4.1.5 Perfect Competition, imperfectly competitive markets
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the Concentration Ratio?
concentration ratio (CR) tells us the number of firms that dominate the market
This is linked to the degree of competition within the market
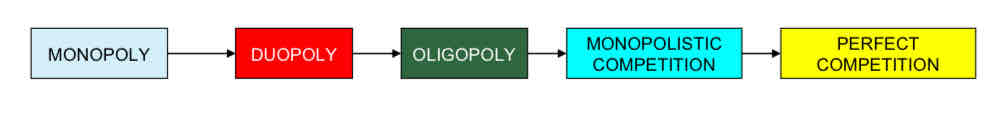
What does market structure mean?
number of firms within an industry and the way in which those businesses behave e.g. differentiating products.
What does monopoly mean?
occurs when one firm dominates the market
What does duopoly mean?
exists where there are only 2 firms in the market
What does oligopoly mean?
occurs when a few firms dominate the market
What does monopolistic competition mean?
occurs when there are many firms in the market but there is some form of product differentiation
Expand on the term monopoly
Government refer to any company that has at least
25% market share as having monopoly powers
Monopolies can exploit consumers by charging high prices.
Therefore, monopolies are regulated in order to protect the customer
Expand on Duopoly:
duopolies can also exploit consumers by charging high price
Similar barriers to entry that exist in monopoly markets also affect duopolies
Duopolies tend to compete on non-price competition such as promotion
Duopolies are often accused of collusion (making agreements between each other that restrict competition).
This is illegal and firms that collude can be heavily fined
Expand on Oligopoly
oligopolies can exploit consumers by charging high prices
Barriers to entry exist in oligopolistic markets, particularly through advertising
compete on non-price competition such as promotion and there may also be an element of collusion
important for oligopolists to take into account the reaction of competitors when making decisions regarding pricing
oligopolists are unlikely to lower price as a long term strategy
What characteristics do oligopolies exhibit?
o Do not tend to compete on price in the long run
o However, oligopolists might compete on price as a tactic (short run)
o Tend to spend heavily on new product development
o Branding is crucial and expensive marketing budgets are available
o Firms must ensure that their products are accessible if they are going to be successful
Expand on monopolistic competition
leads to a small degree of monopoly power as each firm offers something different to the others
in this type of market barriers to entry are very low - Therefore, it is easy for firms to enter the market = creates strong competition
mix between monopoly power and competition leads to the term monopolistic competition
Firms within this market will try to brand their product(e.g through the building up of a reputation)
numerous examples of this type of competition such as hairdressing, restaurants & health and beauty industry
What are barriers to entry?
exist when firms that are within an industry are protected from competition from outside of the industry
These obstacles may occur naturally or through man- made intervention
Barriers to entry include:
o Advertising
o Economies of scale
o Financial
What is product differentiation?
firms try to make their product different to the competition by adapting the actual product in some way or by distinguishing the product through advertising and branding
What is perfect competition & what does it rely on?
ideal* free market which will ensure that the market clearing price (equilibrium) is found.
relies on six assumptions:
o a large number of buyers and sellers
o perfect information
o homogeneous (identical) products
o no barriers to entry/exit from market for sellers
o the ability to buy/sell as much as is desired at the ruling market price
o the inability of any individual buyer/seller to influence the market price
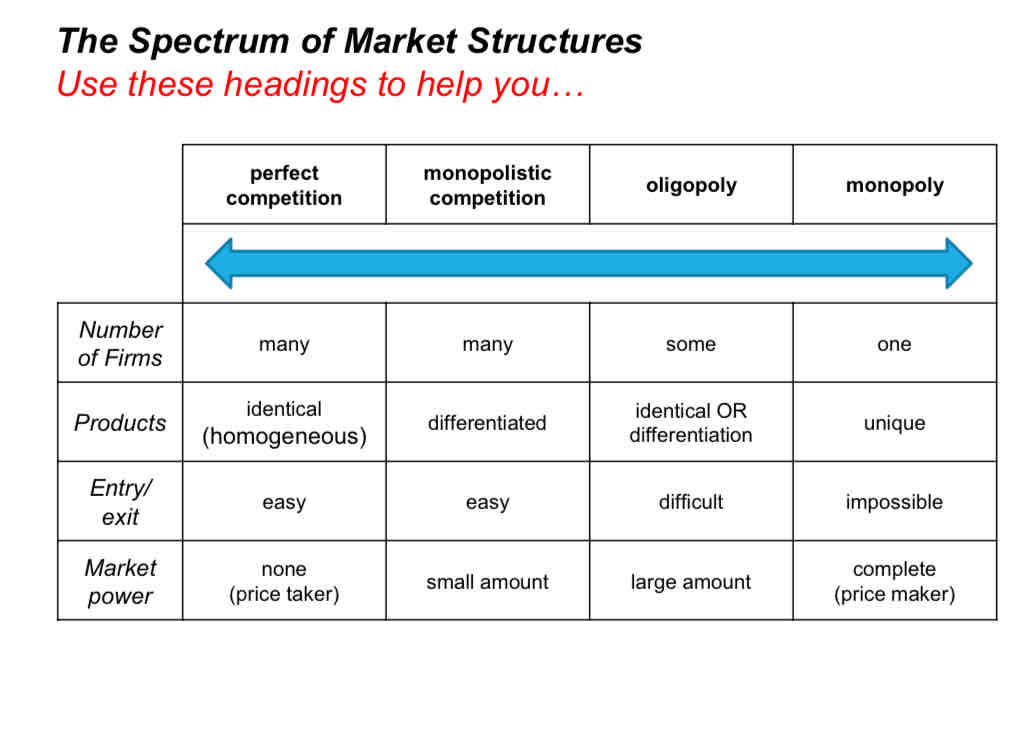
What is a price taker?
(a firm) that has no power to influence price in the market
They must accept (take) the price set by the market.
What is a price maker?
someone (a firm) that has the power to set the price for the market.
What are examples of market types for these?
Milk
T-shirts
Petrol
UK Passports
perfect competition
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Monopoly
What is imperfect competition?
type of market structure that exhibits some but not all elements of perfect competition
Differences include:
o There are less firms in the market
o There is some form of product differentiation
o There are at least some barriers to entry and exit
o The demand curve is downward sloping
o Suppliers can influence prices
What is a competitive market?
any market in which firms strive to out-do their rivals.
Perfect competition is the unrealistic extreme example
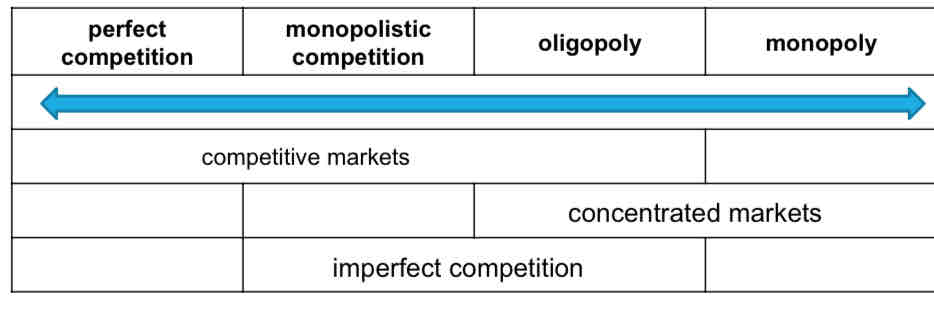
What is a concentrated market?
one in which only a very small number of firms operate.
Pure monopoly is the extreme example.
In the UK the privatisation of the railways and utility companies is an example of moving from monopolies to concentrated markets.
What is Profit maximisation?
Firms will seek to attain the highest level of profit available in their production of goods and services
What is profit satisficing?
A level of profit below profit maximisation that satisfies the needs of the owners or managers of an organisation e.g. working less hours to enjoy more leisure time or behaving ethically
What is sales maximisation?
Some firms will seek to maximise sales i.e. by volume, possibly to gain market share
will increase the size of the firm
is likely to be an objective of senior management as larger businesses tend to pay higher wages than smaller, but more profitable, ones
What is revenue maximisation?
Some firms will seek to maximise sales revenue
What kind of objectives depend on the type of business?
Government businesses looking to supply a service
Worker co-operatives look to benefit their members
Producer co-operatives might look to gain economies of scale with smaller firms joining together
What are other objectives a firm may have?
Survival
The ability of a business to continue to exist
Need enough money to pay expenses
Growth
Organically, through opening own stores
Takeover/merger
What is the model of perfect competition based on?
🢝Large numbers of producers
🢝Identical products
🢝Freedom of entry and exit
🢝Readily available information
What are identical products?
all products are identical or homogeneous
Buyers cannot tell the difference between products from different firms
Therefore, there is no branding of products and brand loyalty does not exist
means that firms are unable to raise prices much beyond their competitors
There are no barriers to entry or exit in….
