Catholic reformer who wrote The Way of Perfection and helped lead a spiritual revival within the Catholic Church.

The Ursulines (The Order of Saint Ursula)
Order of nuns who focused on Christian education for girls in order to improve the family, and thus society.

Martin Luther
Monk and scholar at the University of Wittenberg who posted the Ninety-Five Theses (October 31, 1517) and sparked the Reformation.

Henry IV of Navarre (France)
Granted Huguenots freedom of worship in France (The Edict of Nantes) and brought an end to the French Wars of Religion in 1598.

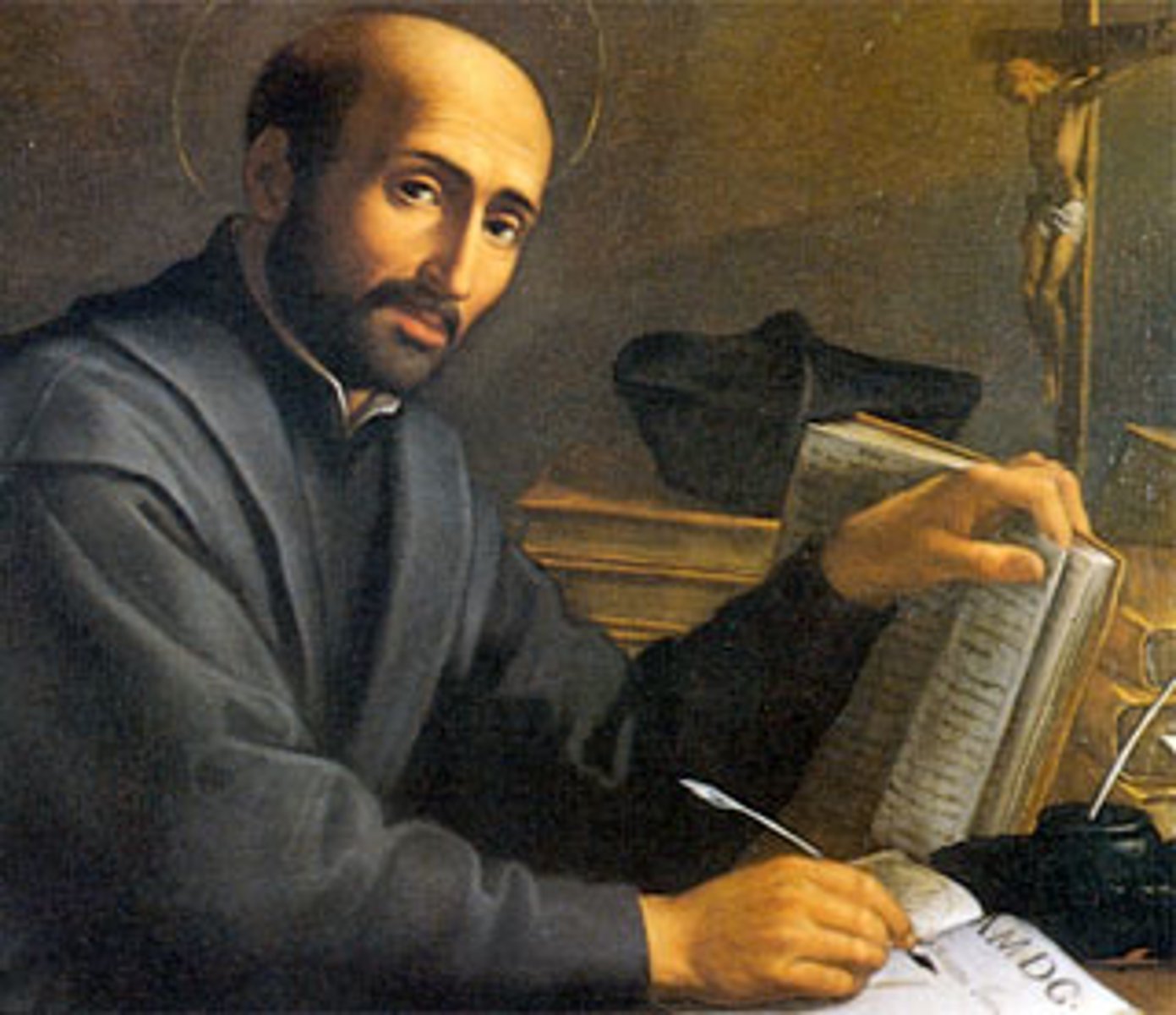
Ignatius of Loyola
Knight who gave up combat for spiritual warfare and established the Jesuit Order as part of the Catholic Reformation.

