U of U PA School ENT Hearing Loss, Dizziness, and Facial Nerve Paralysis
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the difference between vertigo and dizziness?
Dizziness refers to a number of symptoms from weakness to head spinning
Vertigo is a vestibular disorder resulting in illusion of motion
What is conductive hearing loss?
Hearing loss that is due to diminished sound reaching middle and inner ear.
What pathophysiology can lead to conductive hearing loss? (5)
Cerumen accumulation
External ear canal infection
TM perforation
Middle ear fluid
Ossicular chain abnormalities
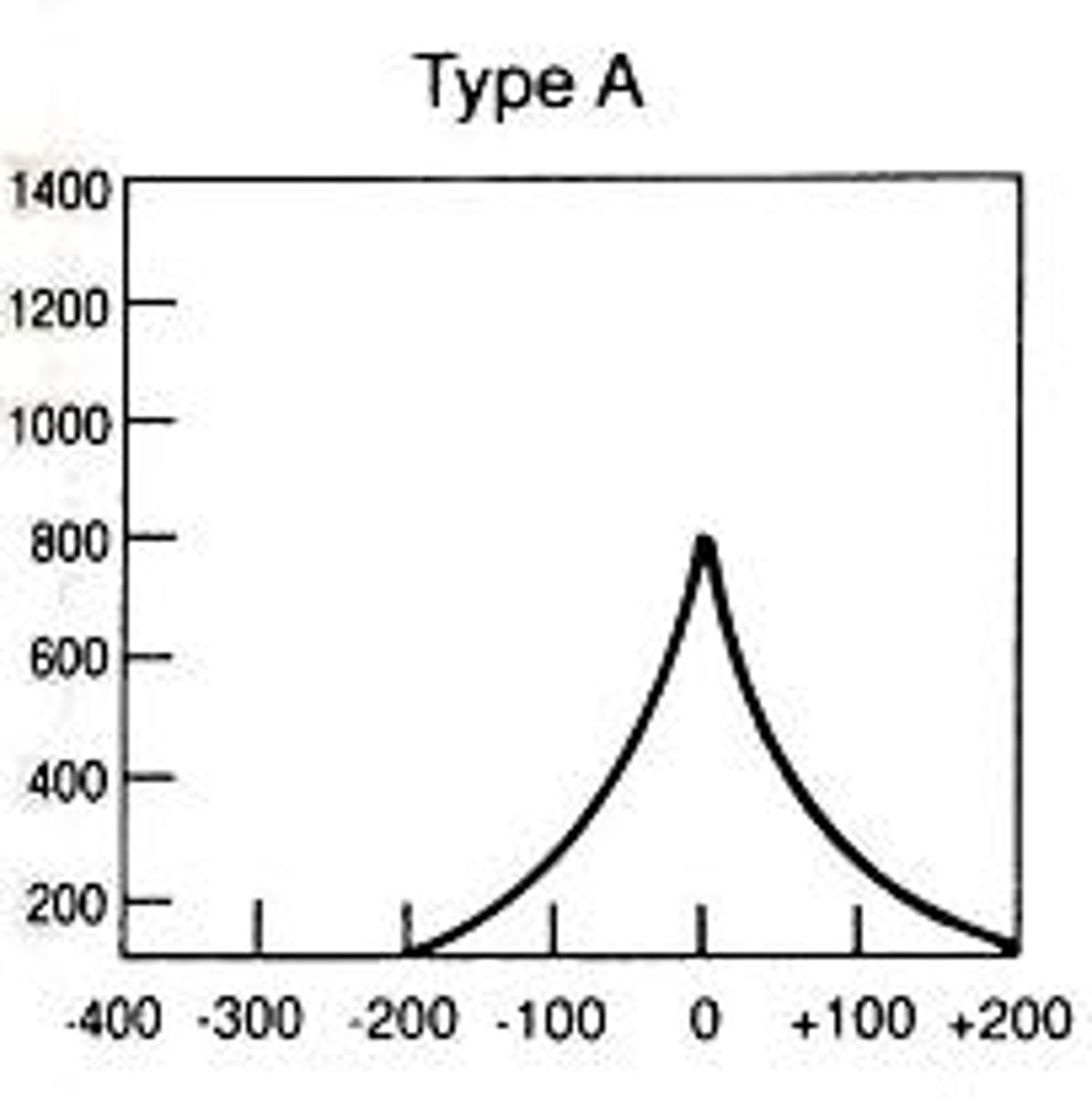
