Comptia A+ 220-1201 Core 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
2.1 A series of moving vans
• Efficiently move large amounts of data
- Use a shipping truck
• The network topology is the road
- Ethernet, DSL, cable system
• The truck is the Internet Protocol (IP)
- We've designed the roads for this truck
• The boxes hold your data
- Boxes of TCP and UDP
• Inside the boxes are more things
- Application information
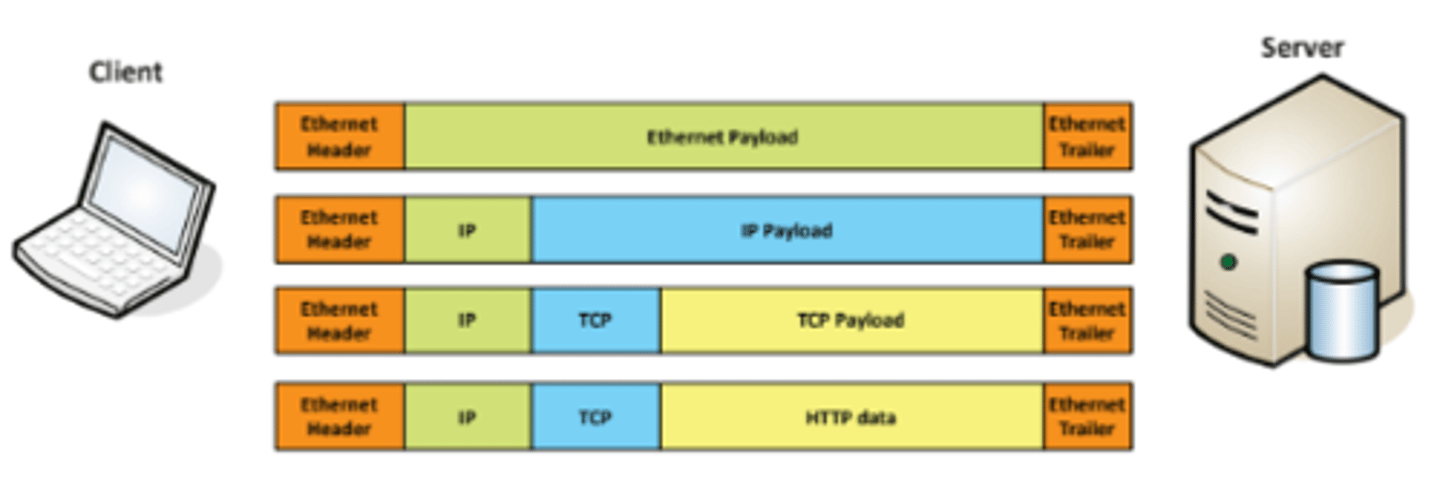
2.1 TCP and UDP
• Transported inside of IP
- Encapsulated by the IP protocol
• Two ways to move data from place to place
- Different features for different applications
• OSI Layer 4
- The transport layer
• Multiplexing
- Use many different applications at the same time
- TCP and UDP
2.1 TCP - Transmission Control Protocol Communication
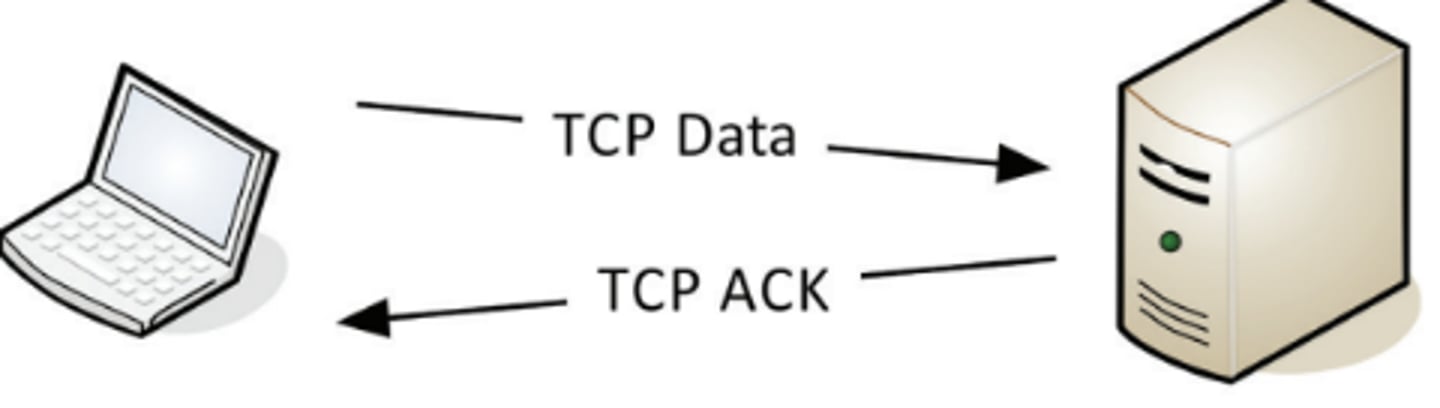
2.1 TCP - Transmission Control Protocol
• Connection-oriented
- A formal connection setup and close
• "Reliable" delivery
- Recovery from errors
- Manages out-of-order messages or retransmissions
• Flow control
- The receiver can manage how much data is sent
2.1 UDP - User Datagram Protocol Communication
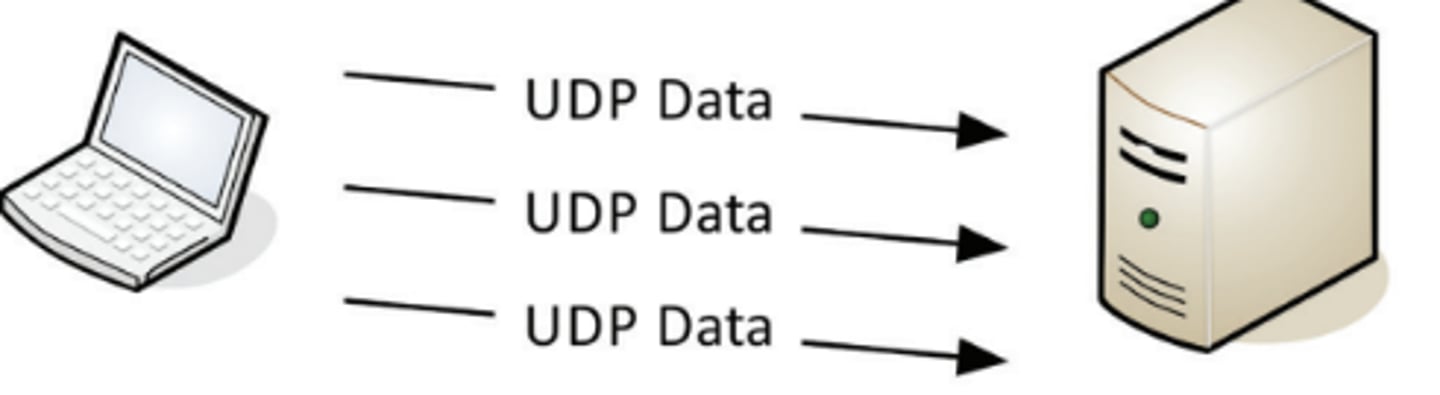
2.1 UDP - User Datagram Protocol
• Connectionless - No formal open/close to the connection
• "Unreliable" delivery
- No error recovery, no reordering of data or retransmissions
• No flow control
- Sender determines the amount of data transmitted
2.1 Why would you ever use UDP?
• Real-time communication
- There's no way to stop and resend the data
- Time doesn't stop for your network
• Connectionless protocols
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
- TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol)
• The data might not get through
- The application keeps track and decides what to do
- It might not do anything
2.1 Communication using TCP
• Connection-oriented protocols prefer a "return receipt"
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
- SSH (Secure Shell)
• The application doesn't worry about
out of order frames or missing data
- TCP handles all of the communication overhead
- The application has one job
2.1 Speedy delivery
• The IP delivery truck delivers from one (IP) address to
another (IP) address
- Every house has an address, every computer
has an IP address
• Boxes arrive at the house / IP address
- Where do the boxes go? - Each box has a room name
• Port is written on the outside of the box
- Drop the box into the right room
2.1 Lots of ports
• IPv4 sockets
- Server IP address, protocol, server application port #
- Client IP address, protocol, client port number
• Non-ephemeral ports - permanent port numbers
- Ports 0 through 1,023 - Usually on a server or service
• Ephemeral ports - temporary port numbers
- Ports 1,024 through 65,535
- Determined in real-time by the client
2.1 Port number (how many)
• TCP and UDP ports can be any number between 0 and 65,535
• Most servers (services) use non-ephemeral
(not-temporary) port numbers
- This isn't always the case - it's just a number.
