AMTS: Unit 1 Part 1
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What is Temperature defined as?
The measure of molecular kinetic energy
What tools are used to measure Temperature
Thermometers & Thermistors
____________ — average speed of molecules (or kinetic energy) in a substance
Temperature
What are the three scales of Temperature
K,F,C
_____________ are measured in shade to avoid solar radiation interference
Thermometers/Thermistors
___________ is where we live and where (most) weather occurs
Troposphere
The Troposphere has ______% of mass
80
In the Troposphere — T usually ________ w/ height
decreases
___________— occurs where temperature increases with height
Inversions
Which part of our Atmosphere has well mixed air?
Troposphere
Which part of our Atmosphere has poorly mixed air?
Stratosphere
The Stratosphere has _______% of mass
19.9
In the Stratosphere — T usually ________ w/ height
increases
Which part of our Atmosphere has an layer that absorbs UV radiation to break O3 molecules
Stratosphere
Thermal expansions causes __________
tropopause
What is is called when T increases with altitude
Inversions
What is the boundary between the Troposphere & Stratosphere
Tropopause
The tropopause is to be lowest over poles at ______km
8
The tropopause is to be highest over poles at ______km
16-18
when the atmosphere has depth or thickness this is because of
Temperature
Layer mixing occurs at the tropopause ____
folds
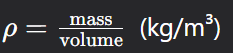
Name this Formula
Density
________ has a downward gravity force that compresses air below it
Density
Their is greater _______ near the surface
Density
If the air temperature remains constant, evaporating water into the air will ________ the dewpoint temperature and _________ the relative humidity.
increase, increase
What unit of pressure is most commonly used by meteorologists?
millibar [mb]
True or False: The troposphere is the layer of the atmosphere where most significant weather occurs.
True
What is the typical surface pressure at sea level?
1000mb
The height of the tropopause varies with latitude. As a result, the deepest storms are likely to develop:
near the equator
True or False: The tropopause can be thought of as a “lid” on Earth’s weather.
True
True or False: Pressure decreases with altitude in the troposphere but increases with altitude in the stratosphere.
False
True or False: Pressure is the weight of the air above a unit area.
True
In general, where in the troposphere is temperature the coldest?
tropopause
What atmospheric gases is the most plentiful in the atmosphere, by percent by volume
Nitrogen [N2]
True or False: As you ascend to the top of a skyscraper in an elevator, your ears may pop due to the increase in pressure.
False
A north wind means that the wind is blowing from:
North to South
What term describes the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere compared to the atmosphere's capacity for moisture at a given temperature?
relative humidity
What term describes the pressure at which the air contains the maximum amount of water vapor possible for the observed temperature and pressure?
saturation vapor pressure
what is saturation vapor pressure
the pressure exerted by a vapor when it is in equilibrium with its liquid phase at a given temperature
What term describes the lowest temperature to which air can be cooled at constant pressure before saturation occurs?
dewpoint temperature
True or False: Relative humidity describes the actual amount of moisture in the air.
False
When dew forms on Earth’s surface, it results in __________ of the air temperature.
decrease
There is more compression and greater density at earths ______
surface
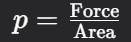
Name this formula (N/m^2)
Pressure
What is the difference between Density and Pressure
Density: how heavy or how much mass something takes up
Pressure: is the force of something (ex. push and pull)
___________— T at which saturation occurs
Dew point
If their is a lot of Air molecules the air is _______
more dense
If their is less of Air molecules the air is _______
less dense
Because of gravity, air molecules are being compressed causing air ________ it to be more dense
below
Pressure is really the ______ of a column of air above a unit area
weight
True or False: force and mass are related
True
The force of an object depends on the:
mass and acceleration of an object
Pressure __________ with increasing altitude
decreases
What are barometers:
Tools used to measure Atmospheric Pressure
What are the types of barometers
Mercury & Aneroid
_________ Barometer: Inverted mercury-filled tube, Higher column indicates greater air pressure
Mercury
_________ Barometer: Collapsible chamber, Expands/compresses proportionally to air pressure
Aneroid
What is the point of Sea Level Pressure Correction
to get accurate reading of the atmosphere
Sea Lvl Pressure is usually ______mb
1013
____mb is added per 100m in elevation when calculating Sea lvl Pressure
10
What is the purpose for Sea Level Pressure Correction:
Enable consistent pressure comparisons across locations, eliminating elevation effect
Surface pressure charts use _________ to plot areas of constant pressure
isobars
___________ Chart: Plot isobars (constant pressure lines), Horizontal pressure variations at sea level
Surface
__________ Chart: Plot isoheights, Identify pressure ridges and troughs, Used above surface level
Upper-Level
________: lines of consistent pressure
isobars
________: lines of consistent heights
isoheights
Upper-Level pressure charts identify _______ of high pressure
ridges
Upper-Level pressure charts identify _______ of low pressure
troughs
What are ridges in pressure charts
high atmospheric pressure
What are troughs in pressure charts
low atmospheric pressure
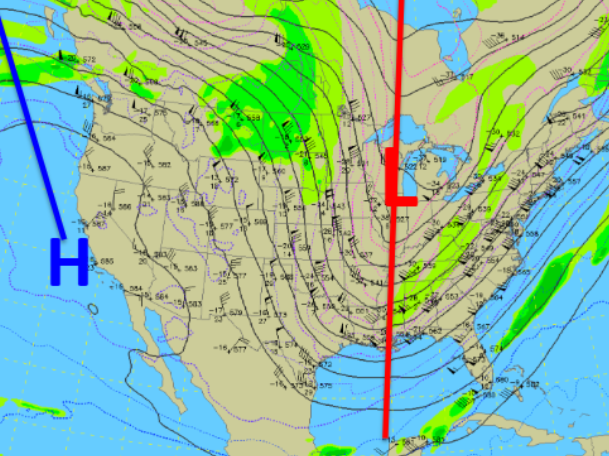
This is an example of
Ridges & Troughs
Pressure can be increased by:
increasing air T & increasing density of air

Name this formula
Ideal Gas Law
_____ measures wind speed and wind vanes
Cup Anemometers
________: indicate wind sped in the direction wind is coming from on a weather map
Wind barbs
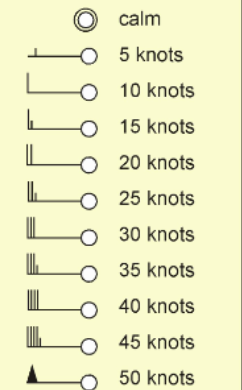
Name this
Wind barbs
_________: measure of how much water vapor the air can hold (saturated)
Relative Humidity