bio plant nutrition
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Why are plants important
Primary food source
Prevents soil erosion
Main oxygen producer
Autotrophs
Organisms that can make their own food using simple sources like carbon dioxide and water
Photo-autotrophs
Green plants use the energy of sunlight to make organic molecules (eg,glucose) from carbon and water
Heterotroph
Organisms that requires complex organic molecules that have been preprocessed by other life forms. Eg .animals
Only energy source for Photosynthesis
Light energy
Photosynthesis definition
Light energy from the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll in the leaf , together with carbon dioxide and water ,glucose and oxygen is produced
Benefit of photosynthesis on humans
Provide oxygen, food + fuel energy
How does photosynthesis benefit plants
Enables plants to produce molecules, which are storehouses for energy
to show starch is produced during photosynthesis ( starch test)
Remove a leaf from a plant that has been placed in bright light
Place the leaf in boiling water ( kill the leaf /weaken cell structure)
Place the lead in boiling ethanol (this will remove the chlorophyll )
Dip the leaf in boiling water (make it soft)
Spread the leaf on a tile and add iodine to the leaf
Have starch = iodine will turn Blue black / no starch iodine turns yellowish brown
To test for importance of chlorophyll
Use variegated ( part of the leaf have chlorophyll, other part does not) leaf, remove the starch, put it in sunlight , test for iodine
Methods to de- starch leaf
Place in darkness for 2 days
Boil in ethanol (removes chlorophyll)
Importance of carbon dioxide procedure