• Port numbers are for communication, not security
• Service port numbers need to be "well known"
• TCP port numbers aren't the same as UDP port numbers
2.1 Port numbers
• Well-known port number
- Client and server need to match
• Important for firewall rules
- Port-based security
• A bit of rote memorization
- Becomes second nature after a while
• Make sure you know port number, protocol,
and how the protocol is used
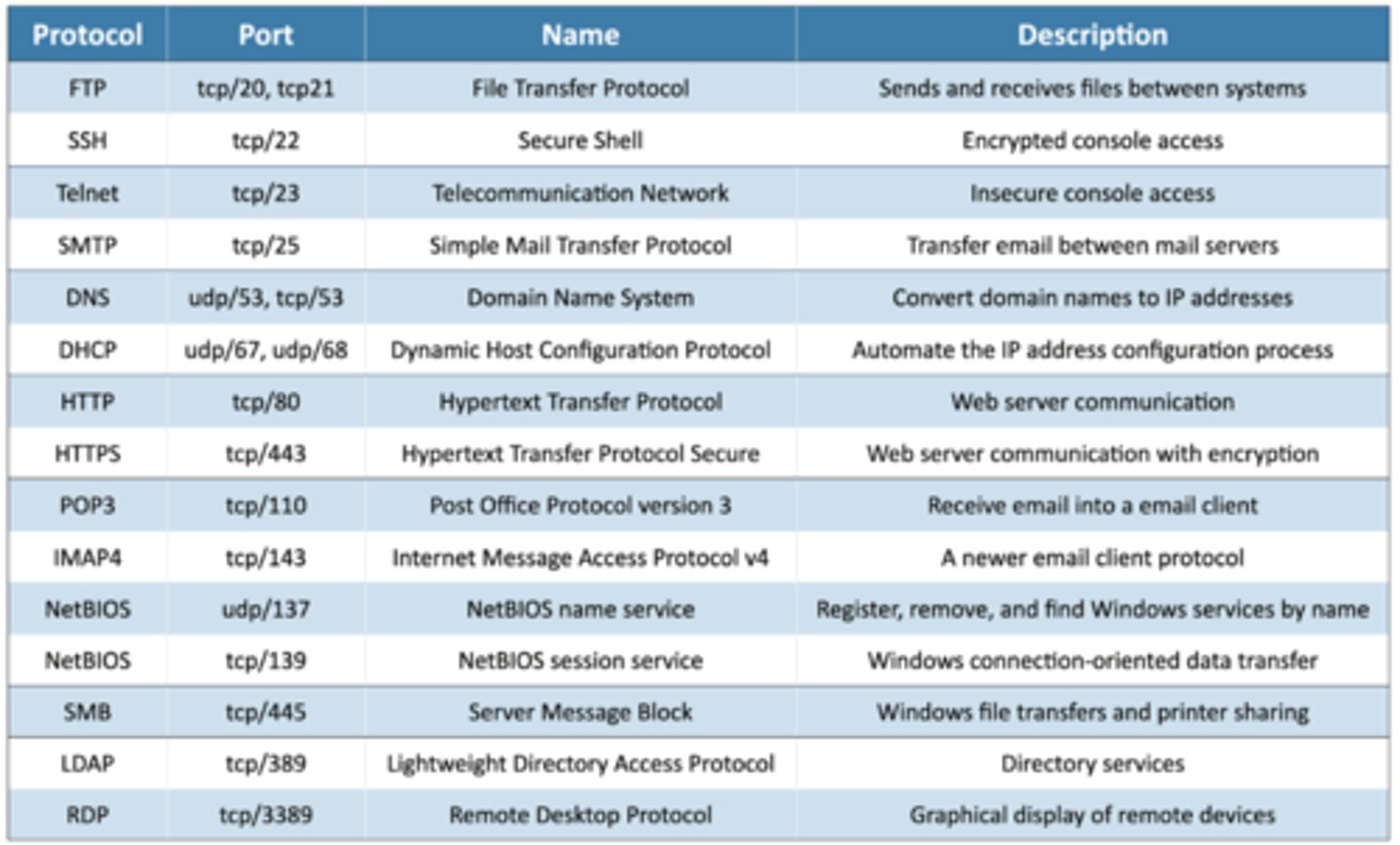
2.1 FTP - File Transfer Protocol
• tcp/20 (active mode data), tcp/21 (control)
- Transfers files between systems
• Authenticates with a username and password
- Some systems use a generic/anonymous login
• Full-featured functionality - List, add, delete, etc.
2.1 SSH - Secure Shell
• Encrypted communication link - tcp/22
• Looks and acts the same as Telnet
2.1 Telnet
• Telnet - Telecommunication Network - tcp/23
• Login to devices remotely
- Console access
• In-the-clear communication
- Not the best choice for production systems
2.1 SMTP - Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
• SMTP - Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
- Server to server email transfer
- tcp/25
• Also used to send mail from a device to a mail server
- Commonly configured on mobile devices and
email clients
• Other protocols are used for clients to receive email
- IMAP, POP3
2.1 DNS - Domain Name System
• Converts names to IP addresses - udp/53
- www.professormesser.com = 162.159.246.164
• These are very critical resources
- Usually multiple DNS servers are in production
2.1 DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
• Automated configuration of IP address, subnet mask and
other options
- udp/67, udp/68
- Requires a DHCP server
- Server, appliance, integrated into a SOHO router, etc.
• Dynamic / pooled
- IP addresses are assigned in real-time from a pool
- Each system is given a lease and must renew at set
intervals
• DHCP reservation
- Addresses are assigned by MAC address in the DHCP
server
- Manage addresses from one location
2.1 HTTP and HTTPS
• Hypertext Transfer Protocol
- Communication in the browser
- And by other applications
• In the clear or encrypted
- Supported by nearly all web servers and clients
2.1 POP3 / IMAP
• Receive emails from an email server
- Authenticate and transfer
• POP3 - Post office Protocol version 3
- tcp/110
- Basic mail transfer functionality
• IMAP4 - Internet Message Access Protocol v4
- tcp/143
- Includes email inbox management from multiple clients
• SMB - Server Message Block
• Protocol used by Microsoft Windows
- File sharing, printer sharing
- Also called CIFS (Common Internet File System)
• Using NetBIOS over TCP/IP
(Network Basic Input/Output System)
- udp/137 - NetBIOS name services (nbname)
- tcp/139 - NetBIOS session service (nbsession)
• Direct over tcp/445 (NetBIOS-less)
- Direct SMB communication over TCP without
the NetBIOS transport
2.1 LDAP/LADPS
• LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)
- tcp/389
- Store and retrieve information in a network directory
- Commonly used in Microsoft Active Directory
2.1 RDP - Remote Desktop Protocol
• Share a desktop from a remote location over tcp/3389
• Remote Desktop Services on many Windows versions
• Can connect to an entire desktop or just an application
• Clients for Windows, macOS, Linux, Unix, iPhone, Android,
and others
2.1 Common Ports
2.2 Wireless technologies
• IEEE standards
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
- 802.11 committee
- Everyone follows these standards
• Also referenced as a generation
- 802.11ac is Wi-Fi 5
- 802.11ax is Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E (extended)
- 802.11be is Wi-Fi 7
- Future versions will increment accordingly
2.2 802.11 technologies
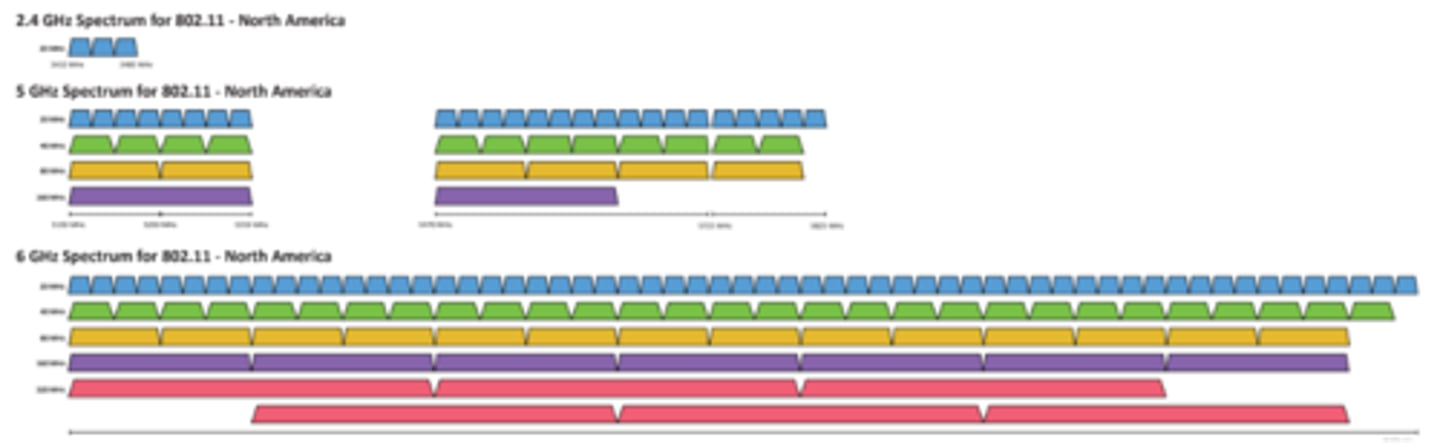
• Frequencies
- 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz - Sometimes a combination
• Channels
- Groups of frequencies, numbered by the IEEE
- Frequencies are managed by governing entities
- Using non-overlapping channels would be optimal
• Bandwidth
- Amount of frequency in use
- 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, 160 MHz, etc.
