D2.3 Water Potential
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is the universal solvent?
Water is the universal solvent because it can dissolve so many other solutes
What’s the difference between a solute, solvent, and solution?
Solutes = substances that are able to dissolve in water
Solvents = substances that are able to dissolve solutes
Solutions = the homogenous mixture formed by a solute dissolving in a solvent
What is an important dipole molecule? What does dipole even mean
Water is an important dipole molecule; It contains 2 hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to one oxygen atom. Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, and this means that the shared electron pair will get pulled slightly closer to Oxygen. So Oxygen has a slightly more negative charge than the Hydrogen, resulting in a dipole molecule.
Dipole means a pair of equal and opposite charges.
What are hydrogen bonds?
A hydrogen bond is a covalent bond that forms between Hydrogen and another electronegative element, such as oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine. Hydrogen is slightly more positively charged, and is therefore attracted to the electronegative element.
Why does water have such a high specific heat capacity?
Water has a very high specific heat capacity (meaning it requires a lot of heat energy to raise its temperature even by 1 degree celsius); Its high specific heat capacity is a result of the hydrogen bonds that form between the partially positively charged hydrogen atoms and the partially negative charged oxygen atom.
Are hydrogen bonds strong or weak?
Hydrogen bonds are generally weak bonds in comparison to ionic and covalent bonds, because they are constantly forming and breaking.
What are ions? What happens when you add an ionic compound into water?
Ions are atoms that have either lost or gained electrons, and as a result, have either a positive or negative charge
Adding an ionic compound into water will cause the negative ions to be attracted to the partially positive charges of the hydrogen atoms in the water molecules;
And the positive ions will be attracted to the partially negative charges of the oxygen atoms; As a result, water molecules will surround the ions, creating hydration shells.
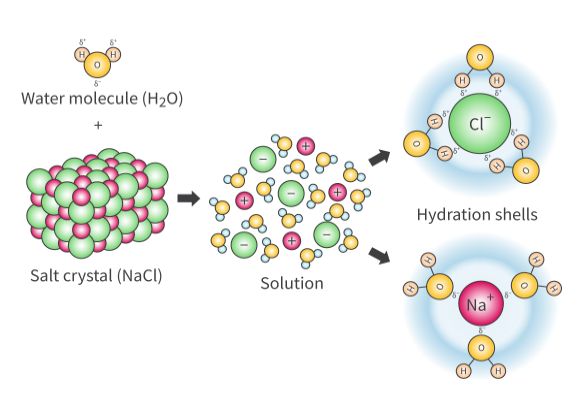
What is dissolution? What is it caused by? Can dissolution only happen in ionic compounds?
Dissolution is the process of solute particles moving and becoming evenly distributed in a solvent. It’s caused by the fact that when hydration shells are formed, they separate solute particles, making them get evenly distributed throughout the solution.
Dissolution can happen in both ionic and covalent compounds; However, in this case/scenario, we are only referring to ionic compounds.
What other covalent compounds can dissolve in water? Can they dissociate?
Glucose, Oxygen, and Alcohol; But they cannot dissociate into ions the same way ionic compounds can;
KEY NOTE: only ionic compounds can dissociate into ions
covalent compounds CANNOT dissociate into ions
What is a solution again? In what direction can water move in a solution? Why is this?
A solution is a homogenous mixture made up of solutes dissolved in a solvent. In a solution, water can only move from low to high concentrations of solution, because it likes to move from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration.
The reason for this is because water is attracted to the solute particles in the solution.
What happens if you have two different regions separated by a permeable membrane, where there is water on one side and a solution on the other?
ONLY THE WATER WILL MOVE from the area of low solute concentration (where it is now) to the area of higher solute concentration (across the membrane); because solutes cannot move across (due to their size or charge)
What’s the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic?
Hypertonic = a solution with a high solute concentration (a higher osmolarity) (because osmosis is the process of water molecules moving from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration)
Hypotonic = a solution with a lower solute concentration (a lower osmolarity)
What is the definition of diffusion?
Diffusion is the process of particles moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
What happens to a cell when you place it in a hypertonic solution? What impact does this have on the cell?
