eukaryotes- transcription factors and steroid hormones
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what are diseases in eukaryotes?
cancers
autoimmune disorders
metabolic conditions
what are transcription factors?
are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences and regulate/ control transcription
what is basal transcription machinery?
attaches to promoter and helps Rna polymerase to attach
unwinds the DNA to initiate transcription
transcription factors that alter the rate of transcription?
turn transcription up/ down or on/ off in response to biological or environmental factors
describe the basal transcriptional complex?
the basal transcriptional machinery
the transcription proceeds at an exceedingly low rate
enhanced by transcription factors
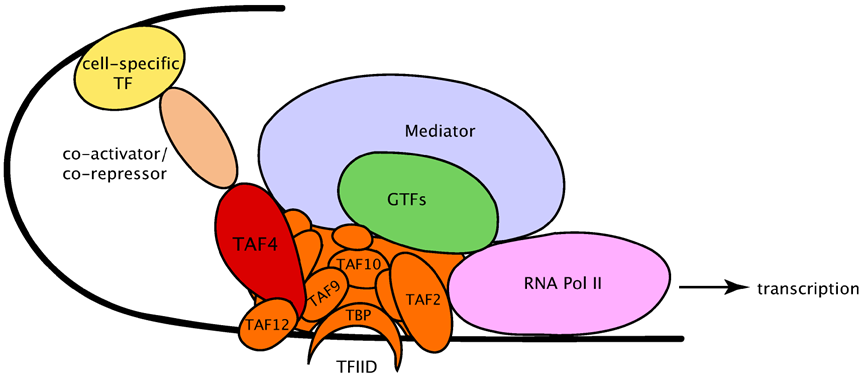
what are key characteristics of transcription factors?

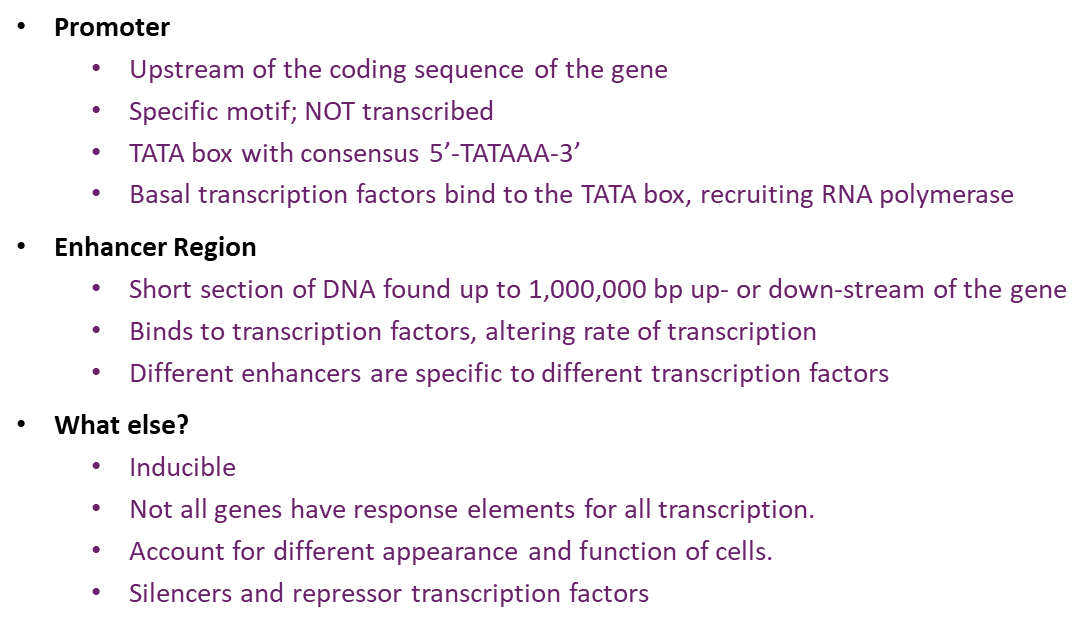
what are promoters and enhancers?
Promoter
Upstream of the coding sequence of the gene
Specific motif; NOT transcribed
TATA box with consensus 5’-TATAAA-3’
Basal transcription factors bind to the TATA box, recruiting RNA polymerase
Enhancer Region
Short section of DNA found up to 1,000,000 bp up- or down-stream of the gene
Binds to transcription factors, altering rate of transcription
Different enhancers are specific to different transcription factors
What else?
Inducible
Not all genes have response elements for all transcription.
Account for different appearance and function of cells.
Silencers and repressor transcription factors
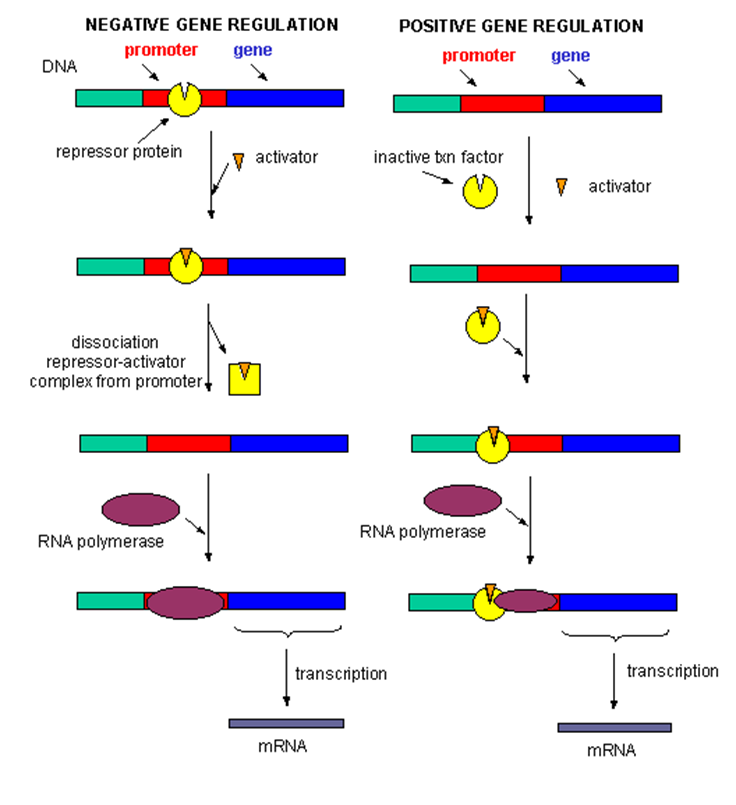
regulation through diagram…
what is combinatorial regulation?