Tympanogram Type A indicates
Normal ear
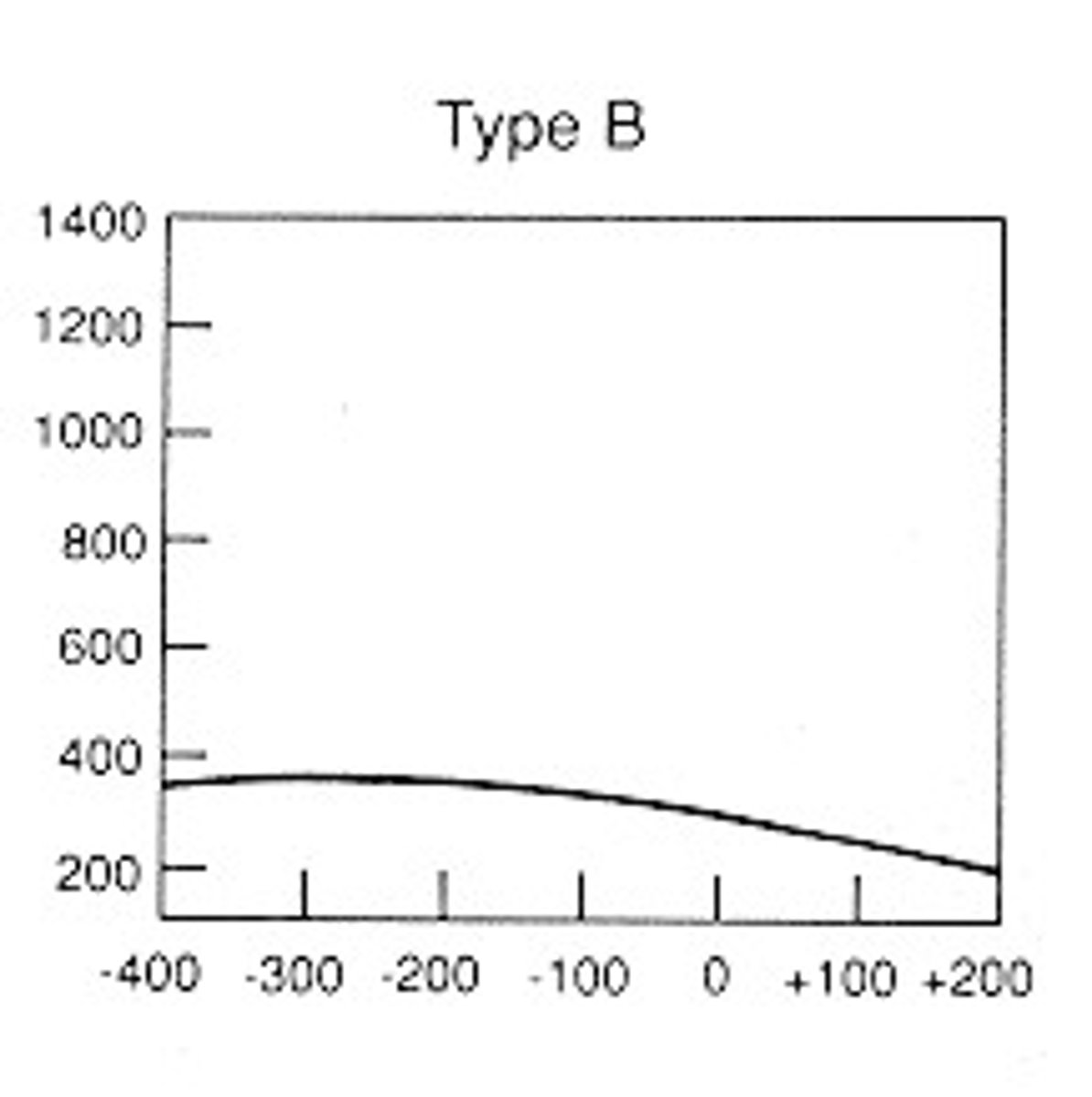
Tympanogram Type B indicates
Fluid filled ear
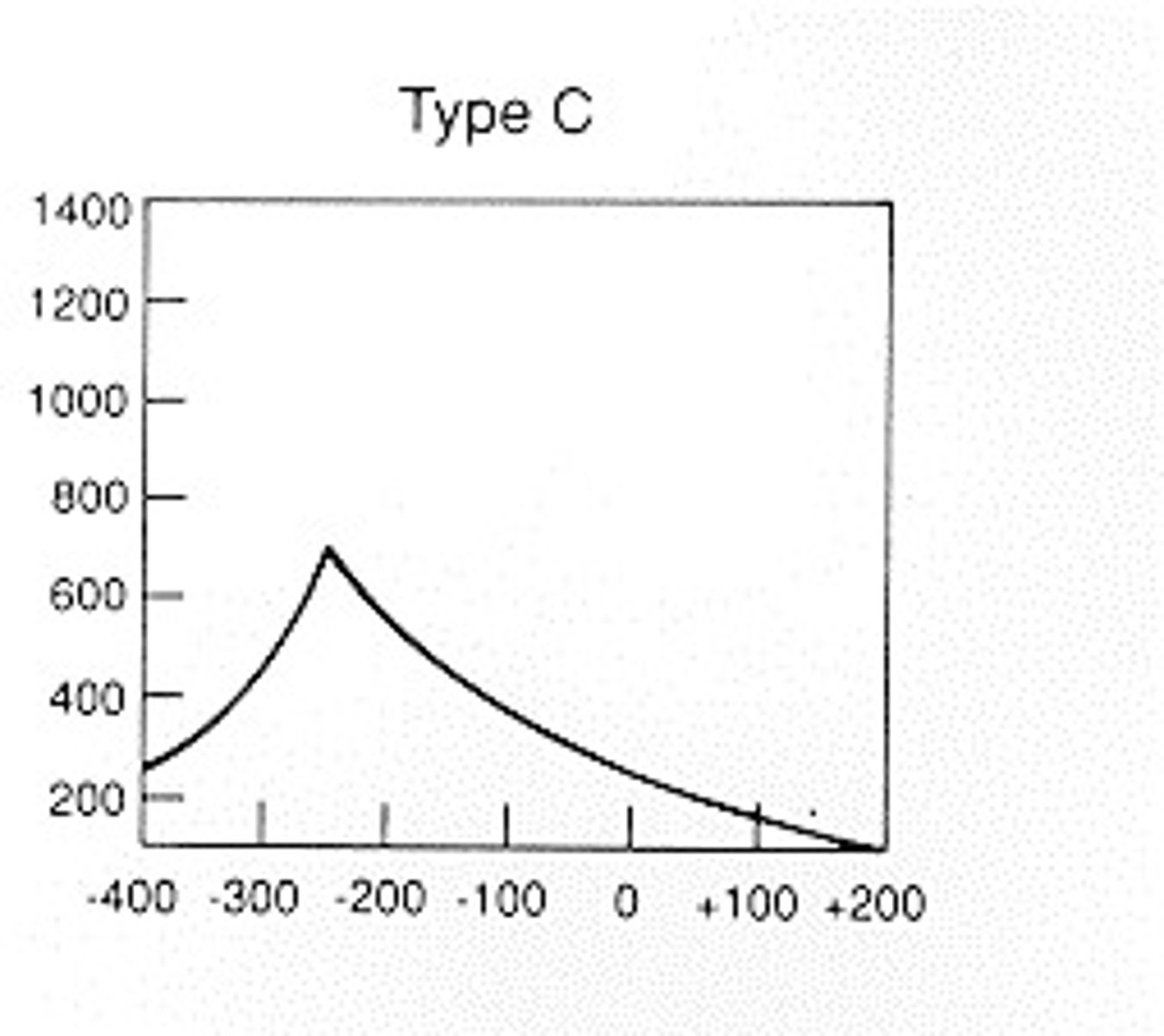
Tympanogram Type C indicates
Drum retracted (negative middle ear pressure)
What tools/tests can be used to investigate conductive hearing loss?
