Chapter 6 and Lecture 5: From Habits to Health: Factors in Behaviour
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
The Role of Behaviour in Health
People’s health-related behaviours (“health habits”) influence their likelihood of developing chronic and fatal diseases, such as heart disease, cancer, and HIV/AIDS
Illness and early death could be substantially reduced if people would adopt lifestyles that promote wellness, such as eating healthy diets, exercising, not smoking, and being safe (whether in the sun or in sex).
But the typical person’s lifestyle includes many behaviours that are risk factors for illness and injury
Leading killers in developed nations: Cancer and cardiovascular disease
Adults who have a healthy lifestyle (exercising, healthy diet, not smoking, not excessive drinking) can expect to live up to 12 years longer
Health behaviors
Activities that ppl perform to maintain or improve health, or prevent illness, regardless of health status or whether the activity actually improves health
People’s health status can affect the type of health behaviour they perform and their motivation to do it...
Well Behaviour
any activity people undertake to maintain or improve current good health and avoid illness.
E.g., eating a healthy diet, exercising, getting vaccinated
Symptom-Based Behaviour
Any activity ill people do to determine the problem and find a remedy.
E.g., complaining about symptoms, seeking advice.
Fear and lack of money can prevent this behavior
Sick-Role Behaviour
any activity people undertake to treat or adjust to a health problem.
E.g., adhering to medical advice, staying home from school/work.
This special “role” let them take a break from normal responsibilities like going to school or work
Breast cancer screening
Only mammograms are proven effective in detecting early breast cancer and reducing mortality
Manual examinations are no longer widely recommended
Identified 7 risk factors (health habits) associated w poor physical health and increased mortality
Smoking cigs (cigs also enhance the effects of other substances like alcohol)
Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol
Being obese
Being physically inactive
Eating between meals (snacking)
Not eating breakfast
Sleeping fewer/more than standard hours (7-8)
10 predisposition factors that increase mortality (in order of significance)
1. current smoker
2. history of divorce
3. history of alcohol abuse
4. recent financial difficulties
5. history of unemployment
6. previous history as a smoker
7. lower life satisfaction
8. never married
9. history of food stamps
10. negative affectivity
Correlation between health habits
Not strongly tied to each other; knowing someone practices one healthy habit does not accurately predict they will practice another.
Attitude and health habits
Not governed by a single set of attitudes (Someone may use seal bests for safety but diet for attractiveness)
Factors for change of health habits
Differential Effects: Different factors in a person's life may affect different behaviours (e.g., social encouragement to overeat while also being encouraged to limit smoking).
Learned from experience (เข็ด)
Changing life circumstances (Ex. The absence of peer pressure)
The Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) Study
A study of the relationship between health outcomes and health habits/behaviours.
Higher carbohydrate and lower total fat intake each associated with higher mortality
Fruit, vegetables, & legumes associated with lower mortality
Ultra-processed foods associated with inflammatory bowel disease
But high healthy fat does not correlate w mortality
Ultra-processed foods are those that are not recognizable in the natural form
3 types of prevention efforts
Behavioural Influence: Promoting health actions (e.g., demonstrating proper brushing/flossing techniques).
Environmental Measures: Public health actions (e.g., adding fluoride to water supplies).
Preventive Medical Efforts: Clinical actions (e.g., dental professional removing tartar).
Primary Prevention
Actions taken to avoid disease or injury (or prevent onset of illness).
E.g., exercise, wearing seatbelt, flossing, immunization/vaccination, handwashing, physical distancing, wearing mask (as in pandemic)
Can technically be undertaken by either the individual or society.
Health promotion initiatives (e.g., providing information about how to stay healthy) are often aimed at primary prevention.
Well behavior
Secondary prevention
Early detection and prompt intervention to halt or reverse a health problem's progression, like cancer screenings or blood pressure checks.
Overlap w symptom-based and sick role
Tertiary prevention
Managing an existing illness to slow its progression, prevent complications, and improve the patient's QoL and function
Ex. Rehab, medication management, support group
Also sick role
Problems in Promoting Wellness: Factors within the Individual
Motivation: Healthy behaviours can be perceived as less convenient or appealing than unhealthy ones, leading to procrastination or a desire to maintain a balance.
