6.2 Adjusting Nominal Values to Real Values and Tracking Real GDP Over Time
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Which of the following descriptions best fits the term nominal value?
the amount of all income earned in a nation
the value of all goods and services produced within a country in a year based on market prices
the value of a good or service actually announced at the time and not adjusted for inflation
the value of what is produced domestically and what is produced by domestic labor and business abroad in a year
the value of a good or service actually announced at the time and not adjusted for inflation
By definition, nominal value is the value of a good or service that is not adjusted for inflation. The nominal value of any economic statistic means that we measure the statistic in terms of actual prices that exist at the time.
Nominal GDP is estimated to be $26,000 while the GDP deflator is currently 98. What is real GDP? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
26,530.61
To calculate real GDP, use the formula:Real GDP =Nominal GDP/Price Index/100
Real GDP =$26,000/98/100
Real GDP =$26,000/0.98=$26,530.61
A new pandemic wipes out most of humanity and decreases worldwide real GDP by $20,000 from $85,000. What is the percentage change in real GDP?
Be sure to:
Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Include a negative sign if necessary.
-23.5%
To find the percentage change in real GDP, we apply the formula for percentage change:
New GDP – Old GDP/Old GDP×100%=% change
In this case, real GDP decreased by 20,000, so the percentage change is negative,
−20,000/85,000×100%≈−23.5%
The government of a country decides to double its current level of spending, causing real GDP to increase from $20,000 to $120,000. What is the percent change in real GDP?
500%
To find the real growth rate, we apply the formula for percentage change:
New GDP – Old GDP/Old GDP×100=% change
In this case, real GDP increased, so the percent change is positive,
120,000–20,000/20,000×100=500%
Nominal GDP recently decreased by 2% following contractionary fiscal policy. Meanwhile, the price level decreased by 7% What is the real GDP growth rate during this period? Round your answer to two decimal places.
5%
We know that, approximately, % change in Quantity =% change in Nominal −% change in Price
Therefore, real GDP growth rate (% change in quantity) approximately equals the growth rate in nominal GDP (% change in value) minus the inflation rate (% change in price).
% change in Quantity =−2%−(−7%)=5%
A(n) ______ is an especially lengthy period, where real GDP experiences a severe drop.
recession
economic boom
stagnation
depression
depression
We call a decline in real GDP that typically lasts at least two consecutive quarters a recession. We call an especially lengthy and deep recession a depression. The severe drop in GDP that occurred during the 1930s Great Depression is clearly visible in the figure, as is the 2008–2009 Great Recession.
A peak _______.
occurs where real GDP stops falling and begins rising
is calculated as exports minus imports
is calculated as imports minus exports
is the highest point in an economy that comes just before real GDP begins falling and recession begins
is the highest point in an economy that comes just before real GDP begins falling and recession begins
A peak is the highest point in an economy that comes just before real GDP begins to fall and recession begins.
Which of the following is the best definition of GDP deflator?
Select the correct answer below:
a measure of inflation based on the prices of all the components of GDP
a measure of inflation based on prices paid for supplies and inputs by producers of goods and services
a measure of inflation based on the prices of merchandise that is exported or imported
a measure of inflation typically calculated by taking the consumer price index (CPI) and excluding volatile economic variables such as food and energy prices to better measure the underlying and persistent trend in long-term prices
a measure of inflation based on the prices of all the components of GDP
The GDP deflator is defined as a measure of inflation based on the prices of all the components of GDP. It is calculated by dividing nominal GDP by real GDP.
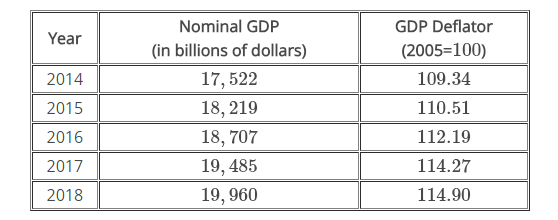
Using the table below, calculate real GDP (in billions of dollars) in 2017. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
$17051.7
To calculate real GDP, use the formula:Real GDP =Nominal GDPPrice Index/100
The GDP Deflator is also known as the price level, so
Real GDP in 2017 =$19,485/114.27/100
A stock market boom causes consumer wealth to increase which results in consumers spending to increase. This increase results in real GDP increasing from $28,000 to $30,000 What is the percent change in real GDP? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
7.14%
To find the real growth rate, we apply the formula for percentage change:
New GDP – Old GDP/Old GDP×100=% change
In this case, real GDP increased, so the percent change is positive,
30,000–28,000/28,000×100=7.14%
Why do economists care about recessions?
Many people lose work and struggle to support themselves financially.
New jobs are created and output increases.
Interest rates increase due to a high demand for money.
None of the above.
Many people lose work and struggle to support themselves financially.
Economists care about recessions because during these periods many people lose work and struggle to support themselves financially. Even those who do not lose work may see cuts in hours or pay, which lowers their standard of living.
Which of the following statements about the business cycle are true?
Note: Please select two correct answers.
A business cycle shows contractions and expansions of the economy.
Economists use business cycles to track real GDP over a number of years.
The business cycle shows ups and downs in interest rate.
Economists do not use the business cycle to make economic decisions.
A business cycle shows contractions and expansions of the economy.
Economists use business cycles to track real GDP over a number of years.
The business cycle shows movements in real GDP. Economists have sought for centuries to explain the forces at work in the business cycle. Not only are the currents that move the economy up or down intellectually fascinating, but also an understanding of them is of tremendous practical importance.