Social Psych Exam #1 Study Guide
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Social psychology
The study of how people affect and are affected by others
– Helps make sense of social worl
The ABCs
Affect, Behavior, and Cognition
Why Do People Study Social Psychology?
Curiosity about people
Experimental philosophy
Making the world better
Social psychology is fun
Scientific Method
– State the problem
– Formulate a testable hypothesis
– Design the study and collect data
– Test the hypothesis with the data
– Communicate the results of the study to the scientific community
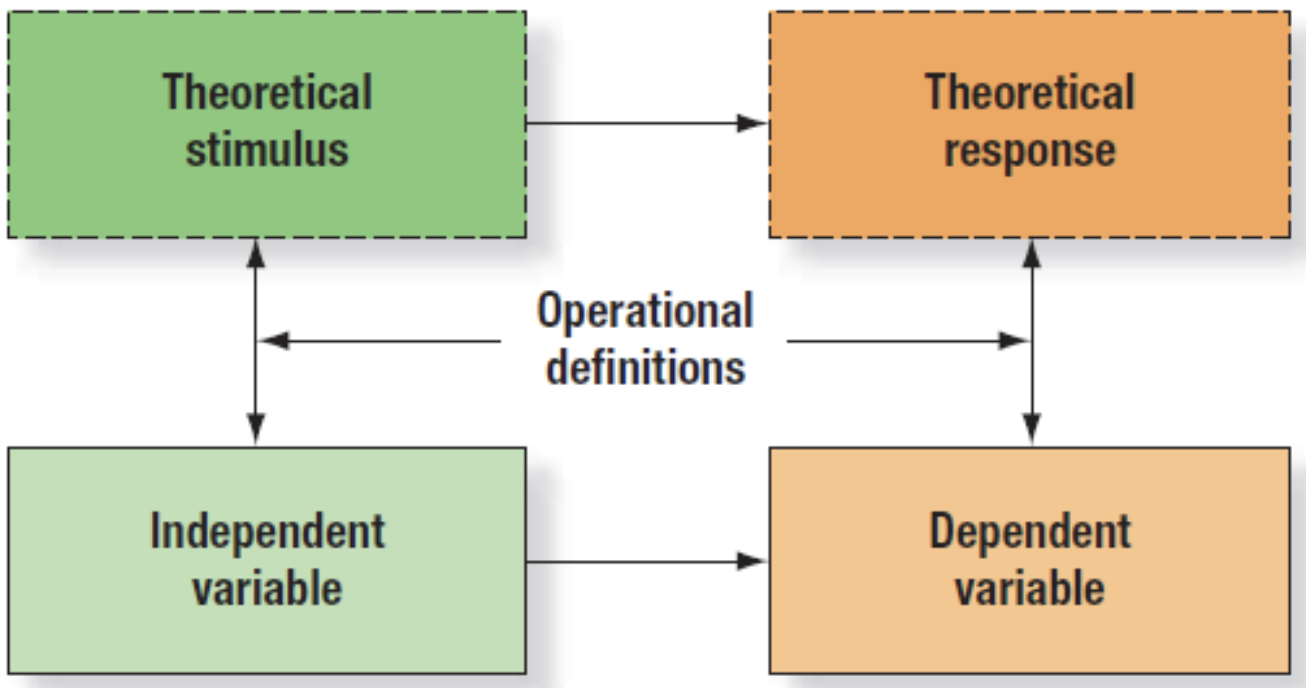
Theories
Constructs linked together in a logical way
Independent variable
Any observable event that causes the person to do something
Dependent variable
Any observable behavior produced by the person
Accomplice
Person who is secretly working for the researcher
Max Ringelmann (late 1800s)
As group size increases, individual effort decreases
Norman Triplett (late 1800s)
Competition enhances performance