Self-Efficacy: Lack of belief in one's ability to successfully carry out a new behaviour.
Habitual/Addictive Behaviours: Long-standing behaviours like smoking are very difficult to modify
Problems in Promoting Wellness: Interpersonal Factors
Social Influence: One partner's unhealthy behaviour (e.g., eating unhealthfully) before marriage can be adopted by the other partner over time.
Interpersonal Conflicts: A family member's healthy behaviour (e.g., exercising) may disrupt the daily routine of another, creating conflict that undermines the change effort.
Problems in Promoting Wellness: Factors in the Community
Lack of Focus on Prevention: Health professionals have traditionally focused on treatment rather than prevention.
Resource and Infrastructure Issues: Public health systems suffer from insufficient funds, and some communities lack safe/convenient places to exercise.
Ethical Dilemmas: Communities face the challenge of balancing public health (e.g., reducing pollution) with economic priorities (e.g., not forcing a job-creating industry out of business)
Health-related behavior determinants: General Factors
Heredity: Genetic factors, such as in the development of alcoholism, can influence health-related behaviours.
Learning: Behaviours are learned through consequences, following the principles of: Reinforcement (consequences that increase a behaviour), Extinction (eliminating the reinforcer weakens the behaviour), and Punishment
Modelling: Learning occurs by observing the behaviour of others and the consequences they receive
Health-related behavior determinants: Social, Personality, and Emotional Factors
Conscientiousness: This personality trait (dutiful, organized) is strongly linked to practicing many healthy behaviours (e.g., high fitness, low tobacco use, following medical instructions).
Stress: High stress is linked to less exercise, poorer diets, and more use of alcohol and cigarettes, as people often cope with stress by using these substances.
Health-related behavior determinants: Perception and Cognition
Misconceptions: People's judgments about their health can be based on misconceptions, such as hypertensive patients incorrectly believing they can sense their high blood pressure.
Unrealistic Optimism: People commonly believe they are less likely than others to develop a health problem. This belief can impair preventive action, but it often gives way to "unrealistic pessimism" when a clear threat of illness is present.
Health Belief Model
The likelihood that a person will perform some health behaviour depends on the outcome of two assessments the person makes:
Perceived threat associated with a health problem: a) perceived vulnerability, b) perceived seriousness, c) cues actions — ex. if alcoholics, then bar close to home
Perceived benefits and barriers of taking action
Widely supported across various health behaviors (e.g., dental visits, vaccinations, exercise programs).
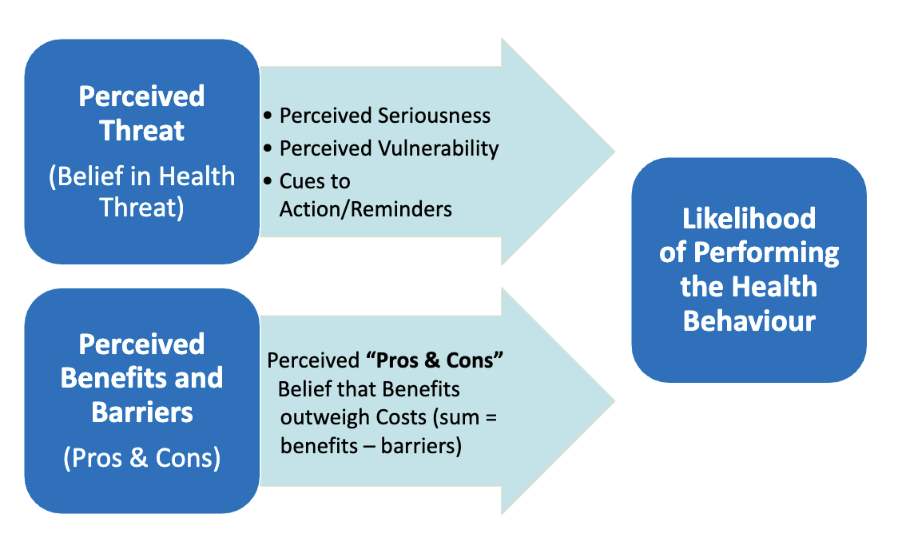
Perceived threat (belief) (Health belief)
Perceived seriousness
Perceived vulnerability
Cues to action/reminders
Ex. feel out of breath again → train endurance, seek help, commit to a sport
Haven’t had a flu shot, I’m at higher risk of getting sick from the flu → get a shot
Perceived benefits and barriers (pros and cons) (health belief)
Belief that benefits outweigh costs (sum = benefits - barriers)
Ex. → Going to gym when you have time/motivated instead of staying in. benefits (healthy, fit) > costs (gym membership, less chill time)
Criticism of health belief model:
Left out self-efficacy
No standard way of measuring components (perceived threat?)
