Osteomyelitis
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PEBC
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
osteomyelitis
inflammation of the bone marrow and surrounding bone caused by infection
hematogenous infection
through the blood
typically monomicrobial: Staph tried stinky salmonella poo
S. aureus
Streptococci
IV drug user = pseudomonas
sickle cell anemia = Salmonella
tuberculosis
age of onset = <20 yr (children), > 50 yr
sites = long bones, vertebrae
risk factors:
bacteria travel via blood to certain bone areas, colonize and cause infection
contiguous
next to (adjacent site)
common pathogens: Sick Guys Prefer Pretty Klean Environments Barefoot
S. aureus
G- bacilli:
Pseudomonas
Proteus,
Klebsiella,
E coli
anaerobic = B. fragilis
age of onset = >40
location = femur, tibia, skull, mandible
clinical presentation:
pain, tenderness, swelling, erythema and drainage in area of infection
fever (can be absent)
unstable joint
risk factors:
surgery
trauma (penetrating injury/ open fractures)
cellulitis/ abscess
vascular insufficiency
most common - when blood doesnt get to an area or pools in an area
polymicrobial: Some Bad Circulation Gets Abscessed
S. aureus
Beta hemolytic streptococci
Coagulase negative staphylococci
Gram negative and anaerobic organisms
Usually mixed infections
age of onset = >40
location = feet
clinical presentation:
localized pain
swelling
drainage
ulcer formation
fever and leukocytosis may be absent
risk factors:
diabetes
PVD (peripheral vascular disease)
goals of therapy
cure infection
eliminate undesirable signs and symptoms
prevent complications of disease and therapy
reduce recurrence risk of infection
non pharm
surgical incision and drainage/ debridement
principles of therapy
empiric therapy
NOT INDICATED UNLESS: sepsis, Inability to culture
duration of therapy:
4 - 8 weeks antibiotics (longer if retained hardware)
switch to oral abx once pt stabilized = normal labs, decreased pain, no complications (no necrosis)
need to have high bioavailability and bone penetration and should be tolerated
Pain management
acetaminophen, NSAIDs, Opioids
empiric therapy options
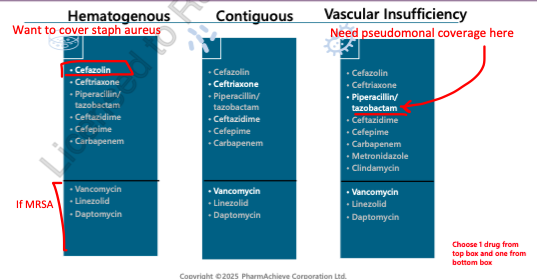
treatment for hematogenous and contiguous osteomyelitis
targeted initial tx:
Staph aureus (MSSA) = Cefazolin, cloxacillin
Staph aureus (MRSA) = Vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid
long term therapy of linezolid has been associated with thrombocytopenia, anemias, peripheral neuropathy! not really a good option
P. aeruginosa = Ceftazidime, Pip/tazo, Cefepime, Meropenem, Imipenem/Cilastin
IV therapy x 7-10 days
if pt responds, consider step down to oral x 6 weeks
generally avoid PO beta lactams
duration = at least 4-6 weeks (oral or IV) or until ESR/ CRP normalized
shorter course in children = 20 days
treatment of vascular insufficiency osteomyelitis
empiric treatment:
Pip-Tazo +/ - Vanco
[Clindamycin or Metronidazole] + [Ceftriaxone/ Cefotaxime] +/ - Vanco
Carbapenem + / - Vanco
IV tx or oral therapy for ≥6 weeks
example oral options:
cephalexin, cefadroxil, cloxacillin (not preferred)
clindamycin or Metronidazole + Levofloxacin
Moxifloxacin
Amoxicillin/ clavulanate
TMP/SMX + / - Clindamycin or Metronidazole
Doxycycline + FQ
Linezolid + FQ
therapeutic alternatives
await microbiology prior to treatment
surgical removal of necrotic bone and poorly vascularised tissue b/c you cant cure it otherwise
IV antibiotics post-surgery - antibiotics selection based on the infection site
Parenteral therapy for 6-8 weeks, then 3-12 months oral
must monitor for side effects since will use for very extended period
surgeon must also do regular re-evaluations
monitoring
ensure pt responding to IV antibiotic (WBC, fever decreased, less drainage, reduced CRP)
monitor Cr, trough levels q7 days if using vancomycin to avoid nephrotoxicity
if using aminoglycosides: monitor levels and avoid long term use due to nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity