Bloodbank 2 unit 1
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
Compatibility testing
A routine procedure performed with donor products containing red blood cells to ensure safe transfusions.
Compatible vs incompatible
Refers to whether the donor's blood can safely be transfused to the patient without causing harm.
Goals of compatibility testing
To prevent patient harm and maximize the survival of transfused red blood cells in vivo.
Pre-transfusion testing
The process of specimen collection, handling, and processing to ensure accurate blood transfusion.
Accurate patient ID
Essential for ensuring that the correct patient receives the correct blood product.
Blood bank history review
A review of the patient's previous blood transfusion history to identify any potential issues.
Antibody screening
A test performed to detect unexpected antibodies in the patient's blood before transfusion.
Major crossmatch
A compatibility test where the patient's serum/plasma is mixed with donor red blood cells.
Minor crossmatch
A compatibility test where donor plasma is mixed with the patient's red blood cells.
Serologic crossmatch
A compatibility test that includes immediate spin and antiglobulin testing.
Computer crossmatch
A method that eliminates the need for serologic crossmatch if certain criteria are met.
Documentation of compatibility testing
Includes grading reactions and ensuring accurate records are maintained.
Causes for incompatible cross-matches
Can include incorrect ABO typing, alloantibodies, autoantibodies, and contamination.
Limitations of compatibility testing
Does not guarantee successful transfusion outcomes or prevent all adverse effects.
Emergency release form
Required for medically necessary transfusions when compatibility testing cannot be completed.
Massive transfusion protocol
Involves administering multiple units of packed red cells, plasma, and platelets in a short time.
Neonatal transfusion requirements
Specific ABO and Rh typing, antibody screening, and special considerations for infants.
Post-transfusion reaction monitoring
Involves checking for hemolysis and ensuring proper documentation after transfusion.
Resolving ABO discrepancies
Steps taken when there is a mismatch between forward and reverse typing results.
Additional testing for persistent discrepancies
May include checking for weak or missing antigens and unexpected reactions.
Hematopoietic stem cell transplants
A procedure that can treat various conditions and does not require ABO compatibility.
Advanced methods in antibody screening
Techniques to detect clinically significant antibodies that may affect transfusion safety.
Adsorption
A method to remove antibodies from plasma by incubating with red blood cells of known antigens.
Elution
The process of removing antibodies from red blood cells, which can be total or partial.
Calculation for antigen-negative phenotypes
A formula used to determine the number of units needed based on percentages.
A patient with blood type O pos can get what type of blood?
O pos
O neg
A patient with blood type O neg can get what type of blood?
O neg
A patient with blood type A pos can get what type of blood?
A pos
A neg
O pos
O neg
A patient with blood type A neg can get what type of blood?
A neg
O neg
A patient with blood type B pos can get what type of blood?
B pos
B neg
O pos
O neg
A patient with blood type B neg can get what type of blood?
B neg
O neg
A patient with blood type AB pos can get what type of blood?
All blood types
A patient with blood type AB neg can get what type of blood?
AB neg
A neg
O neg
B neg
A patient with O pos blood type can get what type of plasma products?
O
A
B
AB
A patient with O neg blood type can get what type of plasma products?
O
A
B
AB
A patient with A pos blood type can get what type of plasma products?
A
AB
A patient with A negative blood type can get what type of plasma products?
A
AB
A patient with B pos blood type can get what type of plasma products?
B
AB
A patient with B neg blood type can get what type of plasma products?
B
AB
A patient with AB pos blood type can get what type of plasma products?
AB
A patient with AB neg blood type can get what type of plasma products?
AB
Major crossmatch uses …
Patient’s serum/plasma and donor red blood cells
Minor crossmatch uses…
DOnor plasma and patient’s red blood cells
What is the interpretation for crossmatch compatibility test?
Compatible or incompatible
Why dont we do a reverse type on neonatal blood?
Antibodies revealed in the reverse type could be mother’s
Massive transfusion is …
the administration of 8-10 packed red cells units to an adult patient in less than 24 hours
An intrauterine transfusion is done when …
there is a severe case of fetal anemia
Units for transfusion must be checked for…
Hemolysis and clots
What are ABO discrepancies?