2.2 Bluetooth
• Remove the wires
- Headsets, speakers, keyboards / mice
• Uses the 2.4 GHz range
- Unlicensed ISM
(Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band
- Same as 802.11
• Short-range
- Most consumer devices operate to about 10 meters
2.2 RFID (Radio-frequency identification)
• It's everywhere
- Access badges
- Inventory/Assembly line tracking
- Pet/Animal identification
- Anything that needs to be tracked
• Radar technology
- Radio energy transmitted to the tag
- RF powers the tag, ID is transmitted back
- Bidirectional communication
- Some tag formats can be active/powered
2.2 NFC (Near field communication)
• Two-way wireless communication
- Builds on RFID, which is mostly one-way
• Payment systems - Major credit cards, online wallets
• Bootstrap for other wireless
- NFC helps with Bluetooth pairing
• Access token, identity "card"
- Short range with encryption support
2.2 Wireless Network Technologies
2.3 DNS server
• Domain Name System
- Convert names to IP addresses
- And vice versa
• Distributed naming system
- The load is balanced across many different servers
• Usually managed by the ISP or IT department
- A critical resource
2.3 DHCP server
• Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- Automatic IP address configuration
• Very common service
- Available on most home routers
• Enterprise DHCP will be redundant
- Usually running on central servers
2.3 File share
• Centralized storage of documents,spreadsheets,
videos, pictures, and any other files
- A fileshare
• Standard system of file management
- SMB (Server Message Block),
Apple Filing Protocol (AFP), etc.
• The front-end hides the protocol
- Copy, delete, rename, etc.
2.3 Print server
• Connect a printer to the network
- Provide printing services for all network devices
• May be software in a computer
- Computer is connected to the printer
• May be built-in to the printer
- Network adapter and software
• Uses standard printing protocols
- SMB (Server Message Block), IPP (Internet
Printing Protocol), LPD (Line Printer Daemon)
2.3 Mail server
• Store your incoming mail
- Send your outgoing mail
• Usually managed by the ISP or the IT department
- A complex set of requirements
• Usually one of the most important services
- 24 x 7 support
2.3 Syslog
• Standard for message logging
- Diverse systems, consolidated log
• Usually a central logging receiver
- Integrated into the SIEM
• You're going to need a lot of disk space
- No, more. More than that.
2.3 Web server
• Respond to browser requests
- Using standard web browsing protocols - HTTP/HTTPS
- Pages are built with HTML, HTML5
• Web pages are stored on the server
- Downloaded to the browser
- Static pages or built dynamically in real-time
2.3 Authentication server
• Login authentication to resources
- Centralized management
• Almost always an enterprise service
- Not required on a home network
• Usually a set of redundant servers
- Always available
- Extremely important service
2.3 Database servers
• Database table storage
- Save information in columns and rows
- Similar to a spreadsheet
• Relational database
- Link tables together