Otoscope/opthalmascope
Tuning fork
Audiometry testing
What case of conductive hearing loss would warrant immediate ENT referral?
Unilateral or acute/rapid onset
What case of tinnitus would warrant ENT referral?
Pulsing tinnitus
What is sensorineural hearing loss?
Hearing loss caused by damage to the cochlea's receptor cells or to the auditory nerves
What pathophysiology can cause sensorineural hearing loss? (7)
Injury to hair cells on cochlea
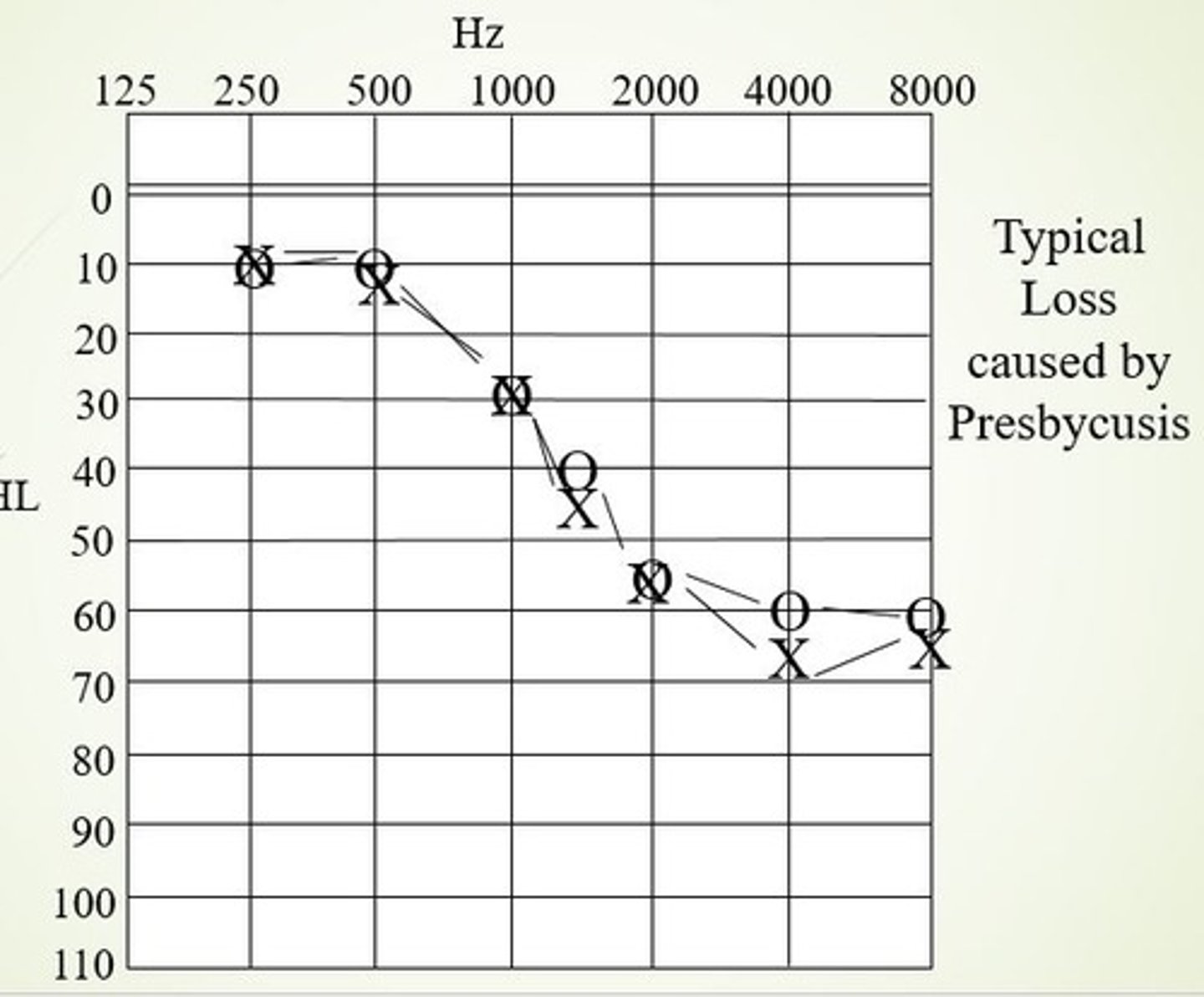
Presbycusis
Persistent noise exposure
Genetics
Stroke
Ototoxic substance
Vestibular schwannoma on 8th nerve
What medications are most commonly associated with sensorineural hearing loss?
