CNS Lecture 24-26: Pharmacotherapy of Bipolar Disorder
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
What is bipolar disorder?
chronic disorder characterized by shifts in mood that can range from severe depression to extreme mania
Bipolar disorder is more common in ____________.
women
Men typically have __________ onset of bipolar symptoms than women.
earlier
What is the median age of onset for bipolar disorder?
25 years
What are the risk factors of bipolar disorder?
**** 1st degree relative with BD ****
Genetics
Drug/alcohol use
Major life events for at risk individuals
Early adulthood
What is the BIGGEST risk factor for bipolar disorder?
having a 1st degree relative with BD
What are the adverse health behaviors associated with BD?
Substance use
Suicide
Risky behaviors
About how many patients with BD will attempt suicide at least once?
25-50%
What other diseases should be ruled OUT before diagnosing bipolar disorder?
***Substance-induced mood disorder*****
Schizophrenia
MDD
Hypothyroidism
Anemia
Neurologic illness
What is the #1 most important thing to rule out before diagnosing BD?
whether it was induced by a substance
If someone presents with mania (current or historical), what is their most likely diagnosis?
Bipolar 1
If someone presents with hypomania (current or historical), what is their most likely diagnosis?
Bipolar 2
If someone presents with depression and mania (assuming you ruled out MDD), what could they be diagnosed with?
Mixed features
If someone presents with depression and hypomania (assuming you ruled out MDD), what could they be diagnosed with?
Bipolar 2
Which type of bipolar disorder has the worst outcomes and highest suicide risk?
Mixed features
Bipolar 1
manic episode +/- depressive episode
What does a patient need to have in order to be diagnosed with bipolar 1?
Manic episode
Bipolar 2
hypomania and depression
Cyclothymic disorder
hypomanic + depression that are not severe enough to meed criteria for the DSM
What are the DSM criteria for a manic episode?
at least 1 week of sx almost daily
abnormally elevated, expansive, or irritable mood
Abnormally and persistently increased goal-directed activity
How long do manic symptoms have to last to be considered mania?
at least 1 week with symptoms almost daily
DIG FAST
Symptoms of Mania
Distractibility
Irresponsibility
Grandiosity
Flight of Ideas
