Sensation
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:13 PM on 12/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
1
New cards
Light
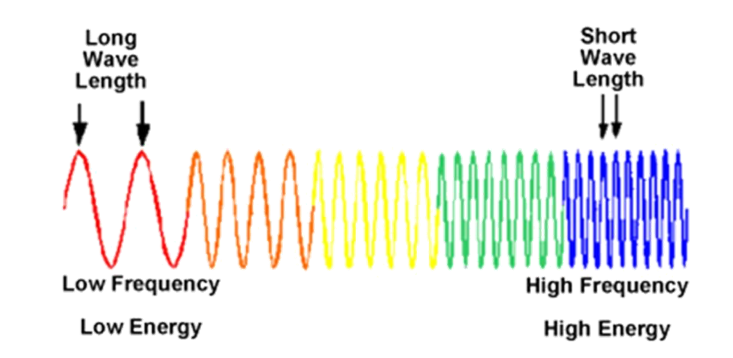
Energy -> waves
-wavelengths - distance of peaks
-wavelengths - distance of peaks
2
New cards
Color
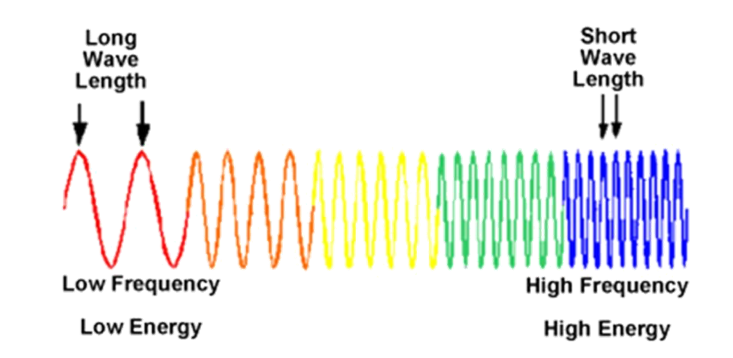
-longest to shortest
-ROYGBIV (red longest / violet short)
-ROYGBIV (red longest / violet short)
3
New cards
cornea
protects the outer layer of the eye
4
New cards
pupil
hole in the eye that absorbs light
5
New cards
iris
makes the pupil dilate and shrink
6
New cards
lens
contract / expand
focus on one thing
focus on one thing
7
New cards
fovea
cones
8
New cards
retina
(film of camera) vision cells and the light/photo receptors; project from the brain
-eye concentration : "you are my phobia, everyone else is in my retina." (inner layer) (opposite of cornea)
-eye concentration : "you are my phobia, everyone else is in my retina." (inner layer) (opposite of cornea)
9
New cards
optic nerve
retina to brain
10
New cards
Blind Spot
cannot see anything (Brain knows/ fills in side of sight); no retina
11
New cards
visual acuity
sharpness of vision (people with glasses don't have good acuity)
12
New cards
Photo receptors
receive the light information
-transductions - The conversion of the extersion stimuli into neural impulses
-rods
-cones
-transductions - The conversion of the extersion stimuli into neural impulses
-rods
-cones
13
New cards
rods
outlines and shapes
14
New cards
cones
color - vision; color blindness
15
New cards
Trichromatic Theory(Young-Helmholtz)
3 types of cones pick up blue, red, and green
16
New cards
opponent process theory
2 sets of opposing colors: blue and yellow; red and green
17
New cards
air molecules
what you hear
18
New cards
Sound
air molecules
19
New cards
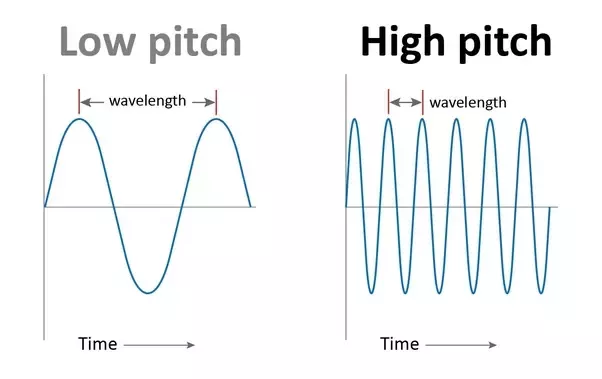
Pitch
higher/low frequency
20
New cards
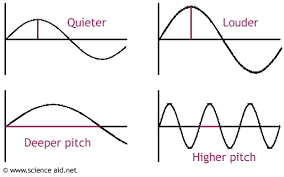
loudness
higher wave
21
New cards
outer ear
part you can see -- Pinna
22
New cards
auditory canal
funnel sound wave
23
New cards
hammer
malleus - a small bone in the middle ear which transmits vibrations of the eardrum to the incus.
