biology- receptors, reflexes and responses
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is a stimulus
a change in the environment which can be detected
What is a receptor
Energy transducer
Converts the energy in the stimulus into the energy in an action potential
Some receptors exist as individual cells (eg in skin) while others are concentrated into sense organs (eg in the eye)
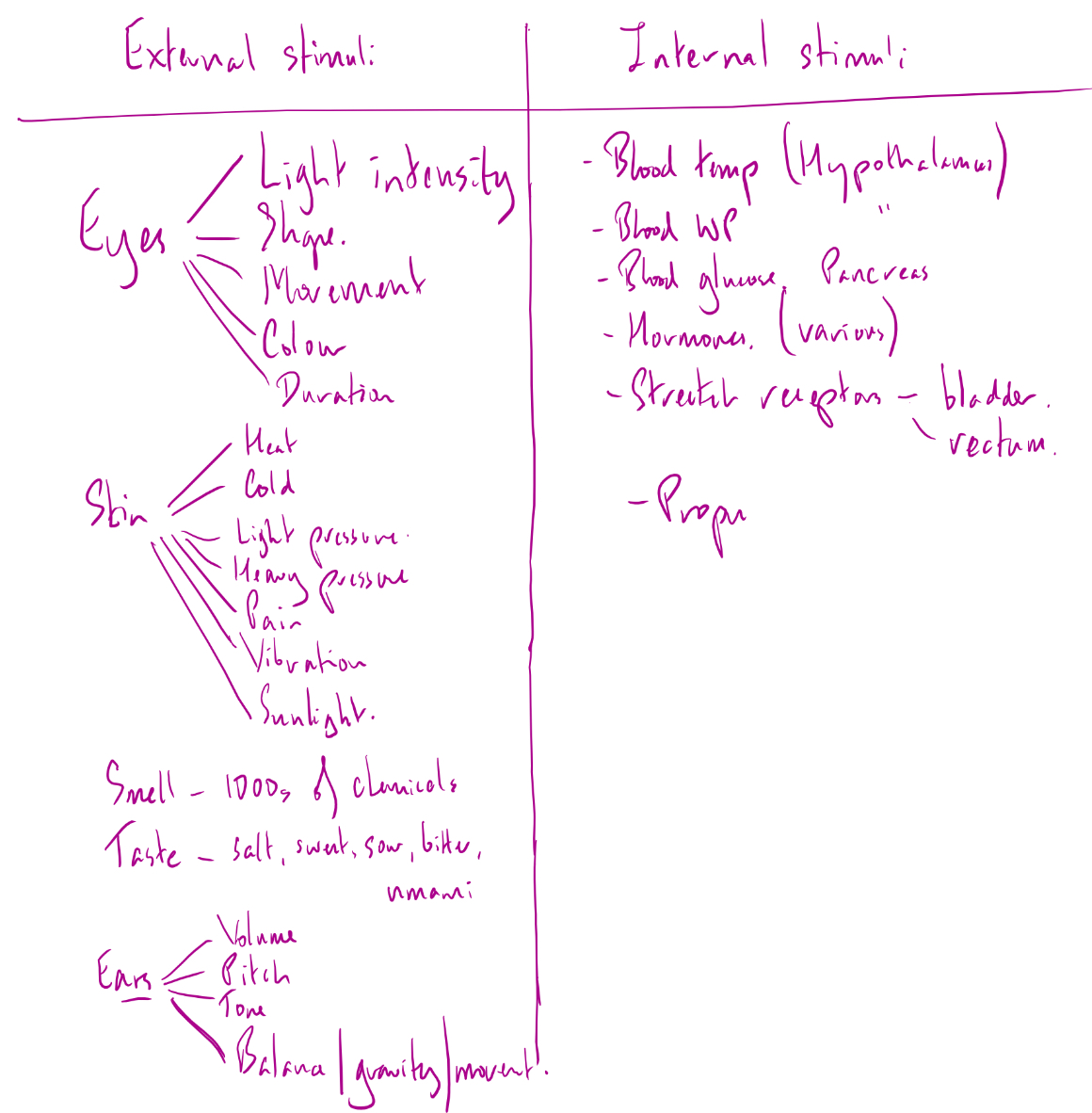
External and internal stimuli
Definition of a tropism
Different tropisms
Plant growth response
Phototropism- light
Geotropicsm/gravitropism- gravity
Chemotropism- chemicals
Hydrotropism- water
Thigmotropism- touch
How is movement brought about in plants
Cells can divide
Cells can elongate
Movement towards a stimulus is a positive tropism, away is negative. Tropisms are controlled by hormones.
