Lecture 7 - Vascular Disorders and Thrombosis
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what is the thymus organ?
The thymus is a lymphoid organ located in the upper chest, responsible for the maturation of T-cells, which are crucial for the adaptive immune system. It plays a key role in the development of immune responses.
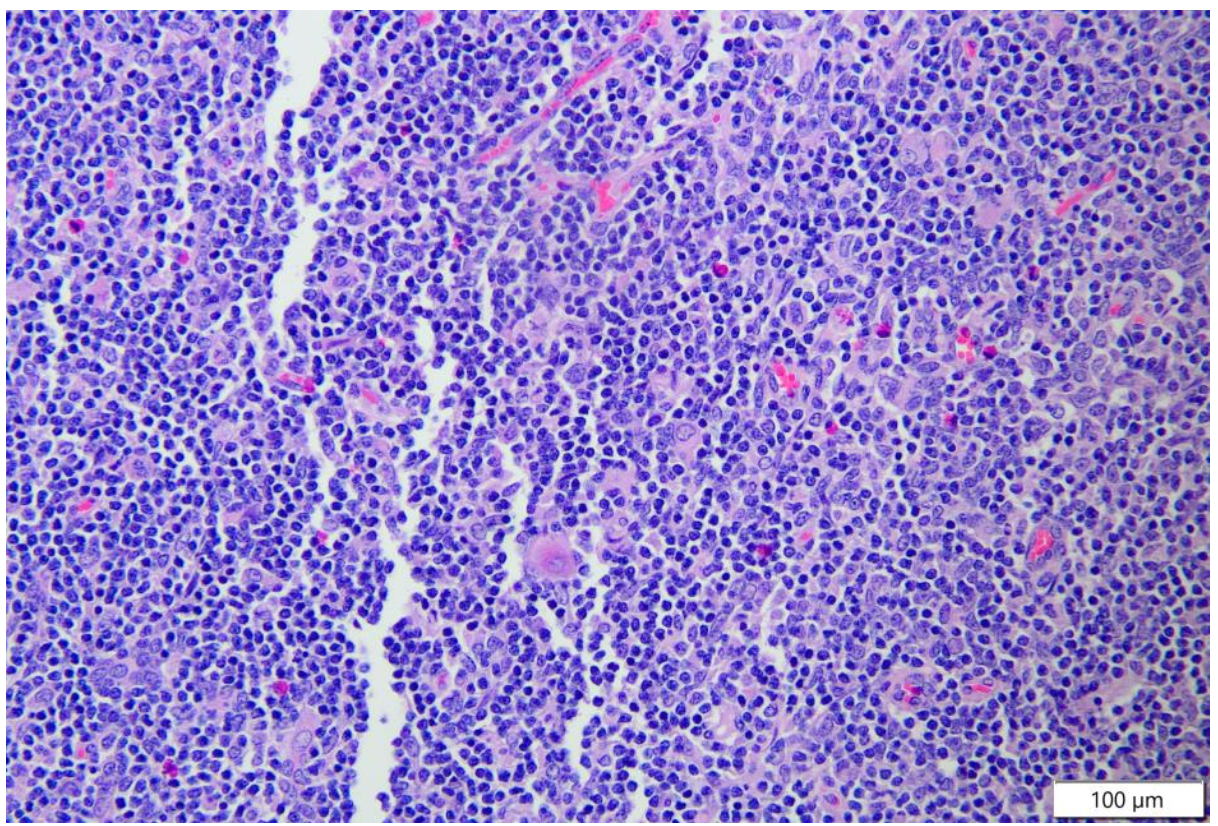
is this thymus normal?
yes
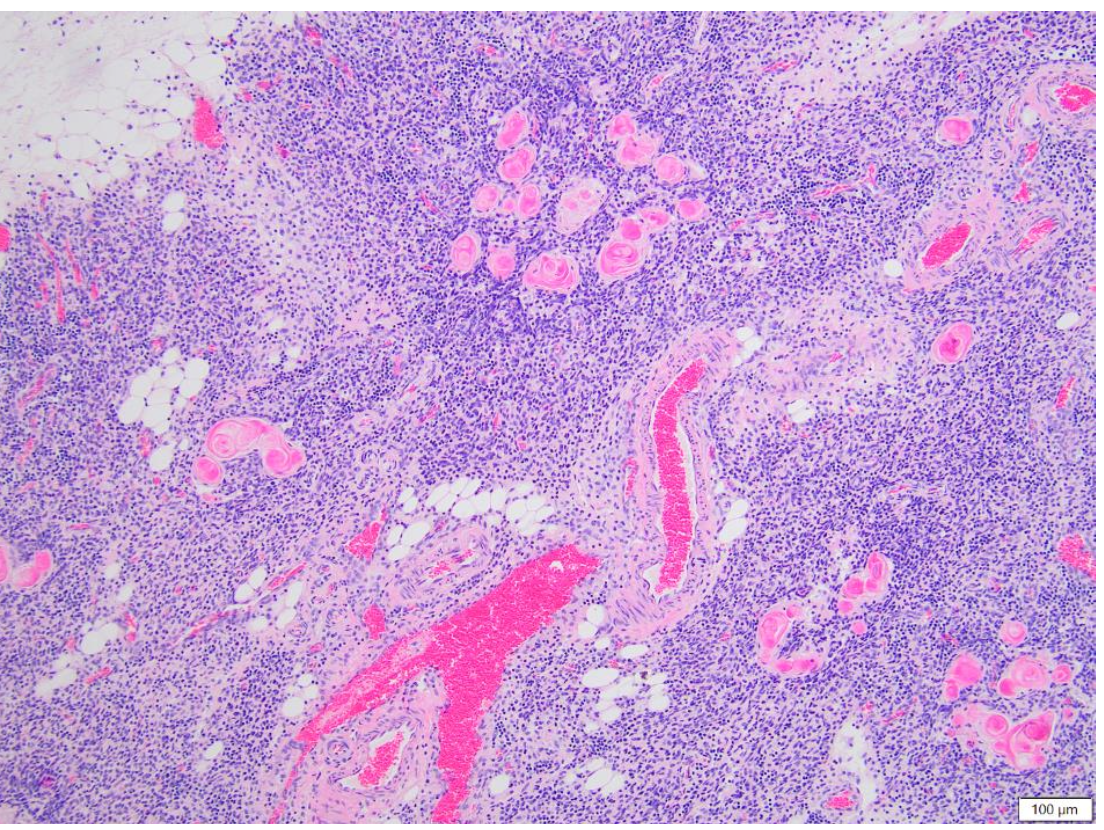
is this normal thymus?