If you place a cell in a hypertonic solution (meaning a solution with a high solute concentration), then the water will gradually start to move out of the cell into the surrounding solution (moves from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration);
This causes the cell to shrink and become crenated as an animal cell or go through plasmolysis as a plant cell.
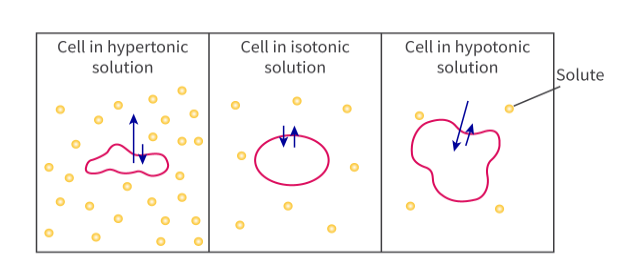
What happens to a cell when you place it in a hypotonic solution? What impact does this have on the cell?
If you place a cell in a hypotonic solution (lower solute concentration), then the water from the solution will start to move into the cell, causing it to swell.
This can cause animal cells to burst (as a result of too much water).
What is an isotonic solution?
An isotonic solution is a solution that has the same concentration of solutes as another solution, usually referring to the concentration of solutes in a cell's cytoplasm.
What happens when you place a cell in an isotonic solution?
When you place a cell inside an isotonic solution, it means you’re putting it in a solution with the same solute concentration as the cytoplasm. As a result, no water will move in or out of the cell, and there won’t be any change in the shape or size of the cell. So no NET movement of water
What is crenation and plasmolysis?
Crenation = when an animal cell shrivels up and shrinks due to water loss
Plasmolysis - when the cell membrane in plant cells shrinks away from the cell wall because of water loss
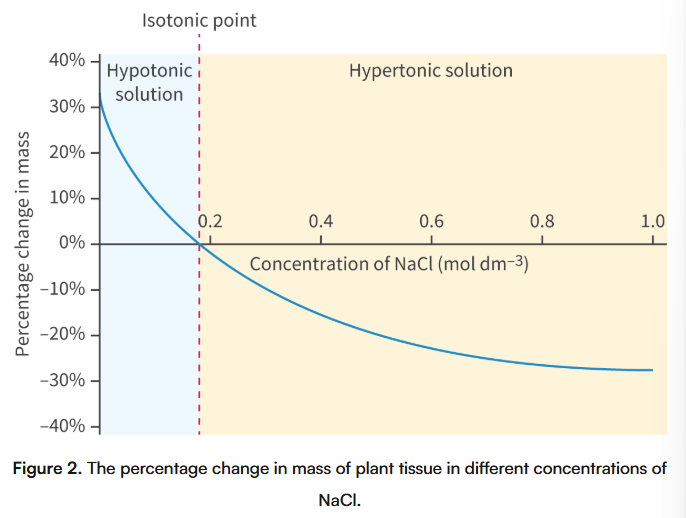
How can we calculate the isotonic solute concentration of a plant tissue? Why does this method work?
By measuring the % change of tissue mass and the length of the plant tissue when its placed in different concentrations of solution. The actual process requires placing samples of plant tissue in different solute concentrations for a set period of time, removing them from the solution, calculating the % change in the mass or size of the plant tissue, then plotting all of the data on a graph, and interpolating it to estimate the exact solute concentration when plant tissues didn’t experience a change in mass or length
This method works because plant tissues gain water in hypotonic solutions, causing both the length and mass of the plant tissue to increase; This also works in hypertonic solutions, because the plant tissue loses its length and its mass
**HOWEVER we can only measure the mass and length of pieces of plant tissue that are the same shape and size
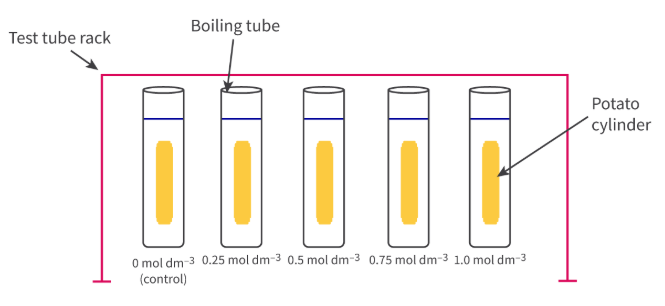
Why is it important to repeatedly measure the mass and length of plant tissue for each of the different concentrations?