- These links are relationships
- Flexible and fast
• Structured Query Language (SQL)
- Access data using a standard language
- Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, etc.
2.3 NTP servers
• The time of day is more important than you might think
- Encryption, logins, backups, log timestamps
- Everything needs to work from the same clock
• NTP server
- Listens on udp/123
- Responds to time requests from NTP clients
• NTP client
- Requests time updates from NTP server
- Daily synchronization is common
2.3 Spam gateways
• Unsolicited messages
- Email, forums, etc.
• Various content
- Commercial advertising
- Non-commercial proselytizing
- Phishing attempts
• Significant technology issue
- Security concerns, resource utilization,
storage costs, managing the spam
• Unsolicited email
- Stop it at the gateway before it reaches the user
- On-site or cloud-based
2.3 All-in-one security appliance
• Next-generation firewall, Unified Threat
Management (UTM) / Web security gateway
• URL filter / Content inspection
• Malware inspection
• Spam filter
• CSU/DSU
• Router, Switch
• Firewall
• IDS/IPS
• Bandwidth shaper
• VPN endpoint
2.3 Load balancers
• Distribute the load
- Multiple servers - Invisible to the end-user
• Large-scale implementations
- Web server farms, database farms
• Fault tolerance
- Server outages have no effect - Very fast convergence
2.3 Proxy server
• An intermediate server
- Client makes the request to the proxy
- The proxy performs the actual request
- The proxy provides results back to the client
• Useful features
- Access control, caching, URL filtering, content scanning
2.3 SCADA / ICS
• Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition System
- Large-scale, multi-site Industrial Control Systems (ICS)
• PC manages equipment
- Power generation, refining,
manufacturing equipment
- Facilities, industrial, energy, logistics
• Distributed control systems
- Real-time information
- System control
• Requires extensive segmentation
- No access from the outside
2.3 Legacy and embedded systems
• Legacy systems
- Another expression for "really old"
- May also be "really important"
- Learning old things can be just as important as
learning the new things
• Embedded systems
- Purpose-built device
- Not usual to have direct access to
the operating system
- Alarm system, door security, time card system
2.3 IoT (Internet of Things) devices
• Appliances
- Refrigerators
• Smart devices
- Smart speakers respond to voice
• Air control
- Thermostats, temperature control
• Access
- Smart doorbells
• May require a segmented network
- Limit any security breaches
2.4 Domain Name System
• Translates human-readable names
into computer-readable IP addresses
- You only need to remember
www.ProfessorMesser.com
• Hierarchical
- Follow the path
• Distributed database
- Many DNS servers
- 13 root server clusters (over 1,000 actual servers)
- Hundreds of generic top-level domains (gTLDs) -
.com, .org, .net, etc.
- Over 275 country code top-level domains (ccTLDs) -
.us, .ca, .uk, etc.
2.4 DNS lookup
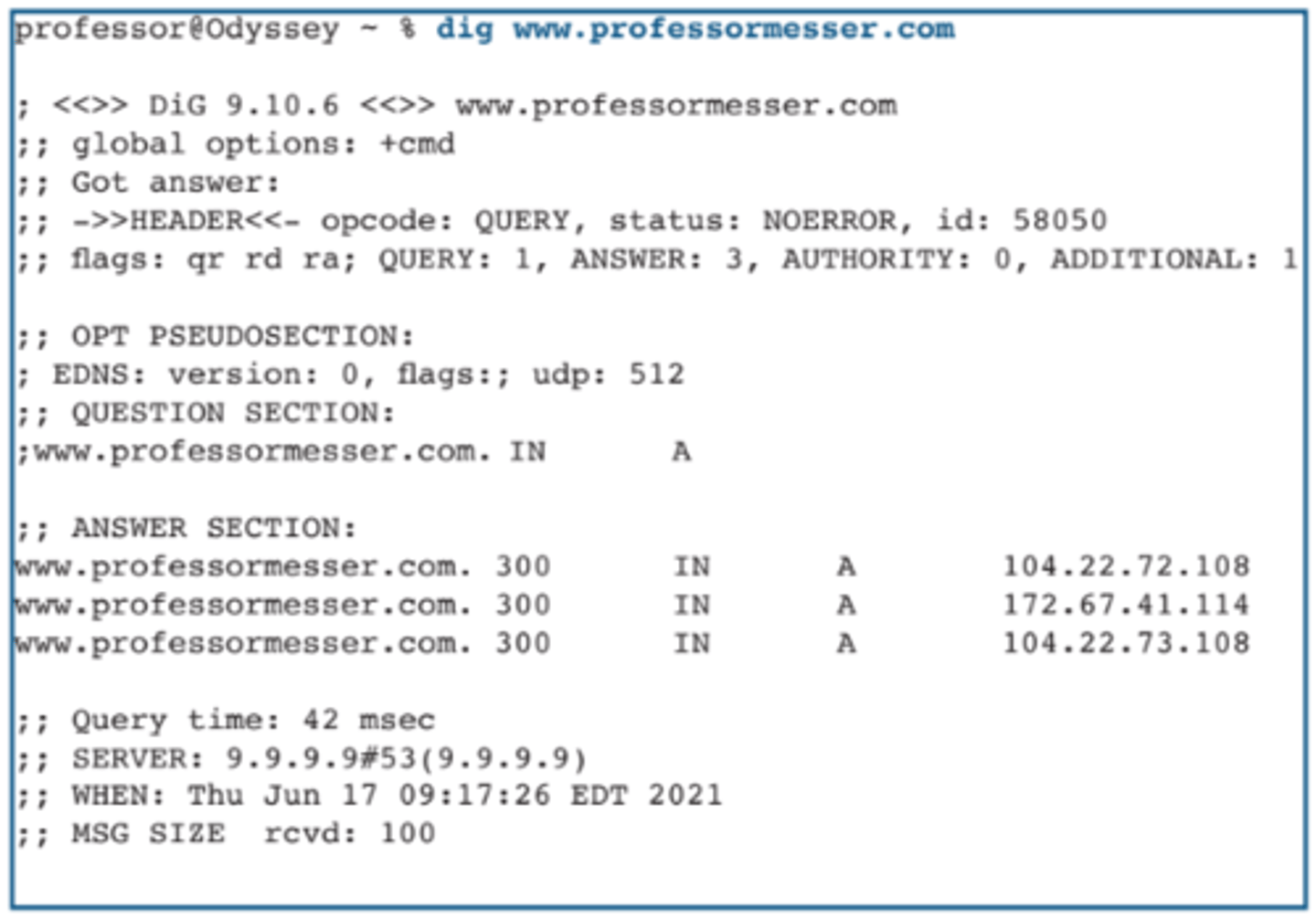
2.4 The DNS hierarchy