How does auxin work eg (IAA)
The tip makes auxin
By AT the auxin moves to the dark side
Auxin diffuses down the dark side
Auxin stimulates cell elongation
So the tip bends to the light
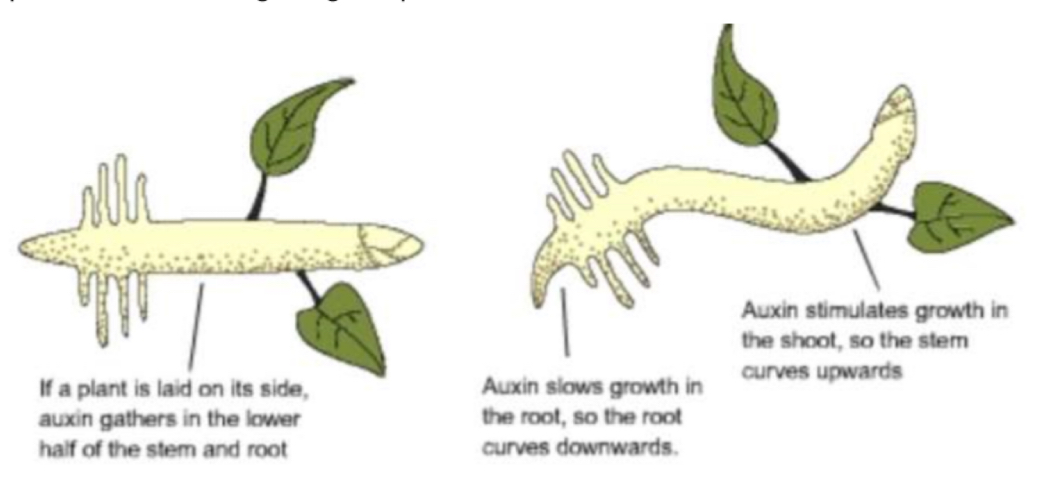
How does auxin work in shoots/roots
Auxin is made at the top
It diffuses down the seedling
It settles on the lower side (possibly due to starch grains: statoliths)
In shoots auxin stimulates cell elongation → grows up
In root auxin inhibits cell elongation → grows down
What is a kinesis
A non directional response to a stimulus: it explores the environment relatively quickly, making wide turns
When it find favourable conditions it slows down, makes tighter turns and stops
What is a taxis
A directional response, towards or away from a stimulus
Features of a reflex
Unconscious
Rapid
Fixed- one stimulus = one response
As few synapses as possible
3 neurones involved in a reflex arc
sensory neurone- links the receptor with the spinal cord
Short relay neurone that connects the incoming and outgoing neurones
The motor neurone that transmits impulses to the effector