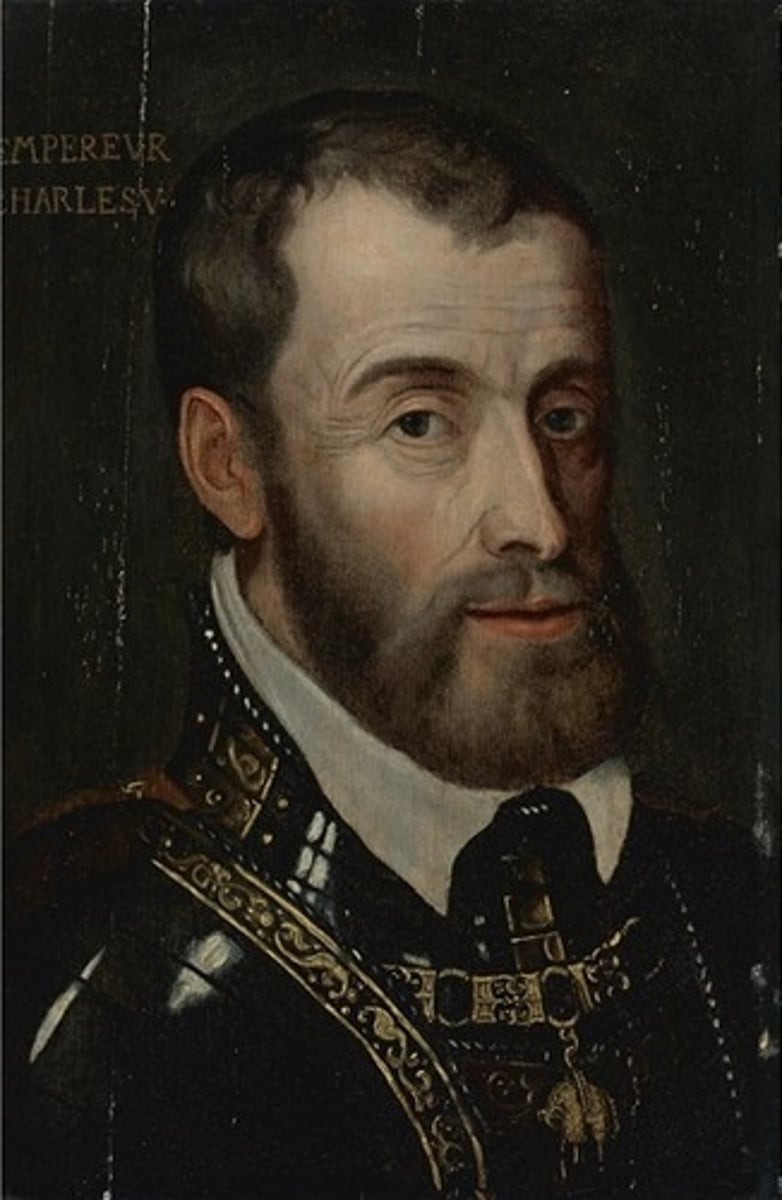
Charles V
Habsburg Holy Roman Emperor who tried to maintain Catholic unity in the HRE (Holy Roman Empire) but had to settle for the Peace of Augsburg (Schmalkaldic Wars with Schmalkaldic League).

