Comprehensive Chemistry Notes: Scientific Method, Properties, and Periodic Table
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What marks the beginning of chemistry?
Humans transforming substances using fire (e.g., cooking, smelting metals).

What is alchemy?
A mix of chemical techniques and mystical ideas aiming to turn base metals into gold and create elixirs.

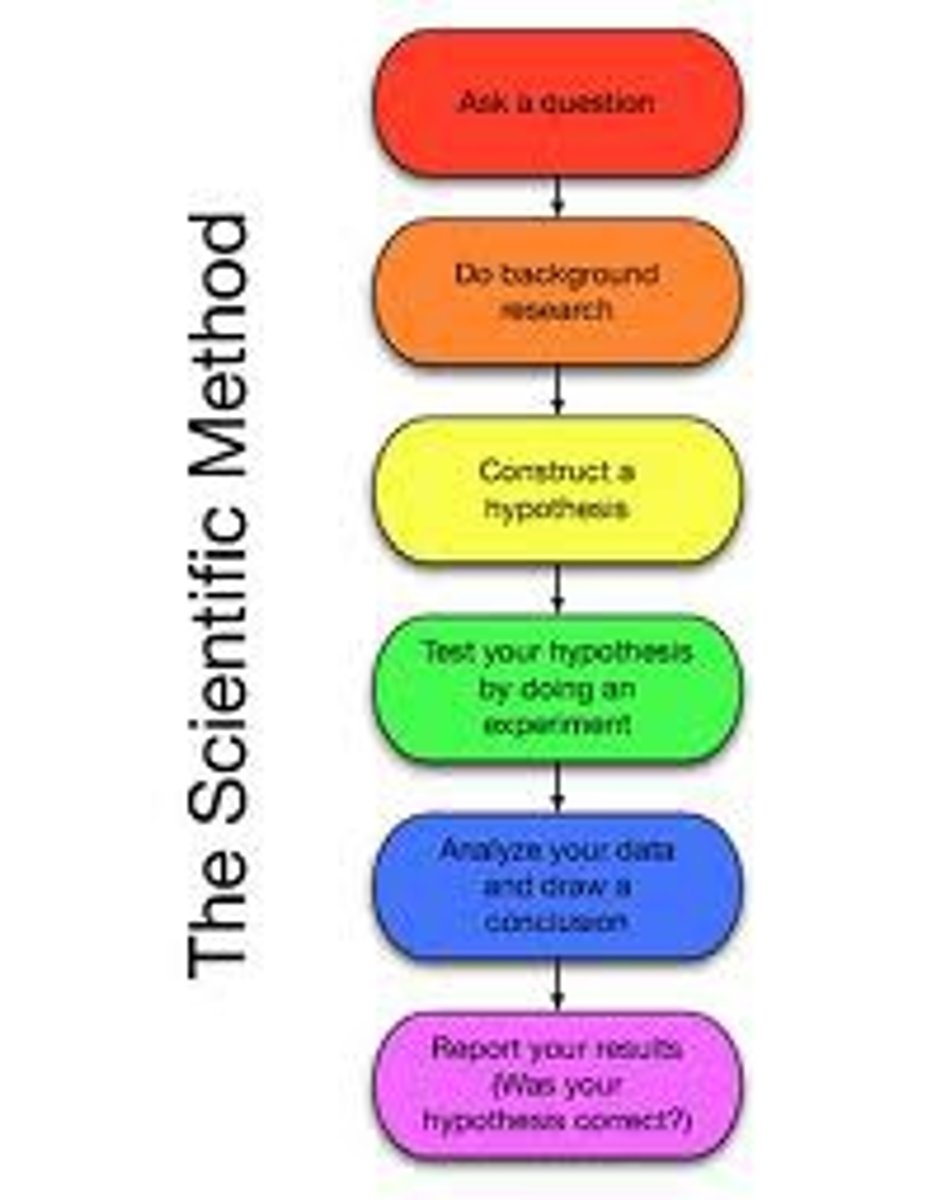
What are the steps of the scientific method?
Observation → Question → Hypothesis → Experiment → Analysis → Conclusion.
Define hypothesis, theory, and law
Hypothesis: testable guess; Theory: well-supported explanation; Law: describes consistent behavior.

What are the three domains of chemistry?