To figure out if the data is reliable or not, as well as calculate standard error and standard deviation.
What is the definition of standard error and standard deviation?
Standard Error = measures the variability (spread) between multiple sets of data
Standard Deviation = measures the variability (spread) between one set of data relative to the mean
What happens if you place a eukaryotic cell, without a cell wall, in a hypotonic solution? What happens if you place this same cell in a hypertonic solution?
The water from the solution is going to move into the cell, causing the cell to swell; since it doesn’t have a cell wall, it can reach a breaking point and lyse (aka burst apart) because of the increased internal pressure.
If you place it in a hypertonic solution, then this will cause water to move out of the cell, causing the cell to shrivel up (crenate) because of water loss.
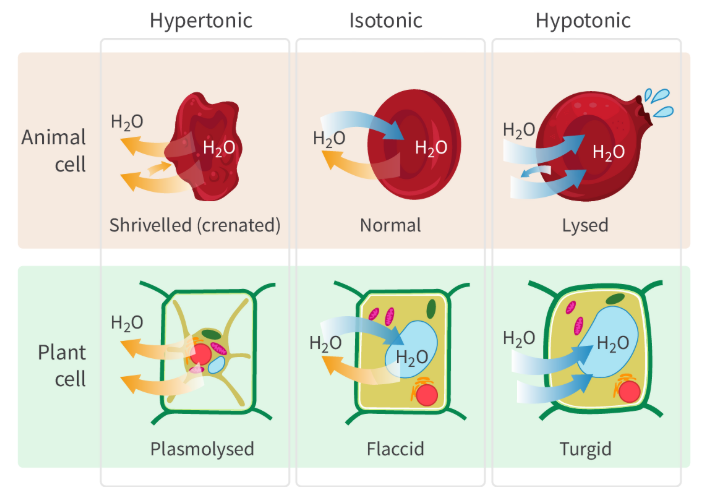
What happens if you place a plant cell, with a cell wall, in a hypotonic solution? What happens if you place this same cell in a hypertonic solution?
If you place a plant cell in a hypotonic solution, water will move into the plant cell, which accumulates and increases the internal Turgor Pressure of the cell. The cell wall is the only thing preventing it from bursting and maintains its shape; However, the plant cell does become turgid, meaning swollen, firm, and rigid because of water intake.
If you place a plant cell in a hypertonic solution, water will move out of the cell, and the cell membrane will shrink away from the cell wall through a process called Plasmolysis. This means the plant cell will shrink and lose turgor pressure, potentially permanently damaging the cell.
What mechanisms do some unicellular organisms have to prevent excess water intake? Why do they have these mechanisms? What are these unicellular organisms?
Some unicellular organisms, like paramecium and amoeba have contractile vacuoles; specifically designed to prevent excess water intake. They need these mechanisms to maintain the proper intracellular solute concentration and to prevent lysis from happening; This is important since they live in hypotonic environments.
What mechanisms do some multicellular organisms have to maintain isotonic tissue fluid? Not very in depth answer
Humans (a multicellular organism) have kidneys that play a role in maintaining the isotonic tissue fluid; this means it makes sure that every single cell is in an environment with an equal concentration of solutes in order to function properly.
What are some of the medical applications of isotonic solutions?
Isotonic solutions can be used to preserve organs that will be donated in their optimal conditions, and protect them against damage associated with water loss or water gain.
Isotonic fluids can also be administered directly into veins to allow other medications or nutrients to get absorbed into the bloodstream without needing to be ingested. This is most commonly used to transfuse blood, replace lost fluids, and administer drugs.
What is water potential? What is it measured in? What is pressure potential? What is it measured in?
Water potential is the energy per unit volume of water, and it determines the direction of water flow.at STP (ATP (atmospheric pressure and 20 degrees celsius)
Water potential is measured in kPA;
Pressure potential is a part of the formula used to calculate water potential; It refers to the pressure that water exerts on the cell membrane (aka turgor pressure)
What is the water potential of pure water? Is this a high or a low water potential? What does a negative water potential mean?
