Psychology, Chapter 2 Biology and Behavior Vocabulary
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
1
New cards
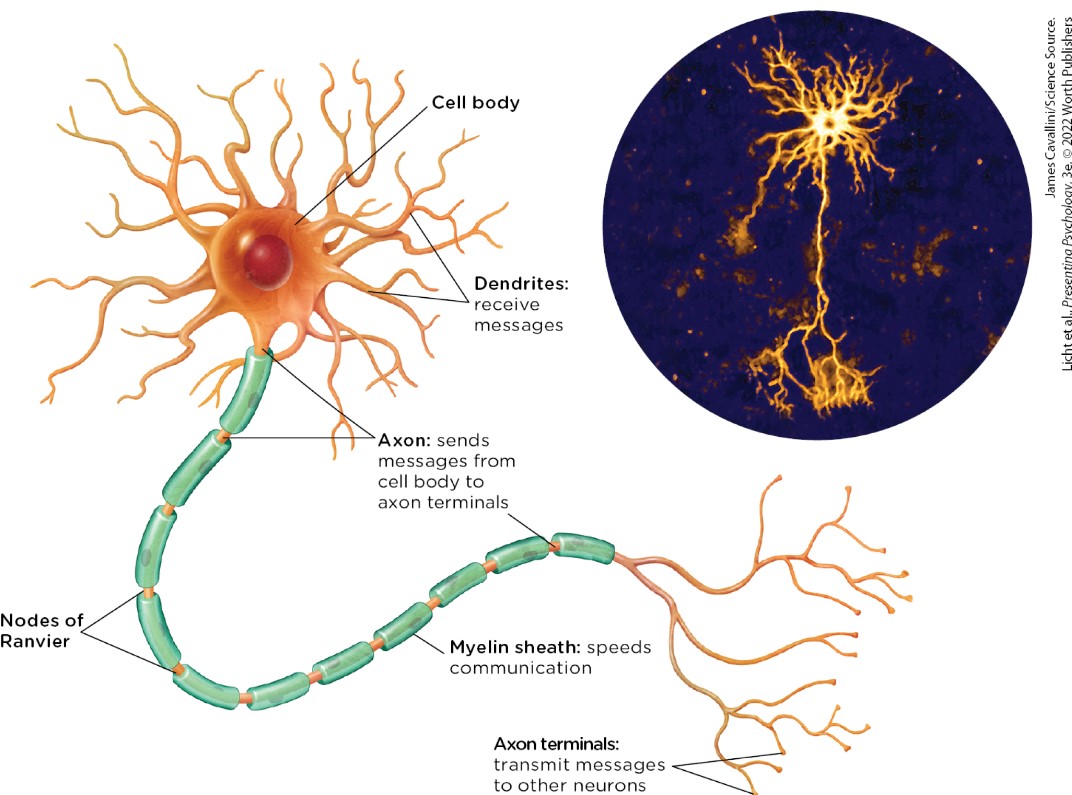
neurons
specialized cells of the nervous system that transmit electrical and chemical signals in the body
2
New cards
neuroscience
the study of the brain and other parts of the nervous system
3
New cards
biological psychology
the branch of psychology that focuses on how the brain and other biological systems influence human behavior
4
New cards
phrenology
an early approach to explaining the functions of the brain by trying to link the physical structure of the skull with a variety of characteristics
5
New cards
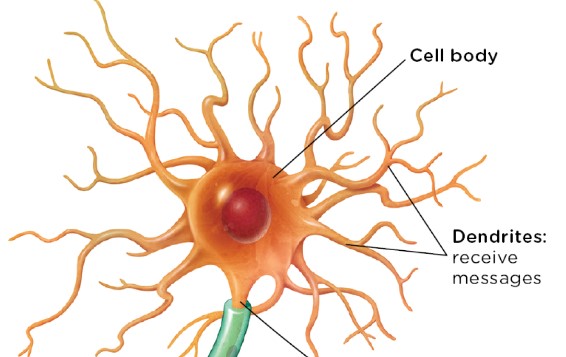
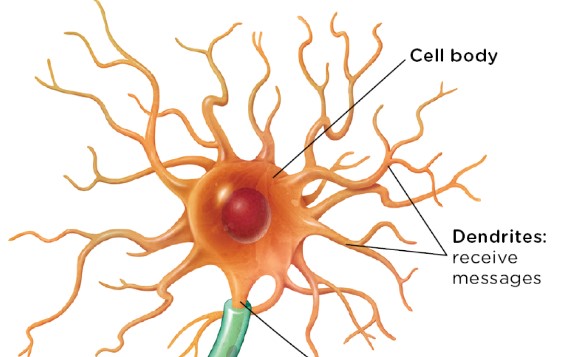
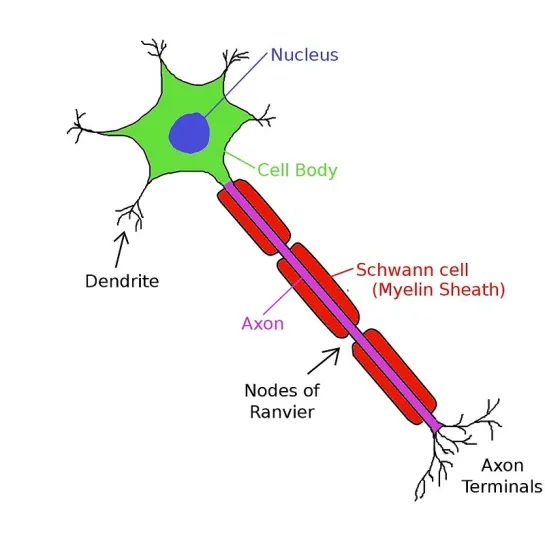
cell body
the region of the neuron that includes structures that nourish the cell, and a nucleus containing DNA
6
New cards
dendrites
tiny, branchlike fibers extending from the cell body that receive messages from other neurons and send information in the direction of the cell body
7
New cards
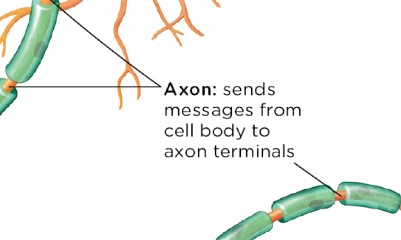
axon
skinny tube like structure of a neuron that extends from the cell body and sends messages to other neurons and sends information in the direction of the cell body. (not all axons are myelinated)
8
New cards
myelin sheath
a fatty substance that insulates the axon and speeds the transmission of neural messages.

9
New cards
synapse
the place where the axon terminal of a sending neuron meets the dendrite of a neighboring neuron or other type of cell receiving its signal; junction between neurons where communication occurs
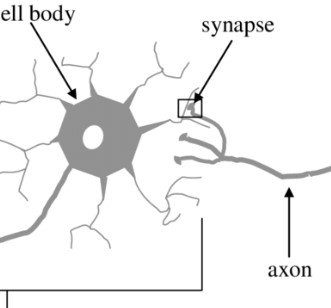
10
New cards
glial cells
cells of the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
11
New cards
resting potential
the electrical potential of a cell "at rest"; the state of a cell when it is not activated
12
New cards
action potential
the spike in voltage that passes through the axon of a neuron, the result of which is to convey information
13
New cards
all-or-none
a neuron either fires or does not fire; action potentials are always the same strength
14
New cards
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that neurons use to communicate at the synapse
15
New cards
receptor sites
locations on the receiving neuron's dendrites where neurotransmitters attach.
