UNIT 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/149
Last updated 7:07 PM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
1
New cards
Anterior
near the front
2
New cards
Posterior
the back
3
New cards
Inferior
low or lower in position
4
New cards
Superior
higher in position
5
New cards
Medial
situated in the middle
6
New cards
Lateral
near the side
7
New cards
Distal
away from the center of the body or from point of attachment
8
New cards
Proximal
near the center of the body or point of attachment
9
New cards
Superficial
occurring at or on the surface, near the top, right beneath the skin
10
New cards
Deep
far down from the surface
11
New cards
Ventral
the belly or abdominal
12
New cards
Dorsal
toward the back of the human body
13
New cards
Abdominal
the stomach
14
New cards
Antecubital
front of elbow
15
New cards
Axillary
armpit
16
New cards
Brachial
upper arm (muscle)
17
New cards
Buccal
cheek
18
New cards
Calcanel
back of heel
19
New cards
Carpal
wrist
20
New cards
Cephalic
top of head
21
New cards
Cervical
near pelvis
22
New cards
Coxal
hip area
23
New cards
Digital
toes
24
New cards
Femoral
thigh
25
New cards
Gluteal
butt
26
New cards
Inguinal
hernia, by pelvic, right below it
27
New cards
Lumbar
loins of vertebre
28
New cards
Nasal
nose
29
New cards
Occipital
back of head
30
New cards
Olecranal
behind the elbow
31
New cards
Oral
mouth
32
New cards
Orbital
eyes
33
New cards
Patellar
kneecap
34
New cards
Pelvic
near pelvis
35
New cards
Popliteal
area behind knee
36
New cards
Sacral
sacrum
37
New cards
Scapular
head
38
New cards
Sternal
near sternum
39
New cards
Tarsal
area between foot and leg
40
New cards
Thoracic
chest
41
New cards
Umbilical
belly button
42
New cards
Vertebral
vertebrae
43
New cards
Describe an example that demonstrates how one human body system impacts the effectiveness of another.
if the nervous system does not give a signal to certain glands in the endocrine system, hormones do not get released when they should, which can impact body function
44
New cards
Describe three body processes or functions that all humans have in common.
(1) All humans excrete liquid waste through the urinary system, which filters out waste products and recycles water and certain ions back through the body.
(2) All humans' heart muscle contracts, which moves blood throughout the body via arteries and veins.
(3) All humans experience muscle contractions that produce movement. These contractions are caused by the electrical signals from the nervous system.
(2) All humans' heart muscle contracts, which moves blood throughout the body via arteries and veins.
(3) All humans experience muscle contractions that produce movement. These contractions are caused by the electrical signals from the nervous system.
45
New cards
Provide an example of an individual difference that may impact the functioning of one of the human body systems.
Type 1 Diabetes is an auto-immune disorder which impacts the endocrine's system ability to produce insulin. This causes many problems in the body which we talked about last year.
46
New cards
Diseases and/or medical conditions often involve more than one system. In fact, the effects on a secondary system may be as serious as the primary system most associated with the problem.
If there is a problem with the hypothalamus (nervous system), it will affect the pituitary gland (endocrine system) so that the pituitary gland is not able to perform its function (stress, growth, reproduction, lactation, etc.).
47
New cards
What are the benefits of using universal terms and anatomical position to refer to location on the human body? How do they help identify all humans?
It gives medical professionals a common language so that they can refer to a specific part of the human body and other medical professionals will know exactly which location on the body they are referring to. These terms are helpful for all humans. Although there are differences between humans, these anatomical reference points exist in every human being and can therefore be used to identify every human.
48
New cards
What does it mean if a doctor says he/she is about to dissect the distal end of the popliteal artery?
The popliteal region is the back of the knee. Since distal refers to being further away from the point of attachment (as opposed to proximal, which is closer to the point of attachment), then the distal end of the popliteal would be the end furthest away from the hip socket where the leg is connected to the rest of the body. Therefore, it would be the lower portion of the popliteal artery (the part of the back of the knee closest to the foot).