Ppl don’t usually assess like this
Cognitive Adaptation Theory
A little denial of physiological risk may have better mental health and cope w risk better.
E.g. HIV positive men who inaccurately, but optimistically, believed that they could halt the progression of AIDS → better health habits than those who were pessimistic.
Only moderate degree of optimism is beneficial (too high or too low is harmful)
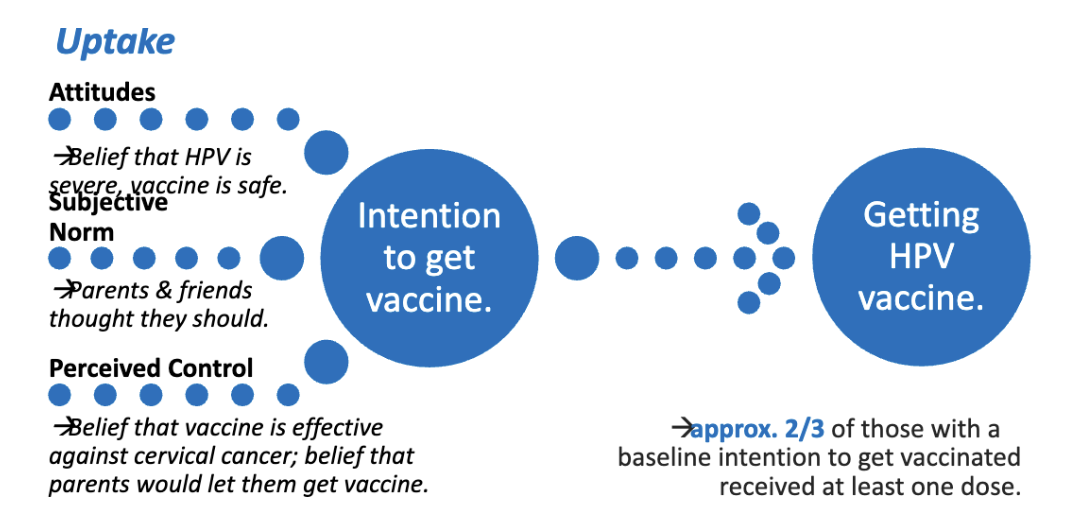
Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB)
Behavior result from intentions. There are 3 factors determine one’s intention to perform a behavior:
Attitude to Behaviour: Judge if the behavior is good or bad.
Subjective Norm: Appropriateness or acceptability of behavior (based on beliefs about others’ opinions, social norms).
Perceived Control: Expectation of success.
Similar to self-efficacy – belief that one can execute a course of action, achieve a goal; correlated with performance/success
Criticism of TPB
Doesn’t account for gap between intention and behavior (ppl don’t always do what they intend)
Leave out other factors
Doesn’t account for the role of past habitual behavior
Theory of Planned Behaviour Applied to HPV Vaccine
Attitude: Believe that HPV is severe and vaccine is safe
Norm: Getting vaccine is common and normalized
Perceived control: Believe that vaccine is effective against cervical cancer
There’s notable increases in online searches abt STD/HIV testing and at-home HIV tests
Celebrity Influence on subjective norms
New York City poison control center received a higher-than-normal number of calls the day after Trump speculated that injecting household disinfectants could be a COVID treatment
The Transtheoretical Model
(Stages of Change Model) recognizes that it may not be possible to change all at once. Recognizes the steps ppl take to change behaviors
Validated across various health behaviours (e.g., quitting smoking, cancer screening, vegetable consumption, safe sex practices).