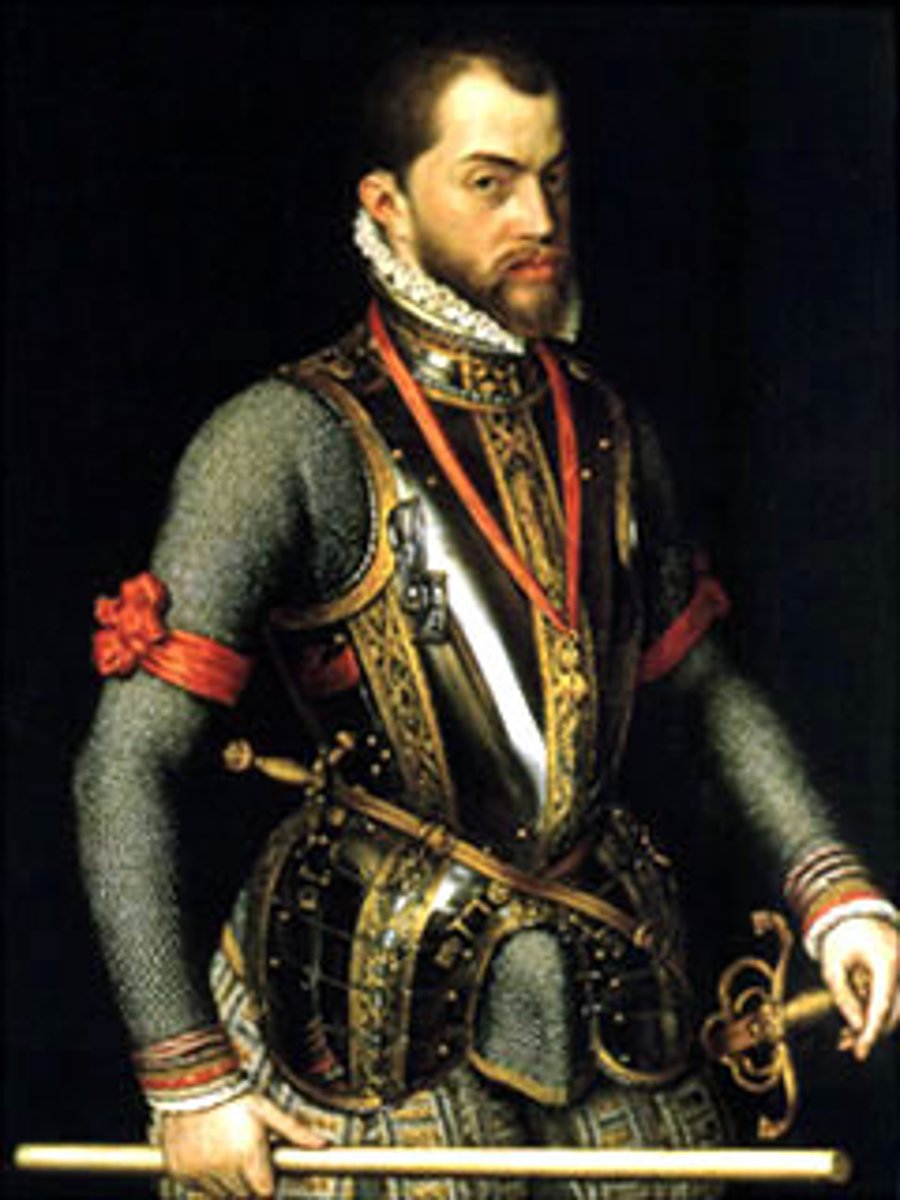
Philip II
Monarch of Spain who sent troops to the Netherlands to suppress the Dutch Revolt and whose armada was defeated by the English (Elizabeth I, the sister of his dead ex-wife Mary (I) Tudor).