Macroscopic (visible), Microscopic (atoms/molecules), Symbolic (formulas/equations).
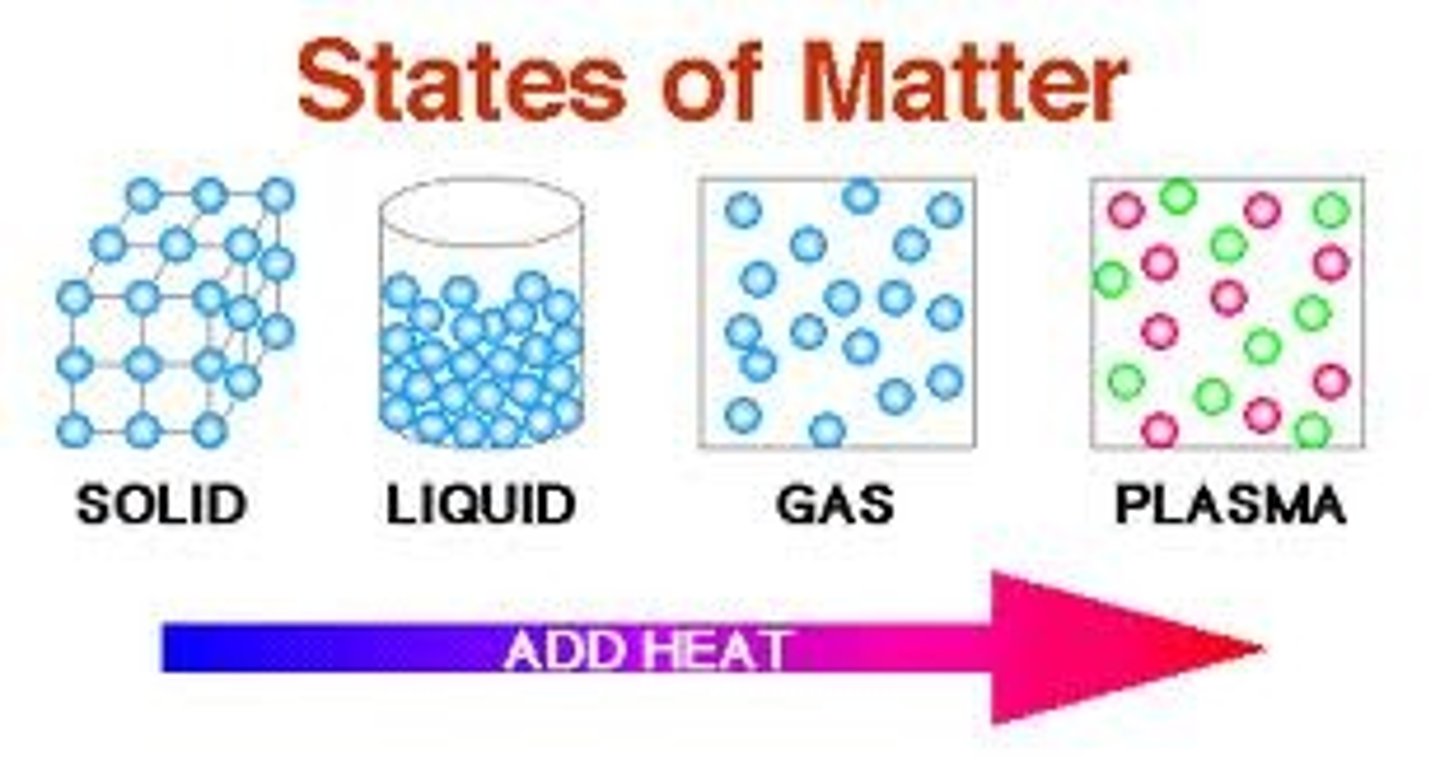
What are the four states of matter?
Solid, liquid, gas, plasma.