2 pots of de starched plants are enclosed in plastic bags , then placed in sunlight. soda lime / sodium hydroxide is added inside to one of the pots to absorb carbon dioxide ( acidic gas). After 3 hours, iodine test .
To investigate whether light is required for photosynthesis
A lot of plant is destarched (place in darkness for 2 days)
One of the leaves is masked by an aluminium foil partially
Then the plant is exposes to light
After 3 hours, iodine test
effects of light intensity on rate of photosynthesis
Plant in the dark = indicator turns yellow (more co2 as only respiration occurs)
Plant in light = indicator turns purple (less co2 as photosynthesis [co2–>o2]and respiration [o2–>co2]occurs
OG indicator colour —> pink/red
Chemical equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O = C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2
In the chloroplast, water and carbon dioxide combine to form glucose
Conditions for photosynthesis
Chlorophyll
Carbon dioxide
Water
Sunlight energy (any light but green light)
Suitable soil and air temperature
Limiting factor def
Any factor that affects a process if its quantity is altered ( anything that restricts rate of reaction)
Limiting factors of photosynthesis
Light intensity
Temperature
Carbon dioxide
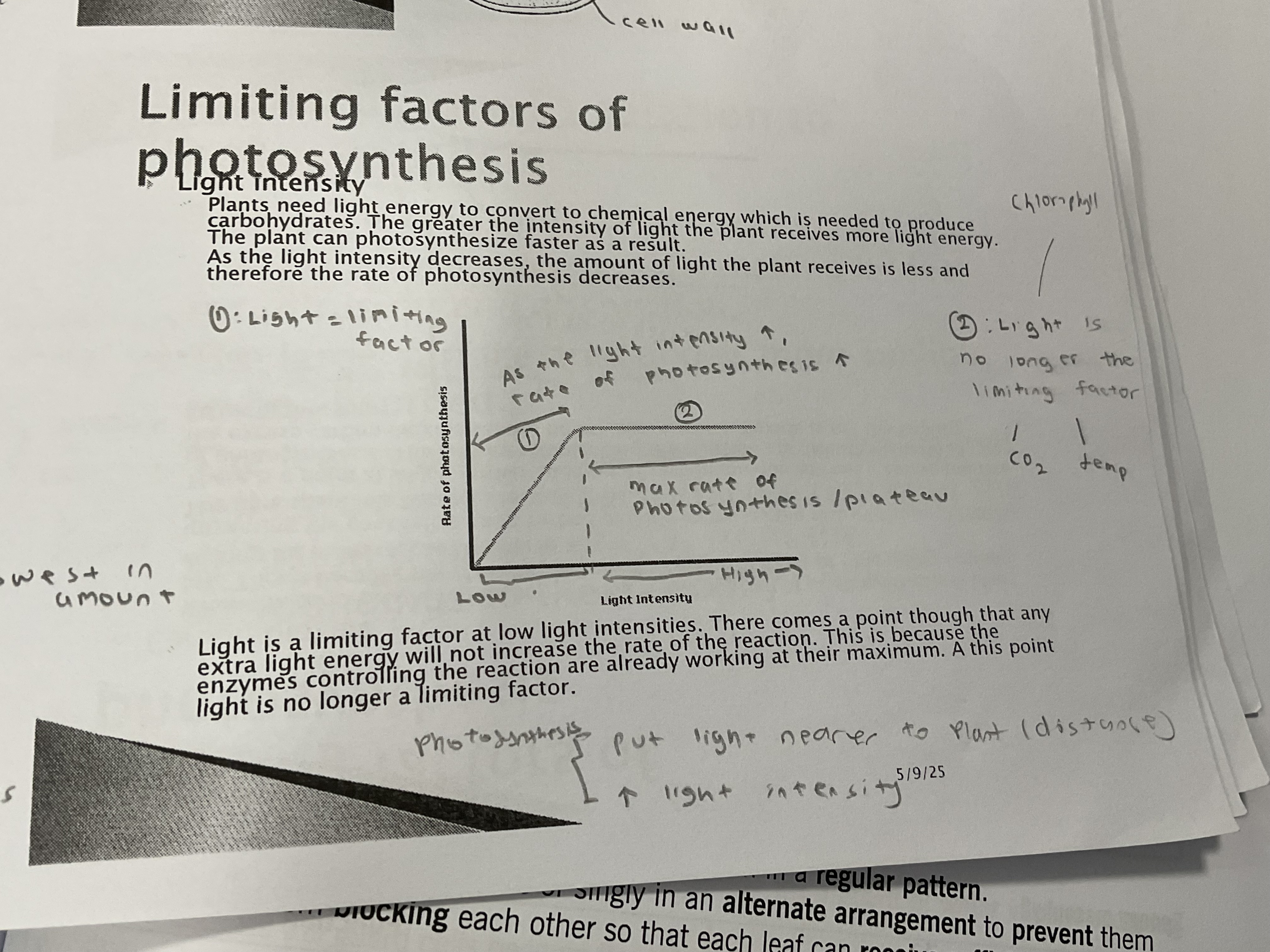
Light intensity
Greater the light intensity =the plant can photosynthesise faster
when the line is straight = max rate of photosynthesis , light intensity is not the limiting factor
Put the light nearer to the experiment or increase the amount of light intensity
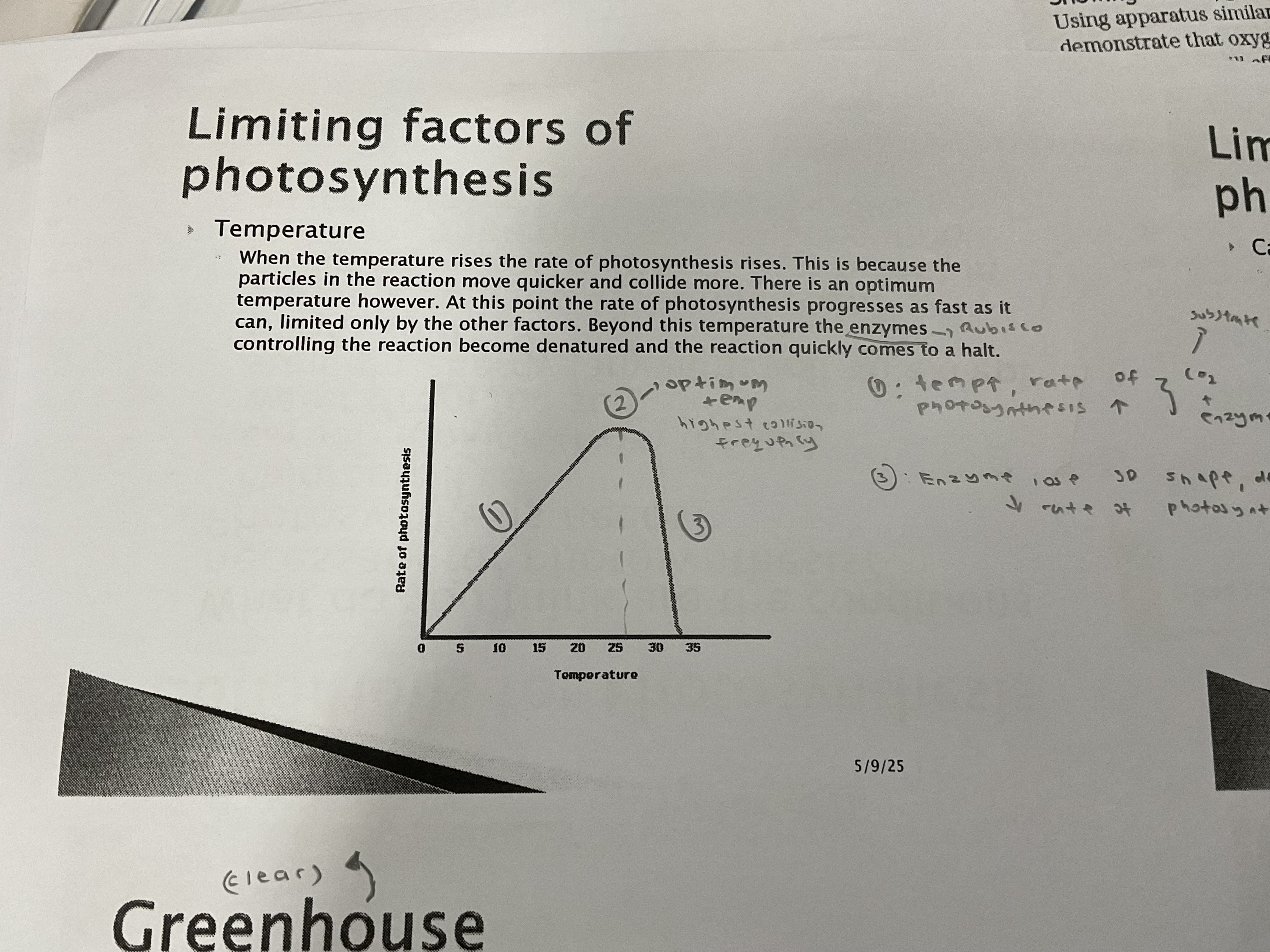
Temperature
Temp increase = rate of photosynthesis increase