Many genes are controlled by several different transcription factors, with a specific combination needed to turn the gene on

what class are steroid hormones?
class of lipophilic molecules derived from cholesterol
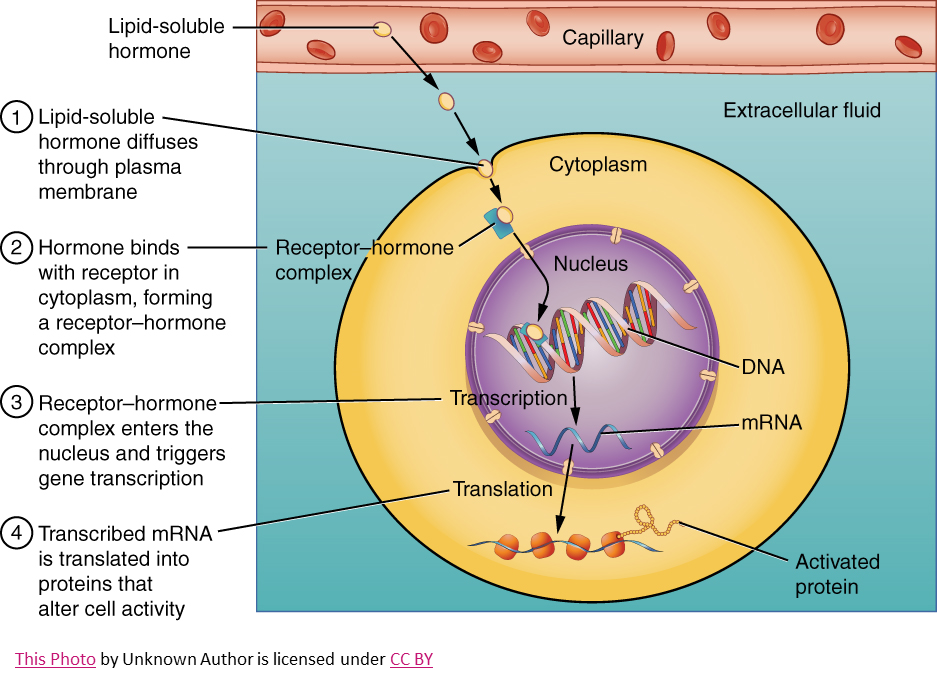
steroid hormones easily pass through the cell membrane and to?
specific receptors inside the cell
what three categories are steroid hormones divided into based on function?
Sex steroids (e.g., oestrogen, testosterone)
Glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol)
Mineralocorticoids (e.g., aldosterone)

