Lecture Exam 3 Study Guide BIO2252K
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Metabolism, digestive system, urinary system, and O2 and CO2 transport
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
How does oxygen bind to hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin changes shape to increase its affinity (binding strength).
It also changes shape when oxygen is released, which decreases its affinity, making it harder to bind.
What are the factors that influence hemoglobin saturation?
PO2 (partial pressure of oxygen)
PCO2 (partial pressure of carbon dioxide)
temperature
blood pH
What does it mean when hemoglobin is fully saturated?
Hemoglobin carries 4 oxygen molecules
What does it mean when hemoglobin is partially saturated?
Hemoglobin only carries 1-3 oxygen molecules
What is the venous reserve?
The oxygen remaining in venous blood that can still be used
How is CO2 primarily transported?
As a bicarbonate ion
What is the enzyme that facilitates the formation and breakdown of carbonic acid (H2CO3)?
Carbonic anhydrase
How is the chloride shift involved in making stomach acid through parietal cells?
As Co2 enters the parietal cells, it combines with water (H20) to form carbonic acid (H2Co3), which splits into bicarbonate and hydrogen by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase. The chloride shift facilitates the exchange of bicarbonate out of the cell for chloride ions. The chloride ion and hydrogen ion leave the parietal cell into the lumen and combine to form hydrochloric acid in the gastric lumen.
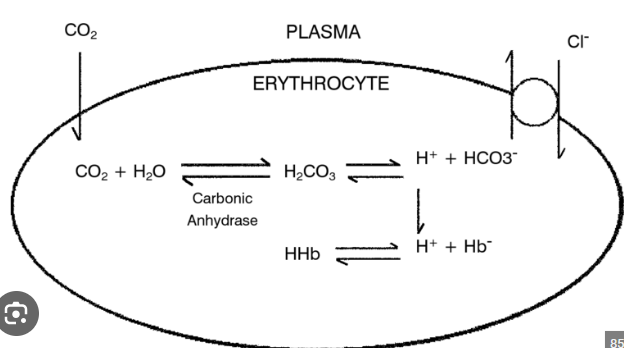
How is CO2 transported in pulmonary capillaries?
As oxygen is used in tissues and goes through glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, Co2 becomes a byproduct.
Co2 then enters a red blood cell and combines with water (H20) to form carbonic acid (H2Co3). It is then split into an H+ ion and bicarbonate (HCo3-) by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase.
What is the oxygen saturation curve?
A graph that graphs the percentage of hemoglobin against the partial pressure of oxygen concentrations.
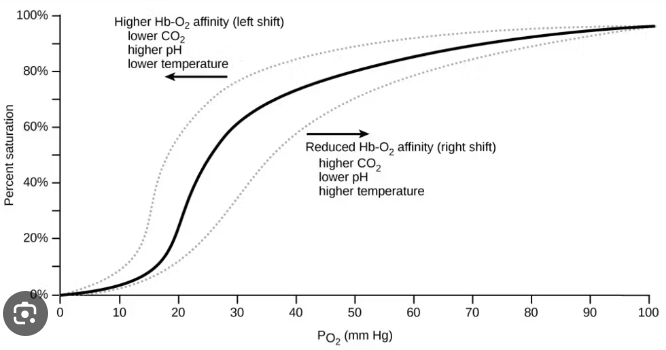
What will make the oxygen saturation curve shift right?
When there is an enhancement of oxygen unloading (metabolically active tissues)
What will make the oxygen saturation curve shift left?
When there is an enhance in oxygen loading (lungs)
Which direction will the oxygen saturation curve shift if there is an increase in temperature?
It will shift right as it increases.
Which direction will the oxygen saturation curve shift if the pH level increases?
It will shift left as it increases
Which direction will the oxygen saturation curve shift if the partial pressure of oxygen decreases?
It will shift right as it decreases.
Which direction will the oxygen saturation curve shift if the partial pressure of CO2 decreases?
It will shift left as it decreases
What is it called when the oxygen-saturated curve shifts right?
Bohr’s effect
What is the role of carbohydrates?
It is the primary source of energy (makes ATP)
Where are carbohydrates primarily found?
Plants. They’re the natural sugars
What are carbohydrates?
Anything that has cellulose (insoluble) fibers and pectin (soluble—example: apples).
What is the most abundant form of lipids?
Triglycerides (“3 tailed”)
Where are lipids found?
In saturated and unsaturated fats
Which organ breaks down lipids?
The liver.
What do lipids offer?
Protection, insulation, and fuel storage
What are complete proteins?
Proteins that have all 9 essential amino acids: ex= animal products
What are incomplete proteins?
Proteins that lack some essential amino acids: ex= nuts, and cereal
What are proteins?
The building blocks of our cells and structures.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism?
Aerobic metabolism uses oxygen, while anaerobic metabolism does not.
What are the by products of glycolysis?
Breaks down glucose into pyruvate.
How does anaerobic metabolism work?
It uses glycolysis and fermentation, which breaks down pyruvate into either lactic acid or ethanol
Where are lactic acid and ethanol from?
Lactic acid is from bacteria cells
Ethanol is from yeast cells
What are the steps of aerobic metabolism?
Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation
What are the steps of anaerobic metabolism?
Glycolysis and fermentation
What is the process of forming new glucose from noncarbohydrate sources that occurs in the liver?
Gluconeogenesis
What is the breakdown of glucose into pyruvate?
Glycolysis
What is “the making of glycogen”?
Glycogenesis
What stimulates glycogenesis?
