Bio132- Endocrine Part 2
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Hormones circulate throughout the body to only affect what?
Target cells that possess specific hormone receptors
The Effect of hormones is to alter what?
Target cell activity
What are the common hormone effects on target cells
stimulating synthesis of enzymes or other proteins within the cell
activating or deactivating enzymes
inducing secretory activity
stimulating mitosis (cell division)
changing membrane permeability (and/or membrane potential) by opening or closing ion channels
Most amino acid-based hormones target what on cell surfaces
Plasma membrane receptors
What is water soluble?
Amino acid-based hormones (except thyroid hormones)
If it’s water-soluble then what can it not do?
It cannot cross the phospholipid bilayer of plasma membrane
When hormones bind to a membrane receptor then what is activated?
G protein that is coupled to intracellular second messengers (non-protein molecules)
When the G protein is activated what does the second messengers do?
It leads into a cell response
For second messenger systems, a small and brief amount of hormone outside the cell can trigger what?
Amplified and pronounced changes inside the target cell
What is the correct order of the G Protein-coupled hormone receptor and cyclic AMP second messenger mechanism?
Read aloud to remember properly.
Receptor activated G protein
Adenylate cyclase converts ATP to cAMP (2nd messenger)
cAMP activated protein kinases leading to cell response
1st messenger hormone binds to the membrane receptor
G protein activated adenylate cyclase
4-1-5-2-3
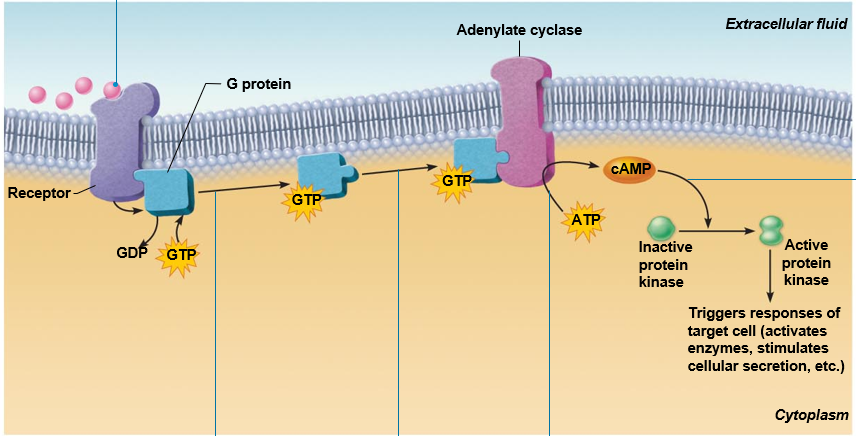
What are each shape in this picture represent?
Hormone
Receptor
G protein
Enzyme
2nd messenger

what do Lipid-soluble steroid hormones do?
Diffuse across the plasma membrane
Bind to intracellular receptors
Activated hormone-receptor complex directly activates what?
Specific genes that lead to protein synthesis
Do thyroid hormones have similar functions to steroids?
Yes
What is the correct order of Direct Gene Activation by Lipid-Soluble Hormones?
Hormone-receptor complex enters the nucleus
Binding initiates transcription of the gene to mRNA
mRNA directs synthesis of new proteins
Hormone-receptor complex binds a specific DNA region
Steroid hormone diffuses through the plasma membrane and binds to an intracellular receptor
5-1-4-2-3
Half-life is what?
Length of time for blood level of a substance (hormone, drug, etc.) to decrease by half
Skin is a source of what?
cholecalciferol (the inactive form of Vitamin D)
What is the active form of vitamin D?
Calciferol
What is the half life in blood for lipid soluble hormones?
Long length of time (mostly metabolized by the liver)
What is the half life in blood for water-soluble hormones?
Short length of time (Mostly removed by kidneys)
Location of receptors for lipid-solubles hormones
Intracellular
Location of receptors for water-solubles hormones
Plasma Membrane
Mechanism of action at target cells for lipid-soluble hormones
Directly activates genes, causing synthesis of new proteins
Mechanism of action at target cells for water-soluble hormones
act through second-messenger systems
Transport in blood in lipid-soluble hormones
Bound to the plasma proteins
Transport in blood in water-soluble hormones
Free in plasma
Lipid-soluble hormone sources
Adrenal cortex, gonads, thyroid gland, and skin
Water-soluble hormone sources
All other endocrine glands
Lipid-soluble hormones
Steroid hormones and thyroid hormones
Water-soluble hormones
Amino acid-based hormones (except thyroid hormone)
What are the three types of stimuli that triggers endocrine glands to synthesize and release hormones?
Humoral stimuli, Neural stimuli, and hormonal stimuli
Humoral Stimuli
Secretes hormones in direct response to levels of key ions or nutrients in the blood
Involves negative feedback
Negative feedback example
Parathyroid glands monitor blood calcium levels
Low blood calcium causes parathyroid glands to secrete parathyroid hormones (PTH), which functions to increase blood calcium
Elevated blood calcium inhibits parathyroid glands from secreting PTH
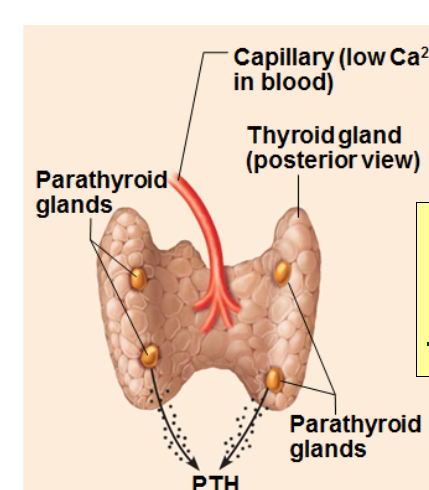
Humoral stimulus
Changing levels of key ions or nutrients in body fluids (humors) triggers hormone release
Neural Stimuli
Hormone release may be stimulated by the nervous system
Example of Neural stimuli
Neurons of the sympathetic nervous system stimulate the adrenal medulla to release epinephrine (E) and norepinephrine (NE) (adrenalin) into the bloodstream
Neural Stimulus
Hormone release caused by neurons
Hormonal stimuli
Tropic Hormones: hormones that control other endocrine glands
Releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones from the hypothalamus regulate the anterior pituitary
Likewise, many hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary control other endocrine organs
Hormonal stimulus
Hormone release caused by other hormones