24
New cards
anvil
incus - a small anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear, transmitting vibrations between the malleus and stapes.
25
New cards
stirrup
stapes - a small stirrup-shaped bone in the middle ear, transmitting vibrations from the incus to the inner ear.
26
New cards
what does the hammer, anvil, and stirrup have in common?
all vibrate and are bones in the ear
27
New cards
oval window
movement of fluid within the cochlea and activation of receptors for hearing.
28
New cards
semicircular canals
the fluid in the ear; upright; dizzy -> fluid still moving
29
New cards
cochlea
sense of hearing and participates in the process of auditory transduction
30
New cards
transduction
ear converts sound waves into electric impulses and sends them to the brain so we can interpret them as sound.
31
New cards
place theory
reading location of the cilia; low, medium, high
32
New cards
frequency theory
all cilia vibrating at same time but with different speed per pitch
33
New cards
deafness
conductive and sensorineural
34
New cards
conductive
hearing aides
35
New cards
sensorineural
problem with nerves in the ear
36
New cards
olfactory
has to do with smell
37
New cards
chemical-odorants
taste / smell
38
New cards
adaptable
-adapt to environment through evolutionary perspective.
-get used to it (filter smell out) (nose blind)
-get used to it (filter smell out) (nose blind)
39
New cards
taste
sent can change taste of food
40
New cards
temperature
smell stronger -> molecules move fast
41
New cards
nose hairs
receptors can be regenerated
42
New cards
memory
connect directly to limbic system (amygdala and hippocampus) and thalamus
43
New cards
pheromones
smell chemicals released
-covid in brain
-"dogs and bees smell fear"
-covid in brain
-"dogs and bees smell fear"
44
New cards
gustation
has to do with taste
45
New cards
5 different tastes
sweet, sour, bitter, saltiness, umami
46
New cards
umami
mushrooms and meat
47
New cards
super tasters
more flavor sensitive
-bitter foods/sour
-coffee
-grapefruit
-chili peppers
-bitter foods/sour
-coffee
-grapefruit
-chili peppers
48
New cards
vestibular
balance
49
New cards
kinesthetic
body position/where limbs are/locate
50
New cards
body senses
vestibular and kinesthetic
51
New cards
perception
organizing and making sense of sensory information
52
New cards
Perceptual processing
top-down processing (concept driven)
-perceptual set
-priming
-perceptual set
-priming
53
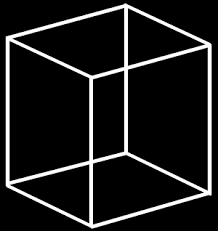
New cards
top-down processing
the way you perceive
54
New cards
perceptual set
mental filing cabinet for sense
55
New cards
priming
perceive differently based on current state of mind
56
New cards
bottom up (data driven)
take data and place together
-monocular depth cues
-monocular depth cues
57
New cards
thresholds
amount/limit (something that needs to be passed)
-absolute threshold
-difference threshold (JND)
-absolute threshold
-difference threshold (JND)
58
New cards
absolute threshold
minimal amount of stimuli needed to detect something
-signal detectiond
-signal detectiond
59
New cards
signal detection
mental/emotional state can effect threshold
-"creepy sound in house"
-"creepy sound in house"
60
New cards
difference threshold (JND)
how much stimuli is needed to detect the difference between stimuli
-Weber's Law
-"how much turning up the temperature to notice"
-Weber's Law
-"how much turning up the temperature to notice"
61
New cards
parallel processing
take in multiple types of sensory information at the same time
62
New cards
selective attention
brain will filter out information that is not important (clothes on skin)
63
New cards
cocktail party effect
listen to other conversation (hear your name)
64
New cards
sensory adaption
getting used to sensory stimuli and brain filtering out unchanging senses
65
New cards
change blindness
inability to notice change in things.