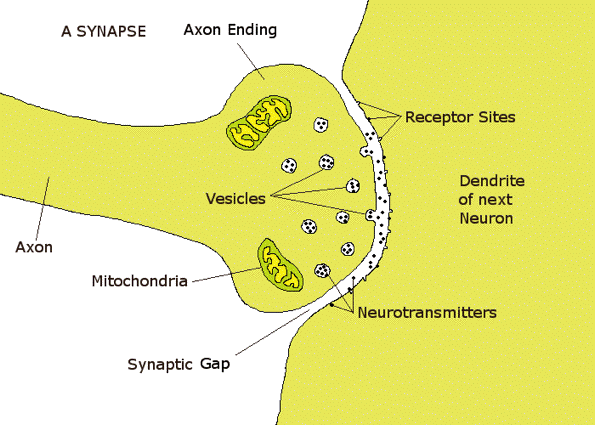
16
New cards
reuptake
a process by which neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the sending axon terminal
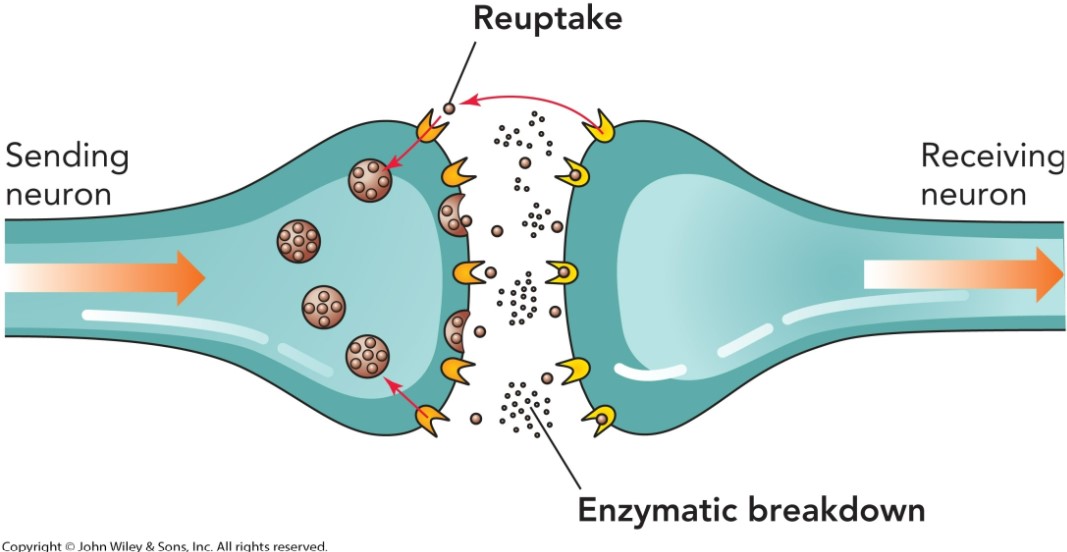
17
New cards
sensory neurons
neurons that receive information from the sensory systems and convey it to the brain for further processing
18
New cards
motor neurons
neurons that transmit information from the central nervous system to the muscles and glands
19
New cards
interneurons
neurons that reside exclusively in the brain and spinal cord; act as a bridge connecting sensory and motor neurons
20
New cards
reflex arc
an automatic response to a sensory stimulus, using a simple pathway of communication from sensory neurons through interneurons in the spinal cord and back out through motor neurons
21
New cards
nerves
bundles of neurons that carry information to and from the central nervous system; enable communication between the central nervous system and the muscles, glands, and sensory receptors.
22
New cards
somatic nervous system
the branch of the peripheral nervous system that includes sensory nerves and motor nerves; gathers information from sensory receptors and controls the skeletal muscles responsible for voluntary movement.
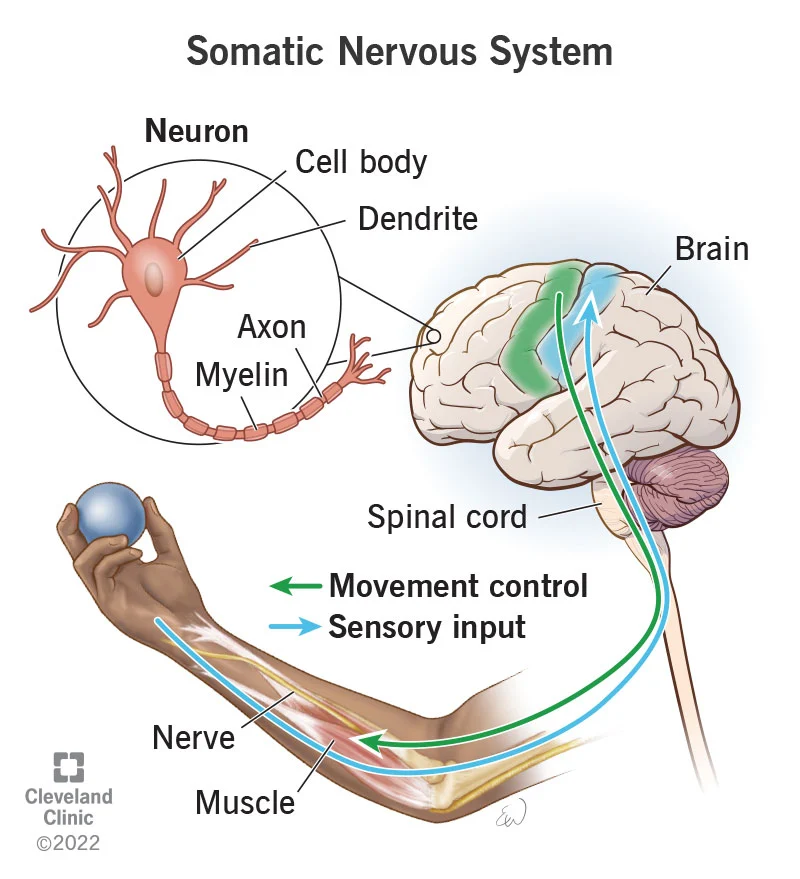
23
New cards
autonomic nervous system
the brance of the peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary processes within the body, such as contractions in the digestive tract and activity of glands.
24
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that mobilizes the "fight-or-flight" response to stressful or crisis situations.
25
New cards
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that orchestrates the "rest-and-digest" response to bring the body back to a noncrisis mode.
26
New cards
endocrine system
the communication system that uses glands to convey messages by releasing horomones into the bloodstream.
27
New cards
horomones
chemical messengers released into the bloodstream that influence mood, cognition, appetite, and many other processes and behaviors.
28
New cards
pituitary gland
the small endocrine gland located in the center of the brain just under the hypothalamus; known as the master gland.