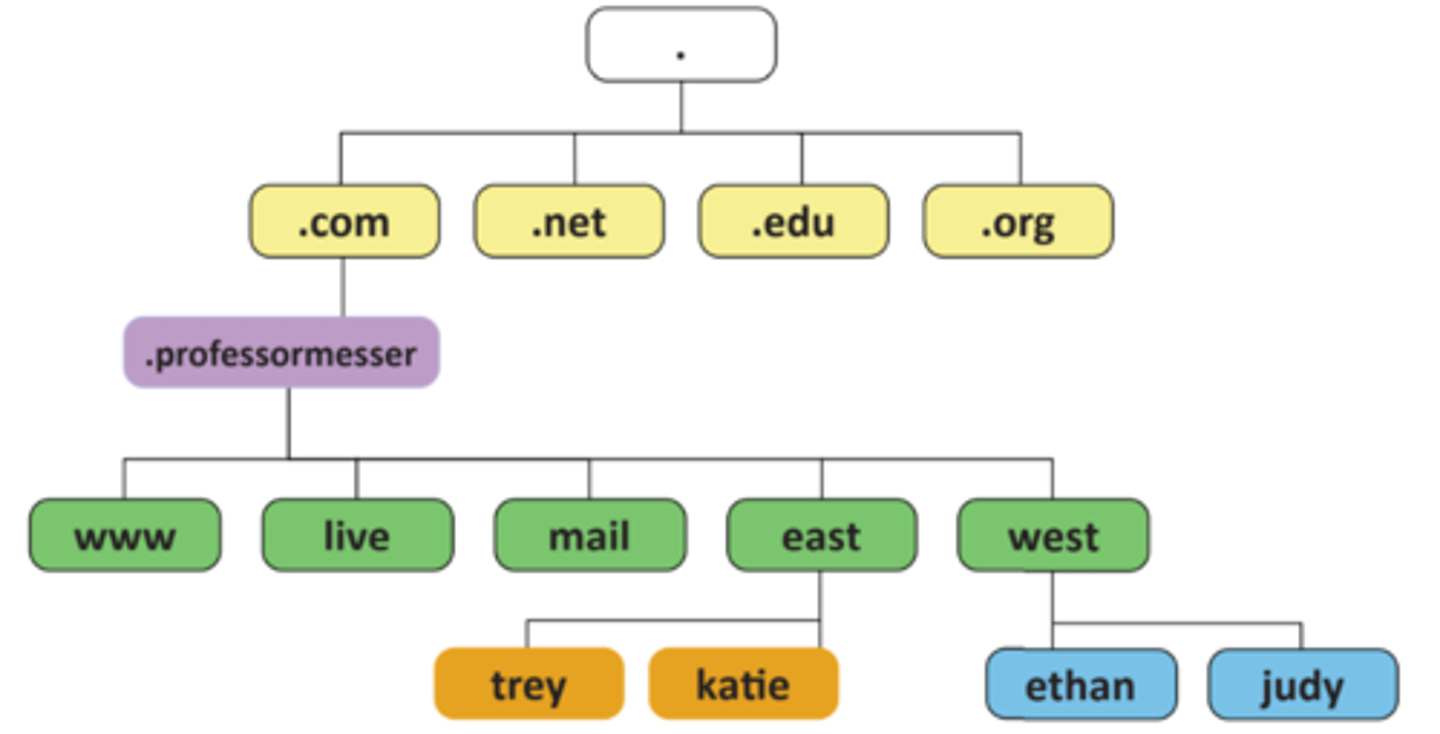
2.4 DNS records
• Resource Records (RR)
- The database records of domain name services
• Over 30 record types
- IP addresses, certificates, host alias names, etc.
• These are important and critical configurations
- Make sure to check your settings, backup, and test!
2.4 Address records (A) (AAAA)
• Defines the IP address of a host
- This is the most popular query
• A records are for IPv4 addresses
- Modify the A record to change the
host name to IP address resolution
• AAAA records are for IPv6 addresses
- The same DNS server, different records
2.4 Canonical name records (CNAME)
• A name is an alias of another, canonical name
- One physical server, multiple services

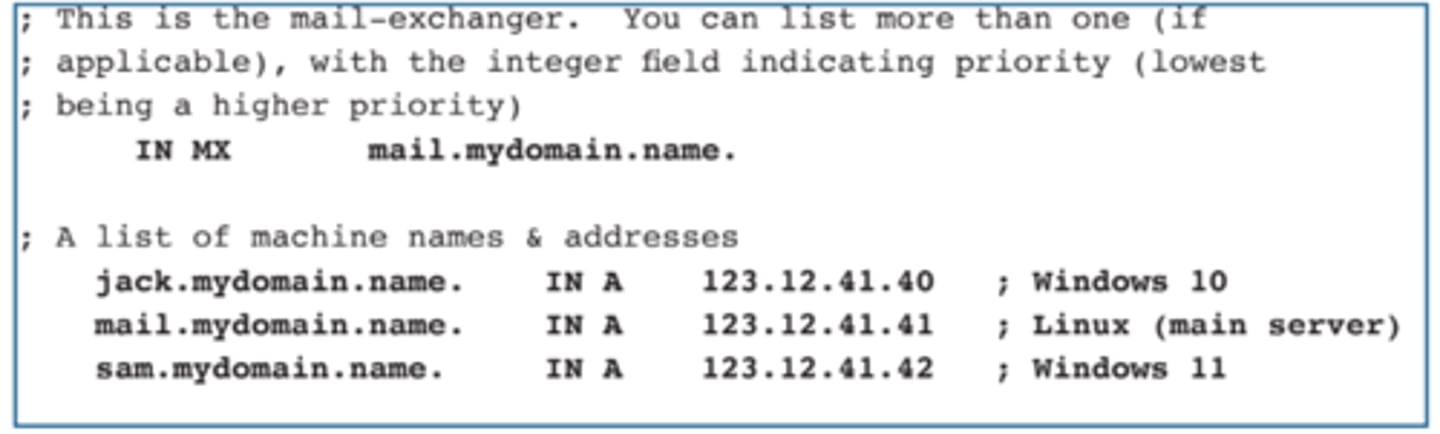
2.4 Mail exchanger record (MX)
• Determines the host name for the mail server - this isn't an IP address; it's a name
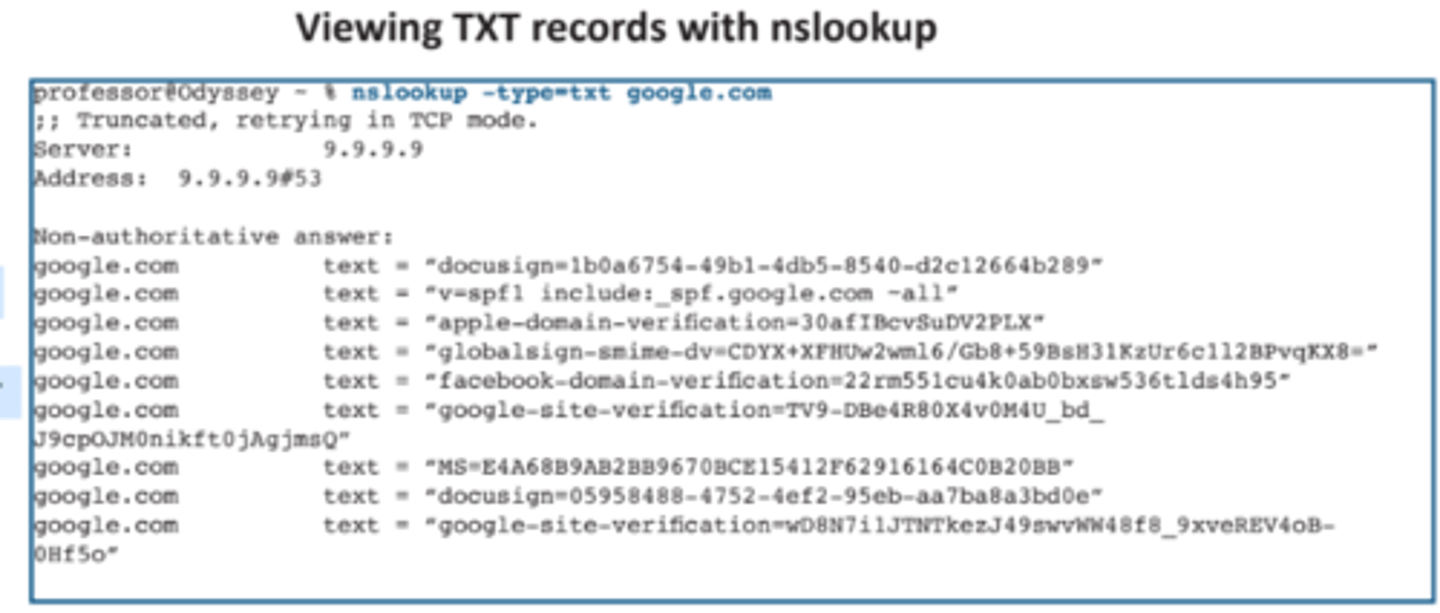
2.4 Text records (TXT)
• Human-readable text information
- Useful public information
- Was originally designed for
informal information
• Can be used for verification purposes
- If you have access to the DNS,
then you must be the administrator
of the domain name
• Commonly used for email security
- External email servers validate
information from your DNS
2.4 Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM)
• Digitally sign a domain's outgoing mail
- Validated by mail servers, not usually
seen by the end user
- The public key is in the DKIM TXT record

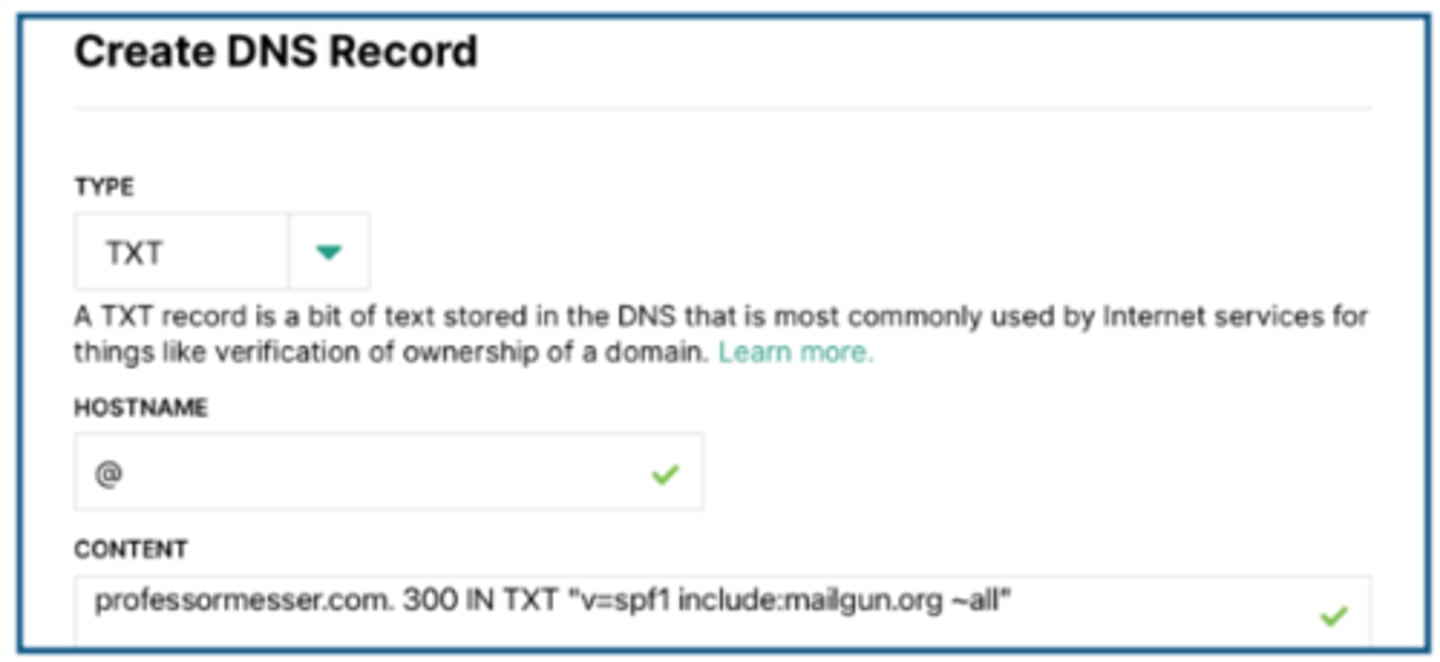
2.4 Sender Policy Framework (SPF)
• SPF protocol
- A list of all servers authorized to send emails
for this domain
- Prevent mail spoofing
- Mail servers perform a check to see if incoming mail
really did come from an authorized host
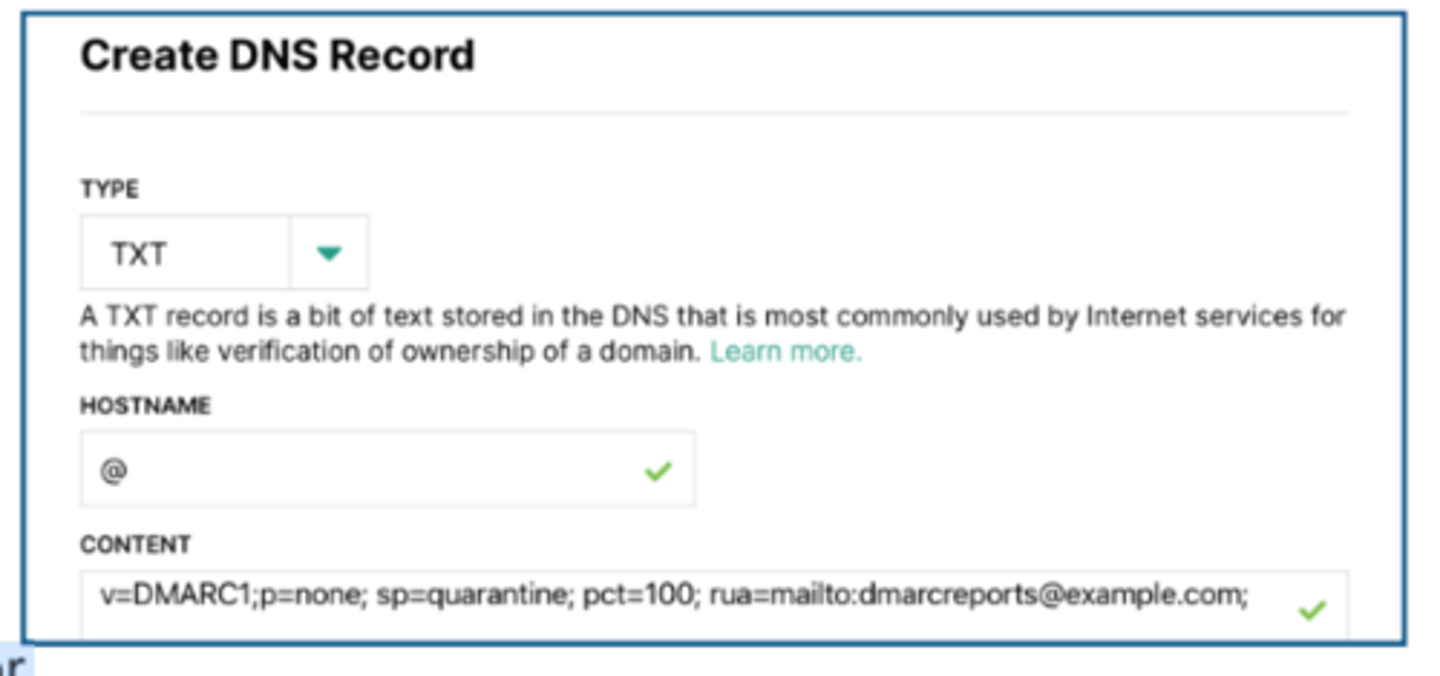
2.4 DMARC
• Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting,
and Conformance (DMARC)
- Prevent unauthorized email use (spoofing)
- An extension of SPF and DKIM
• You decide what external email servers should do with
emails that don't validate through SPF or DKIM
- That policy is written into a DMARC TXT record
- Accept all, send to spam, or reject the email
- Compliance reports can be sent to the email administrator
2.4 DCHP
• IPv4 address configuration used to be manual
- IP address, subnet mask, gateway, DNS servers,
NTP servers, etc.
• Needed a more automatic method
- Scale to thousands of systems
- Hands-off IP configurations
• Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- Initially released in 1997, updated through the years
- Provides automatic address / IP configuration
- Used for almost all devices
2.4 DHCP leases
• DORA
- A four-step process
• Discover
- Find a DHCP server
• Offer
- Get an offer
• Request
- Lock in the offer
• Acknowledge
- DHCP server confirmation
2.4 DHCP scopes
• Configured on the DHCP server
• IP address range
- And excluded addresses
• Subnet mask
• Lease durations
• Other scope options
- DNS server
- Default gateway
- VOIP servers
2.4 DHCP pools
• Grouping of IP addresses
- Each subnet has its own scope
- 192.168.1.0/24
- 192.168.2.0/24
- 192.168.3.0/24
- ...