Experimental studies
– Researcher has control over the procedures
– Participants are randomly assigned
Quasi-experiment
– No random assignment
Internal validity
– Confidence that changes in the independent variable caused changes in the dependent variable
Laboratory experiments
High control level
Field experiments
Real-world settings
Experimental realism
Participants forget they are in an experiment
Mundane realism
Settings physically resemble the real world
External validity
Findings generalize to other people, other settings, and other time periods
Epigenetics study
PTSD from 9/11 can cause the victim’s baby to have a higher chance of getting ptsd and it can mess up their cortisol levels
Nature
The physical world around us, including its laws and processes
Nature and development
Social animals (including humans) accomplish satisfying their needs and ultimately survive and reproduce by means of social interaction
Being social offers evolutionary benefits (find more food, mate easier, alert others to danger, take care of the sick)
Sex Differences in Mate Preferences study
Status and power is more attractive to women while looks and ability is to men
Meta-Analysis of Relationships and Health study
Mortality rates increase without social interaction
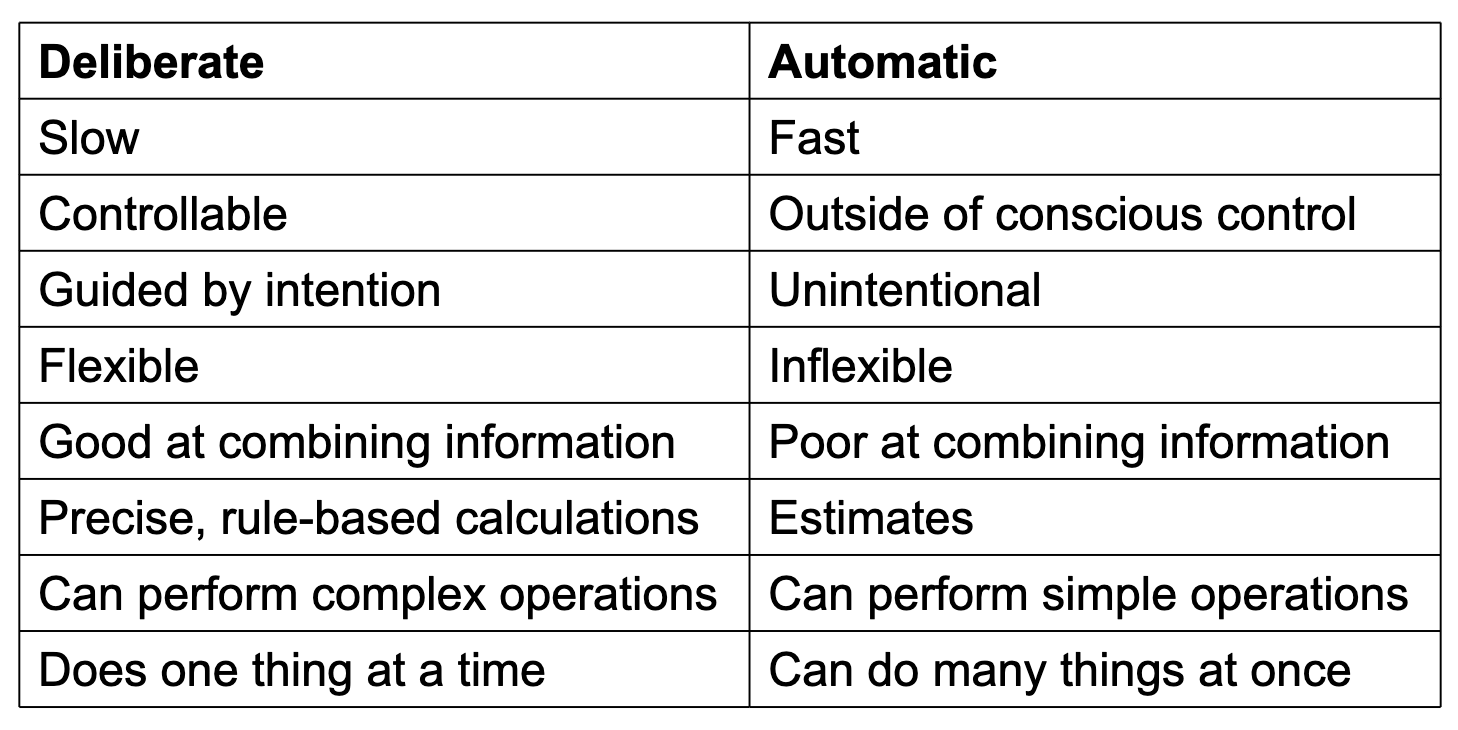
The Duplex Mind
Deliberate and Automatic Systems
Culture
Advanced way of being social
Brain puts special priority on information directly experienced as shared
A network linking many different people
Depends on shared ideas and shared ways of doing things
Encoding and sharing meaningful information
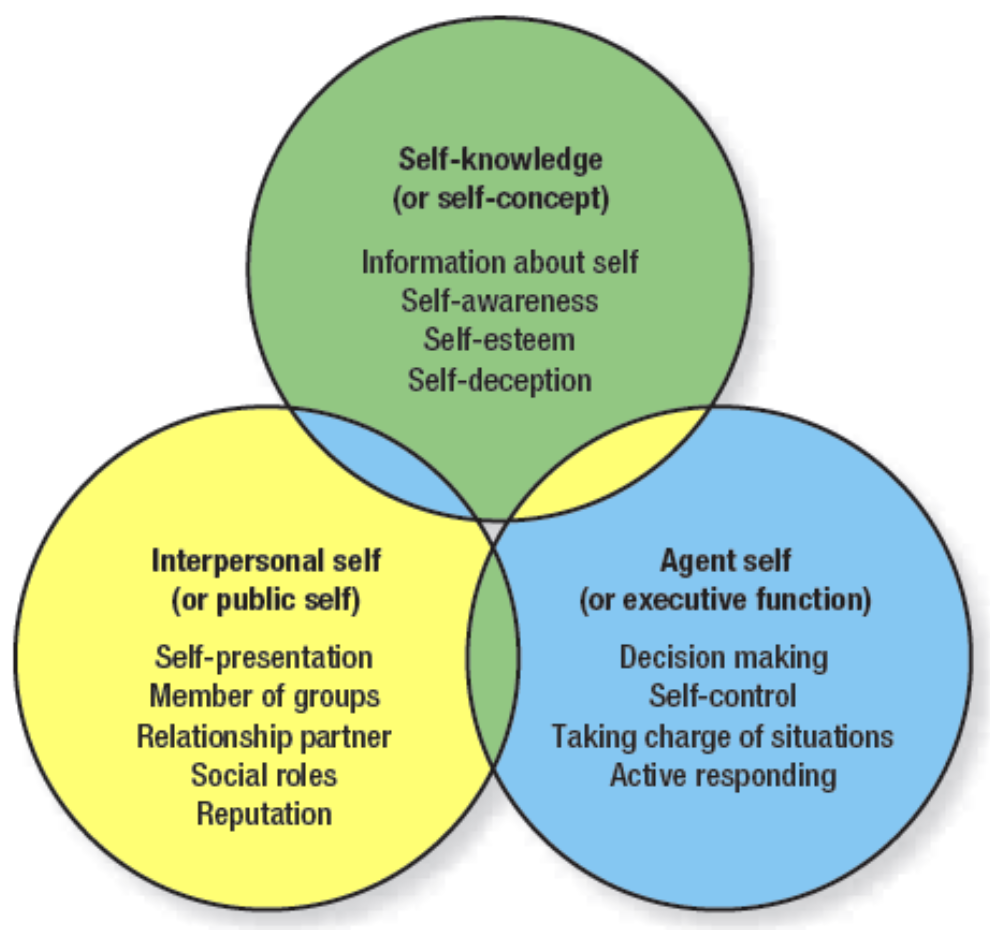
Three Parts of the Self
Self-knowledge, Interpersonal self and Agent self
interface between inner biological processes and one’s sociocultural network
Self-Construals
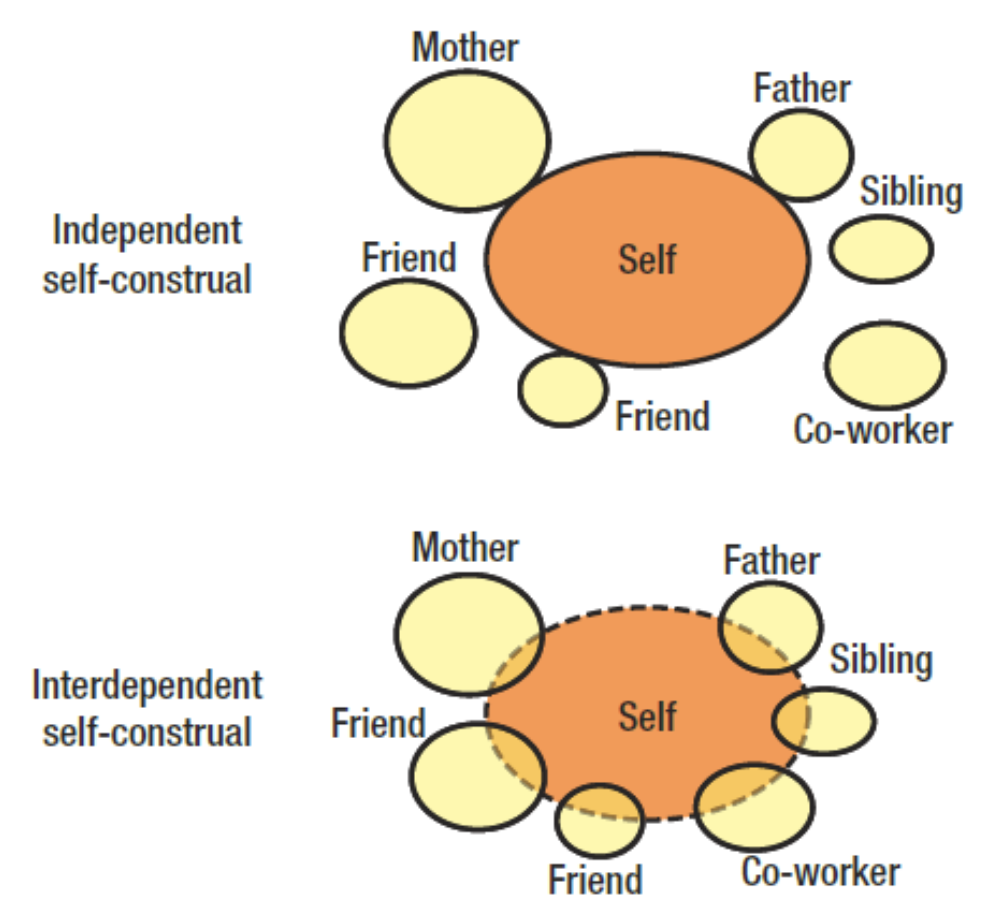
The Behavioral Impact of Self-Construals study
Based on their relational identity, people in a couple carried out different tasks. People with a high relational identity were more likely to do tasks that benefitted both of them.