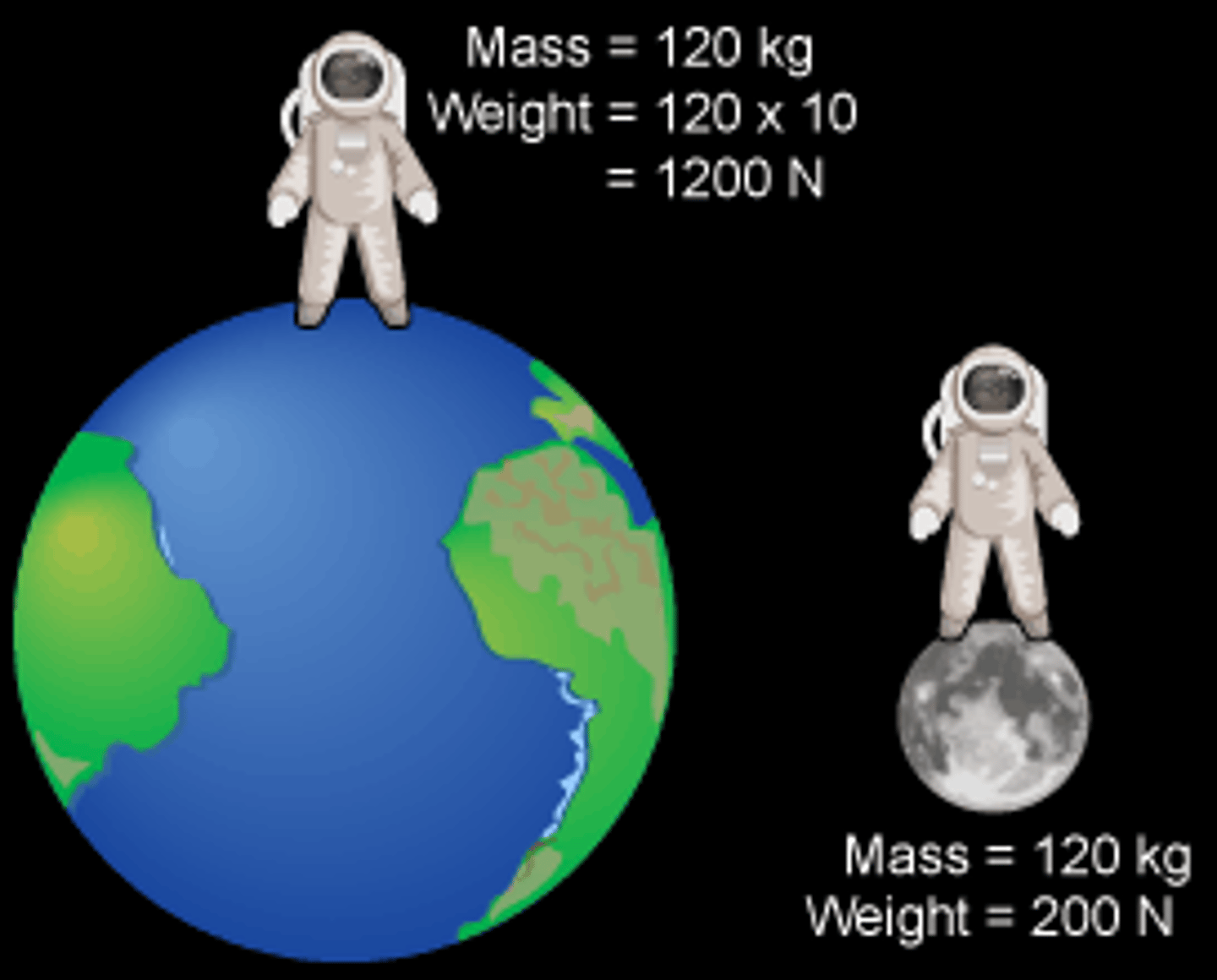
Difference between mass and weight?
Mass = amount of matter (unchanging); Weight = gravity's pull on mass (changes with location).
What is the law of conservation of matter?
Matter is not created or destroyed—only changes form.
Define element, compound, and mixture.
Element: pure substance; Compound: two+ elements chemically combined; Mixture: physical blend of substances.
Difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures?
Homogeneous: uniform throughout; Heterogeneous: uneven composition.
What is an atom?
The smallest unit of an element that retains its properties.