Pure water has a water potential of 0 kPA. 0 kPA is actually the HIGHEST POSSIBLE water potential. Water Potential can only get more negative from there. The more negative water potential is, the harder it becomes for water to move.
What are the two factors influencing water potential? What do these factors mean? What is the formula for calculating water potential?
Water potential is influenced by:
Solute Potential = the attraction of water molecules to solute particles
Pressure Potential = the pressure that water exerts on a cell membrane (known as turgor pressure only in plant cells)
The formula for calculating water potential is:
Ψw = Ψs + Ψp
Water potential = solute potential + pressure potential
What is dynamic equilibrium (referring to water)
Dynamic equilibrium = when the movement of water molecules in and out of a system is balanced
Can you give an example of pressure potential?
The pressure potential in plant root hair cells; This is called root pressure, and it is the upward force that drives water and nutrients into the plant from the soil.
What does negative and positive pressure potential generally represent?
Negative pressure potential = more like a vacuum (pulling water up).
Positive pressure potential = more like pushing or exerting pressure on the cell (pushing water).
Positive Pressure: Remember positive water potential is like pressure being exerted, so it’s associated with pushing or moving the water out, like turgor pressure in a plant.
Negative Pull: Negative water potential refers to water being pulled by tension or suction, like during transpiration when water is drawn up from the roots.
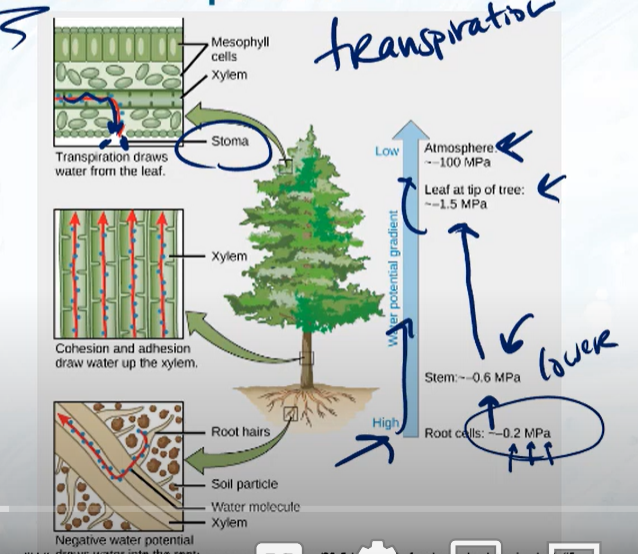
How does water move in relation to water potential? What is an example of this?
Water moves from HIGH to LOW water potential; An example of this is in the transpiration of a tree; The root cells have a water potential of -0.2 and the leaf at the tip was a water potential of -1, while the atmosphere has a water potential of -100, and therefore the water will diffuse upwards and out of the tree through the stoma in the leaves.
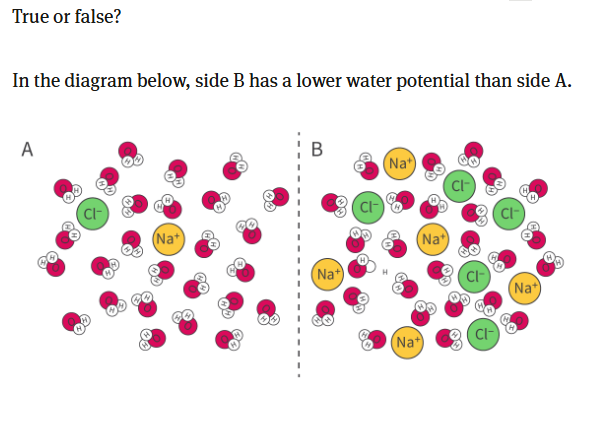
Recall: Water moves from high to low water potential;
and water also moves from low to high solute concentrations;
so here, we can clearly see that side b has a higher solute concentration. Therefore the water will move from Solution A to Solution B, and so Solution B also has a lower water potential.
ANSWER: SOLUTION B HAS A LOWER WATER POTENTIAL

Positive pressure potentials are generally forces that are pushing water, and negative pressure potentials are forces that pull water upwards, think of it as suction or a vacuum. Transpiration creates negative pressure potential because water is being sucked up the tree (so it is negative, going against gravity, like a suction/vacuum)
Positive pressure
Negative pull