Reflex arc for online colour change reaction timer
Eyes detected colour change → 2 synapses in retina → optic nerve to visual cortex in brain → motor cortex in brain → motor neuron in hand → muscle contracts
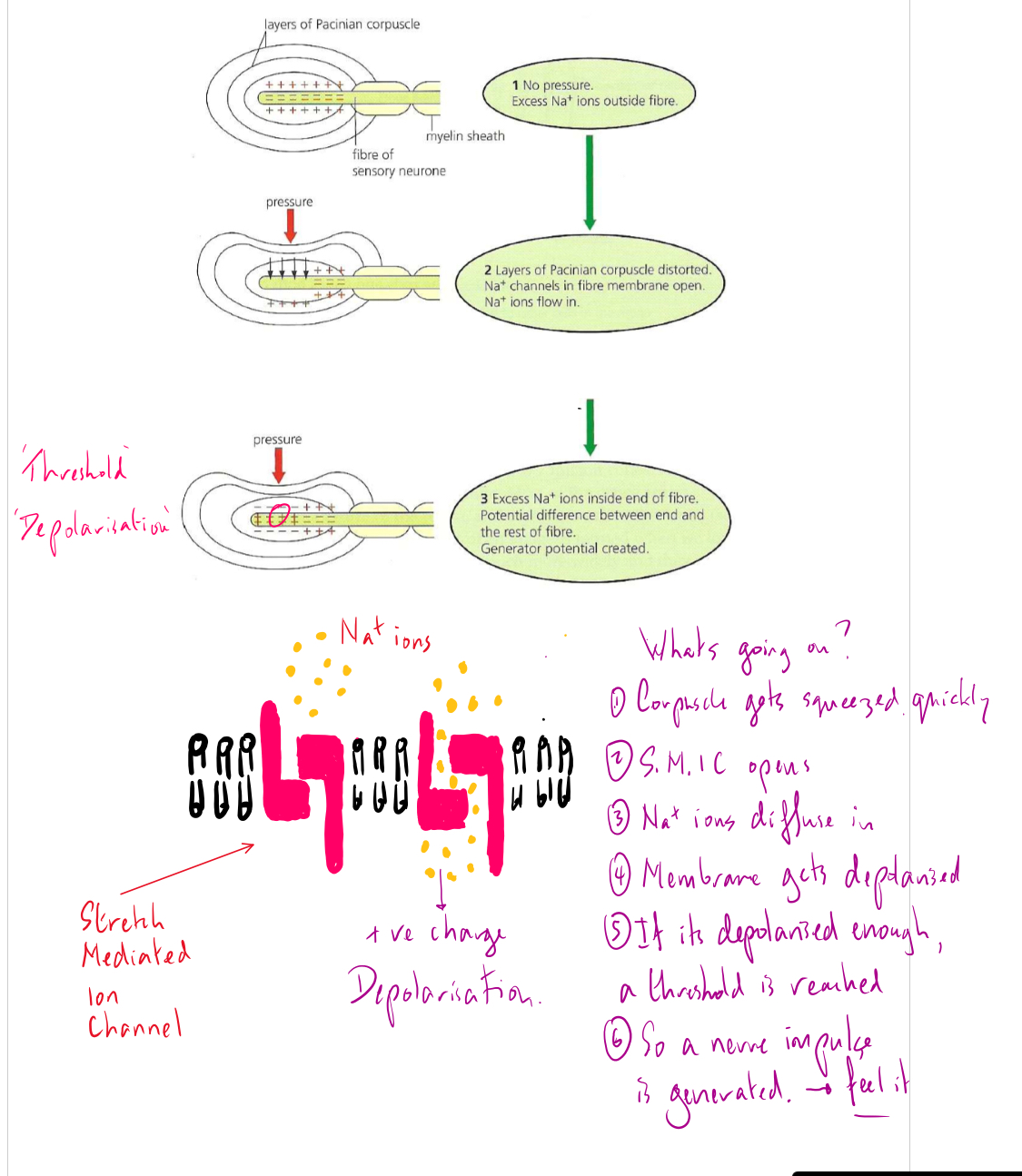
Pascinian corpuscle structure
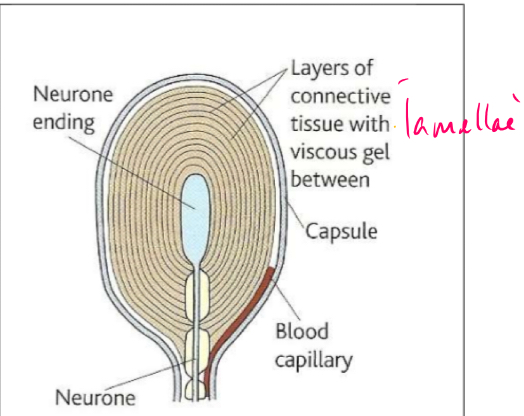
What is a Pacinian corpuscle
a receptor found deep in skin- detects pressure and vibration
Each corpuscle consists of a single sensory neurone- often described as a ‘nerve ending’ surrounded by lamellae (layers) of fibrous connective tissue separated by a viscous gel
A rapid change in pressure on the corpuscle is transmitted through to the sensory nerve, which deforms, causes stretch-mediated sodium ion channels in the axon membrane to open. This allows sodium ions to diffuse in, creating a generator potential. If this potential reaches a threshold, action potential pass down the sensory nerve. This passes to the brain and we feel the sensation. The greater the stimulus, the higher the frequency of the impulses.