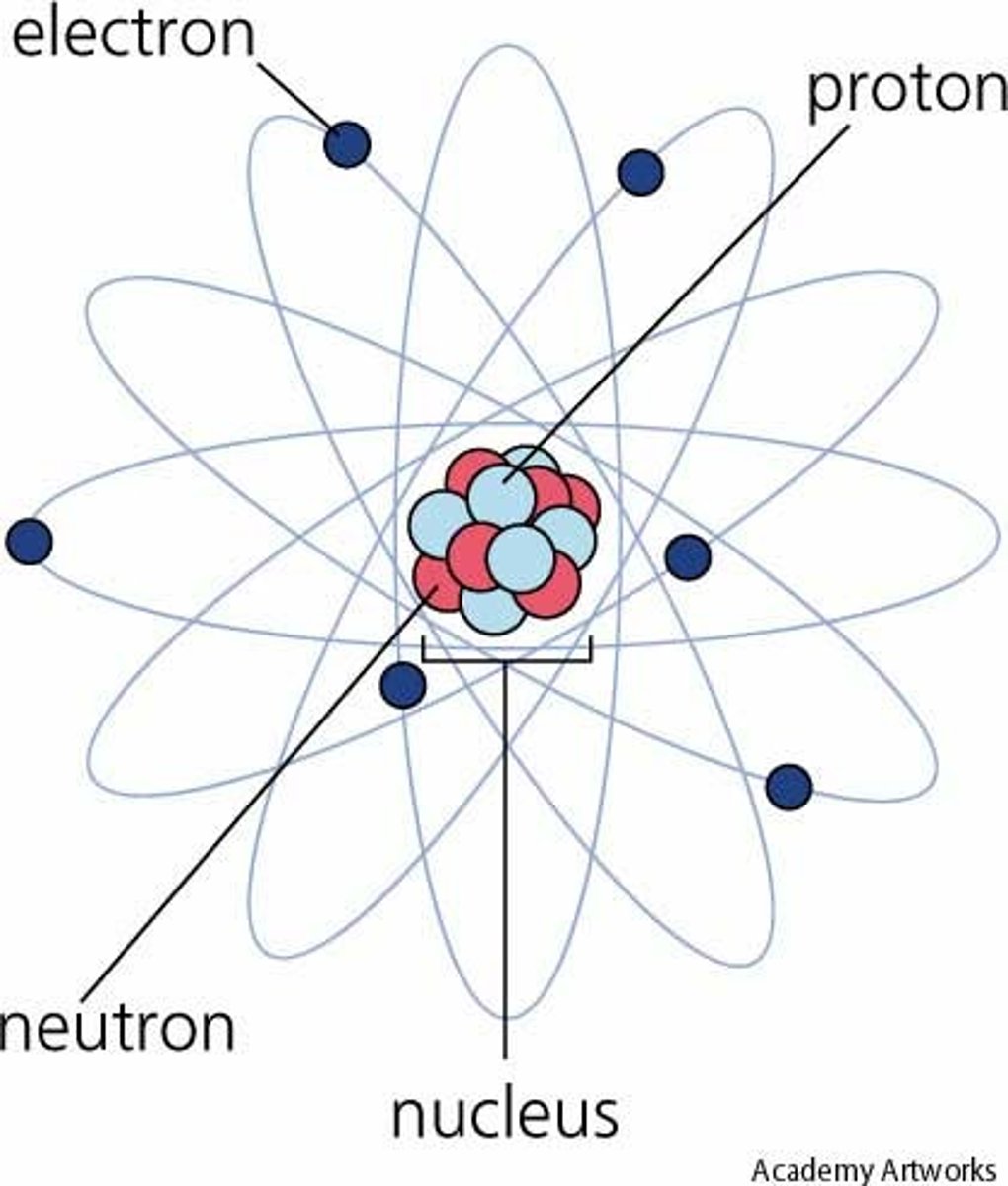
What is a molecule?
Two or more atoms bonded together.