Activity and Agitation
Sleep (decreased need)
Talkativeness
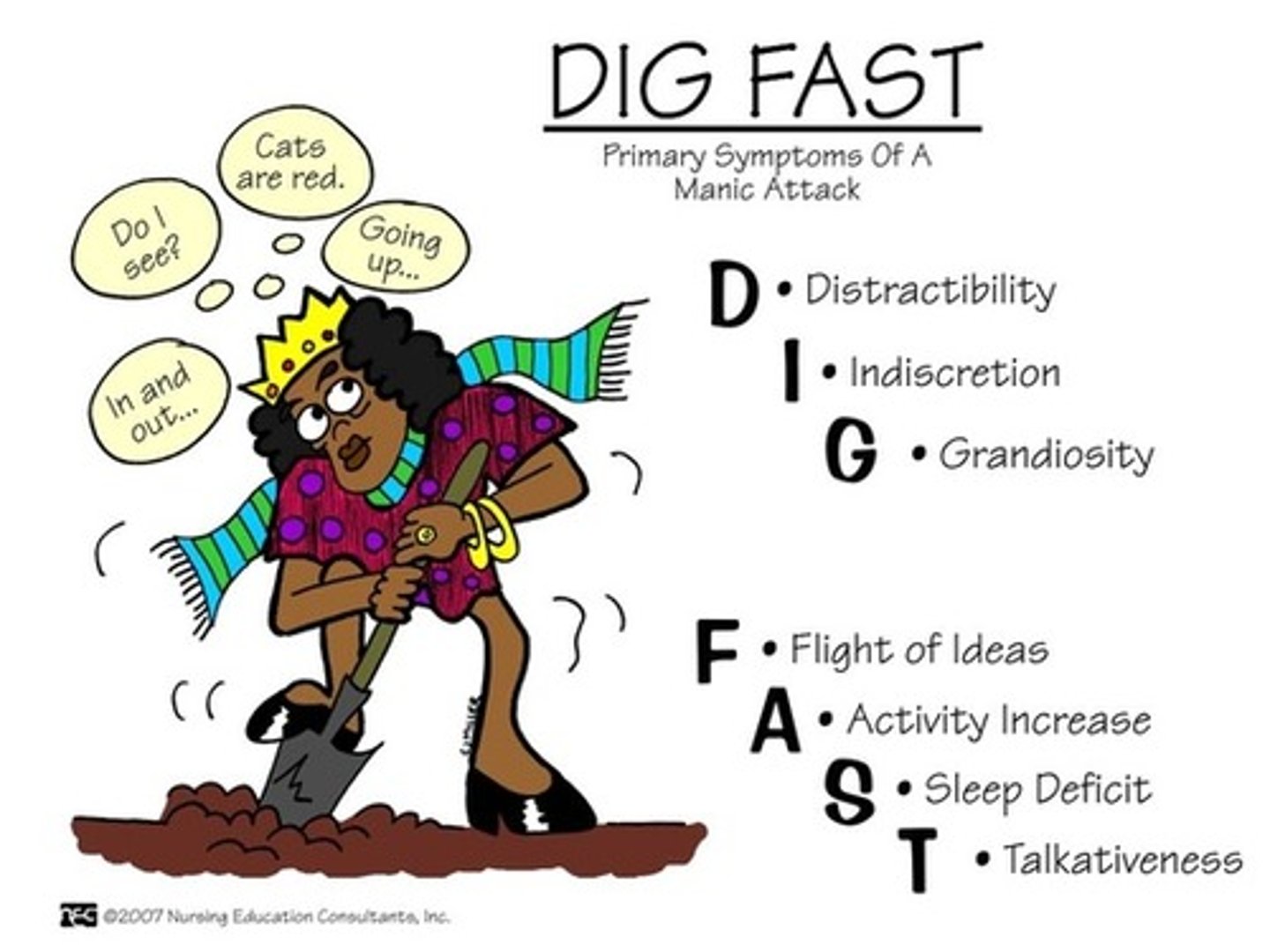
A manic episode is what to the brain?
TOXIC
How many DIG FAST symptoms does the DSM state a patient has to have for a manic episode?
3 or more
Hypomania is exclusive to what?
Bipolar 2
What are the DSM criteria for a hypomanic episode?
at least 4 days of sx
3+ DIG FAST symptoms (not as severe)
NOT SEVERE ENOUGH TO BE HOSPITALIZED
What is the main distinguisher between a hypomanic episode and a manic episode?
Mania is severe enough to require hospitalization whereas hypomania is NOT
Does Lithium work for BD with mixed features?
NO
What is the worst case scenario in BD?
Mixed features
When is BD considered to be rapid cycling?
4 or more mood episodes per year
Besides mixed features, which other type of BD has a poor prognosis?
Rapid cycling
Are antipsychotics mood stabilizers?
NO
What is a mood stabilizer?
anti-manic
What are the treatment options for bipolar disorder?
Lithium
Carbamazepine
Valproic acid
Lamotrigine
SGAs
When is Lithium used in BD?
Maintenance of BD
Acute mania
Lithium __________ the risk of suicide.
decreases
Lithium is considered to be the MOST effective medication at what?
Preventing re-hospitalization in BP1
Preventing mania relapse
What level of Lithium is considered to be subtherapeutic?
< 0.6 mmol/L
What level of Lithium is too high and can cause ADRs?
>0.8 mmol/L
What is the approximate Lithium level we want to achieve for acute mania?
0.8 - 1.5 mEq/L
What is the approximate Lithium level we want to achieve for maintenance?
0.6-1 mEq/L
At what level of Lithium would we see someone with GI upset and/or tremors?
1.5-2 mEq/L
At what level of Lithium would we see someone with confusion or somnolence?
2-2.5 mEq/L
At what level of Lithium would we see someone with seizures or even death?
>2.5 mEq/L
What are the different levels of Lithium toxicity?
GI upset/tremor = 1.5-2 mmol/L
Confusion/somnolece = 2-2.5 mmol/L
Seizures/death = >2.5 mmol/L
When should Lithium levels be drawn?
8-12 hours after last dose
How long until Li reaches steady state?
About 5 days
What drugs interact with Lithium?
Diuretics (Loops, Thiazides)
NSAIDs
ACE/ARBs
Caffeine/Theophylline
Lithium is considered a salt, so it relies heaily on what two things?
Fluid balance
Renal Function
What labs MUST be monitored for a patient on Lithium?