The gel acts as 'shock absorber' and quickly allows the sensory nerve to assume its normal shape, this is called adaptation. From this it can be seen that Pacinian corpuscles will detect rapid changes of pressure, but not prolonged pressure. No more impulses will be generated until the pressure changes again. This is an important point about receptors - they will generally respond to changes in environment, not constant stimuli.
How does pascinian corpuscle work (exam answer)
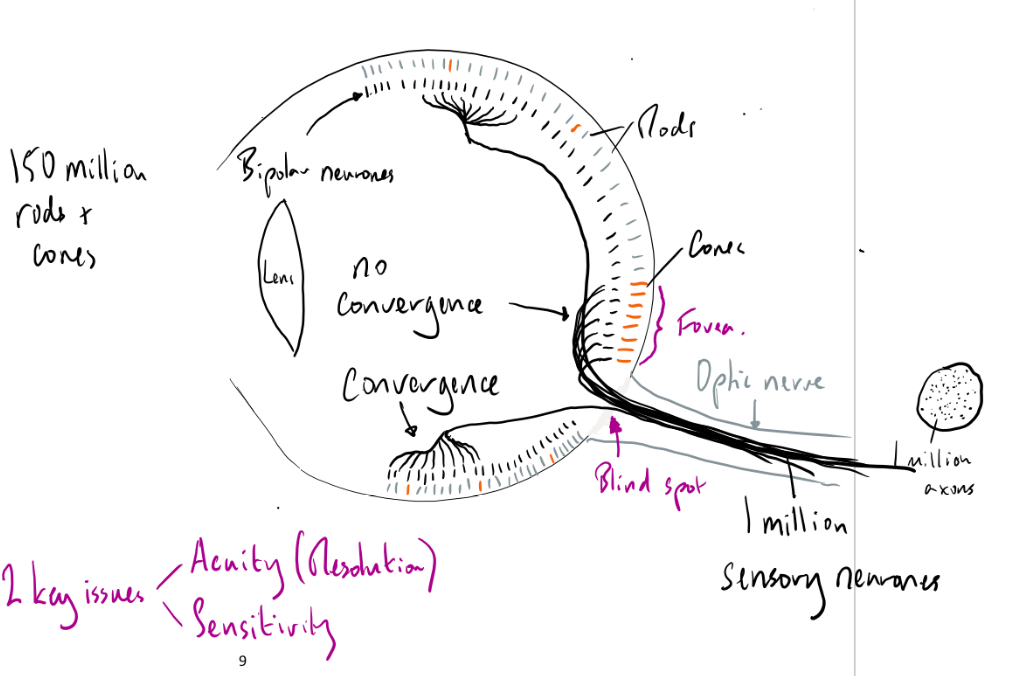
What is retina