(Contrast to Health belied model and theory of behavior) Especially useful in clinical settings (therapist assess readiness and guide)
Stages of change in the Transtheoretical model
Precontemplation: Not considering changing, no intention (No plan to get vaccinated in next 3 months)
Contemplation: Aware of need to change, contemplating change (Considering getting vaccinated)
Preparation: Ready to change (ex., Planning to change diet tmr)(Try to schedule to get vaccinated)
Action: Start successfully making changes to behav
Get 1 dose of vaccine and schedule for 2nd
Maintenance: (should be maintained >6) Work to maintain new behav, avoid relapse (esp imp for therapists so they can support ppl in avoiding relapses) (lapse is one time, normal, the imp thing is to avoid multiple relapses)
To help ppl change, it depends on
…which stage they are currently, in their readiness to change. Each stage need diff kinds of support
Ways to help ppl advance through the stages
Describe in detail how a person would carry out the behavior change (e.g. give info)
Match strategies to the person’s current needs to promote advancement to the next stage
Precontemplation stage is the BEST stage to give ppl w basic info abt health risks (ex. If person smokes daily and not thinking abt quitting, it’s the best time to give info abt harms)
Discuss perceived barriers work best in contemplation
Plan for problems that may arise when trying to implement the change (imp to prevent relapses in maintenance stage)
Less rational processes
The flawed decisions that people make about their health often result from other motivational and emotional processes.
There’s: Motivated reasoning and conflict theory
Motivated reasoning
Emotionally-biased reasoning intended to produce justifications or make decisions that are most desired rather than those that reflect the evidence
Ppl may search for reasons to accept supportive info and ignore disconfirming information (denial/confirmation bias)
Explain why ppl still maintain unhealthy behaviors (like sugary food)
Conflict theory (emotional factors, and vigilance/hypervigilance)
Ppl have stress due to conflict between perceived risk, hope, and adequate time
In certain instances (e.g. hypervigilance, when risk is high, hope remains, but have little time) ppl will be desperate for a solution and may act irrationally (like alternative health practice in their search)
Vigilance vs Hypervigilance in Conflict Theory
Vigilance (Adaptive): Perceiving serious risks and having adequate time/hope leads to moderate stress and a tendency to search carefully and make rational choices.
Hypervigilance (Maladaptive): Perceiving serious risks but feeling time is running out leads to high stress → searching for a quick solution, often resulting in hasty, non-rational choices
The 2 other cognitive factors in less rational processes
False Hope: Believing without a rational basis that one will succeed in a difficult change (like weight loss) after a previous failure, often by concluding they "didn't try hard enough" before.
Willingness: For spontaneous risky behaviours (e.g., drinking), the factor predicting the behaviour is willingness rather than intention; this is heightened by having a favorable social image of the behaviour.
Development and health
Gestation: The mother's behaviour (e.g., nutrition, avoidance of addictive drugs/alcohol) directly impacts fetal development and birth outcomes (e.g., preventing Fetal Alcohol Syndrome).
Adolescence: A critical time where teens, despite having the cognitive ability for healthy choices, are highly susceptible to taking part in risky behaviours like substance use, which is a key driver of death by accident in this age group.
Adulthood/Aging: Older adults are generally less likely to engage in high-risk behaviours and are more likely to practice healthy habits, in part because they perceive themselves as more vulnerable to illness
Gender and Health:
Life Expectancy: Women live a few years longer than men due to biological factors (e.g., lower cardiovascular reactivity to stress, estrogen's protective effect on the heart) and behavioural factors.
Men's Risk: Men are more likely to smoke, drink, use drugs, and engage in risky activities.