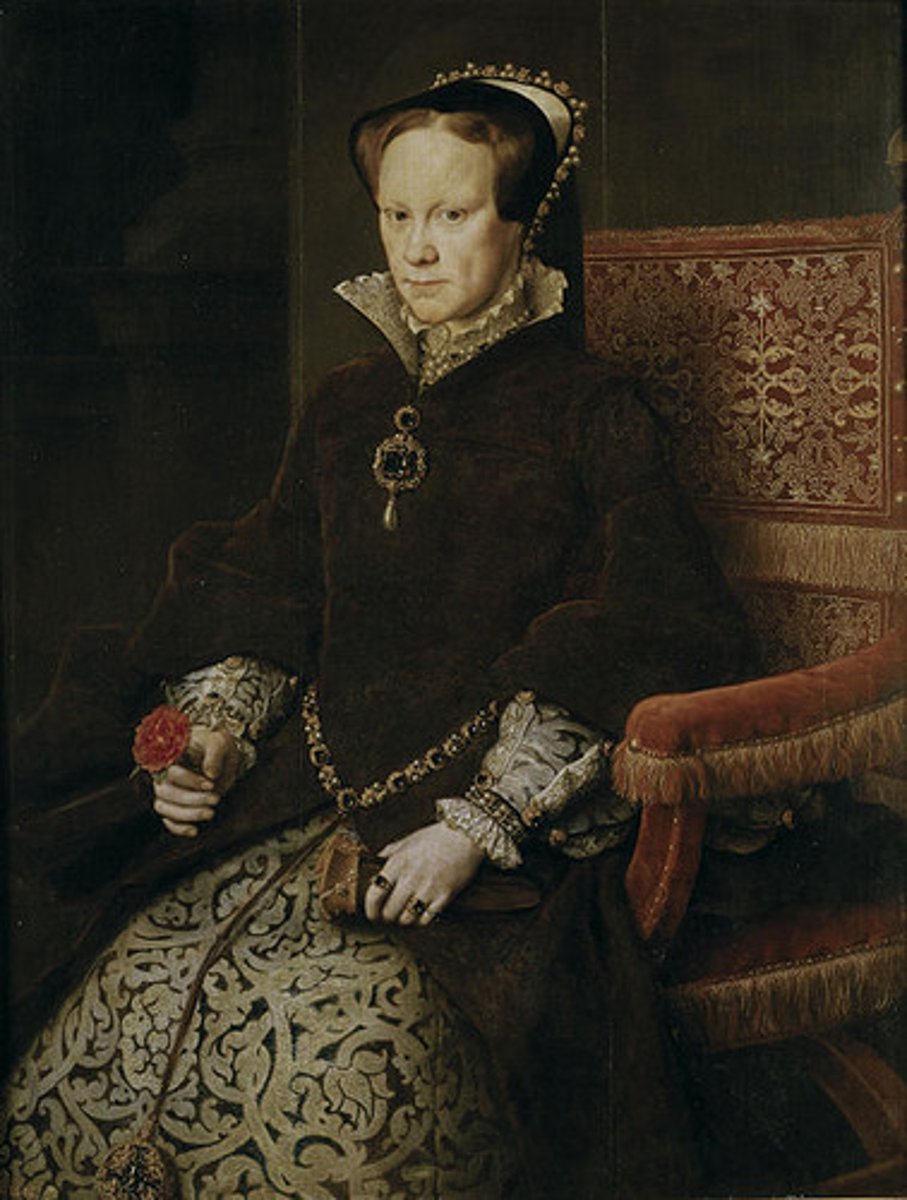
Mary (I) Tudor
English monarch who tried to restore Catholicism in England (daughter of Catherine of Aragon, abolished The Book of Common Prayer first established by brother Edward Tudor VI) and earned the nickname "Bloody Mary."

Elizabeth I
English monarch who brought relative religious peace to England by pursuing moderately Protestant policies (The Elizabethan Religious Settlement, return of The Book of Common Prayer first established by brother Edward Tudor VI).

Ulrich Zwingli
Swiss Protestant reformer from Zurich who clashed with Luther over beliefs about the Eucharist.

John Calvin
Swiss (French) Protestant reformer and leader in Geneva who believed in predestination and the concept of the "the elect."

The Anabaptists
Protestant religious group who were persecuted for their beliefs which included pacifism and adult baptism (modern-day Quakers and Mennonites).

The Council of Trent
Series of meetings of Catholic and Protestant leaders who discussed Christian doctrine and reaffirmed Catholic beliefs during the Catholic Reformation.

The German Peasants' Revolt (The Great German Peasants' War)
Rebellion in Germany by peasants who were suffering from severe famine believing they would get support from Luther.

Predestination
Protestant idea that God already knows who will be saved.

Henry VIII
His need for a divorce from Catherine of Aragon (daughter of Ferdinand and Isabella (sponsors/patrons of Christopher Columbus), aunt of Charles V, mother of Mary (I) Tudor, and great aunt to Philip II) led to the establishment of the Anglican Church.

Francis I of France
Monarch of France who sought to weaken the Holy Roman Empire by aiding Lutheran princes during the Schmalkaldic Wars.

The Council of Trent
Established by Pope Paul III to root out heresy and preside over the Roman Inquisition.
John Knox
Calvinist who brought his beliefs to Scotland and made Calvinism the official religion of Scotland, now known as Presbyterianism.

The Huguenots
Term for French Calvinists who faced persecution during the French Wars of Religion.

The Index of Prohibited Books (Index Librorum Prohibitorum)
List of Protestant books and other works banned and deemed heretical by the Catholic Church.

The Concordat of Bologna
Agreement between the pope and Francis I (1516) that gave the French monarch the power to appoint religious leaders within France.