Self-awareness
Attention directed at the self
Private self-awareness
Looking inward at private aspects of the self, including emotions, thoughts, desires, and traits
Public self-awareness
Looking outward to understand the self and how you are perceived by others
Vital for self-regulation, social acceptance, perspective taking, and goal reaching
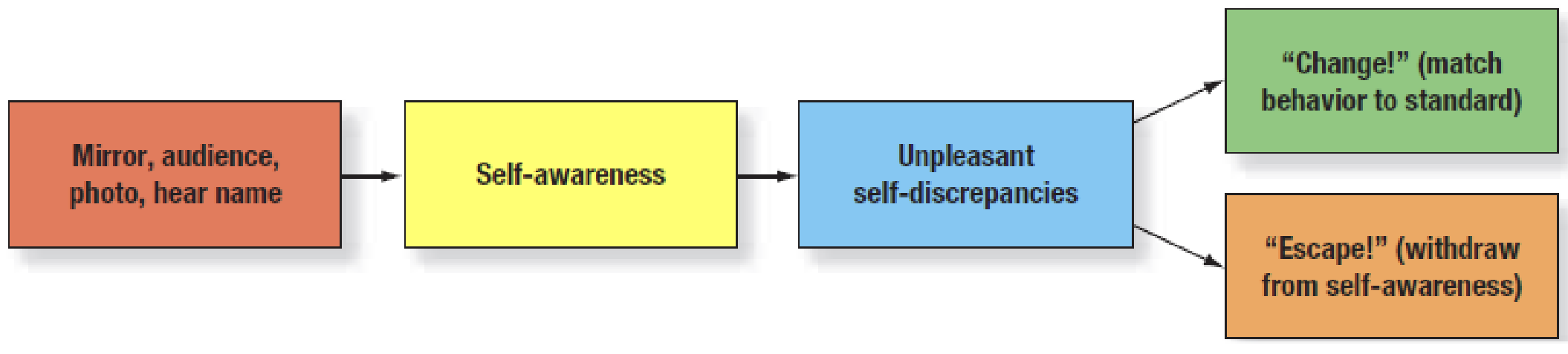
Self-Awareness Effects on Moral Behavior study
Self-awareness leads to a decrease in transgressive behavior. It directly influences impulse.
Introspection
Examining your thoughts and feelings
Theory of social comparison
Examining the difference between oneself and another person
Self-esteem
How favorably someone evaluates himself or herself
– High self-esteem: competent, likable, attractive, and morally good
– Low self-esteem: incompetent, ugly, unlikable, and morally wicked
– Self-protection: trying to avoid loss of self-esteem
Self-knowledge
Appraisal motive (truth)
– Weakest motive
Self-enhancement motive (flattery)
– Strongest motive
Consistency motive (feedback that confirms)
– Second preference
Two steps of choosing
– Whittle the full range of choices down to a few
– Carefully compare highlighted options
Influences on choice
– Risk aversion
– Temporal discounting
– The certainty effect
– Keeping options open
Decision avoidance
– The general theme is anticipated regret
– Postponing, status quo bias, and omission bias
Reactance theory
– People desire freedom of choice, and react negatively when freedom is
reduced
• Choices or options taken away
Goals
Ideas of some desired future state
Setting goals
• Choosing among different possible goals
• Evaluating their feasibility and desirability
Pursuing the goals
• Planning and carrying out behaviors to reach goals
• Optimism and positive illusions help build confidence and foster better performance
Deliberate and automatic systems help us pursue goals
Goal shielding
Shutting off thoughts about other goals while pursuing a single goal
Decision avoidance
– The general theme is anticipated regret
– Postponing, status quo bias, and omission bias
Self-determination theory
People need at least some degree of autonomy and internal motivation