Women's Advantage: Women are more likely to consult a physician when they feel ill
Effective promoting of health
Requires a biopsychosocial perspective and a grassroots, culturally relevant approach
SuperAmma Handwashing Campaign
Designed to increase handwashing of moms in rural villages in South India (Handwashing prevents diarrhea)
Targeted emotional drivers found to be the most effective levers for behavior change
6 months later, increase 30% of handwashing behavior, and sustained for 12 months
Targeted emotional drivers found to be the most effective levers for behavior change in handwashing campaign (4)
Status (desire to have greater access to resources than others)
Affiliation (desire to fit in)
Nurture (desire for a happy, thriving child)
Disgust: Desired to avoid and remove contamination. (most likely to feel disgust to outward group, could be explained by evolutionary – disgust toward possible disease outsiders bring in)
Nurse/physician handwashing study
Monitored contents of hand soap/gel dispensers in a hospital and measure how much it’s used, before vs after putting new signs near them
Few reasons why they don’t wash as often as they should: Constant, soap is irritating, don’t think they’re at risk, no one tracks it anyway
3 signs in this study at the handwashing station
Hand hygiene prevents you from catching diseases
This sign was most effective: Hand hygiene prevents patients from catching diseases
Gel in, wash out
Patient-focused sign had 17% increase in soap/gel, cuz it triggered empathy. 1st and 3rd signs didn’t show increase in hand-washing behavior
Studies of epidemic/outbreaks and empathy
Studies of coping during the SARS epidemic, West Nile virus outbreaks in NA, H1N1 pandemic (india), and seasonal influence (2015) found the same relationship:
Epidemic is diff from outbreaks in terms of availability of vaccines
Behavioral responses to disease threat: Empathic responding is the most imp, the other one that’s MORE imp is perceived threat
Healthier or younger ppl may not perceive as much threat, so empathy may help to supplement in giving more motivation

What are the effects of disease threat?
Inequality → socioeconomic disparities in disease threat
Pandemics can either worsen inequality (by leading ppl to defend and protect the status quo or reduce it (The rich got richer during the pandemic)
Infectious diseases have been asso w “othering” (racism, xenophabia, bigotry)
Outbreaks create fear. (Fear is key to racism)
Historical pathogen prevalence asso w closed-mindedness, and authoritarianism
Higher conformity to traditional gender roles/support for gender stereotypes after COVID-19
Empathy during COVID-19
Increases empathic responding (as well as an imp role of trait empathy) → increases uptake of health health precautions during COVID (consistent w health belief model)
Perceived threat is low, empathy matters in increasing preventative behaviors (In short, empathetic responding is especially imp when perceived threat is low)
Perceived threat is high: There’s not much difference in preventative behaviors between high vs. low empathetic response
Empathy and perspective-taking have been shown to reduce…(3)
Prejudice
Stereotype expression
Interpersonal aggression
In addition to increasing health precautions, empathic responding may also:
Mitigate the negative social consequences of pandemics (racism, discrimination, “othering”)
While improving support and care provision to the sick
Herd immunity
Some ppl are allergic to smth in vaccines (can’t get vaccinated themselves) so they rely on herd immunity for protection from many diseases
The more people that are immunized for a virus, the more infections are disrrupted
So everyone thinking of other ppl → encourage them to get vaccine to build immunity and protect other ppl who are more vulnerable (to allergies/diseases) than others
Study of Antisocial traits in COVID in Brazil
Antisocial Traits: Lower levels of empathy, higher levels of callousness (negative views of society), deceitfulness, and risk-taking (like psychopathy)
Assoc w lower engagement in recommended health precautions (measures) (ex. Social distancing, mask-wearing, handwashing)
These traits asso narcissism and more hoarding (prevention) during COVID-19
Antisocial = socially disruptive, violating the rights of others
Study on intention to wear mask during COVID in the US
Where masks were not mandatory, men were less likely wear mask than women
They said cuz wearing mask is shameful, not cool, a sign of weakness, and a stigma (Toxic masculinity! Other behaviors from this is like not washing hands, eat more red meat)
Study: messages focusing on “your community” were effective?