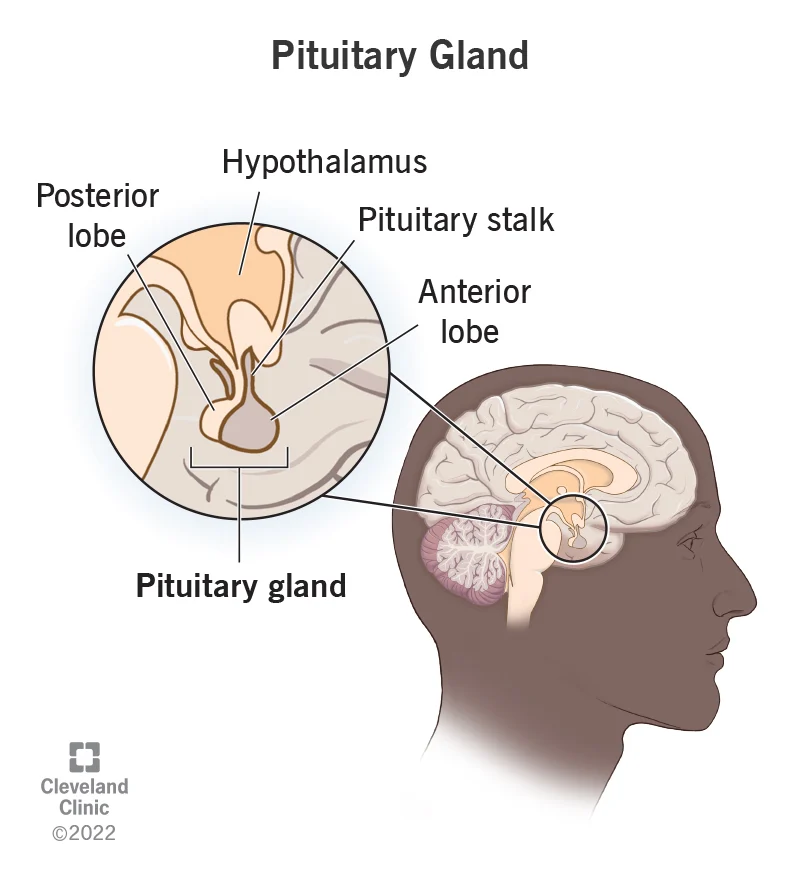
29
New cards
thyroid gland
the endocrine gland that regulates the rate of metabolism by secreting thyroxin
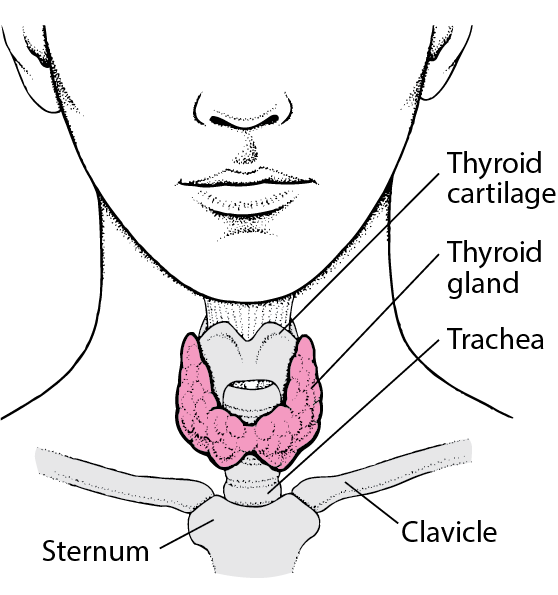
30
New cards
adrenal glands
endocrine glands involved in response to stress and the regulation of salt balance.
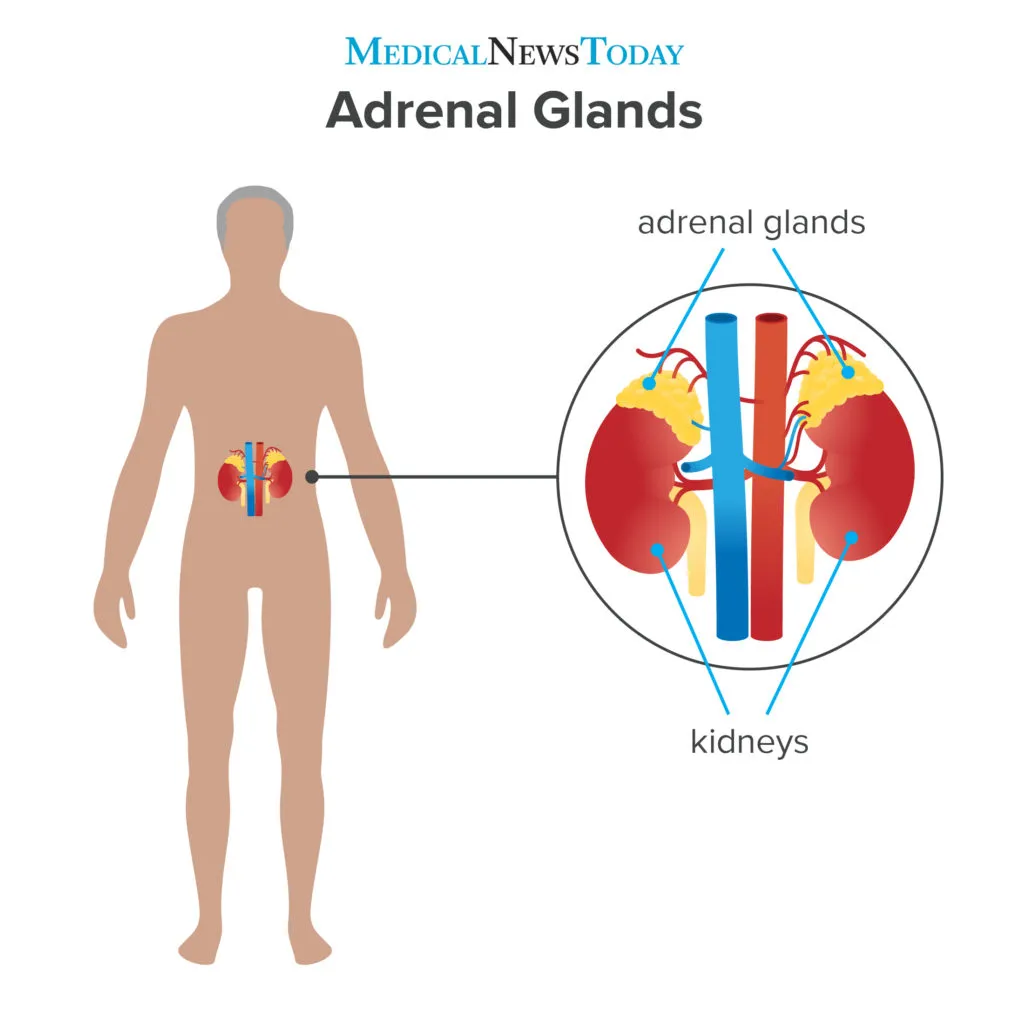
31
New cards
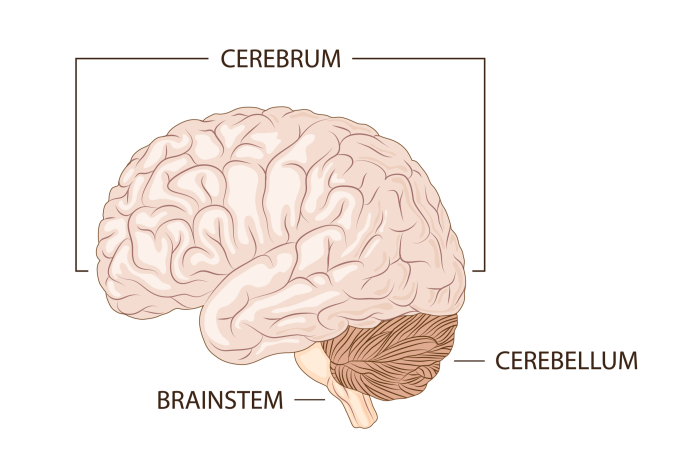
cerebrum
the largest area of the brain, includes virtually all parts of the brain except the brain stem structures; has two distinct hemispheres
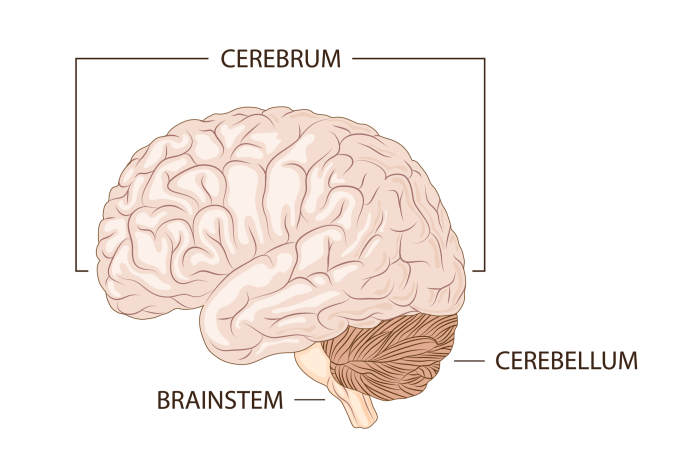
32
New cards
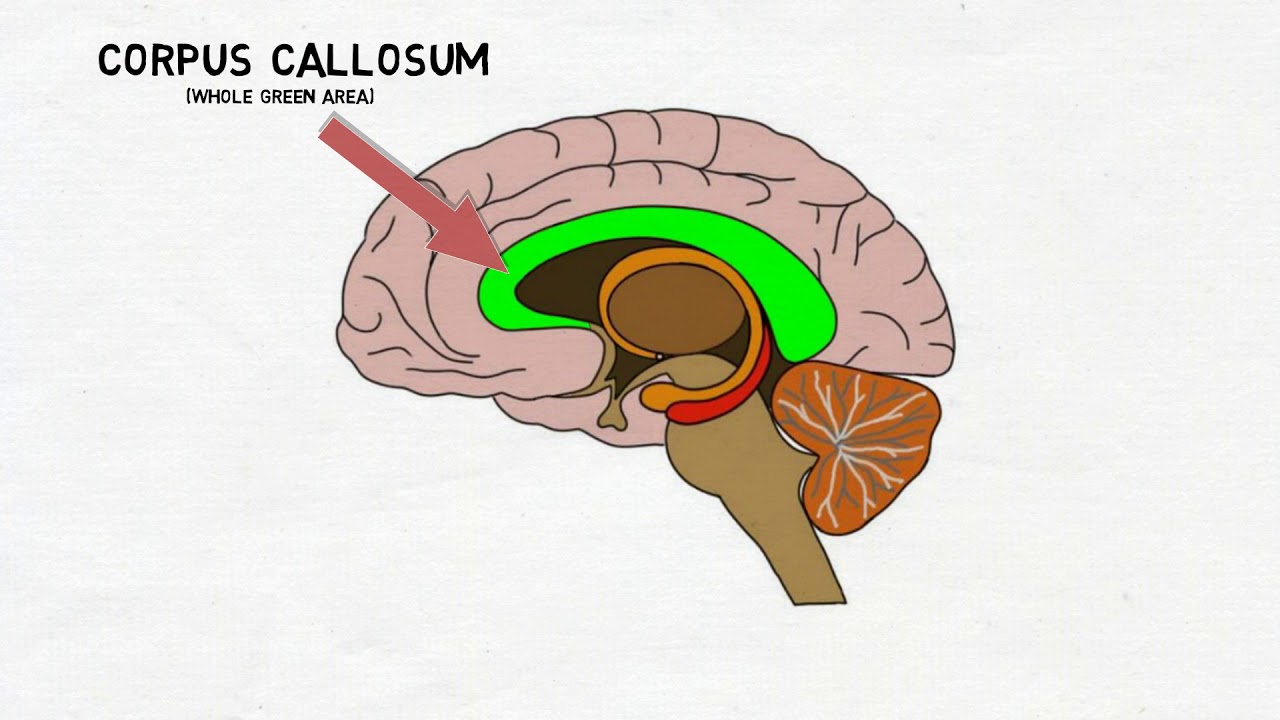
corpus callosum