49
New cards
Your friend assures you that anterior and posterior can always be used interchangeably with ventral and dorsal. Politely explain to him/her that this statement is not always true. (HINT: think about what these terms mean for four-legged animals)
Anterior refers to the portion of the body that is situated toward the front. On a human, that would be the front portion of the body. On a dog (for example), the anterior portion would be the portion closest to the head and away from the tail. Ventral refers to the abdominal portion of the body (in a two-legged animal), or the underside portion (in a four-legged animal). Dorsal refers to the back portion of the body (in a two-legged animal), or the upper side portion (in a four-legged animal). So for a dog (or any four-legged animal), anterior is toward the head and ventral means the underside. These terms are not interchangeable for a dog. And likewise, posterior is the region close to the tail and dorsal means the back portion or top side of the dog. So these terms are also not interchangeable. On a human (or any two-legged animal), they are, since anterior and ventral both refer to the front side, and posterior and dorsal both refer to the back side.
50
New cards
Tissue
A group of similar cells designed to carry out a specific function.
51
New cards
Cells
main function: transportation of molecules, conversion of energy, and reproduction
52
New cards
Epithelial Tissue
Protect tissues that lie beneath it, regulation and exchange of chemicals between underlying tissues.
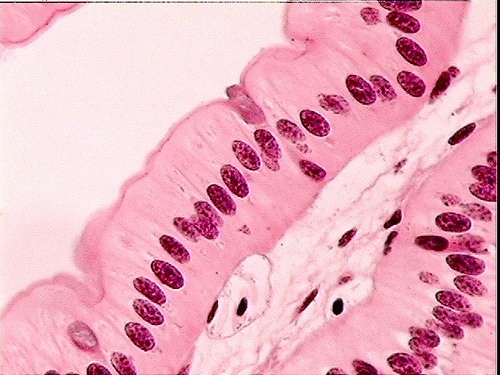
53
New cards
Connective Tissue
example of connective: blood. provides a transport system within our body for oxygen and other important substances. main types of connective: dense connective, loose connective and cartilage.
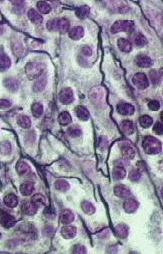
54
New cards
Muscle Tissue
Can be divided into smooth, skeletal, or cardiac. Has ability to relax and contract. Responsible for maintaining posture, physical movement, and movement of internal organs. 650 skeletal muscles in our body.
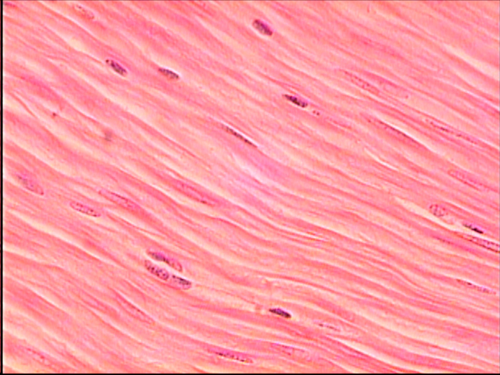
55
New cards
Nervous Tissue
CNS, brain, and spinal cord. Used to react to stimuli and conduct impulses. Made up of neurons. Made up of nerve cell fibers bound together by connective tissue.
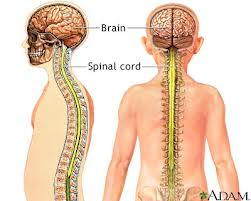
56
New cards
Neurons
Nerve cells that transmit nerve signals to and from the brain. Consists of a cell body with branching signal receivers and axon, which conduct the nerve signal.
57
New cards
Cartilage
(connective tissue) provides support, less rigid than the bone. Allows flexibility of movement, more stability than muscle. Produced by cells called chondroblasts.
58
New cards
Blood
Supplies nutrients to cells.
59
New cards
Tendons
(connective tissue) Usually connects muscle to the bone. Capable of withstanding tension. Similar to ligaments.
60
New cards
Ligaments
(connective tissue) Connect bone to another bone. Serves to hold structures together and keep them stable.
61
New cards
Mandible
lower jaw
62
New cards
Maxilla
upper jaw and mouth
63
New cards
Zygomatic Process
cheek bone
64
New cards
Frontal Bone
forehead
65
New cards
Temporal Bone
underneath the tempal
66
New cards
Parietal Bone
back of skull
67
New cards
Orbicularis Oculi
muscle that closes eyelids, helps you blink, major component of eyelid.
68
New cards
Orbicularis Oris
a muscle that encircles the mouth. controls movement of the mouth and lips.
69
New cards
Temporalis
fan shaped muscle on each side of the head. covers much of the temporal bone. Lifts the lower jaw to open the mouth.
70
New cards
What do you notice is the main difference between the structure of the connective tissues and the structure of the epithelium? Make sure to note the organization of cells in these two tissue types.