66
New cards
closure
tendency to fill gaps between lines.
67
New cards
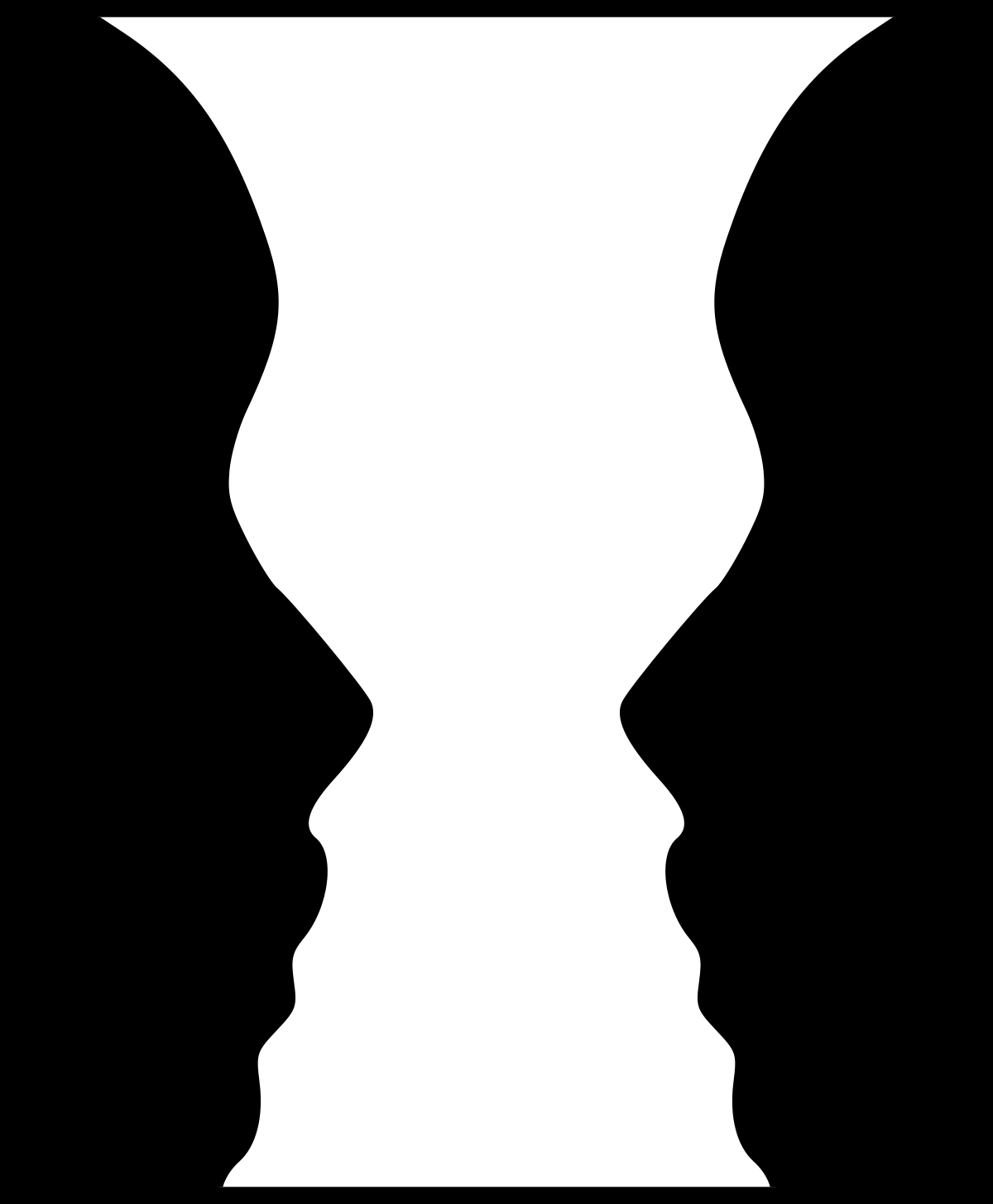
figure ground perception
the ability to differentiate an object from its background
68
New cards
proximity
grouping close objects together
69
New cards
simulartity
grouping similar looking items
70
New cards
continuity
continued lines grouped
71
New cards
orientation
contentedness
72
New cards
depth perception
ability to tell how far/close something is
73
New cards
visual cliff
test babies depth perception to cross over
74
New cards
relative size
monocular cues; close:big - far:small