Single layer of light sensitive receptor cells- rods and cones- together with connecting neurones on the back of the eye
Function of retina
Gather information about the incoming light and relay it to the brain via the optic nerve
The actual image is formed in the brain- in the visual cortex
Define
Sensitivity
Acuity
Sensitivity- level of light needed for the cells to function
Acuity- ability to perceive detail
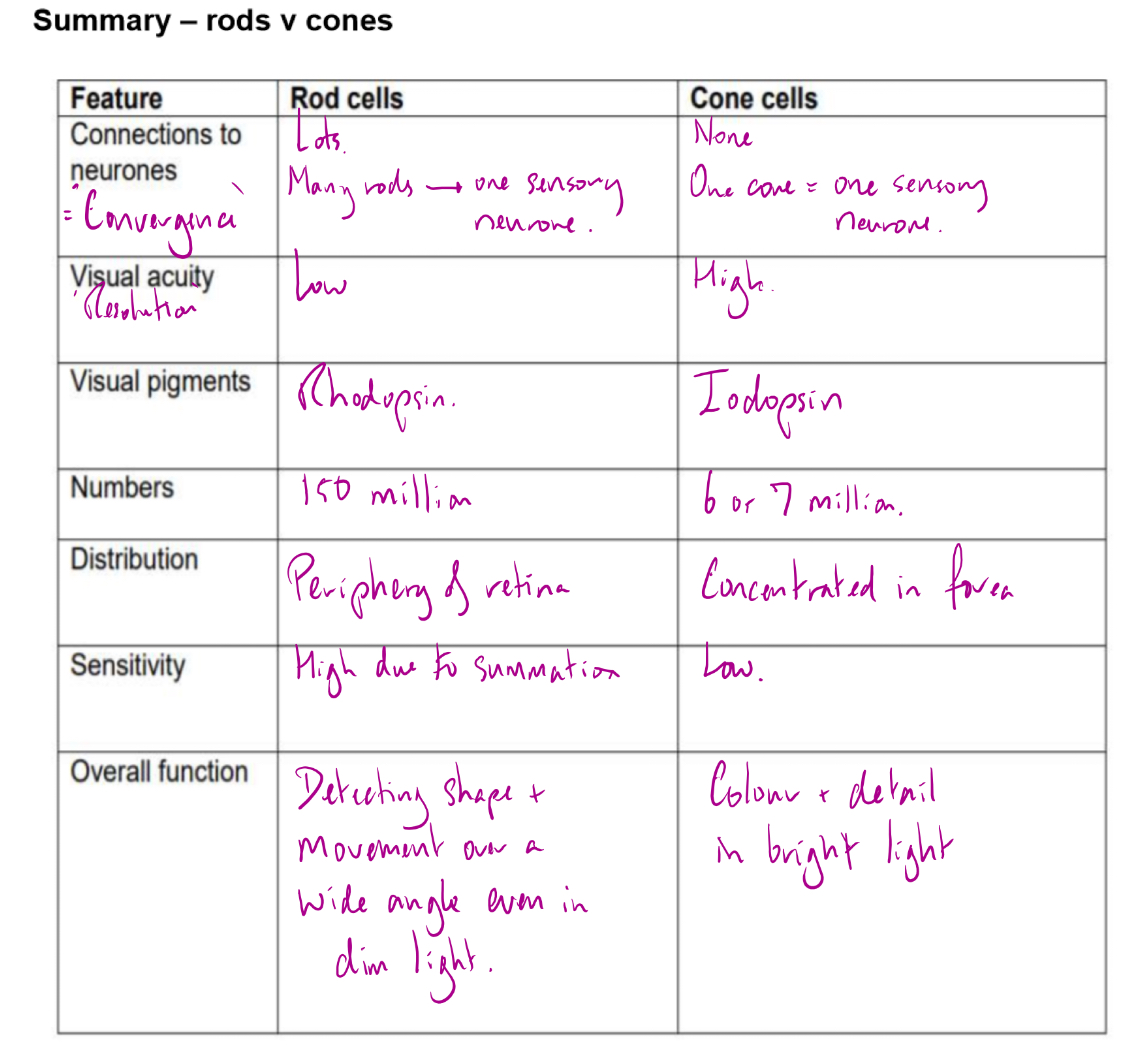
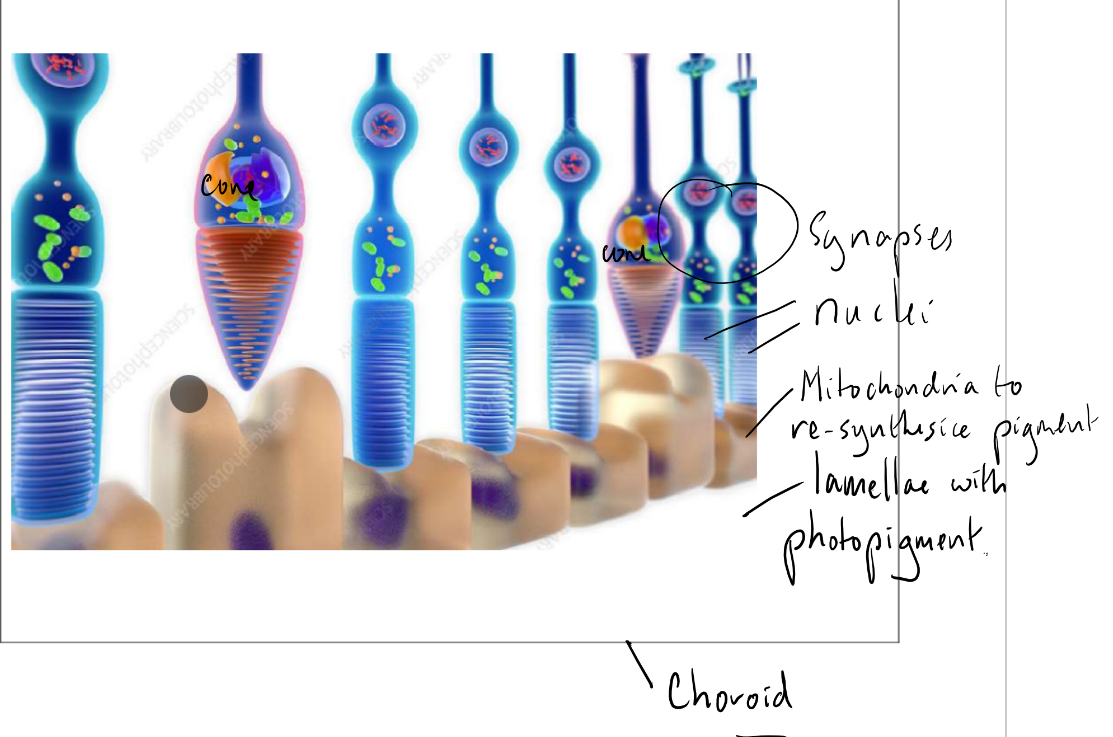
Rods vs cones- sensitivity and reasons why
Rods more sensitive than cones- can function even in dim light