• A scope is generally a single contiguous
pool of IP addresses
- DHCP exceptions can be made inside of the scope
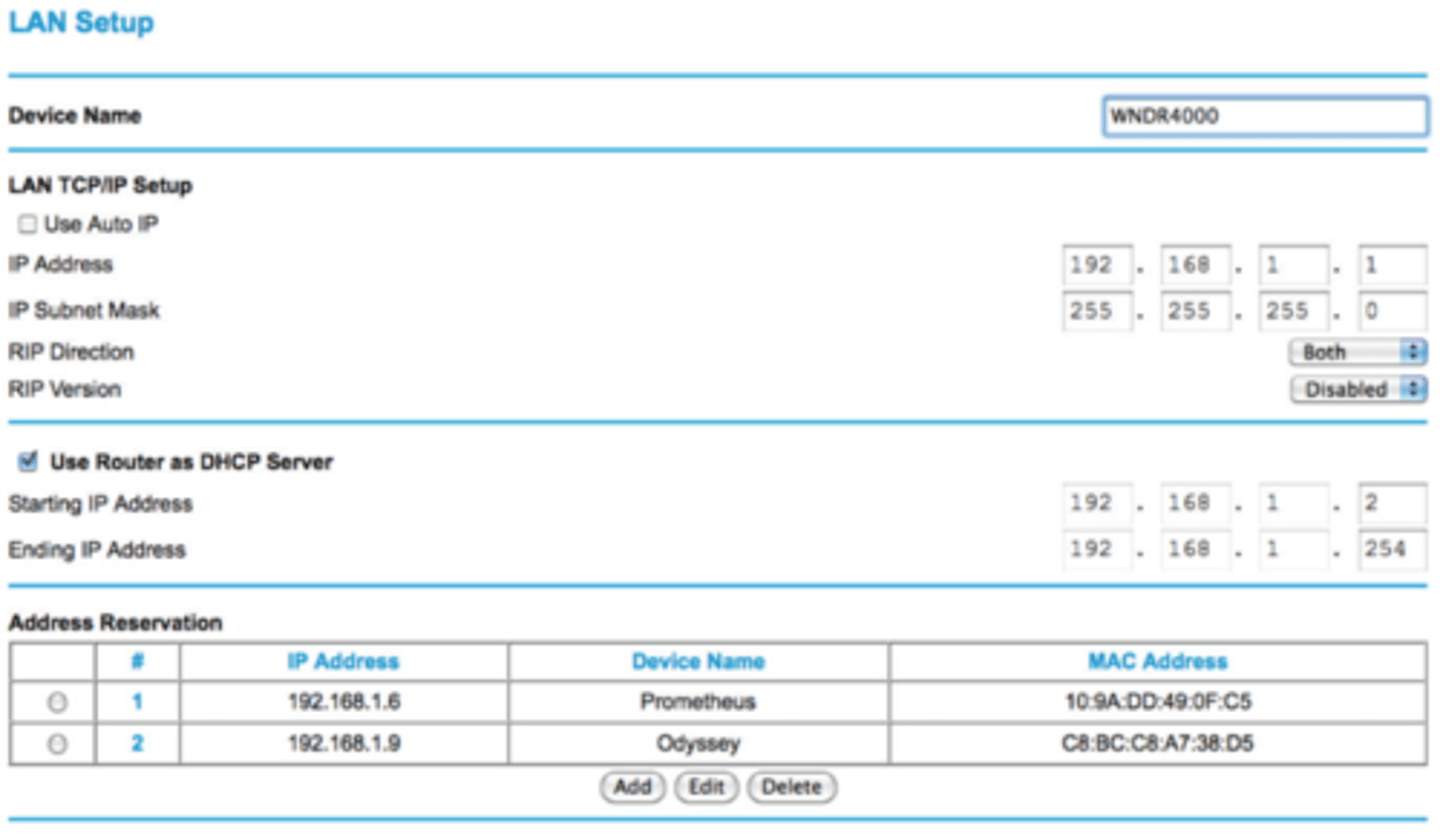
2.4 Address reservation
• Address reservation
- Administratively configured
• Table of MAC addresses
- Each MAC address has a matching IP address
• Other names
- Static DHCP Assignment
- Static DHCP
- IP Reservation
2.4 Address Reservation
2.4 LANs
• Local Area Networks
• A group of devices in the same broadcast domain

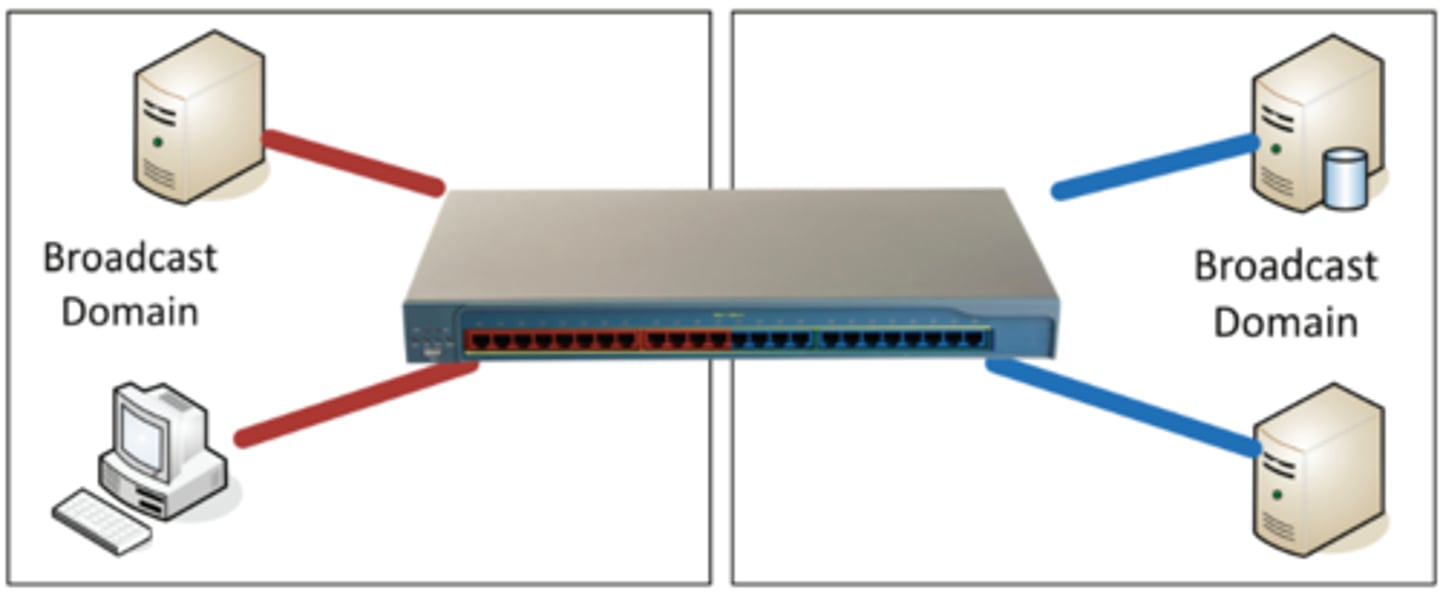
2.4 Virtual LANs
• Virtual Local Area Networks
- A group of devices in the same broadcast domain
- Separated logically instead of physically
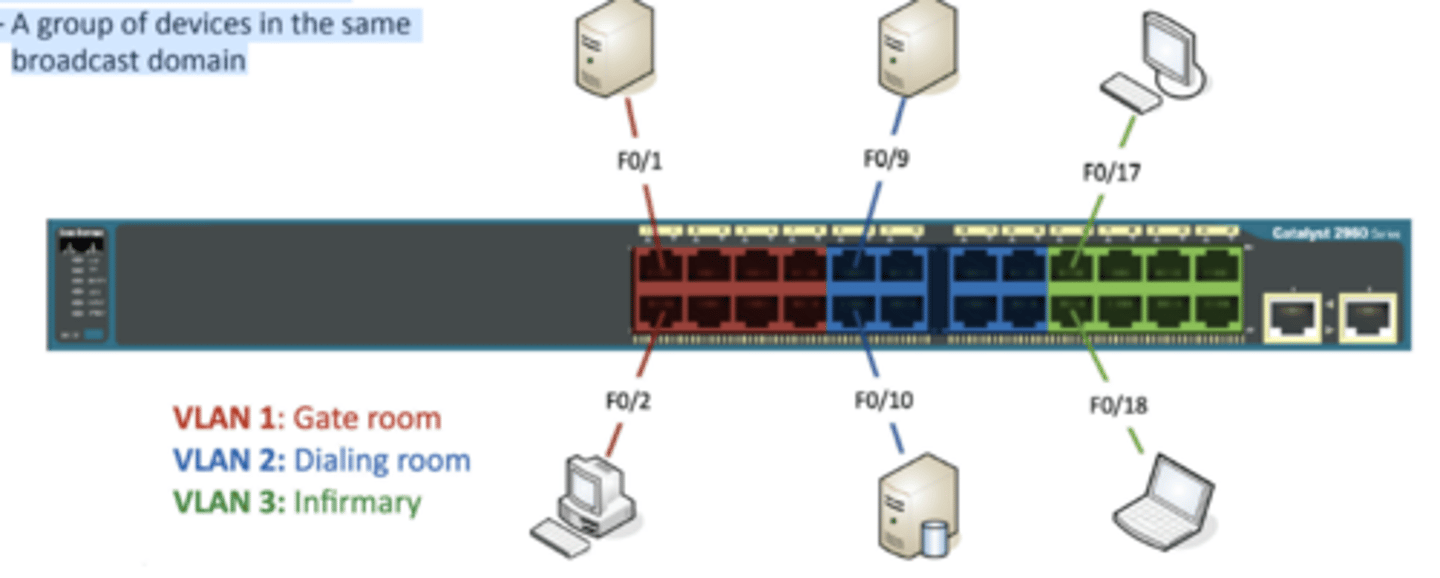
2.4 Configuring VLANs
• Virtual Local Area Networks
- A group of devices in the same
broadcast domain
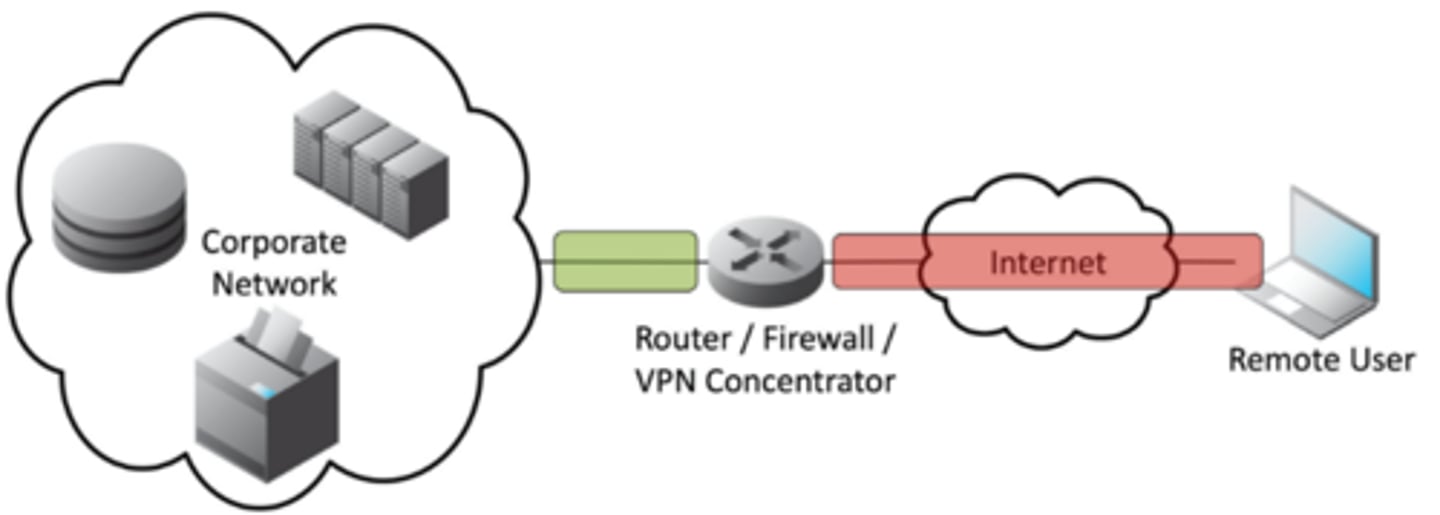
2.4 VPNs
• Virtual Private Networks
- Encrypted (private) data traversing a public network
• Concentrator
- Encryption/decryption access device
- Often integrated into a firewall
• Many deployment options
- Specialized cryptographic hardware
- Software-based options available
• Used with client software
- Sometimes built into the OS
2.4 Client-to-Site VPN
• On-demand access from a remote device
- Software connects to a VPN concentrator
• Some software can be configured as always-on
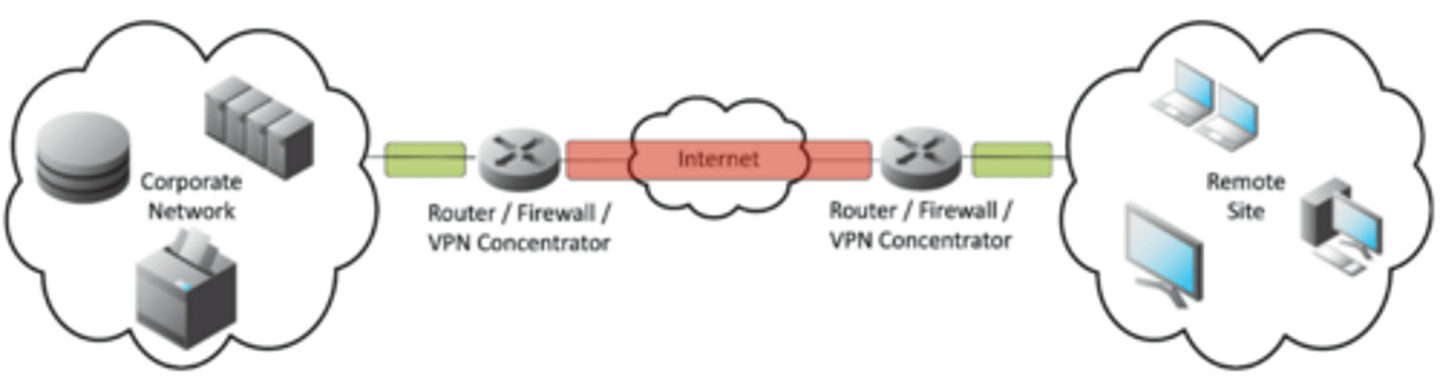
2.4 Site-to-site VPN
• Always-on
- Or almost always
• Firewalls often act as VPN concentrators
- Probably already have firewalls in place
2..4 Client-to-Site VPN
2.4 Site-to-site VPN
2.5 Network devices
• Many different devices and components
- All have different roles
• Some of these functions are combined together
- Wireless router/switch/firewall
• Compare different devices
- Understand when they should be used
2.5 Routers
• Routes traffic between IP subnets
- Makes forwarding decisions based on IP address
- Routers inside of switches sometimes called
"layer 3 switches"
• Often connects diverse network types
- LAN, WAN, copper, fiber
2.5 Switches
• Bridging done in hardware
- Application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC)
- Forwards traffic based on data link address
• Many ports and features
- The core of an enterprise network
- May provide Power over Ethernet (PoE)
• Multilayer switch
- Includes routing functionality
2.5 Unmanaged switches
• Very few configuration options - plug and play
• Fixed configuration - no VLANs
• Very little integration with other devices
- No management protocols
• Low price point - simple is less expensive
2.5 Managed switches
• VLAN support
- Interconnect with other switches via 802.1Q
• Traffic prioritization
- Voice traffic gets a higher priority
• Redundancy support
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