because the particles in the reaction move quicker and collide more
Beyond optimum temp , enzymes controlling the reaction will become denatured and the reaction will stop

Carbon dioxide
Concentration of carbon dioxide low = low rate of photosynthesis ( plant spends a certain amount of time doing nothing, waiting for more co2 to arrive )
when line is straight = the enzymes controlling the reaction are already maximise, additional amount of carbon dioxide will not increase rate of photosynthesis , co2 not limiting factor
Greenhouse
Can artificially increase carbon dioxide to increase crop yield , help to prevent crop damage due to pests and diseases
Structure of leaf
Leaf stalk = petiole
Leaf blade = lamina
Veins = support blade ( contains vascular bundles to transport water , minerals and glucose )
vascular bundles =xylem + phloem
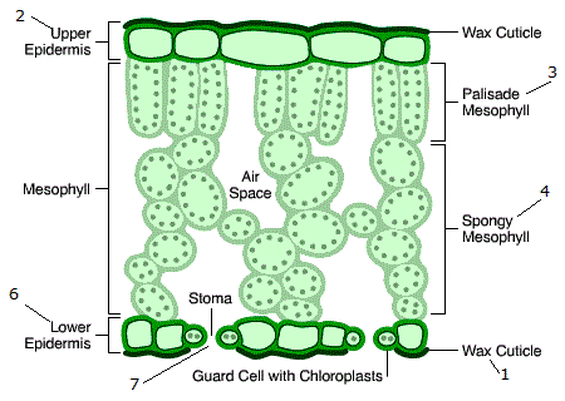
Leaf structure
top to bottom
Cuticle
Upper epidermis
Mesophyll cells
palisade mesophyll
Spongy mesophyll
Bundle sheath (outer), vascular bundle ( inner)
Lower epidermis
stoma
Guard cell
Cuticle
Advantages of thin and large surface area to volume ratio leaves
Large surface area = ideal for diffusion and absorption , allow more sunlight to be absorbed
Thin = so that mesophyll cells are close to the surface, reducing the diffusion distance of carbine dioxide from the surrounding to the mesophyll cell
Cuticle
Made of wax, waterproof , secreted by cells of upper epidermis, reduce rate of evaporation
Upper epidermis
Cells are thin and transport to allow light to pass through (no chloroplast) , act as a barrier to disease organisms
Palisade mesophyll
Contains numerous chloroplasts, main region for photosynthesis
