economics flashcards
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
what is the economic problem?
how to satisfy unlimited needs and wants with scarce resources
what does siamese stand for?
scarcity, making choices, specialization and trade, interdependence, allocation and markets, economic performance and living standards
What are the factors of production?
Land (natural resources), labour(human resources), capital (tools and machinery) and enterprise (managing these resources)
what does making choices mean?
since resources are scarce, producers and consumers need to make choices on what to produce or buy
what does specialization and trade mean?
individuals and countries can’t have all resources, meaning they must specialize and trade with other individuals/countries.
why is specialization and trade important?
individuals/countries can focus on producing a good/service to become efficient and cheaper
what is interdependence?
we rely on others to satisfy needs, based on the circular flow diagram
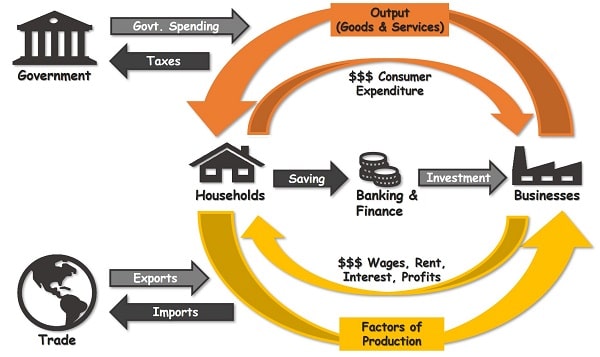
what is allocation and markets?
this refers to the distribution of scarce resources amongst producers and also refers to the way we distribute scarce g&s amongst consumers
how are goods and services redistributed?
goods and services are distributed through markets and price determines how much we can produce and consume
what are markets?
interaction between buyer and seller
What is economic performance ?
it is how we measure success of an economy
what are key indicators of economic performance and living standards?
GDP (amount of g&s produced in one year), inflation (levels of prices of G&S) and unemployment rates
What is living standards?
what it is like to live in the country and their level of wellbeing.
what are 3 ways to measure wealth distribution?
calculation of net worth, gini coefficient/lorenz curve and the Henderson Poverty Line
how to calculate net worth?
net worth= assets-liabilities
Gini Coefficient
A number between 0 and 1 that measures income inequality, based on how far the Lorenz Curve is from the line of perfect equality.
Lorenz Curve
A curved line on a graph that shows the difference between perfect income equality and the actual income distribution in a population.
Australia Tax System
has progressive tax system, which means the more you earn the more you pay
which quintiles earn more after tax?
the lower quintiles earn more after tax as the money is redistribute from higher income earners
Henderson Poverty Line
Benchmark for comfortable living- 2 adults and 2 children family need $1130 per/week. If you earn less you are in poverty
What are some policies to improve living standards?
welfare systems, superannuation policies
Budgetary/Fiscal Policy (Budget)
what is the government spending money on and what taxes are being charged. usually delivered in may
Balanced budget
Spending=tax
Deficit budget
spending>tax
Surplus Budget
spending <tax
What is monetary policy?
The reserve bank changes interest rates; affects how much extra money people have
What do higher interest rates do?
higher interest rates mean less fun money which leads to less jobs
What do (microeconomic policies) do?
it affects a company or a market, and focuses on promoting competition, productivity and efficiency
What is trade liberalisation?(microeconomic policies)
it removes tariffs and opens up free trade
What is deregulation?(microeconomic policies)
removes government regulations against certain products
labour market reform(microeconomic policies)
A change to laws or policies to make the job market work better — usually by increasing flexibility, productivity, or efficiency.
Productive Policy (microeconomic policies)
how efficiently resources are used. greater productivity means increased output of goods and services
privatization (microeconomic policies)
When the government sells a business or service it owns to private companies or individuals.
training workforce (microeconomic policies)
which means to develop the skills of workers
migration policies (microeconomic policies)
bringing in skilled workers from other countries to fill in gaps in the Australian workforce
Income Distribution in Australia
poorest 20% has 7.3% of the income whist the top 20% has 40% of income which is 3x as much
Wealth Distribution in Australia
poorest 20% has 1% of wealth whilst the highest 20% has 62% of wealth
how does the government redistribute income?
governments can charge tax on peoples incomes to redistribute income through compulsory superannuation and welfare
Key factors affecting living standards: Natural Resources
affects wealth and living standards as Australia trades with other countries to earn income and improve living standards
Key factors affecting living standards: stability of government
civil war/political instability as war directs resources into war diverting funds for other sectors of govt
Key factors affecting living standards: labour productivity
The more goods a worker produces, the better—helped by better machinery, education, and training.
Key factors affecting living standards:
Labour Resources
proportion of the population thats employed . employment means more income is earnt to spend and more people get taxed meaning more money to improve living standards
Factors influencing major consumer and financial decisions: Price
Most people want lower prices, but some think cheap means low quality or that high prices aren’t worth it. Others see high prices as a sign of status or luxury.
Factors influencing major consumer and financial decisions: Availability of Credit
an agreement to borrow and repay later usually with interest. credit cards are easy to obtain making it easier to go bankrupt
Factors influencing major consumer and financial decisions: Marketing
influences consumers to buy products
Factors influencing major consumer and financial decisions: age and gender of consumers
young/old/men/woman all different products are targeted
Factors influencing major consumer and financial decisions: Convenience
saves us time- fast food over 23 billion and ready maid meals over 900 million
Ethics
right or wrong/environment friendly/human or animal rights
Australia GDP
ranked 13th and produces 2% of world GDP. 25 years of uninterrupted economic growth, Covid stopped GDP growth
Australia Unemployment
4% (good), 12 lowest for unemployment in OCED countries
Australia economic growth
0.8% which is not good
Australia inflation rates
2.4% which is ok —> ideal rate is 2-3%
Australia Youth unemployment
around 8%- some regions suffer more because it can be difficult to get a job due to technological change