• Port mirroring
- Capture packets
• External management
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
2.5 Access point
• Not a wireless router
- A wireless router is a router and an access point
in a single device
• An access point is a bridge
- Extends the wired network onto the wireless network
- Makes forwarding decisions based on MAC address
2.5 Patch Panels
• Combination of punch-down blocks and
RJ-45 connectors
• Runs from desks are made once
- Permanently punched down to patch panel
• Patch panel to switch can be easily changed
- No special tools - use existing cables
2.5 Firewalls
• Filters traffic by port number
- OSI layer 4 (TCP/UDP)
- Some firewalls can filter based on the application
• Can encrypt traffic into/out of the network
- Protect your traffic between sites
• Can proxy traffic
- A common security technique
• Most firewalls can be layer 3 devices (routers)
- Usually sits on the ingress/egress of the network
2.5 Power over Ethernet (PoE)
• Power provided on an Ethernet cable
- One wire for both network and electricity
- Phones, cameras, wireless access points
- Useful in difficult-to-power areas
• Power provided at the switch
- Built-in power - Endspans
- In-line power injector - Midspans
2.5 PoE switch
• Power over Ethernet
- Commonly marked on the switch or interfaces
2.5 PoE, PoE+, PoE++
• PoE
- The original PoE specification
- Now part of the 802.3 standard
- 15.4 watts DC power, 350 mA max current
• PoE+
- Now also part of the 802.3 standard
- 25.5 watts DC power, 600 mA max current
• PoE++
- 51 W (Type 3), 600 mA max current
- 71.3 W (Type 4), 960 mA max current
- PoE with 10GBASE-T
• Compare the device with the switch support
- PoE+ won't power a PoE++ device
2.5 Cable modem
• Broadband
- Transmission across multiple frequencies
- Different traffic types
• Data on the "cable" network
- DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification)
• High-speed networking
- Speeds up to 1 Gigabit/s are available
• Multiple services - Data, voice, video
2.5 DSL modem
• Digital Subscriber Line - uses telephone lines
• Download speed is faster than
the upload speed (asymmetric)
- ~10,000 foot limitation from the central office (CO)
- Faster speeds may be possible if closer to the CO
2.5 ONT
• Optical network terminal - fiber to the premises
• Connect the ISP fiber network to the copper network
- Demarcation point (demarc) in the data center
- Terminal box on the side of the building
• Line of responsibility
- One side of the box is the ISP
- Other side of the box is your network
2.5 Network Interface Card (NIC)
• The fundamental network device
- Every device on the network has a NIC
- Computers, servers, printers, routers, switches,
phones, tablets, cameras, etc.