what type of receptors to steroid hormones bind to?
intracellular receptors
diagram of how steroid hormones work…
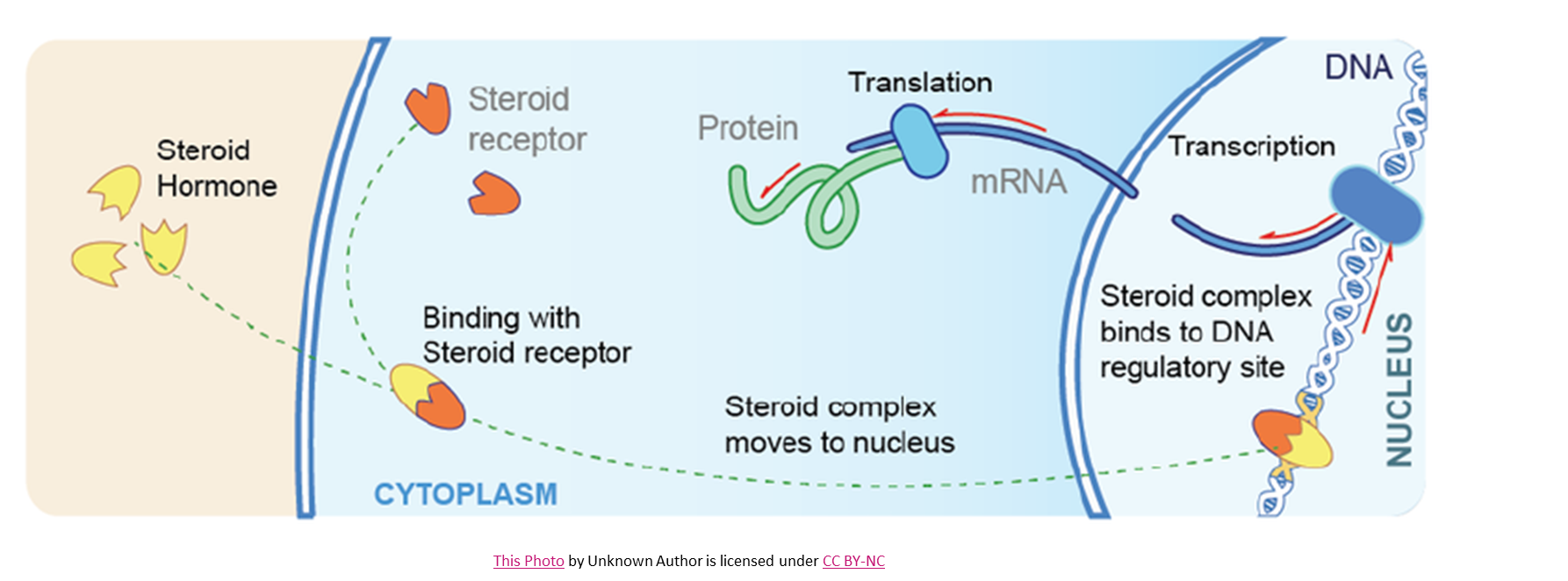
how are steroid hormones different from other hormones?
not stored in vesicles
Production can be stepped up rapidly, but still takes time
Ligands for transcription factors (SHR)
Alter gene expression
Therefore, response measured in hours to days

describe osmolarity in hormones (e.g. aldosterone)?
Osmolarity: amount of solute per unit volume
Drives water movement if it can!
is important in the kidney
Sodium
Control sodium movement...
...water movement will follow

what does aldosterone do to the body?
That last sodium transporter is aldosterone-sensitive
Acts on the kidney to enhance Na+ retention
Therefore enhances water retention
Increases blood volume (and pressure)
Increases pressure driving formation of tissue fluid
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system

describe gene target for aldosterone?
Two-step process:
First is passive (Na conc in the lumen is very high)
Facilitated by ENaC
Second is active
Driven by Na+/K+-ATPase
Both are gene targets of aldosterone
Response elements present in the promoter

describe transcription in oestrogen and testosterone?
Key in reproductive health
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
Synthetic versions of these hormones
Post – menopausal symptoms or hormone deficiencies