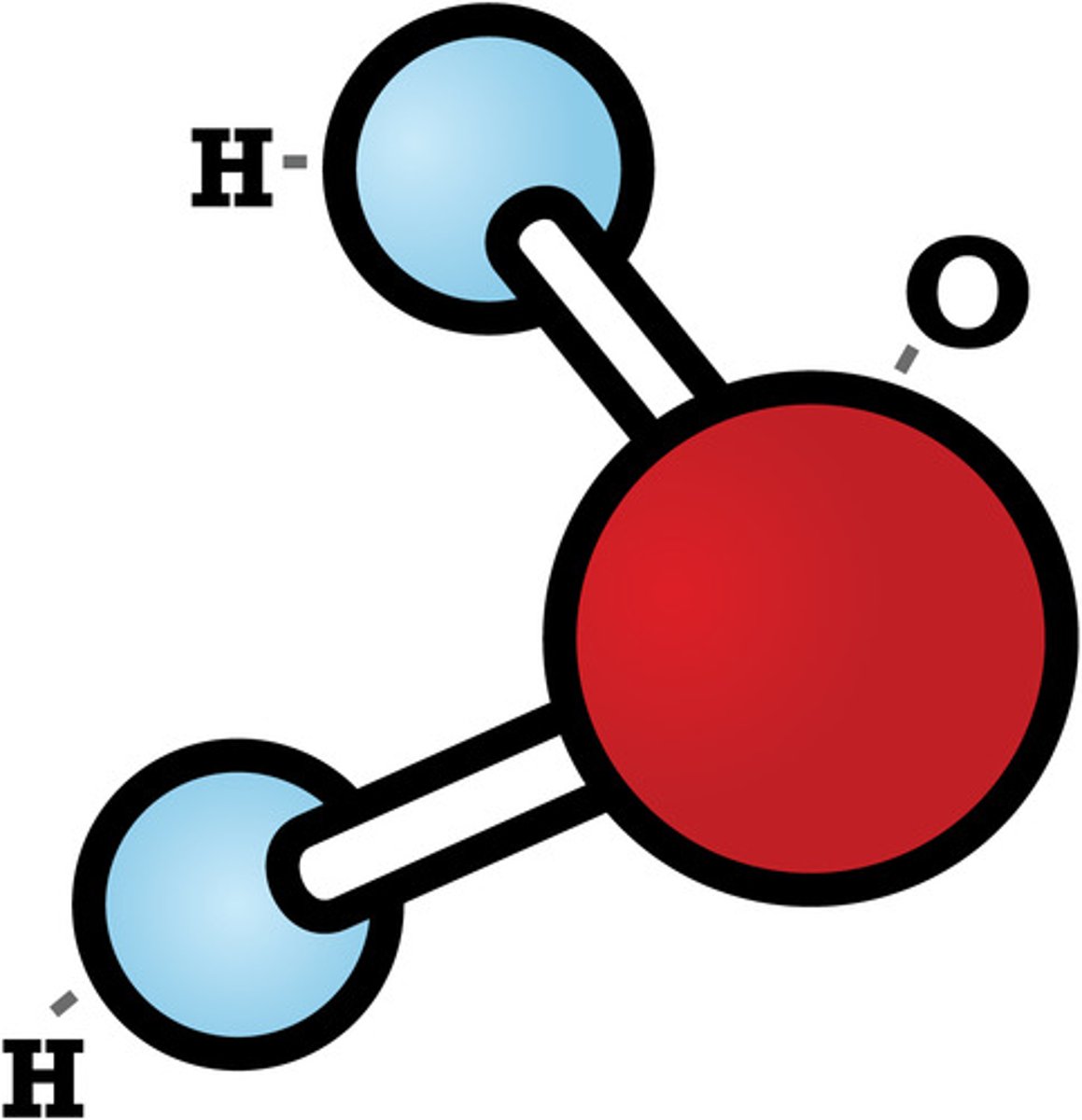
What's the difference between an element and a compound?
Element = one type of atom; Compond = two or more types of atoms.
What happens when water decomposes?
H₂O → H₂ + O₂ (hydrogen and oxygen gases form).
What are fuel-cell vehicles (FCVs)?
Cars powered by hydrogen that produce only water as waste.
How is chemistry used in cell phones?
Phones use ~30% of natural elements—plastics, metals, semiconductors, and battery materials.

What is a physical property?
A trait observed without changing the substance (e.g., color, melting point).
What is a chemical property?
A trait that describes how a substance reacts (e.g., flammability, rusting).

What is a physical change?
A change in form or state without changing the substance (e.g., melting, dissolving).

What is a chemical change?
A change that creates new substances (e.g., burning, cooking, rusting).
Difference between extensive and intensive properties?
Extensive: depends on amount (mass, volume); Intensive: doesn't depend on amount (temperature, density).