the thick band of nerve fibers connecting to the right and left cerebral hemispheres; principal structure for information sharing between the two hemispheres
33
New cards
split brain operation
a rare procedure used to disconnect the right and left hemispheres; involves cutting the corpus callosum
34
New cards
lateralization
the idea that each cerebral hemisphere processes certain types of information and excels in certain activities
35
New cards
broca's area
a region of the cortex that is critical for speech production

36
New cards
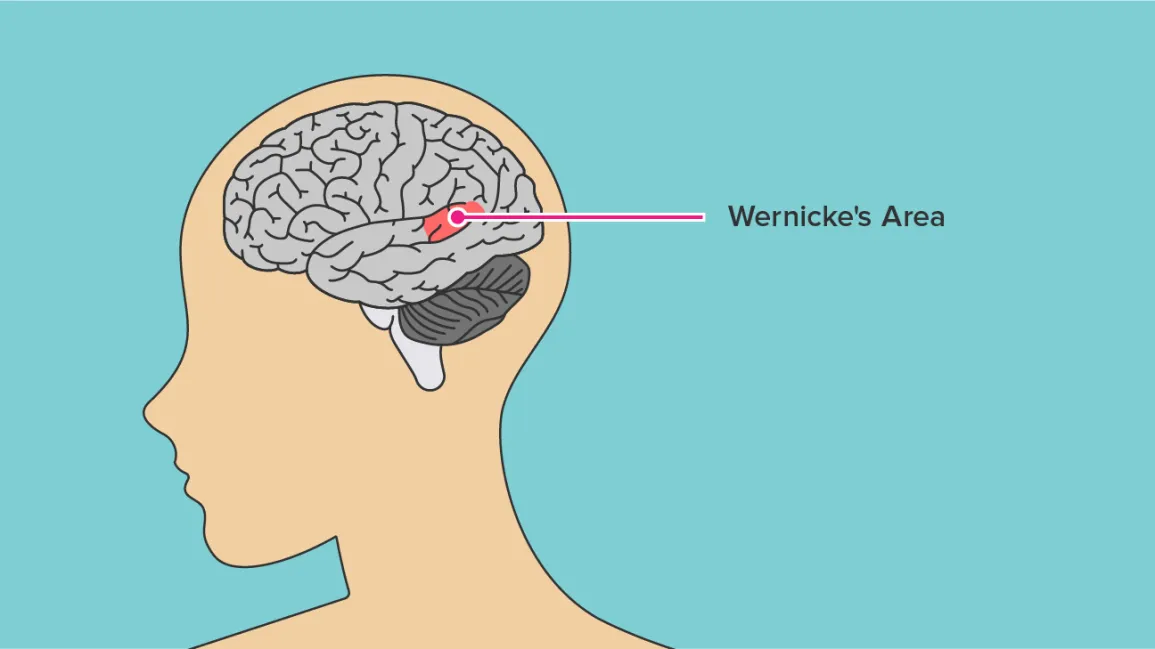
wernicke's area
a region of the cortex that plays a pivotal role in language comprehension.