When the forward type does not match the reverse type
What are some of the main reasons for ABO discrepancies?
weak or missing antigen, weak or missing antibody, unexpected antigen/antibody reaction
Can we proceed with a transfusion if there is an ABO discrepancy?
No, it must be delayed until it is solved
Who sings an emergency release form for a unit of blood that is needed STAT?
A physician must sign the release form
What is the first step to solve an ABO discrepancy?
Repeat the testing
Undercentrifugation of specimen will give you a …
False negative
Overcentrifugation of specimen will give you…
False positive
Too warm temperature in an ABO test will give you …
False negative
Too cold temperature in an ABO test will give you …
A false positive
A too weak cell suspension (prozone) is …
Excess antibody
A too heavy cell suspension (postzone) is …
Excess antigen
Collect a new specimen if…
mislabeled tube, specimen collected above IV site, traumatic draw
Forward typing are a common issue? True or false
False
A1
A2

A3
Ax
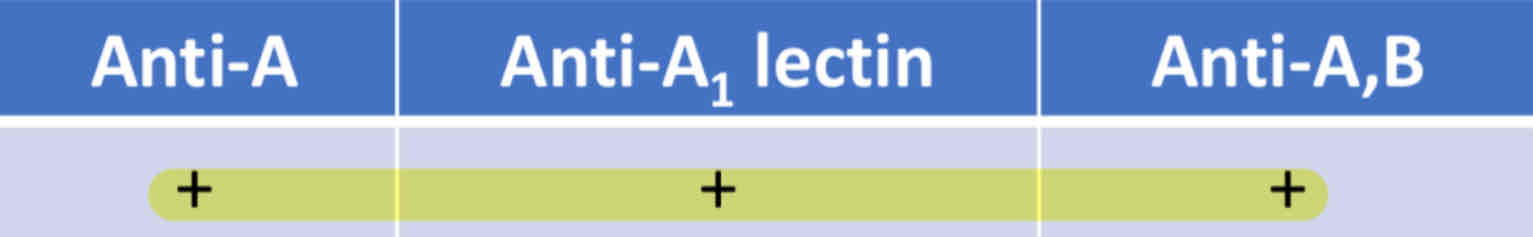
What subgroup of A has the most A antigen sites?
A1
What subgroup of A has the least A antigen sites?
Ax
What is the resolution for weak or missing reactions in the front type?
Incubate at room temperature for 15-30 minutes.
Incubate at 4 degrees Celcius for 15-30 minutes.
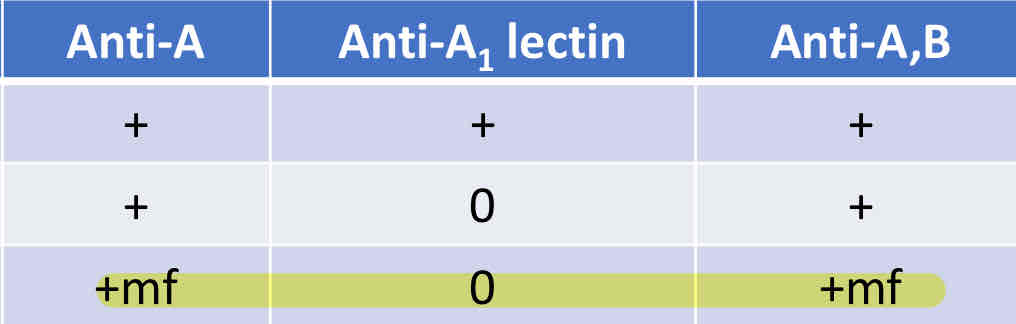
What is the resolution for subgroups of A1 discrepancy reactions?
Test using Anti-A1 lectin
What kind of reaction would Rouleaux give?
An unexpected positive reaction
What is the solution to rouleaux in the forward type?
Wash RBC with saline multiple times
Why does cord blood often give forward type discrepancies?