The Habsburg-Valois Wars
Series of wars over Italy between the monarch of France and the Spanish Habsburgs settled by the Treaty of Cateau Cambresis.

The Diet of Worms (1521)
Meeting of the Holy Roman Empire's princes and emperor during which Martin Luther was asked to recant but he refused, further fueling the spread of Protestantism.

Politique
Term for Henry of Navarre (Elizabeth I) and other moderates who put the needs of their country over their desire for religious unity.

Gustavus Adolphus
Swedish (Lutheran) king whose tactical brilliance in the Thirty Years' War brought success, though he eventually died in battle.

Cardinal Richelieu
French minister whose efforts during the Thirty Years' War weakened the Holy Roman Empire and made France a dominant European power.
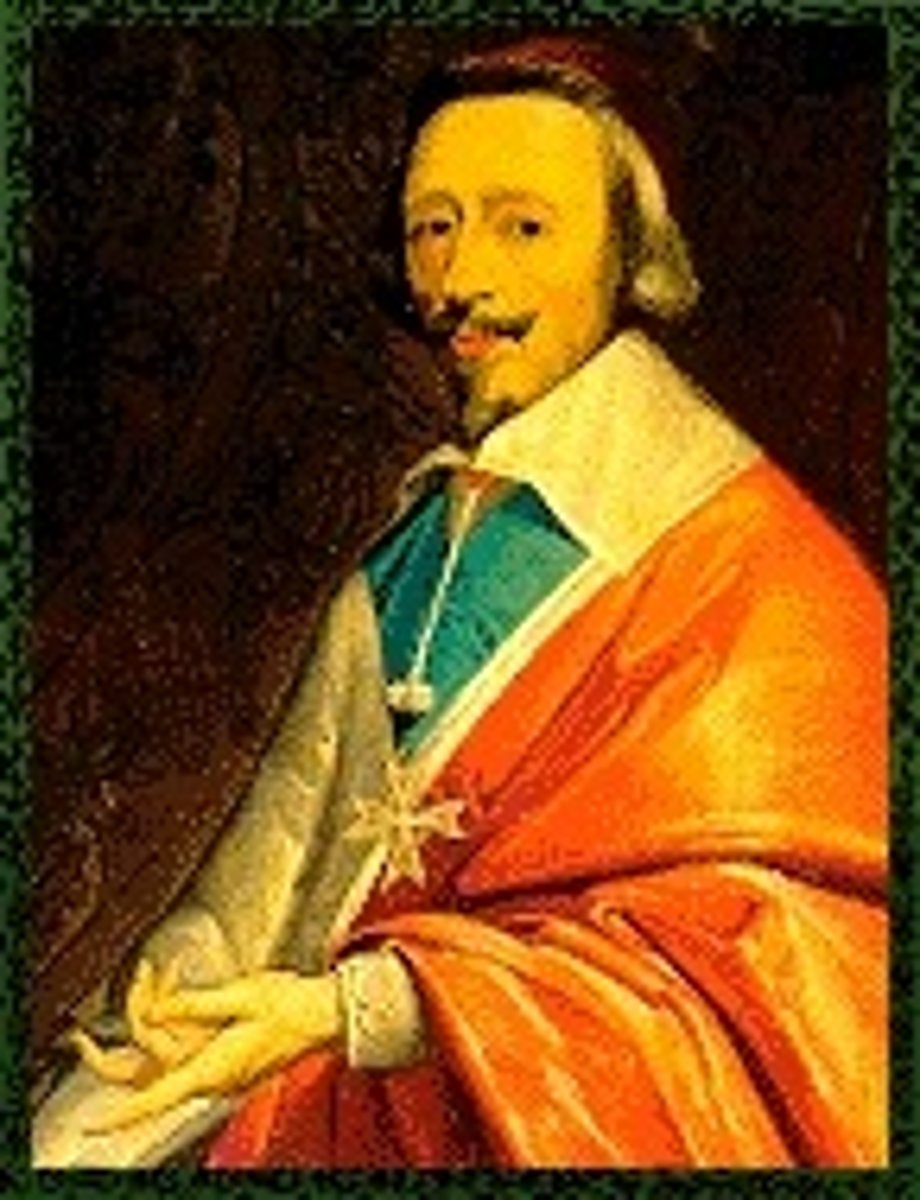