75
New cards
relative height
monocular cues; high:far - low:close
76
New cards
interposition
monocular cues; things that are behind are therefore further away
77
New cards
relative clarity
monocular cues; clear:closer - foggy:far
78
New cards
texture gradient
monocular cues; smooth:far - rough:close
79
New cards
linear perspective
monocular cues; converge together to meet at one point
80
New cards
motion paralax
monocular cues; back:slow - close:fast
81
New cards
binocular cues
pencil test - two pencils show
retinal disparity - each retina overlays and creates depth (3-D movie)
convergence - closer your eyes are, it will aim sharply
retinal disparity - each retina overlays and creates depth (3-D movie)
convergence - closer your eyes are, it will aim sharply
82
New cards
Stroboscopic movement
one object layer over multiple shots
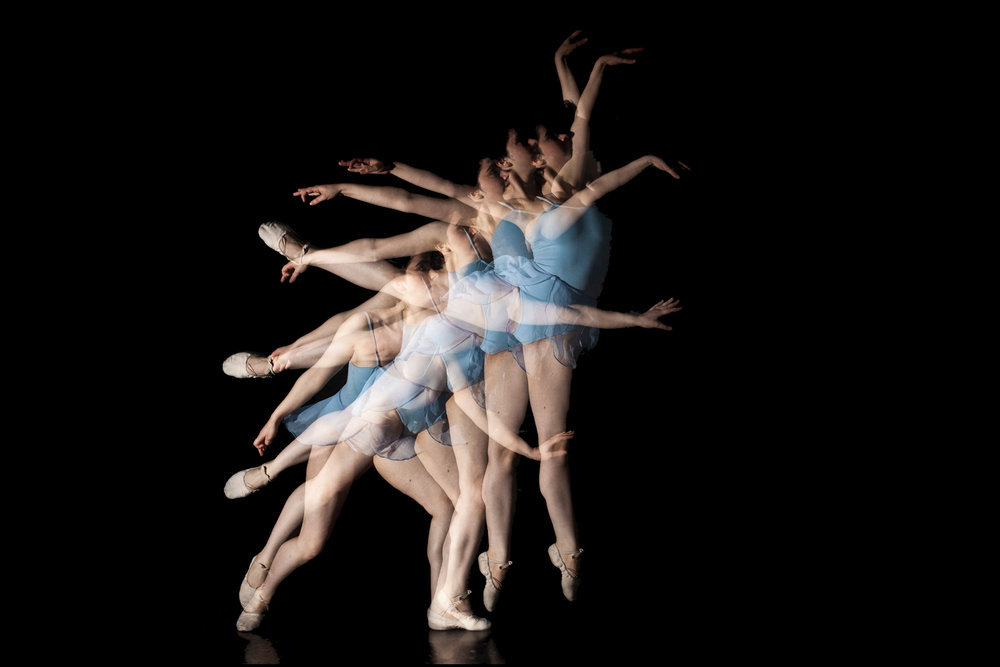

83
New cards
phi phenomenon
perception of motion in lights
84
New cards
size constancy
the same size but different positions
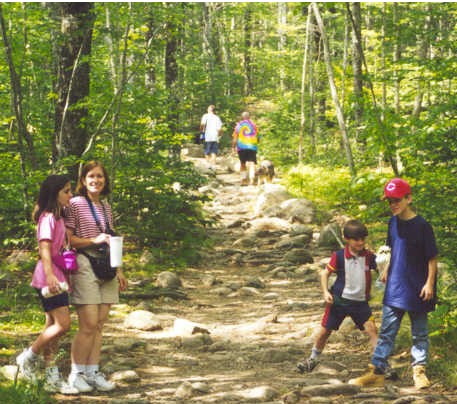

85
New cards
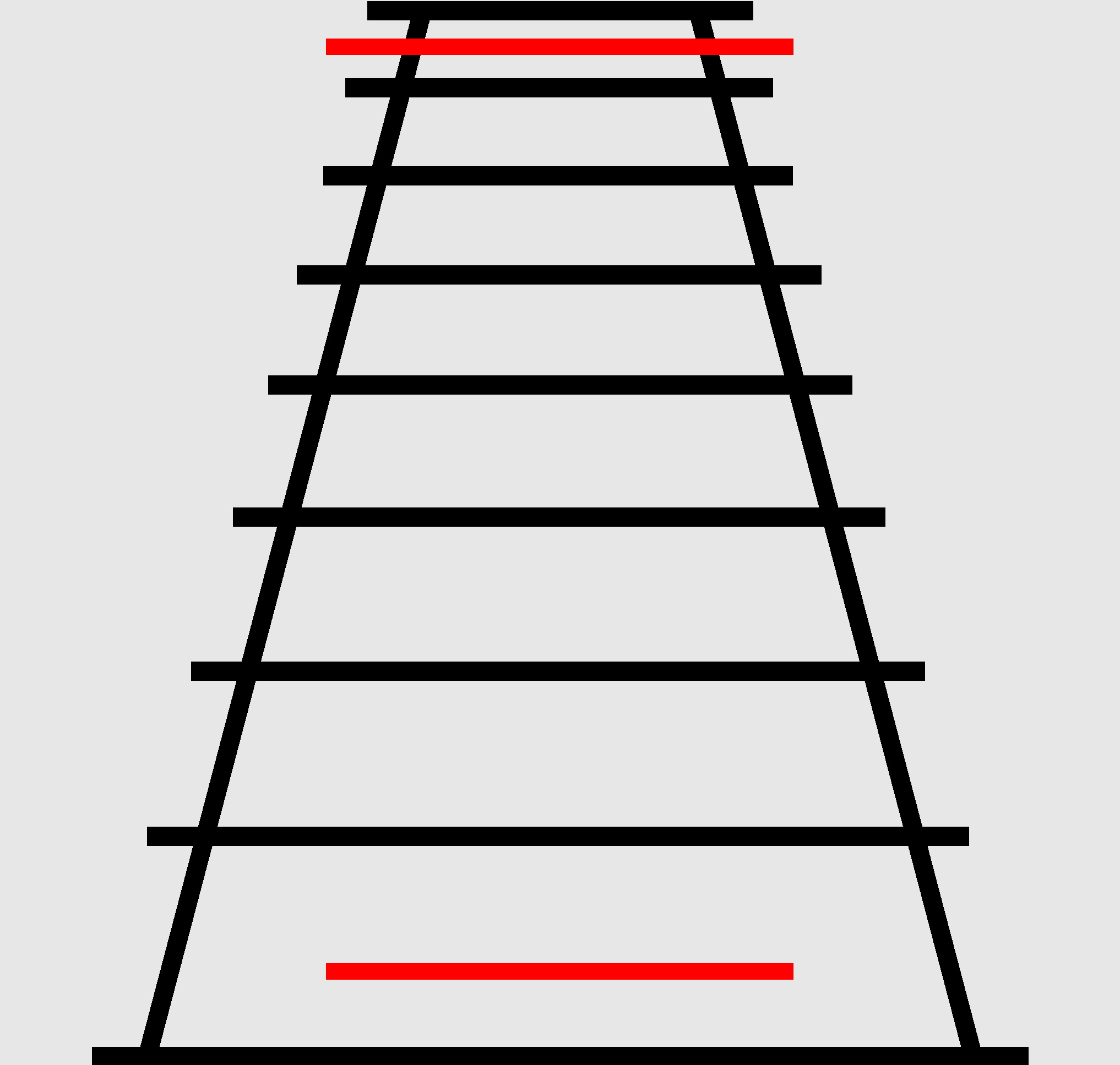
ponzo allusion
judges an object's size based on its background.