Effective in motivating mask-wearing behavior
Study: White Americans exposed to info abt COVID-19 racial disparities
REDUCED support to engage in health precautions and perceived overall lower threat
Explaination
Reduced fear (cuz White ppl were told that white ppl are at lower risk of COVID than other races → less fear)
Reduced empathy (To outgroup! They don’t care much aside from white ppl themselves)
Vaccine riot in Montreal in 1800s
Ppl have been protesting for anti-vaccine since the first vaccine
Measles party
Ppl throw a party, expose their kids to kid who has the measles, and that’s their way to build immunity
Getting measles → impairs (harmed) 7-8 years after infection
Anti-Vax Movement & Vaccine hesitancy
Most ppl that didn’t get vaccine were more reluctant to get it than being anti-vaccine
Easy to convince Vaccine hesitant ppl by a talk w physician, but it’s IMPOSSIBLE to convince anti-vax ppl
It takes ONE social media post to make ppl reluctant abt vaccine
Lead to declining immunization rates and an increasing frequency of outbreaks in viruses like measles and whooping cough in Western nations and other parts of the world → Now affecting other vaccines like the flu vaccine, and has had a sig impact on COVID-19 vaccine
Rise in negative attitudes abt vaccines (vaccine hesitancy - anti-vaccine)
Vaccine hesitancy is a bigger threat every year (listed as major threat by WHO, even before COVID, becoming more worldwide)
Spillover effect within and between countries
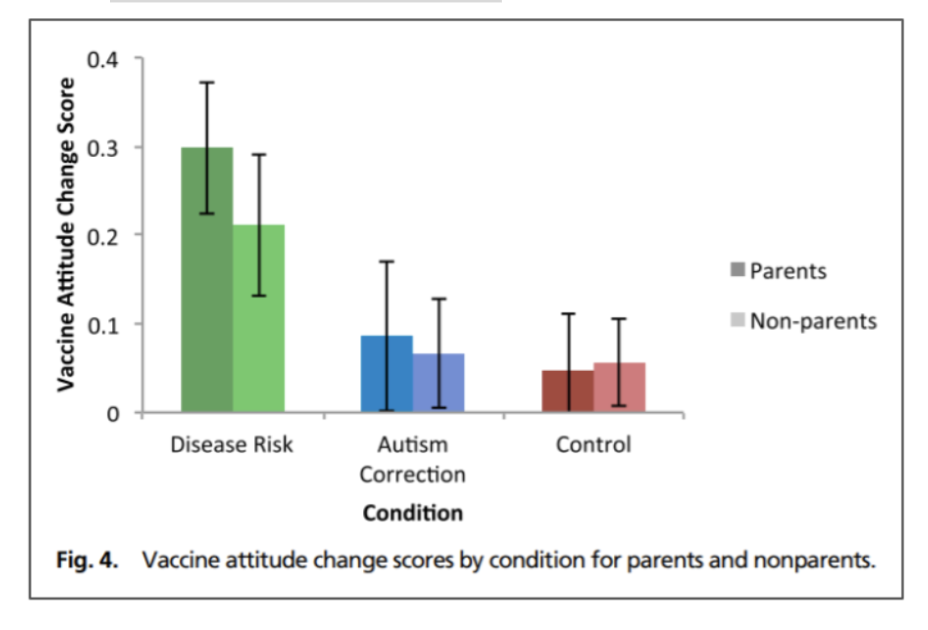
Fraud study: MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) Vaccine & Autism – Wakefield
Found that Wakefield falsified medical records to find the result, and he also didn’t follow ethic methods
Wakefield was PAID a lot by a law firm that was looking to sue the vaccine manufacturer
He even did invasive vaccination onto children in his studies (some kids were reported abused!)
He has continued to be one of the leading voices in anti-vaccine (wtf)
Led by celebrities like Jenny McCarthy → had even more attention on media
Books published by doctors/scientists (ex. Diet books) that are not peer-reviewed.
Measles outbreaks in NA (recent)
More and more throughout few past decades, even spreaded to Europe
In Canada, it was mostly in Alberta
Measles death in the past was more common, but dropped prevalence sharply 1964-1970 cuz of vaccine
On Childhood Vaccinations...
A 2014 Review of 11 different childhood vaccines (including MMR, hepatitis B, and chickenpox).
No link with childhood leukemia (blood cell cancer)
No link between MMR vaccine and autism.
No link between hepatitis B vaccine and multiple sclerosis
A lot of money was wasted to combat w anti-vax attitude
Adverse reactions are extremely rare: (including seizure & fever), ranging in frequency, far less likely than complications due to the viruses being vaccinated.