The pigment n rod cells is more easily bleached (broken down) than than pigment in cones
Retinal convergence- many rod cells converge into one neurone so they can all contribute to the generator potential, making it more likely that the threshold will be reached. Each rod has its own connection. Any impulses generated by an individual cone are transmitted to the brain but any impulses generated by a rod are fed into a neurone along with impulses from many others
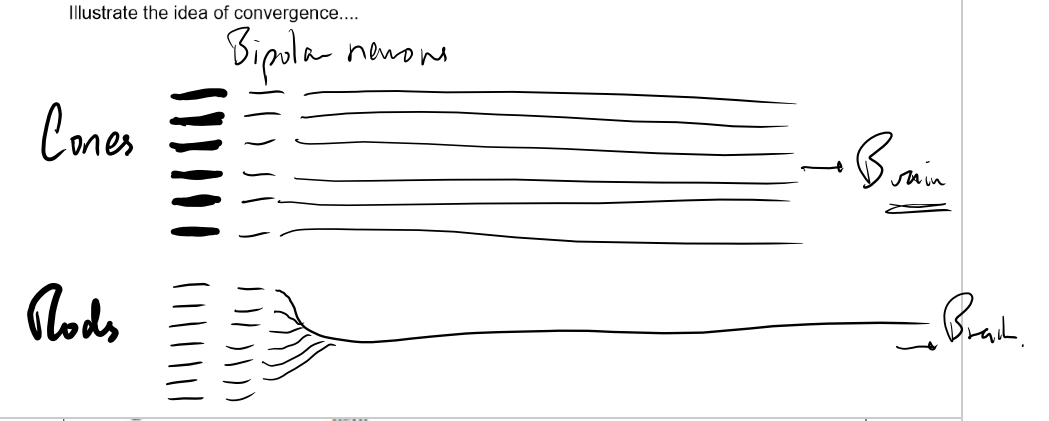