no
what are the major parts of the circulatory system?
heart
arteries/veins
lymphatics
which direction do arteries send blood?
carry blood away from the heart to the body; extreme vascular resistance and increased pressure
which direction do veins carry blood?
from body towards heart, low pressure
whats the micro-anatomy of the vessels?
Aorta > Arteries > Arterioles > Capillaries < Venules < Veins < Vena Cava
Characteristics of arteries?
large lumen: minimal resistance
Thick vessel walls: smooth muscle / elastic fibers
characteristics of arterioles?
narrow lumen
respond to sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation (constriction and relaxation of vessels)
what are the 3 layers in the endothelium in the vessels?
tunica intima
tunica media
tunica adventitia
what is the tunica intima - arteries
endothelium
basement membrane
internal elastic lamina
what is the tunica media - arteries?
smooth muscle
collagen, reticular, and elastin fibers
external elastic fibers
what is the tunica adventitia - arteries?
connective tissue
vasa vasorum (microvessels)
lymphatic vessels
nerve fibers
what is the function of the capillaries?
site of nutrient and waste exchange
what are the three types of capillaries?
continuous
fenestrated
discontinuous
Continuous capillaries characteristics?
uninterrupted endothelial cell layer, allowing for selective transport.
They are primarily found in muscle, lungs, and central nervous system.
BRAIN important - whole reason for blood brain barrier
They have tight junctions and minimal intercellular clefts.
Fenestrated capillaries characteristics?
Endothelial cells with pores (fenestrae), facilitating greater permeability to larger molecules.
Found in areas requiring extensive exchange, such as renal glomeruli, intestinal villi, endocrine glands, choroid plexuses, and ciliary processes of the eye
Discontinuous capillaries characteristics?
Large gaps between endothelial cells, allowing for free exchange of larger molecules and even cells.
Commonly found in the liver, spleen, bone marrow and lymph nodes
immune surveillance and detoxifying blood
characteristics of veins/venuoles?
mostly collagen (distention > contraction)
little smooth muscle and elastin
can hold up to 65% of total blood volume
Blood passage depends on:
valves to prevent backflow
contraction of skeletal muscles
tunica intima - veins?
endothelium
basement membrane
tunica media - veins?
smooth muscle
collagen, reticular, and elastin fibers
predominantly collagen and less smooth muscle
tunica adventitia - veins?
modest connective tissue
vasa vasorum (microvessels)
occasional nerve fibers
why is elastin stain important?
Microanatomy:
tunica intima (endothelium, elastin)
tunica media (smooth muscle)
Tunica adventitia (connective tissue)
Elastin gives elasticity to vessels
what are lymphatics?
surround microcirculation
begin as blind ended lymphatic capillaries
overlapping endothelial cells and large interendothelial gaps (can accommodate larger particles)
valves and contraction of skeletal muscles to move lymph forward towards heart
what is found in lymphatics?
lymph
lipids
ECF
inflammatory cells
endothelium?
single layer of endothelial cells lines all components of the circulatory system
endothelium function?
fluid distribution
inflammation
immunity
angiogenesis
hemostasis
what is Rete Mirabile?
specialized vascular networks formed by arterial blood vessels through the center of large venous sinuses
what is the function of Rete Mirabile?
countercurrent exchange
regulating temperature
ionic contraction gradients
O2/CO2 exchange
equalizes blood pressure
what is the interstitium?
extravascular compartment
space between parenchymal and stromal cells and microcirculation
Functions of Interstitium?
provides pathways used by the microvasculature (vascular adventitia), lymphatic vessels, nerves and trafficking leukocytes
module systemic physiologic properties exerted by parenchymal cells
General fluid pool/reservoir providing cushioning effects for organs, water/ion reserves
structural framework for cell survival
what is the extracellular matrix?
the structural, adhesive, and absorptive components within the interstitium
what is the extracellular matrix composed of?
type 1 collagen (mainly)
glycoproteins
glycosaminoglycans
proteoglycans