It contains protein substacnes that can trap the RBCs and cuase them to stick together
What is the solution to cord blood?
Wash the cells 4-6 times before testing
If the RBCs are coated with a cold autoantibody, what results would we see?
postive DAT and auto-control
What is the solution to RBCs coated with cold autoantibodies?
Wash RBCs using warm saline
How would we see polyagglutination in the tests?
Patient’s cells react with all antisera, including control
The Tn type of polyagglutination is due to …
abnormality of the red cell membrane, not bacterial
The Tk, Th, and VA type of polyagglutination are caused by …
Bacterial
The Cad and NOR type of polyagglutination are caused by …
inherited disorders
What is the solution to polyagglutination in the forward type?
Switch to monoclonal reagents
What is acquired B antigen phenomenon?
Group A1 RBCs acquire B-like antigens due to bacterial enzymes
What is the resolution for acquired B antigen phenomenon?
Check diagnosis after a possible infection with E. coli, Proteus vulgaris or Chlostridium spp.
What is chimerism?
dual population of red blood cells are present in one individual
Waht is the solution for chimerism?
check patient history
What is the solution if a patient has an antiobody to the yellow dye in the anti-B reagent?
Dont use reagents
Reverse type discrepancies are the most common. True or false?
True
What is the solution to missing antibody reactions in the back type?
Incubate at room temperature for 15-30 mins.
Incubate at 4 degrees celcius for 15-30 mins
What is solution for Rouleaux if discrepancies are seen in the back type?
Saline replacement technique
What is one of the most common cold autoantibodies that cause reverse type discrepancies?
Anti-I
What results can we expect from a patient with a cold autoantibody?
All screen cells and autocontrol are positive
What should we do if a patient has a cold alloantibody?
Anti-M or anti-P1. Perform antibody ID
What is the solution for cold autoantibody?
prewarm technique
Cold auto adsorption for cold autoantibody
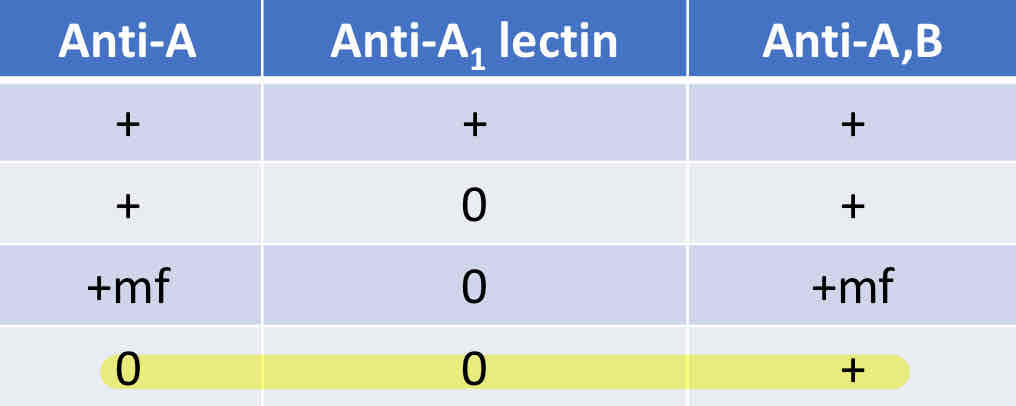
What is the solution of discrepancy in reverse type caused by Anti-A1?
Confirm patient is A1 antigen negative by testing with Anti-A1 lectin
ABO compatibility is necessary for Hematopoietic stem cell transplants (HSC). True or false?
False
Patients receiving HSC switch their blood group. True or false?
True
ABO incompatible HSC transplants can be succesful. True or false?
True
An antibody screen will…
Detect as many clinically signifincat antibodies as possible that cause HDN, HTR or decreased RBC survival
22% albumin potentiator
Reduces zeta potential but requires longer incubation time
LISS potentiator
increases the amount of antibody taken up by the red cells and reduces the zeta potential.
PEG potentiator
Accelerates antibody and red cell binding by removing water