37
New cards
neurogenesis
the generation of new neurons in the brain
38
New cards
stem cells
cells responsible for producing new neurons
39
New cards
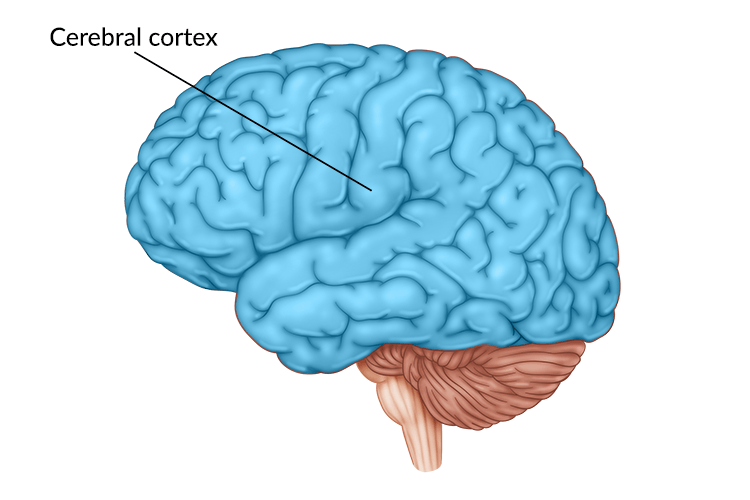
cerebral cortex
the wrinkled outermost layer of the cerebrum, responsible for higher mental functions, such as decision making, language, and processing visual information.
40
New cards
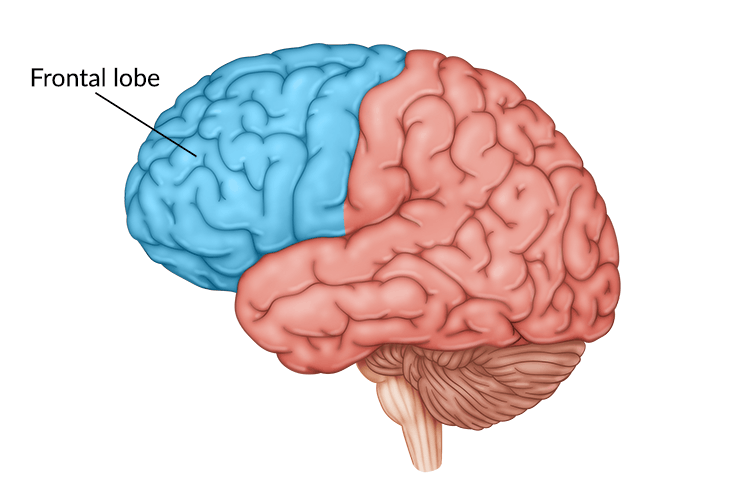
frontal lobes
the area of the cortex that directs higher-level cognitive activities, such as language, emotions, control of social behavior, and decision making.
41
New cards
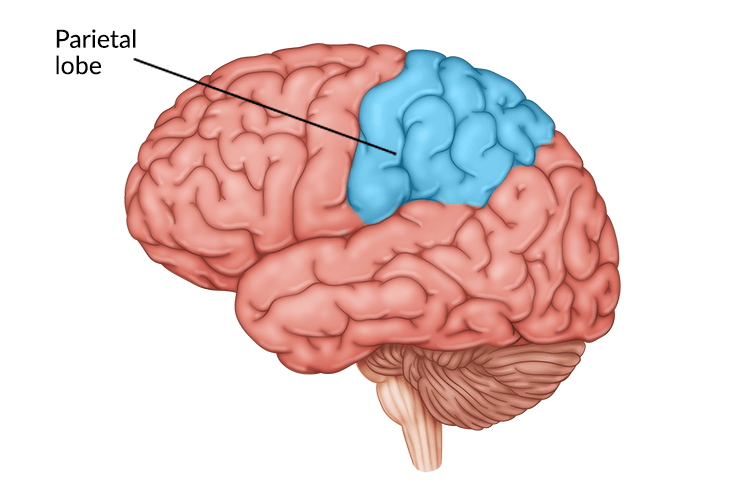
parietal lobes
the area of the cortex that receives and processes sensory information such as touch, pressure, temperature, and spatial orientation.
42
New cards
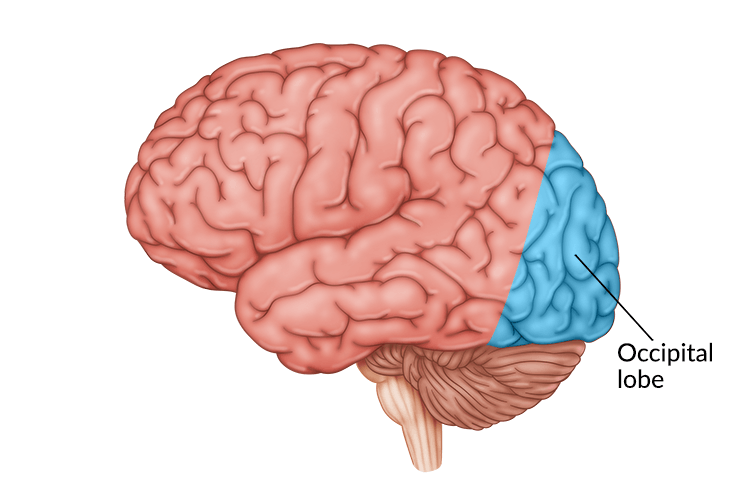
occipital lobes
the area of the cortex in the back of the head that processes visual information
43
New cards
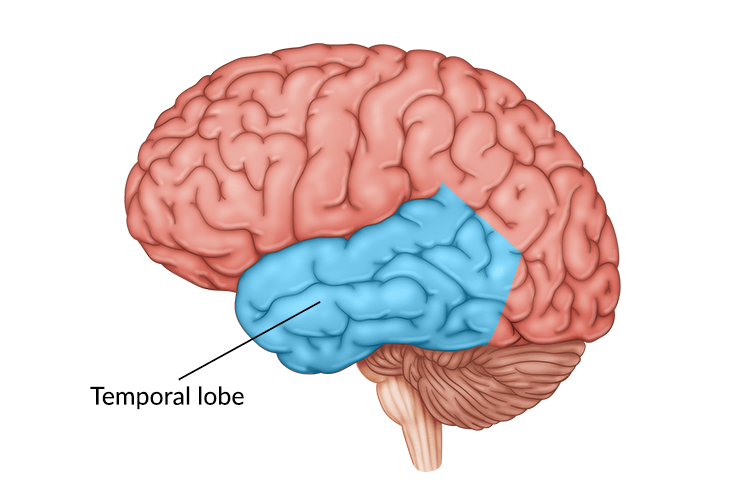
temporal lobes
the area of the cortex that processed auditory stimuli and language
44
New cards
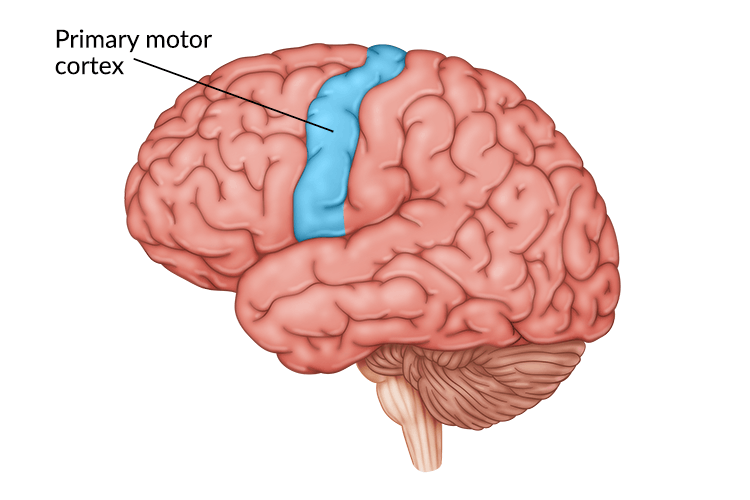
motor cortex
a strip of brain tissue toward the rear of the frontal lobes that works with other brain regions to plan an execute voluntary movements
45
New cards
association areas
regions of the cortex that integrate information from all over the brain, allowing us to learn, think in abstract terms, and carry out complex behaviors.