Diagram showing distribution of rods and cones in retina
Rod cells and cone cells
How does colour vision work
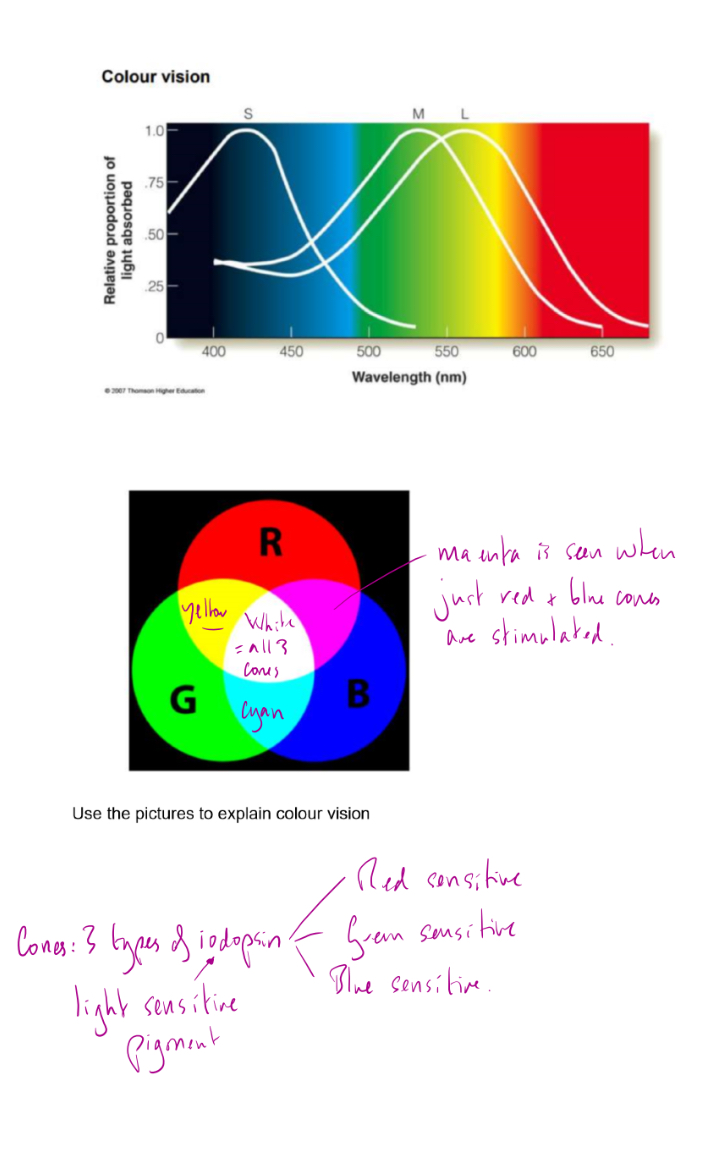
How are after images produced
Eg
look at blue for 30s then see yellow
look at red for 30s then see cyan
look at green for 30s then see magenta
Eg look at red
Red cones are stimulated. Pigment in them is bleached (red cones get ‘fatigued’ and can’t be stimulated again until the pigment is re-synthesised)
So when you look immediately at white red cones dont work but blue and green do so we see cyan
Summary rods v cones