Which factors from each model (Health belief and planned behav) help to explain vaccine hesitancy?
Perceived threat asso w prevention of disease (likelihood to get vaccine), not w the disease itself (likelihood to get COVID)
A lot of burden to try to encourage
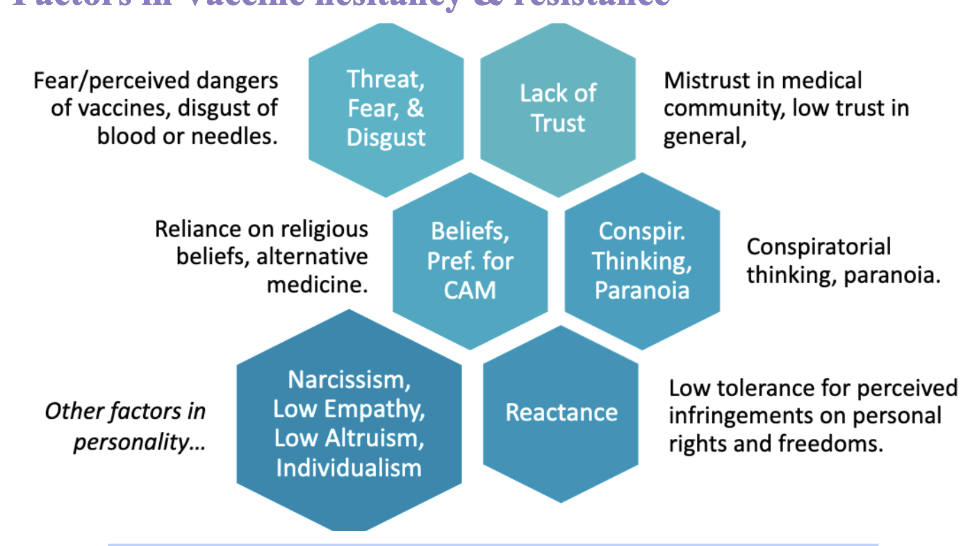
Factors in Vaccine hesitancy & resistance
Fear/perceived dangers of vaccines, scared of blood/needle
Lack of trust: Ppl who don’t trust other ppl in general also don’t trust medical community
More vaccine resistancy in discriminated popul (Indigenous)
Conspiracy theory:
Associated w low agreeableness, low trust in others (suspicious)
high thinking that the world is a dangerous place
Rejected socially, isolated
Reliance on religious beliefs, alternative medicine (think abt Na oai situation)
These are all correlated: Narcissism (more likely to believe in conspiracy theory, low in inhulimity–less likely to take advice from other ppl), low empathy, low altruism, individualism (focus on how they’re “not like other ppl”)
High reactance to the perceived their rights and freedoms “taken away” (they just don’t get vaccinated just cuz they don’t wanna be told what to do)
Individualism and narcissism are correlated with anti-vaccine attitudes and defiance of COVID-19 precautions like mask-wearing
More individualistic countries have higher COVID-19 cases and mortalities from it (like conservative states in US like kentucky, florida, texas)
Messages that frame social challenges as issues of individual choice do not advance public support for policy systems, or environmental solution
The Dunning-Kruger Effect
a cognitive bias whereby people with limited knowledge or competence in a given intellectual or social domain greatly overestimate their own knowledge or competence in that domain
(Like people who never took a psych class and only know a few Freud’s theories, think they know a lot abt Psych, more than us psyc students)
Overconfidence (Dunning-Kruger effect) is also associated with
Anti-vaccine attitudes (and opposition to vaccine mandates); and overconfidence in anti-vaccine ideas is highest among those w low levels of knowledge abt vaccine and diseases
Also increased support of non-expert views in policy decisions
Backfire effect
cognitive bias that causes people who encounter evidence that challenges their beliefs to reject that evidence and strengthen their support of their original stance.
Ppl concerned abt side effects of flu shot were given info abt how it COULDN’T cause the flu, they actually became less willing to get it
So kinda like motivated reasoning
Solution to convince ppl to give vaccine
Info on disease threat, rather than info debunking vaccination myths, works best to change attitudes about vaccine