46
New cards
limbic system
a collection of structures that regulates emotions and basic drives such as hunger, and aids in the creation of memories
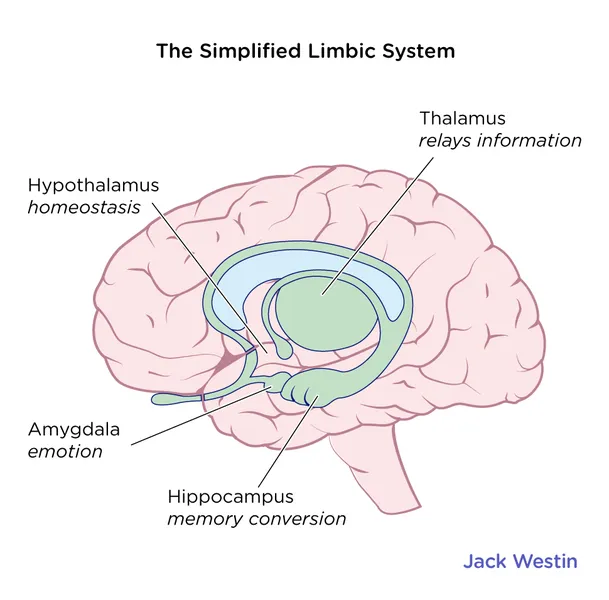
47
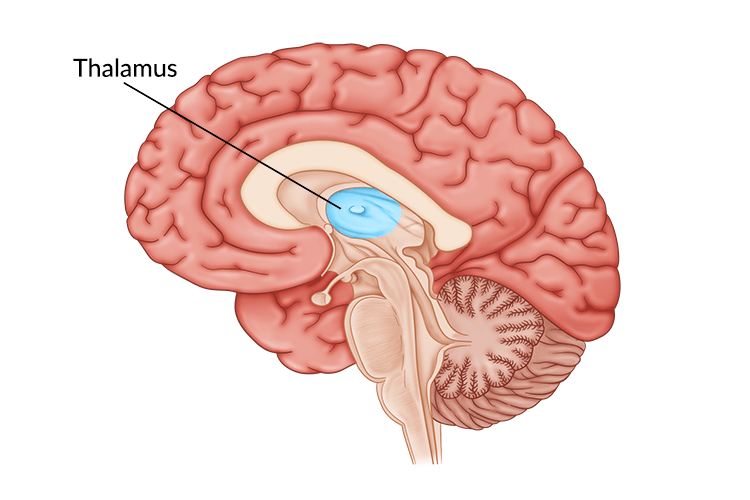
New cards
thalamus
a structure in the limbic system that processes and relays sensory information to the appropriate areas of the cortex
48
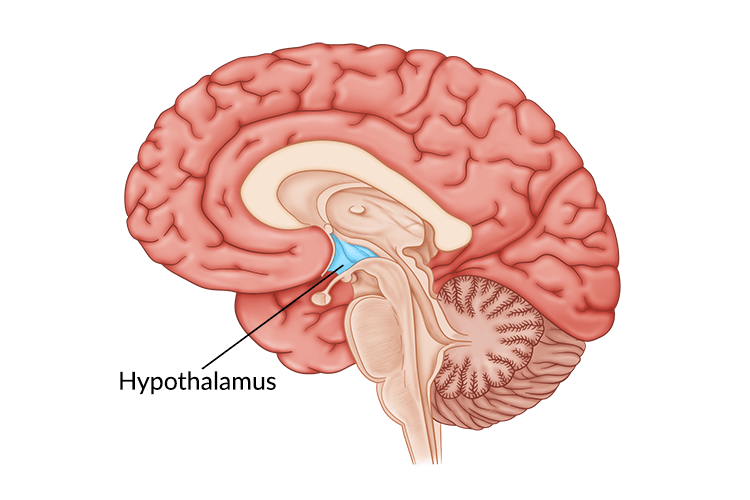
New cards
hypothalamus
a small structure located below the thalamus that maintains the internal environment within a healthy range; helps regulate sleep-wake cycles, sexual behavior, and appetite
49
New cards
amygdala
a pair of almond-shaped structures in the limbic system that processes aggression and basic emotion such as fear, as well as associated memories.

50
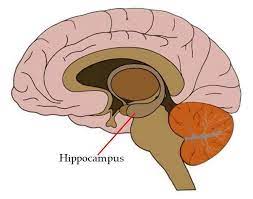
New cards
hippocampus
a pair of sea-horse shaped structures located in the limbic system; primarily responsible for creating new memories.
51
New cards
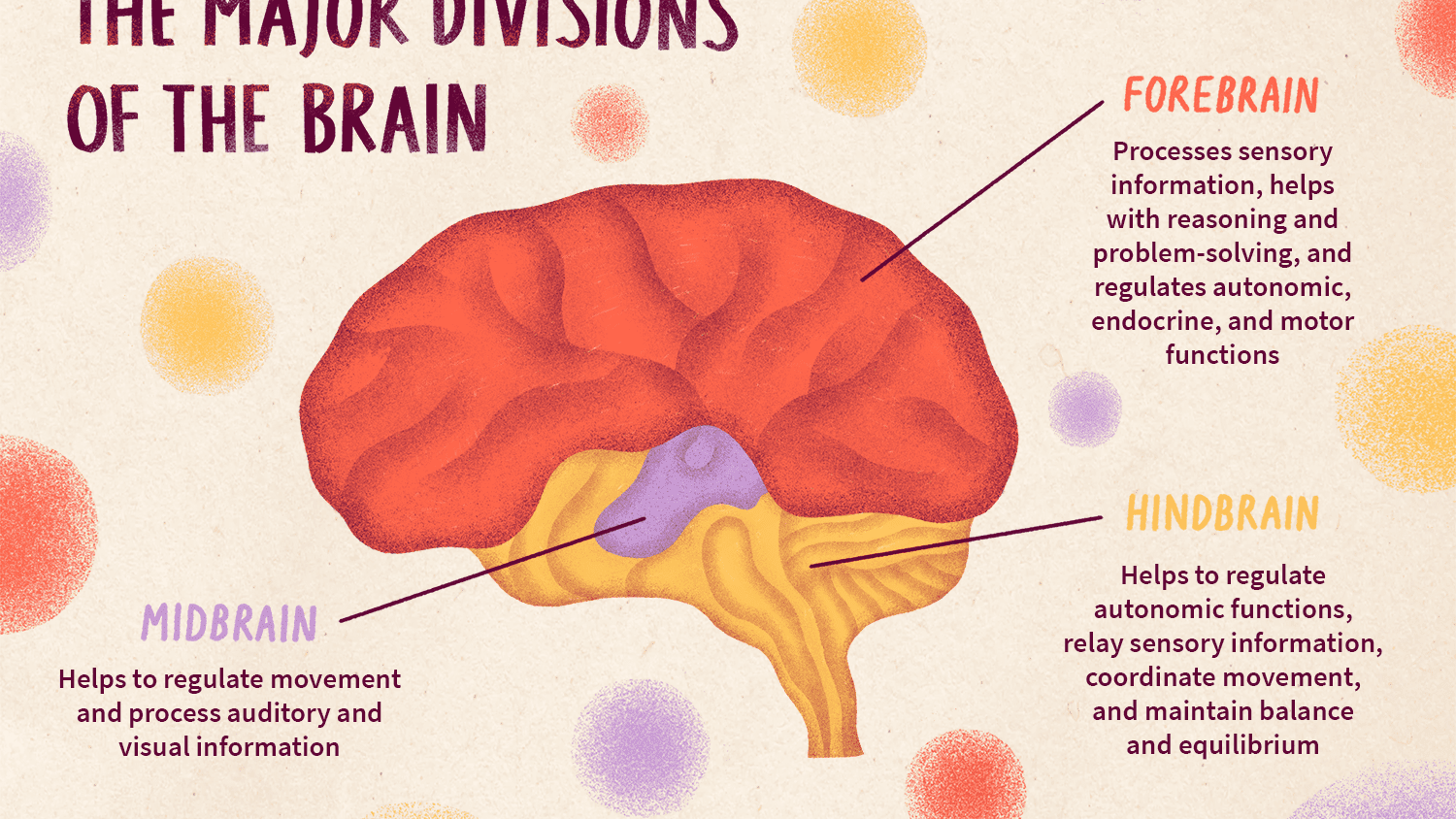
forebrain
the largest part of the brain; includes the cerebrum and the limbic system.