**SCr and BUN
**Thyroid fxn
CBC and Electrolytes
EKG
Pregnancy
ADRs of Lithium
Hand tremor (intention)
Acne
Non-toxic goiter
Weight gain
GI upset
Cardiac
What is the BBW of Lithium?
lithium toxicity - monitor therapy
What are important counseling points with Lithium?
Dietary consistency
Drug interactions
S/sx of Toxicity
Can patients take Lithium while pregnant?
No - Ebstein Anomaly
Can patients take Lithium while breastfeeding?
NOOOO
Carbamazepine is ALWAYS ___________ ________.
second line
What is Carbamazepine used for?
2nd line for Acute manic or mixed episodes
Carbamazepine therapy is __________ effective than Lithium.
less
Carbamazepine has ________ effect on release to depression.
little
Carbamazepine is considered to be a metabolism ___________.
inducer
What drugs interact with Carbamazepine?
Birth control (less effective)
Inducers
Clozapine
Can you combine Clozapine with Carbamazepine?
NO - both affect WBC counts
What parameters need to be monitored with Carbamazepine (triple C)?
CBC (platelets, WBC)
CMP (Na, LFTs)
ADRs of Carbamazepine
Rash
Leukopenia
Thrombocytopenia
Hyponatremia
BBW of Carbamazepine
Anemia or agranulocytosis
SJS/TENs
What gene puts people at higher risk of SJS with Carbamazepine?
HLA-B*1502 (asain people)
If a female patient of childbearing age needs to be on Carbamazepine, they should also be on what medication?
Birth control
What are the counseling points to hit with Carbamazepine?
~2 months for effect
Lab monitoring
Drug interactions
Rash education
Avoid sudden d/c
What is the indication for Valproic Acid?
Acute mania
Mixed episodes
Maintenance
What is the max dose of VPA?
60 mg/kg/day
What dose do we normally target with Valproic acid?
~20 mg/kg
Which BD treatment is weight based dosing?
Valproic acid
Valproate should be used very __________ in people who ovulate/menstruate.
CAUTIOUSLY
What drugs increase levels of VPA?
Inhibitors
Guanfacine
Salicylates
Topiramate
What drugs decrease levels of VPA?
Inducers
Carbamazepine
Carbapenems
Phenytoin
Rifampin
VPA is a metabolism _____________.
Inhibitor
What lab parameters must be monitored with VPA?
Pregnancy
CBC
CMP
Which BD treatment is hepatically burdensome?
VPA
ADRs of VPA
GI upset
Sedation
Tremor
Thrombocytopenia
BBW of VPA
Hepatic failure
Pancreatitis
Which medication is category C for migraines but category D for BD?
VPA
What are the counseling points to hit wtih VPA?
Pregnancy and Lactation
Avoid sudden d/c
Follow-up
Drug interactions
Lamotrigine is used for what?
bipolar depression
Does Lamotrigine treat mania?
NO
Can Lamotrigine be used as maintenance monotherapy for BD 1?
NO
What is critical with Lamotrigine?
Titration
How is Lamotrigine titrated?
Start at 25 mg/day then increase by 25mg every 2 weeks to a target dose of 200mg
If a drug regimen includes Carbamazepine, what should be done with the Lamotrigine dose?
Double dose
If a drug regimen includes VPA/Divalproex, what should be done with the Lamotrigine dose?
half the dose
What is the drug interaction between birth control and Lamotrigine?
BC decreases the levels of Lamotrigine
What should be monitored with Lamotrigine?
Renal fxn
LFTs
ADRs of Lamotrigine
Rash (titrating too quickly)
BBW of Lamotrigine
SJS/TEN
What are important counseling points for Lamotrigine?
Medication adherence
Pregnancy and lactation
Skin Self Examinations
How long can a patient miss their dose of Lamotrigine before having to restart titration?
5 days or more
What drug(s) are considered to be the mainstay of bipolar disorder treatment?
SGAs
Which treatments can be used for mania?
Olanzapine
Quetiapine
Risperidone
Ziprasidone
Abilify
Asenapine (?)
Which treatments can be used for bipolar depression?
Olanzapine
Quetiapine
Lamotrigine
Which treatments can be used for mixed features?
Olanzapine
Quetiapine
Risperidone
Ziprasidone
Abilify
Asenapine (?)
Olanzapine
Zyprexa