Perfect competition
What does it mean when there are no barriers to entry or exit, In perfect competition?
means firms are free to enter or exit the market if they wish
Therefore, entry costs will be low or non-existent
Barriers to entry such as costs associated with capital expenditure, research and development and start-up of the business are low or non- existent
means firms can move into the market if they see that profits are higher than normal
restricts the opportunities available for firms to charge higher prices
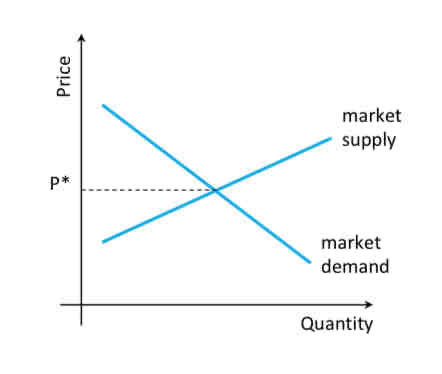
What are firms in perfect competition?
price takers
cannot affect the price, but can sell however much they wish at the ruling market price, P*.
What does a horizontal demand curve indicate?
perfect PED
the Average Revenue (revenue per unit) of firms in this market, as AR = unit price
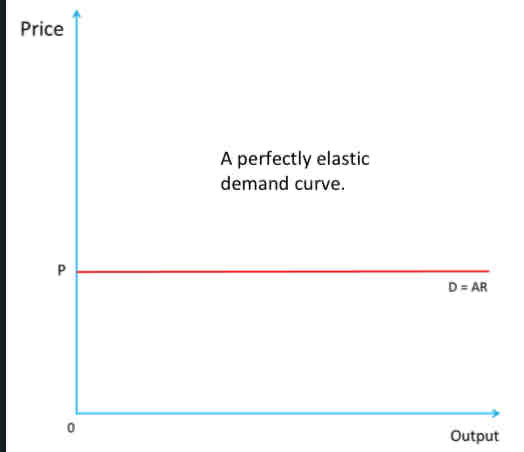
In perfect competition firms face a
perfectly elastic demand curve.
Each firm can sell all of its output at the current market price, P.
Therefore, it would not lower its price. If it were to raise price it would sell nothing as buyers would go to another seller.
Thus, the D curve is horizontal.
The D curve is also the AR curve as total output divided by price is always the same.
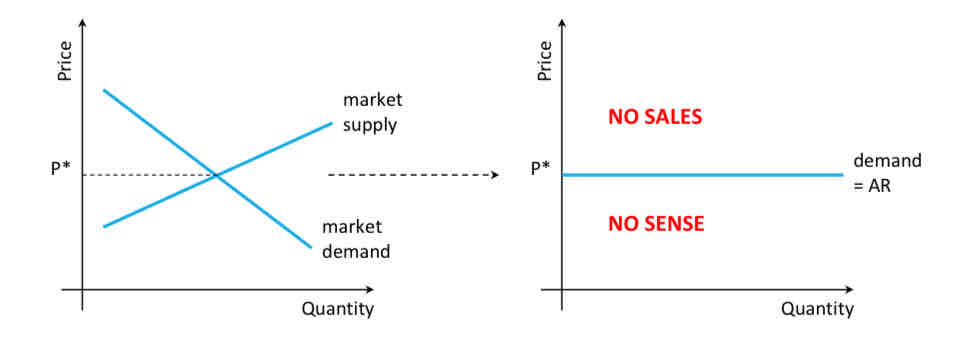
What does the demand curve for the individual firm within the market look like?
If the firm were to charge above the ruling market price, they would get no sales.
If they were to charge below market price it would make no sense as they can already sell as much as they like so profits would be harmed for no good reason.
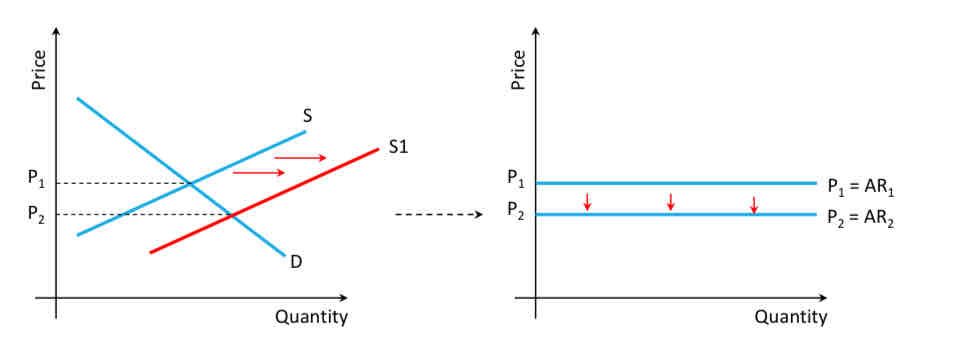
What do high profits bring into the market?
new entrants, increasing supply
Barriers to entry exist in monopoly markets that stop firms from entering the market. What do these include?
high costs to enter the market, especially high capital costs
economies of scale experienced by large firms e.g. bulk buying
legal barriers e.g. only pharmacies can sell prescription drugs
A pure monopoly has only one firm in the industry