A level Bio 1.6 ATP
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Describe the structure of ATP. Outline how named enzymes break down and resynthesise ATP. (4)
Ribose, Adenine and 3 phosphates (1)
ATP to ADP + Pi by ATP hydrolase in hydrolysis (reaction) (1)
ADP + Pi to ATP by ATP synthase (1)
(In) condensation (reaction) (1)
Hydrolysis of ATP is catalysed by the enzyme ATP hydrolase.
A student investigated the effect of ATP concentration on the activity of ATP hydrolase. She used shortening of strips of muscle tissue caused by contraction as evidence that ATP was being hydrolysed.
• She took four slides A, B, C and D, and added strips of muscle tissue of
the same length to each slide.
• She then added the same volume of ATP solutions of different
concentrations to the four slides and left each slide for five minutes.
• She then recorded the final length of each strip of muscle tissue.
Other than those given, name two variables the student should have controlled. (2)
pH of the ATP solution (1)
Temperature of the muscle tissue / ATP solution / slides (1)
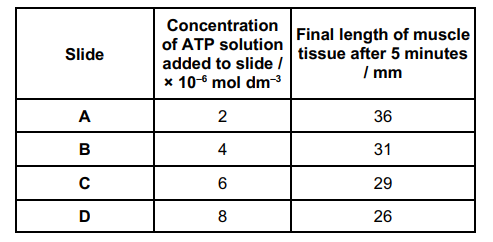
Hydrolysis of ATP is catalysed by the enzyme ATP hydrolase.
A student investigated the effect of ATP concentration on the activity of ATP hydrolase. She used shortening of strips of muscle tissue caused by contraction as evidence that ATP was being hydrolysed.
• She took four slides A, B, C and D, and added strips of muscle tissue of
the same length to each slide.
• She then added the same volume of ATP solutions of different concentrations to the four slides and left each slide for five minutes.
• She then recorded the final length of each strip of muscle tissue.
Describe and explain the pattern shown by the data in the table. (2)
As concentration of ATP increases, length of muscle decreases (1)
More ATP (hydrolysed by ATP hydrolase), so more energy released, so more muscle contraction / shortening of muscle (1)
The new antibiotic is safe to use in humans because it does not inhibit the ATP synthase found in human cells.
Suggest why human ATP synthase is not inhibited and bacterial synthase is inhibited (1)
Human ATP synthase has a different tertiary structure to bacterial ATP synthase (1)
ATP is an energy source used in many cell processes. Give four ways in
which ATP is a suitable energy source for cells to use. (4)
Releases relatively small amount of energy / little energy lost as heat (1)
Releases energy instantaneously (1)
Can be rapidly re-synthesised (1)
does not leave cells (1)
Give two ways in which the hydrolysis of ATP is used in cells (2)
To add phosphate to other substances and make them more reactive (1)
to provide energy for other reactions (1)