Ferdinand II
Holy Roman Emperor during the Thirty Years' War who revoked the Letter of Majesty and sought to restore Catholicism.
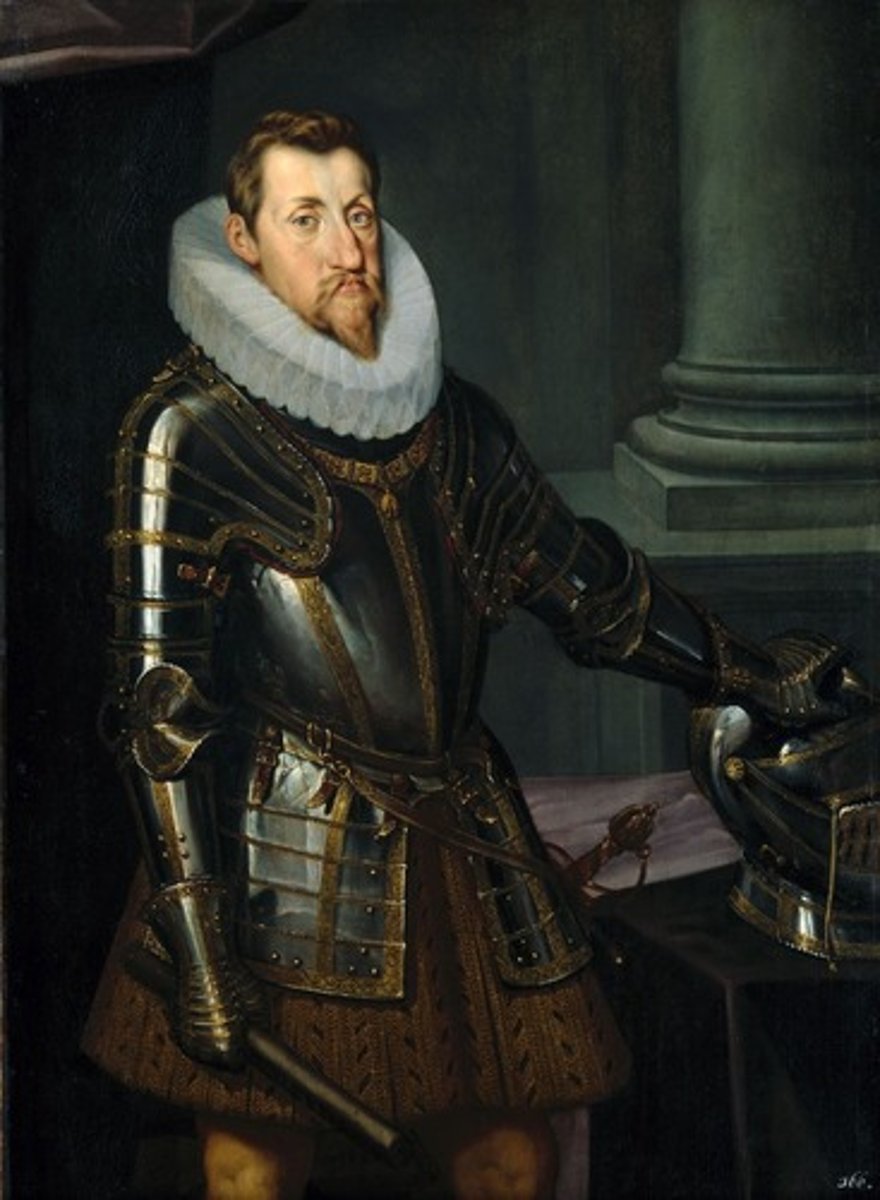

Bohemia
Territory where the Defenestration of Prague took place, sparking the Thirty Years' War (1618).
Johan Tetzel
Archbishop of Mainz, whose need to sell indulgences in Saxony irritated Martin Luther and led to the Ninety-Five Theses.

Anticlericalism
Increasing resentment of church leaders in the sixteenth century due to ignorance and corrupt practices.

Sola Fide
Luther's belief that salvation can only come through one's faith, not their good works.

Sola Scriptura
Luther's belief that one's faith must only be derived through reading of the Scripture.

Vernacular
Use of common language in printing and writing.
The Treaty of Westphalia
Treaty that ended the Thirty Years' War and brought an end to the wars of religion in Europe (1648).