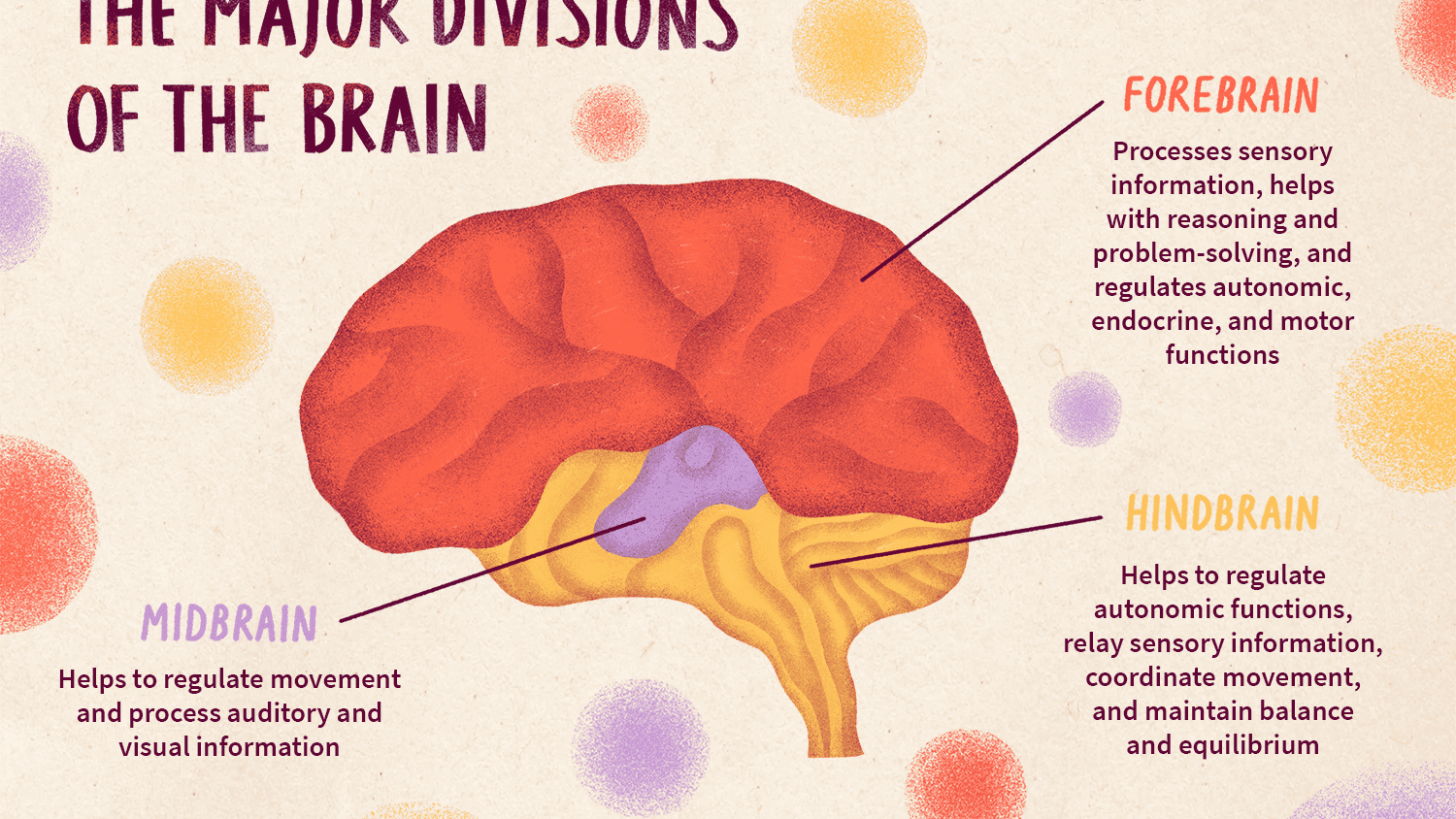
52
New cards
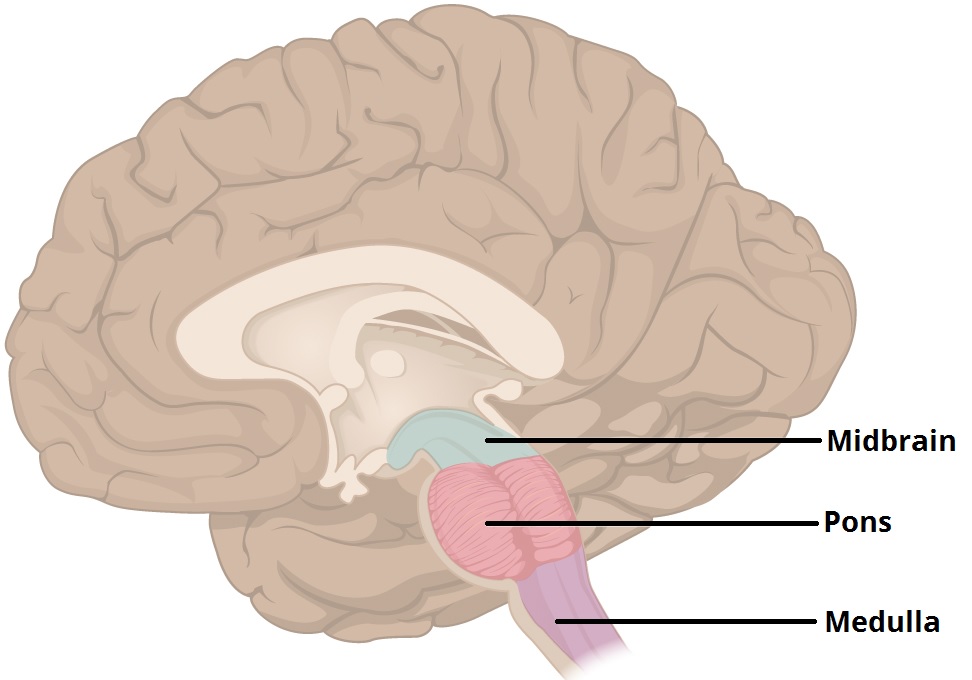
midbrain
the part of the brainstem involved in levels of arousal; responsible for generating movement patterns in response to sensory input.