Aminoglycosides
Loop diuretics
Platinum chemotherapy agents
What does a presbycusis audiogram look like?
What does a noise induced hearing loss audiogram look like?
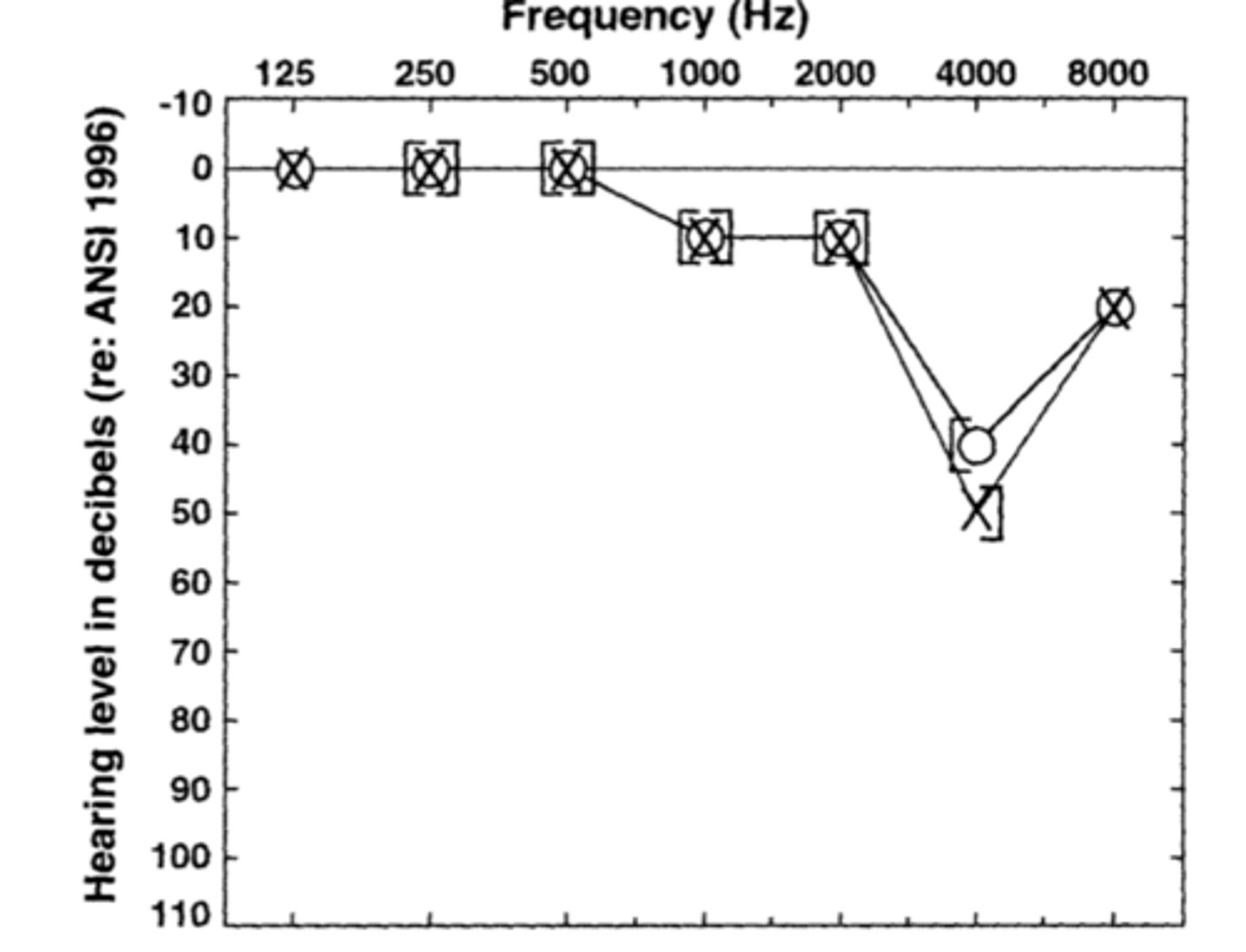
When should sensorineural hearing loss be referred to ENT?