Rising ATP levels inhibit the breakdown of glucose; the excess glucose is formed in glycogen by glyogenesis.
What is the breakdown of glycogen via glycogen phosphorylase to low blood glucose levels?
Glycogenolysis
What are the byproducts of aerobic metabolism?
Carbon dioxide and water
What are the byproducts of anaerobic metabolism?
Lactic acid and ethanol
What is lipid metabolism also called, and what is it?
Beta oxidation, which is the combination of lipolysis and lipogenesis
What is protein metabolism also called?
Amino acid catabolism or deamination
What are ketone bodies?
A marker for poor carbohydrate metabolism
What is the absorptive state?
Also known as the “fed state.” This is when the nutrients are being absorbed. Lasts 4 hours after eating.
In the liver, what are carbohydrates being converted into?
Glycogen or fat
What is the enzyme responsible for breaking down lipids?
Lipoprotein lipase
In the liver, what are proteins absorbed into?
Into keto acids that can be used in the Krebs cycle, stored, or used for protein synthesis.
What is the hormone for glucagon?
Hyperglycemic hormone
What is the hormone for insulin?
Hypoglycemic hormone
What is the postabsorptive state?
Also called the “fasting state.” This is after you absorb the nutrients and your body is actively using reserves rather than your intake to maintain glucose levels
What enzyme breaks down carbohydrates, and what produces them?
The enzyme amylase. Salivary glands produce saliva that contains the enzyme amylase.
How are lipids broken down? What is the enzyme that further breaks down lipids?
The liver makes bile, which packages lipids and prepares them for lipid breakdown.
The enzyme lipase further breaks down lipids.
How are proteins broken down?
Stomach acid, which denatures the proteins.
What enzyme breaks protein down into amino acids?
Proteases
What is the alimentary canal?
Muscular tube that runs from mouth to anus
Includes: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, small and large intestine, and anus
What are the accessory digestive organs?
Teeth, tongue, gall bladder, and digestive glands
What are the digestive glands, and what do they do?
Salivary glands, liver, and pancreas.
They produce secretions that help break down food
What are the three salivary glands?
Parotid
Submandibular
Sublingual
What does the pharynx do for digestion?
Passes food down to the esophagus and prevents food from entering the trachea
What does the esophagus do?
Brings food down (by peristalsis) to the stomach.
What connects the esophagus and stomach?
Gastroesophageal (cardiac) sphincter. It opens and closes to prevent backflow back up the esopagus.
What does peristalsis do?
Pushes food down with muscle contraction. Mainly used in upper digestive system
What does the stomach do?
Breaks down proteins
What connects the stomach and the small intestine?
Pyloric sphincter
What connects the small intestine and large intestine?
Iliocecal sphincter/valve
What is the function of the liver?
Produces bile
What is the function of the gallbladder?
Stores bile
What does the pancreas do?
Delivers bicarbonate/pancreatic juice to the small intestine to raise pH levels (more basic)
What is the vasa recta?
The blood vessel below the distal convulated tubule. They form concentrated urine.
What organs use segmentation?
Intestines
What are the digestive cells of the digestive system?
Mucous neck cells
Parietal cells
Chief cells
Enteroendocrine cells
What do mucous neck cells do?
Produce mucus to prevent stomach acid from burning a hole in the stomach.
What do parietal and chief cells do?
They make hydrochloric acid
What do enteroendocrine cells do?
They are signaling cells that tell the parietal cells and chief cells what to do.
What is the pH level in the stomach?
1.5-3.5
What is the pH level in the intestines?
6-7.5
How does segmentation work?
It holds food longer to absorb all the nutrients. It cups, dumps, repeatedly. Occurs after a meal.
What transports urine from kidneys to urinary bladder?
Ureters
What stores urine?
Urinary bladder
What transports urine out of the body?
Urethra
Which organ filters blood, regulates salt and water balance, and maintains consistent filtration rate?
Kidneys
What collects urine from the pyramid papillae?
Minor calyces
What collects urine from minor calyces?
Major calyces
What is composed of medullary pyramids?
Renal medulla
How does blood flow in the kidneys?
Afferent arteries carry blood to the glomerulus and efferent arteries carry blood away.
Which renal artery has a wider diameter?
Afferent artery
What are the two parts of a kidney nephron?
Renal corpuscle/capsule and renal tubule
What is the renal corpsucle’s role and what does it consist of?
Filtration. Consists of glomerulus and bowman’s capsule
What is the renal tubule’s role and what does it consist of?
Formation of urine. Consists of proximal convoluted tubule, nephron loop, and distal convoluted loop.
How do the kidneys concentrate and dilute urine?
Blood enters glomerulus through the afferent artery and creates filtrate (filtered blood). Concentrated filtrate (less water) goes down the PCT. As the concentrated filtrate goes down the descending nephron loop, sodium channels open to make Na+ ions leave to make the filtrate more diluted. When the filtrate goes up the ascending nephron loop, water channels open to leave to make the filtrate concentrated again and to level out the amount of sodium that was released. Filtrate reaches the distal convoluted tubule and forms urine. Urine stays in the collecting ducts until it is released through the ureters.
How does ADH play a role in water balance?
It sends a signal to the brain to know how many Na+ or water channels need to be opened in the kidney nephron.
Where is ADH released from?
Adrenal glands
What activates ADH in the kidney nephron?
Macula densa cells
What are the byproducts of the Krebs cycle?
CO2, NADH, FADH2, and ATP
What are the byproducts of oxidative phosphorylation?
Water and ATP