53
New cards
reticular formation
a network of neurons running through the midbrain that controls levels of arousal and quickly analyzes sensory information on its way to the cortex.
54
New cards
hindbrain
includes areas of the brain responsible for fundamental life-sustaining processes
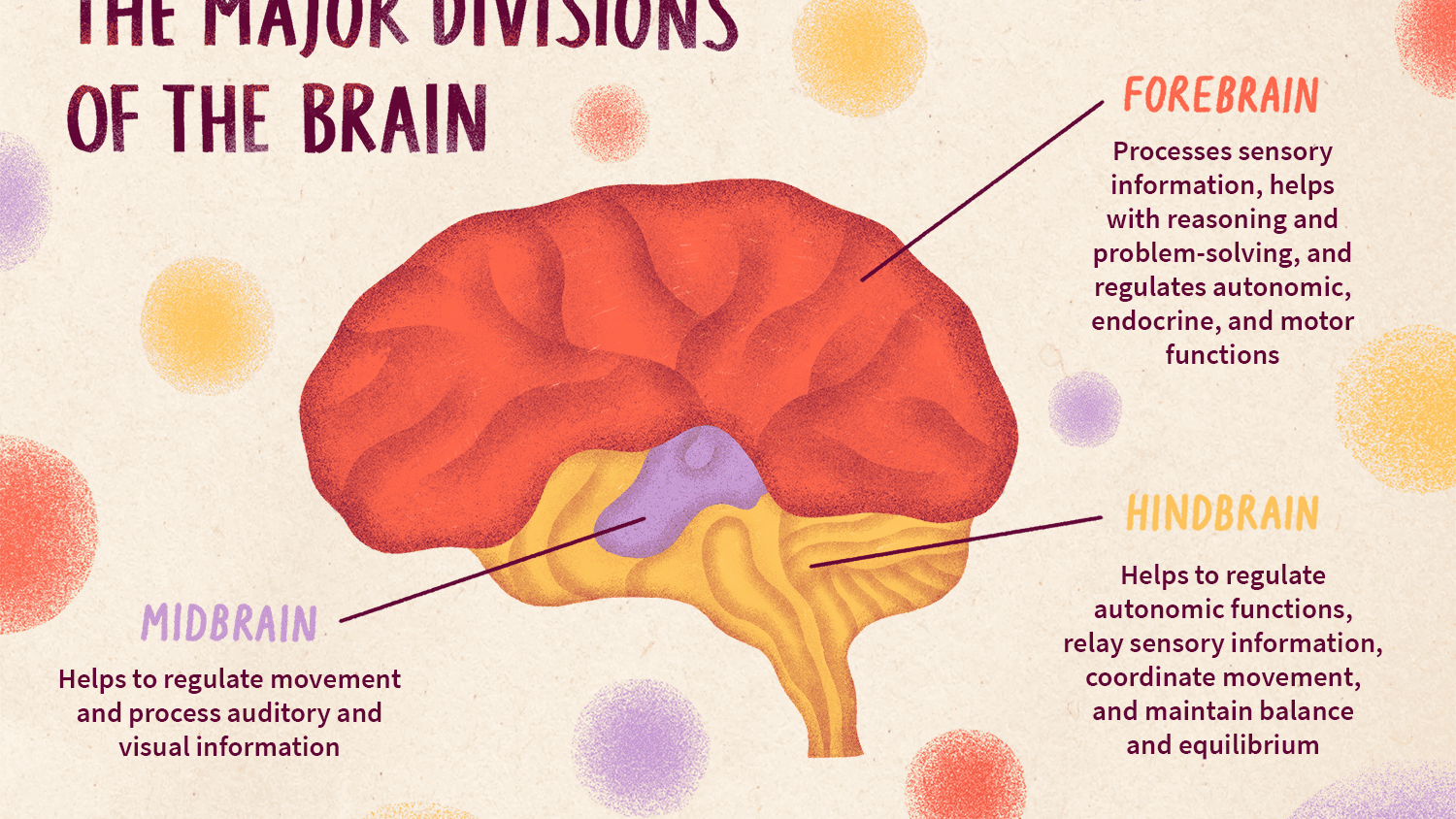
55
New cards
pons
a hindbrain structure that helps regulate sleep-wake cycles and coordinate movement between the right and left sides of the body
56
New cards
medulla
a hindbrain structure that oversees vital functions, including breathing, digestion, and heart rate.
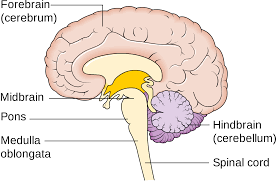
57
New cards
cerebellum
a hindbrain structure located behind the brainstem that is responsible for muscle coordination and balance; Latin for "little brain"
58
New cards
Terminal buttons (axon terminals)
Transmit signal to the next neuron
59
New cards
Node of Ranvier
A gap in the myelin sheath
60
New cards
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Relays messages from neurons to muscles, enabling
movement (botulism [e.g., Botox] inhibits release of ACh)
Too much = spasms; too little = paralysis
Low levels in the brain linked to Alzheimer’s disease
movement (botulism [e.g., Botox] inhibits release of ACh)
Too much = spasms; too little = paralysis
Low levels in the brain linked to Alzheimer’s disease
61
New cards
Glutamate
Excitatory neurotransmitter (e.g., MSG)
Plays a central role in learning and memory
Too much = strokes; too little = symptoms of
schizophrenia
Plays a central role in learning and memory
Too much = strokes; too little = symptoms of
schizophrenia
62
New cards
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Inhibitory neurotransmitter
Plays role in controlling sleep, wakefulness, and
intoxication
Plays role in controlling sleep, wakefulness, and
intoxication
63
New cards
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
energy
64
New cards
Norepinephrine
Prepares the body for stress.
In the brain, norepinephrine is involved in regulating
arousal and sleep.
High levels could lead to overarousal and hypervigilance.
In the brain, norepinephrine is involved in regulating
arousal and sleep.
High levels could lead to overarousal and hypervigilance.
65
New cards
Endorphins
A group of naturally produced opioids
Released in response to pain and block pain receptor
sites
Also released with brisk exercise (e.g., “runner’s high”)
Released in response to pain and block pain receptor
sites
Also released with brisk exercise (e.g., “runner’s high”)
66
New cards
Serotonin
Helps control appetite, aggression, and mood, and
regulates sleep and breathing.
Abnormally low activity is thought to drive depression.
SSRIs help boost the effects of serotonin.
regulates sleep and breathing.
Abnormally low activity is thought to drive depression.
SSRIs help boost the effects of serotonin.
67
New cards
Dopamine
Emotional arousal (fear, anxiety), motivation/reward
(hunger, thirst, sex), pleasure, drug abuse (e.g., cocaine
and amphetamines)
Plays a key role in attention, learning through
reinforcement, and regulating body movements
Parkinson’s disease is linked to a deterioration of
neurons that produce dopamine.
(hunger, thirst, sex), pleasure, drug abuse (e.g., cocaine
and amphetamines)
Plays a key role in attention, learning through
reinforcement, and regulating body movements
Parkinson’s disease is linked to a deterioration of
neurons that produce dopamine.