Always
What treatments can be used for sensorineural hearing loss?
Cochlear implants
Hearing protection
Hearing aides
What is benign paroxysmal vertigo?
-brief episodes (20-60 sec) of intense whirling vertigo with changes in head position
What is the most common cause of vertigo?
Benign paroxysmal vertigo
What pathophysiology is associated with benign paroxysmal vertigo?
Sediment becoming free floating n semicircular canals and moves in fluid, stimulating the vestibular nerve causing brief vertigo
What history can lead to benign paroxysmal vertigo? (3)
Head trauma
Vestibular neuronitis
Spontaneous
What are the signs and symptoms of benign paroxysmal vertigo?
Patient can usually describe motion that causes the vertigo
What tests can be diagnostic for benign paroxysmal vertigo?
Dix-Hallpike is main one
Supine roll test
What is the treatment for benign paroxysmal vertigo? (4)
Epily maneuver
Canalith repositioning maneuver
Brandt-Daroff exervises
Surgery if severe
What is vestibular neuronitis?
Inflammation of the vestibular portion of the 8th cranial nerve
What history can lead to vestibular neuronitis?
Recent flu like symptoms/URI
What are the symptoms of vestibular neuronitis?
Sudden onset of room spinning for 24-48 hours with vertigo/nausea
How is vestibular neuronitis diagnosed?
Gait assessment
Eye movements
ENG testing
What is the treatment for vestibular neuronitis?
Treatment of nausea
Vestibular nerve suppressants and rehabilitation
What is labyrinthitis?
Inflammation of the labyrinth (inner ear)
What is Meniere's disease?
Fluctuating sensorineural hearing loss in adults with dizzy spells, fullness in ear and tinnitus
Usually unilateral
What is the triad of Meniere's disease?
Vertigo
Hearing loss and aural fullness
Tinnitus
How long do Meniere's disease spells last? What can activate the spells?
Brief 2-4 hours
Salt, high water intake, and caffeine
How is Meniere's disease diagnosed?
Clinically:
->1 episode lasting > 20 minutes
-Documented hearing loss, tinnitus and aural fullness at least once
Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (VEMP) testing confirms
What is the treatment for Meniere's disease?
Salt restriction and diuretics
Vestibular ablation
Surgery if severe
What is Bell's Palsy?
Inflammation or viral infection of the facial nerve that causes one sided weakness or the entire face
What is the pathophysiology of Bell's Palsy?
Inflammation causes facial nerve to pinch off
What history can lead to Bell's Palsy?
Recent infection
Idiopathic
What are the signs of Bell's Palsy?
Unilateral facial paralysis
What testing is used to diagnose Bell's Palsy?
Diagnosis of exclusion after looking for other causes
What is used to treat Bell's Palsy?
Oral steroids within 3 days of onset
Antivirals possibly effective
What is Ramsay Hunt syndrome?
Herpes infection that commonly involves CN VIII
What history can lead to Ramsay Hunt syndrome?
Vesicular lesions preceeding paralysis
What are the signs and symptoms of Ramsay Hunt syndrome?
Facial nerve paralysis with severe pain
Vesicular eruption in external auditory canal and auricle
Treatment for Ramsay Hunt syndrome
Antiviral agents
Oral steroids
What are the 5 branches of the facial nerve?
Temporal
Zygomatic
Buccal
Mandibular
Cervical