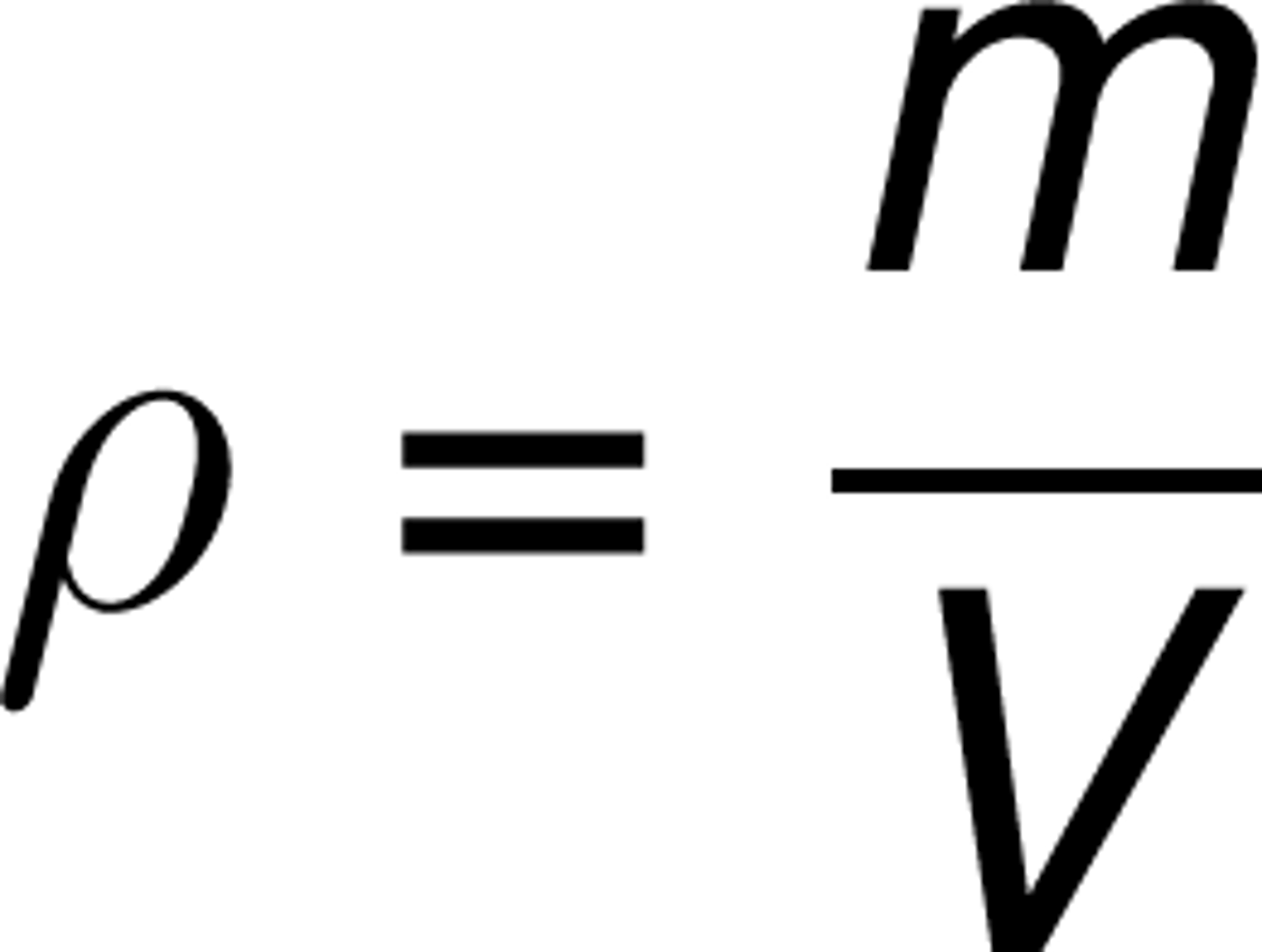
What does the NFPA hazard diamond show?
Chemical risks—fire (red), health (blue), reactivity (yellow), special hazards (white), rated 0-4.