86
New cards
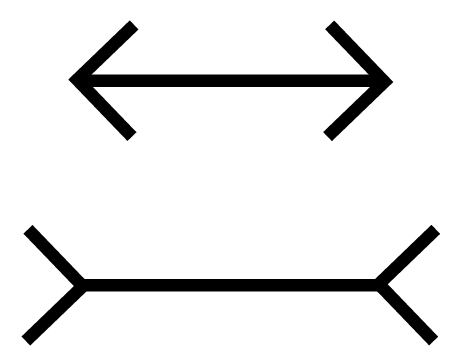
muller-lyer illusion
makes lines of the same length appear to be different.
87
New cards
shape constancy
the image is different but imagine it the same
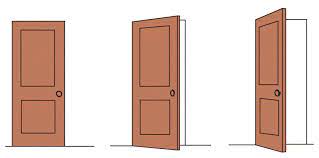
88
New cards
brightness and color constancy
if the color is under a shadow, we think of it still the same color
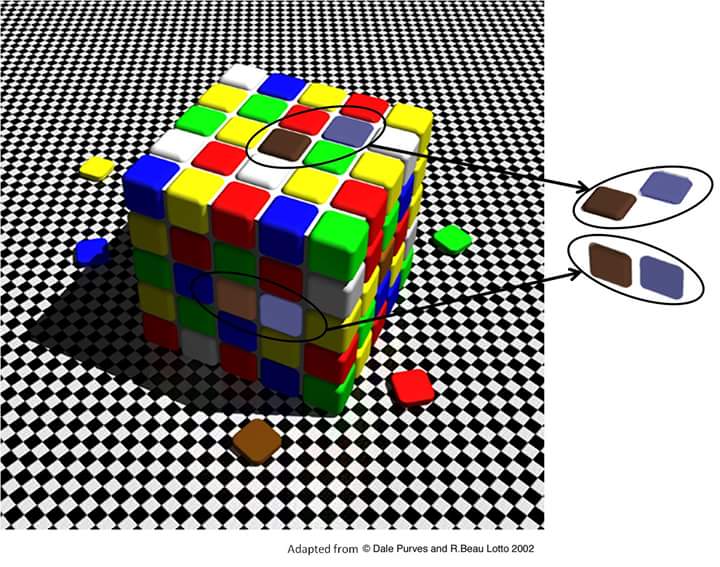
89
New cards
violethumans experience the shortest visible electromagnetic waves as what?
humans experience the shortest visible electromagnetic waves as what?
90
New cards
transduction
what is the conversion of stimulus energies into neural impulses called
91
New cards
subliminal
perceived by or affecting someone's mind without their being aware of it.
92
New cards
gate - control
pain signals can be sent up to the brain to be processed to accentuate the possible perceived pain, or attenuate it at the spinal cord itself.
93
New cards
signal detection
method of differentiating a person's ability to discriminate the presence and absence of a stimulus
94
New cards
feature detectors
individual neurons—or groups of neurons—in the brain which code for perceptually significant stimuli.
95
New cards
context effects
cognitive psychology that describes the influence of environmental factors on one's perception of a stimulus.
96
New cards
gestalt
"the whole exceeds the sum of it's parts"
97
New cards
color constancy
a red rose looks equally as red when wearing sunglasses vs when not, why is that?