• Specific to the network type - Ethernet, WAN, wireless
• Often built-in to the motherboard
- Or added as an expansion card
• Contains the hardware address
- Media Access Control (MAC) address
- A unique hardware designation
2.6 IP addressing
• IPv4 is the primary protocol for everything we do
- You probably won't configure anything else
• IPv6 is now part of all major operating systems
- And the backbone of our Internet infrastructure
2.6 IPv4 addresses
• Internet Protocol version 4
- OSI Layer 3 address
2.6 Public IPv4 addresses
• Each IPv4 address on the Internet is unique
- 1.1.1.1 can communicate to 2.2.2.2
• It is estimated that there are over 20 billion devices
connected to the Internet (and growing)
- IPv4 supports around 4.29 billion addresses
- There's an obvious scalability issue
• We've found ways to manage the demand
- Network Address Translation (NAT)
2.6 IPv4 addresses format
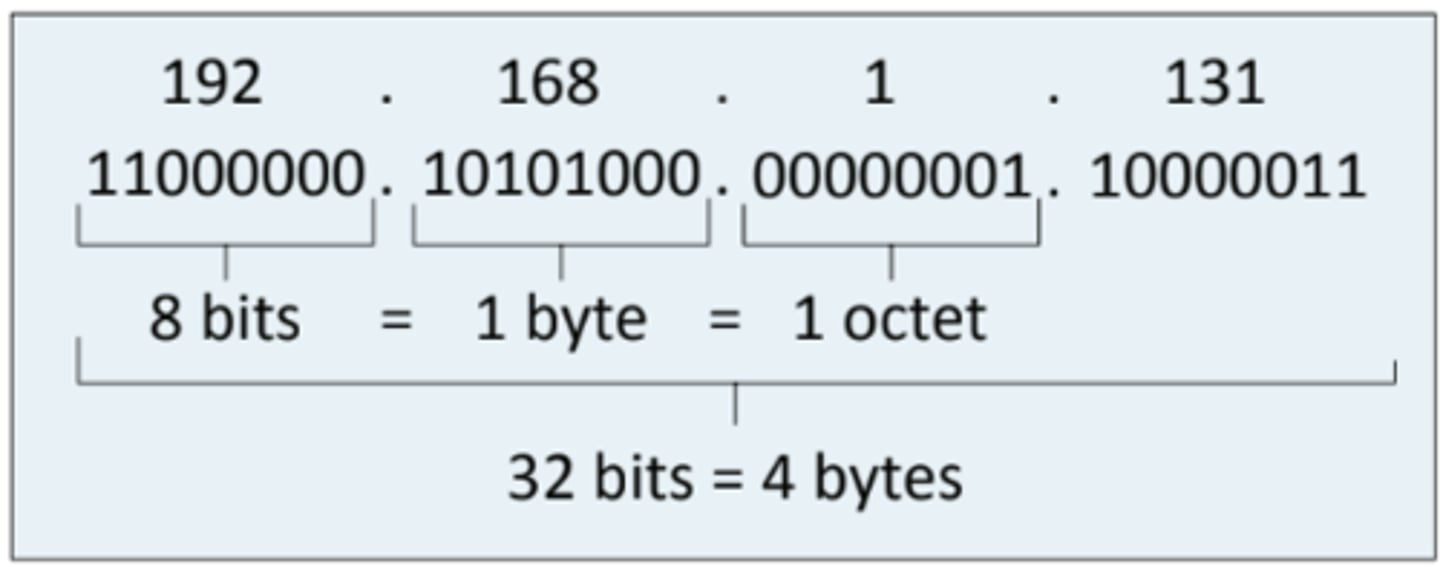
2.6 IPv6 addresses format

2.6 Private IP address ranges
• Large private IP address ranges
- Properly design and scale large networks
• Private IP addresses are not Internet-routable
- But can be routed internally
- Use NAT for everything else
• Defined in RFC 1918
- Request for Comment
2.6 IPv6 addresses
• Internet Protocol v6 - 128-bit address
- 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,
431,768,211,456 addresses (340 undecillion)
- 6.8 billion people could each have
5,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 addresses
• Your DNS is very important!
• First 64 bits is generally the network prefix (/64)
• Last 64 bits is then the host network address
2.6 RFC 1918 private IP addresses
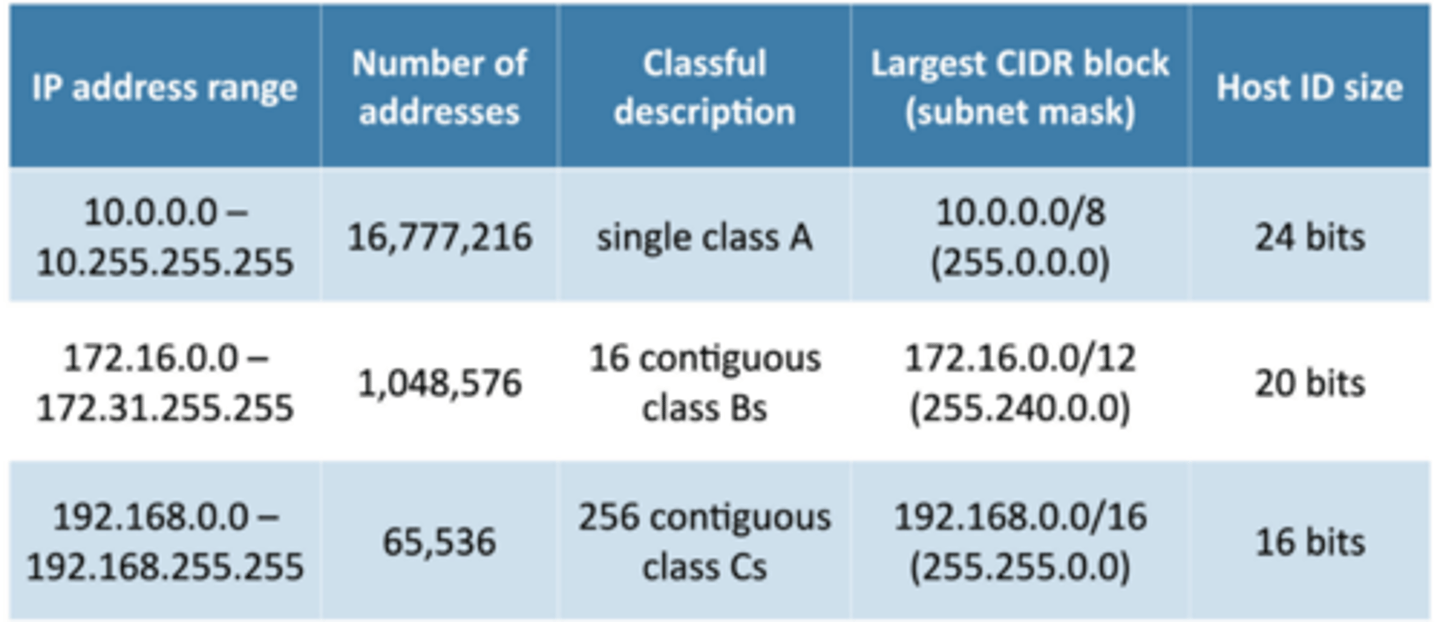
2.6 Networking with IPv4
• IP Address, e.g., 192.168.1.165
- Every device needs a unique IP address
• Subnet mask, e.g., 255.255.255.0
- Used by the local device to determine
what subnet it's on
- The subnet mask isn't (usually) transmitted
across the network
- You'll ask for the subnet mask all the time
- What's the subnet mask of this network?
• Default gateway, e.g., 192.168.1.1
- The router that allows you to communicate
outside of your local subnet
- The default gateway must be an IP address
on the local subnet
2.6 Static IP addressing
• An IP address that doesn't change
- Without a manual configuration change
• Manually configure the IP address
- Type it from the keyboard on each device
• Can be difficult to manage
- If the address changes, you must visit the device
- This obviously does not scale
• Try to avoid using manual IP addressing
- There are better ways to assign addresses
- DHCP reservations
2.6 Turning dynamic into static
• DHCP assigns an IP address from the first available
from a large pool of addresses
- Your IP address will occasionally change
• You may not want your IP address to change
- Server, printer, or personal preference
• Disable DHCP on the device
- Configure the IP address information manually
- Requires additional administration
• Better: Configure an IP reservation on the DHCP server
- Associate a specific MAC address with an IP address
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)
• A link-local address - No forwarding by routers
• APIPA uses 169.254.0.0 through 169.254.255.255
- First and last 256 addresses are reserved
- Functional block of 169.254.1.0 through 169.254.254.255
• Randomly assigned in this block
- Uses ARP to confirm the address isn't currently in use
2.7 Satellite networking
• Communication to a satellite
- Non-terrestrial communication
• High cost relative to terrestrial networking
- 100 Mbit/s down, 5 Mbit/s up are common
- Remote sites, difficult-to-network sites
• High latency
- Some systems have 250 ms up, 250 ms down
- Starlink advertises 25 ms to 60 ms
• Not always a perfect option
- Line of sight, rain fade
2.7 Fiber
• High speed data communication
- Frequencies of light
• Higher installation cost than copper
- Equipment is more costly
- More difficult to repair
- Communicate over long distances
• Large installation in the WAN core
- Supports very high data rates
- SONET, wavelength division multiplexing
• Fiber is slowly approaching the premises
- Business and home use
2.7 Cable
• Broadband
- Transmission across multiple frequencies
- Different traffic types
• Data on the "cable" network
- DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification)
• High-speed networking
- 50 Mbits/s through 1,000+ Mbit/s are common
• Multiple services
- Data, voice, video