The epithelial tissue seemed to be organized in a more closely-packed pattern. The connective tissue was more spread out (although the cells were still connected to one another through the matrix). You may not have seen this, but the epithelial tissue did not have any blood vessels connected to it, whereas the connective tissue did.
71
New cards
Explain how the structure of epithelium and the structure of connective tissue, specifically bone, relate to the function of the tissue.
One main function of epithelial tissue is protection. It forms protective layers or linings in the body. So it makes sense that epithelial tissue cells would be closely packed together. Bone tissue cells are structured in a more spread-out matrix with blood vessels connected to the tissue. This makes sense when considering that the bones need to support while being lightweight. This structure also supports the bone cell function of making new blood cells (enabled by the fact that the tissue has blood vessels that can bring needed supplies to it).
72
New cards
How does the distribution of tissues contribute to our appearance and to our identity?
One major way that we get our appearance is by the shape of our skeleton (determined by the distribution of our bone connective tissue). Our muscle tissue is also unique, which can give us a more or less full figure. Fat (or adipose) tissue, as we have seen on our Maniken, can also determine things like the shape of the cheeks and the eyes.
73
New cards
Describe the role of fat in our cheeks and behind our eyes.
The buccal fat pads have been hypothesized to help infants chew and suckle. They also may help to cushion the temporalis muscle as it makes the chewing motion. And they may help to cushion other facial muscles as well.
The fat behind our eyes serves a similar function to the cheek fat. It protects the eyeball to keep it from being damaged by rubbing up against the bone in the skull.
The fat behind our eyes serves a similar function to the cheek fat. It protects the eyeball to keep it from being damaged by rubbing up against the bone in the skull.
74
New cards
Think about the action of the muscles you have built on your maniken. Describe specific motions that you would not be able to complete if you damaged your temporalis, your orbicularis oculi or your orbicularis oris. How would this affect your ability to communicate?
If the temporalis was damaged, it would be difficult to open and close your mouth. This would obviously make it more difficult to form words. (And it would affect your ability to chew food, not that this has much to do with communication.)
If you damaged your orbicularis oculi, you would not be able to blink or wink. We show many different emotions by raising or lowering our eyelids, so facial expression would be much more difficult without the orbicularis oculi.
If you damaged your orbicularis oris, you would have difficulty opening and closing your mouth, which is crucial for forming words correctly. Also, it would be difficult to communicate to someone that you want to kiss them if you can't pucker your lips.
If you damaged your orbicularis oculi, you would not be able to blink or wink. We show many different emotions by raising or lowering our eyelids, so facial expression would be much more difficult without the orbicularis oculi.
If you damaged your orbicularis oris, you would have difficulty opening and closing your mouth, which is crucial for forming words correctly. Also, it would be difficult to communicate to someone that you want to kiss them if you can't pucker your lips.
75
New cards
Which of the following bones was not used to help us estimate our height?
clavicle
76
New cards
Primary function is communication.
nervous tissue
77
New cards
Primary function is support.
connective tissue
78
New cards
Primary function is movement.
muscle tissue
79
New cards
Primary function is protection.
epithelial tissue
80
New cards
Blood is an example.
connective tissue
81
New cards
Ligaments are an example.
connective tissue
82
New cards
This tissue can be categorized as cardiac, smooth, and skeletal.
muscle tissue
83
New cards
This tissue is made of tightly packed cells which correlate to the tissue's function.
epithelial tissue
84
New cards
Adipose is an example.
connective tissue
85
New cards
Which bone of the body would best help you determine the gender of an individual?
the pelvis, because the angle of the bones that meet at the pubic symphysis is larger in females than in males
86
New cards
Which of the bones in our skeletal hunt best helped determine the ethnicity of your skeleton?
the skull, because the shape of the eye sockets, the nasal index, and the prognathism can all help identify ethnicity
87
New cards
Is the humerus the best bone to use for height estimation?
No, the femur would be better because it is the largest leg bone, and it contributes greatly to the height of an individual
88
New cards
Skull
the head
89
New cards
Sternum
top of rib cage
90
New cards
Radius
near front of elbow, arm
91
New cards
Phalanges
fingers and toes
92
New cards
Rib Cage
ribs
93
New cards
Tibia
larger bone in leg
94
New cards
Fibula
smaller bone in leg
95
New cards
Vertebral Column
vertebrae
96
New cards
Scapula
armpit
97
New cards
Carpals
very bottom of hand/wrist
98
New cards
Metacarples
right below fingers
99
New cards
Pelvic Girdle
right above pelvis
100
New cards
Femur
thigh bone