Spongy mesophyll
has air spaces = allows rapid diffusion of carbon dioxide and oxygen in and out of the mesophyll cell
Has chloroplasts
Contains vascular bundle
Lower epidermis
guard cells that surround the stomata = regulate the opening and closing of stomata for diffusion of carbon dioxide and oxygen in and out of the leaf
Has cuticle
Protective layer
Gas exchange into and out of the leaf
Stomata
Regulates the loss of water vapour (transpiration) x
Use of glucose produced from photosynthesis
Glucose is converted to protein , proteins are components of cytoplasm
Glucose is converted into other sugars which can be found in fruit
Glucose is broken down during respiration to release energy which can be used by living things to carry out daily activities
Glucose can be converted into starch used for storage in plants
Stomata
Opens in the day (sunlight) closes at night (no carbon dioxide intake is needed , plant is short of water causing guard cells to become flaccid )
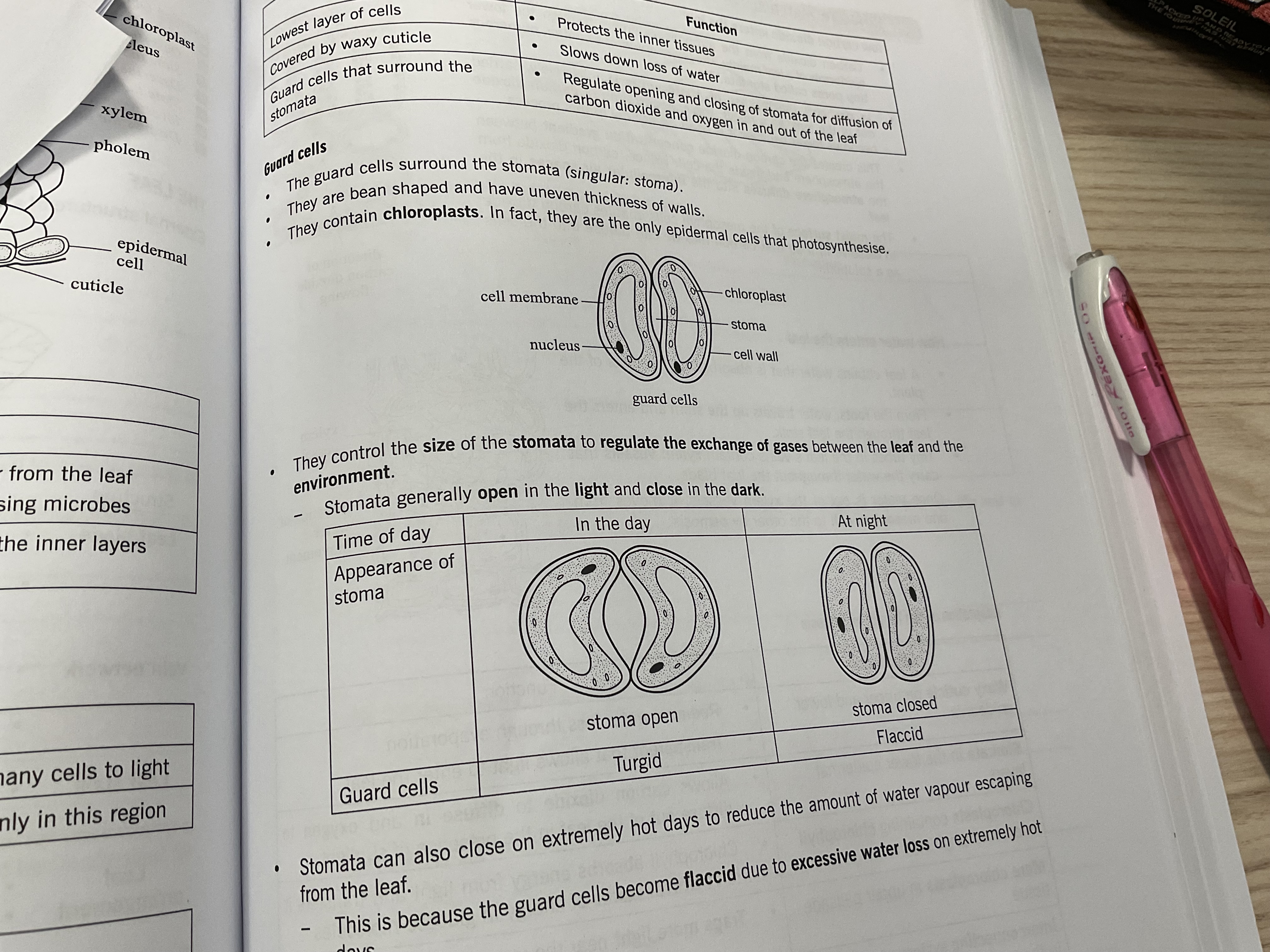
Guard cells
cells that occur in pairs and control the size of stomata to regulate the exchange of gases
When turgid (filled with water) = one side of the guard cell is thicker than the other and does not stretch . Guard cells buckle and stomata opens (day)
When flaccid = guard cells sag and stomatal opening close ( water exits) (night)
How does water deficiency affect the guard cells
Become flaccid and stomata closes , stimulated by the presence of abscisic acid
Plants without nitrate ions
Stunted growth , fewer smaller leaves
Nitrate deficiency
Plants without magnesium
Small plants , yellowish eaves (chlorosis)
Magnesium deficiency