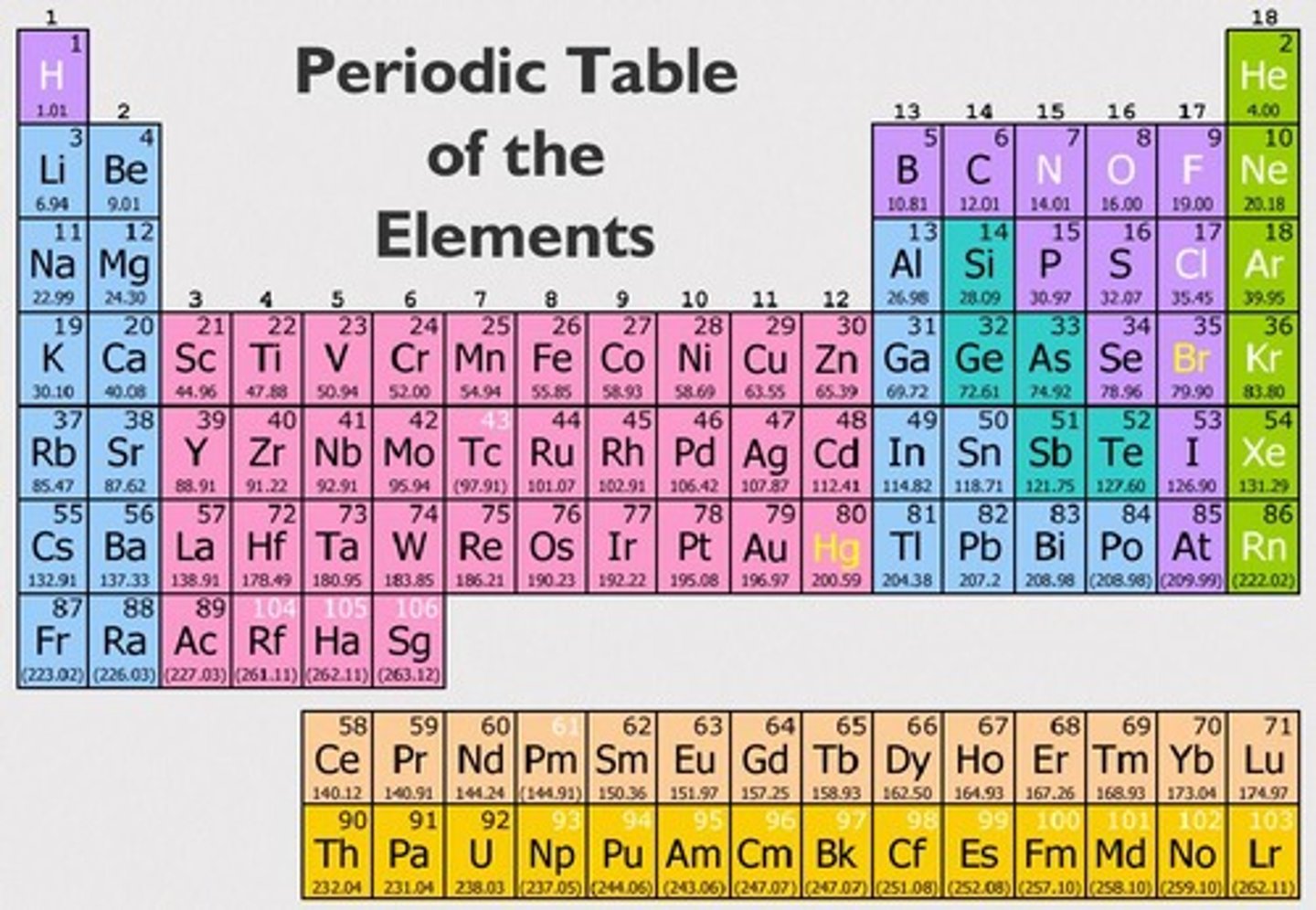
What does the periodic table show?
Groups elements by properties—metals, nonmetals, metalloids; also shows state (solid, liquid, gas).
What are the components of a measurement?
Value, unit, and uncertainty.
What are SI units?
Standard units like meters, seconds, kilograms.
What are derived units?
Units like liters (volume), g/cm³ (density).
What do prefixes like micro and mega mean?
Micro = 10⁻⁶; Mega = 10⁶.
Wat is uncertainty in measurement?
Estimate of how much a measurement may differ from the true value.
What are significant figures?
Digits that reflect the precision of a measurment.
What is accuarcy?
Closeness to the true value.
What is precision?
Consistency among repeated measurements.
What is dimensional analysis?
A method to convert units and solve problems using conversion factors.
What is a unit conversion factor?
A ratio of equivalent values used to change units (e.g., 1 inch = 2.54 cm).