pvcc pediatrics exam 2
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
barbara moris test plan for exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
DM T1
Autoimmune condition resulting in pancreatic damage and lack of insulin.
Diagnose with laboratory testing: hemoglobin A1C
fasting glucose
plasma glucose
Manifestations: weight loss, polydipsia, polyphagia, polyuria, fatigue, blurred vision, and mood changes
Management is multifaceted and includes: Insulin therapy, Glucose monitoring, Insulin education, Maintaining proper nutrition, Patient and family education.
Dehydration
Classified by severity: mild (3%–5% volume loss), moderate (6%–9% volume loss), or severe (≥10% volume loss) based on previous weight
Calculating dehydration:
Treat with a bolus of 20ml/kg bolus of NS over 30-60 minutes moderate-severe dehydration cases may require up to 3 boluses of 20mL/kg isotonic fluids before initiating maintenance fluids.
Reassess cues of dehydration after bolus to determine in another is necessary or start maintenance IVF with electrolyte replacement
NS bolus
Treat with a bolus of 20ml/kg bolus of NS over 30-60 minutes moderate-severe dehydration cases may require up to 3 boluses of 20mL/kg isotonic fluids before initiating maintenance fluids.
Maintenance IVF
Done after rehydration
hydrocephalus
Build-up of CSF in the brain due to increased CSF production and decreased CSF absorption
Mx: depend on age and severity: Dilated scalp veins, bulging fontanel, apnea, irritability, headaches, and vomiting
Posterior fontanelles (smaller): closes 2-3 months
Anterior fontanelles (larger): closes between 12-18 months
Tx: Ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement. May need replacement throughout lifetime as child grows. Monitor head circumference to assess patency.
UTI
Pts at risk pre- and post- hypo&epispadis, during potty training,
Hypospadias
The urethral opening is on the ventral side of the penis
Avoid circumcision because that skin will be used for surgical correction
Surgical correction produces the ability to urinate in the standing position, preserve physical appearance, maintain sexual function
Urinary diversion device may be placed for 5-10 days post-op
Discharge Edu.: Pain relief including Bladder spasms, Bowel care regimen, Reduce risk for infection, No straddle toys
Encopresis
defined as voluntary or involuntary passage of stool into inappropriate places at least once a month for 3 consecutive months after the age of 4 years. 2 types:
retentive encopresis: history of chronic constipation, most common form: 65%–95% of children
Parents may see liquid stools in underwear (why?)
Non-retentive encopresis is when constipation is not present
Can be associated with emotional or psychological disturbances
hypothyroidism
Insufficient thyroid hormone
Manifestations: low T3 and T4, persistent open posterior fontanel, thickened protuberant tongue, dull expression, hypotonia, etc
Treat with sodium levothyroxine (a synthetic thyroid hormone) and frequently monitor levels, track and trend growth
Intussusception
The intestine pushes into itself.
Most common cause of obstruction in 5 months to 3yrs old
Abrupt onset of severe, paroxysmal, and colicky pain.
Currant jelly (red) stools and nausea and vomiting.
Enemas given under imaging to reduce the defect.
Surgery needed if enema is not effective.
congenital clubfoot
More common in boys, can unilateral or bilateral
Heel tilts in and down, forefoot turns in, and bottom of the foot faces inward or upward. Shorter Achilles tendon and foot and calf on affected side.
2 step treatment: 1rst serial casting with long leg casts changed weekly (begin early before bones ossify), then Bracing for 2 to 4 years afterward to maintain correction
bronchiolitis
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
Cells in bronchioles die and accumulate and obstruct.
Mild cough, rhinorrhea, and congestion
Worsening symptoms after 2 days
Symptomatic treatment; self-limiting suction before bedtime and feedings, encourage fluids
Respiratory Failure
Leads to cardiopulmonary arrest if untreated.
Quickly determine cause to choose appropriate interventions.
Manifestations: respiratory rate changes (tachypnea, apnea, or bradypnea), shallow chest rise, altered mental status, and cyanosis.
Tx: open airway, use BVM until intubation can be done
Encourage parents to be present during resuscitation efforts
Hypovolemic shock
Sickle Cell Anemia
Mutation of Hgb causes the body to create “sickled” or “C – shaped” red blood cells that are sticky and have crystals attached. These abnormal cells do not have the same oxygen-carrying capacity as normal hemoglobin and die in 17 days
Pts will typically be asymptomatic until a vasoactive crisis occurs
Seen across the malaria belt
SSA Medications
Prevention: folic acid, iron chelators, penicillin, hydroxyurea
Penicillin is given daily to help reduce risk of infection
Hydroxyurea: helps to prevent crisis but can cause liver damage and immunosuppression due to it being a chemo drug.
Opioids: oxycodone, morphine, hydromorphone, narcan
Narcan at a low rate 0.5-1.5mg/kg w/ a concentration of 8 mcg/ml stops side effects of opioids like itching, respiratory depression, urine retention, without taking away pain relief
NSAIDs: Ibuprofen, tylenol, ketoralac
Misc. Meds: methadone, ketamine, blood transfusion
SSA Complications
Sickle Cell Crisis: occurs when sticky cells create occlusion in blood vessel, preventing oxygenation of the tissues this leads to pain, organ and bone damage, increased morbidity and mortality
Other complications include delayed growth, lack of milestones reached, cognitive/social delays, Failure to thrive or obesity
SSA Emergencies
SSA Nursing Care
SSA Triggers
Cast Care
Handle a wet cast with open palms.
Elevate the cast above the level of the heart and ice to prevent swelling.
Assess for bleeding if applied postoperatively.
Assess for signs of infection (i.e., foul odor, drainage, fever, warmth, and redness).
Assess for skin breakdown and pressure points.
Keep the cast clean and dry.
Never put anything inside the cast – use cool setting on blow dryer for itching.
Prepare patients and caregivers before cast removal.
Nephrotic Syndrome
Tx: prednisone, cyclophosphamide, tacrolimus, furosemide, enalapril
A group of symptoms that indicate kidney damage and results in too much protein from the body in the urine
S/Sx: periorbital, facial, pitting, edema distended abdomen
VP (ventriculoperitoneal) shunt
Used to drain hydrocephalus
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
X-linked genetic disease characterized by muscle wasting and progressive muscle weakness due to muscle fiber degeneration progression and onset vary but disease is fatal
Early diagnosis and therapy is essential, glucocorticoids can delay loss of ambulation, prevent scoliosis, and preserve lung function but cause osteoporosis and nutritional deficiencies.
Dystrophin deficiency leads to pulmonary compromise and a weak myocardium (medications can improve cardiac function).
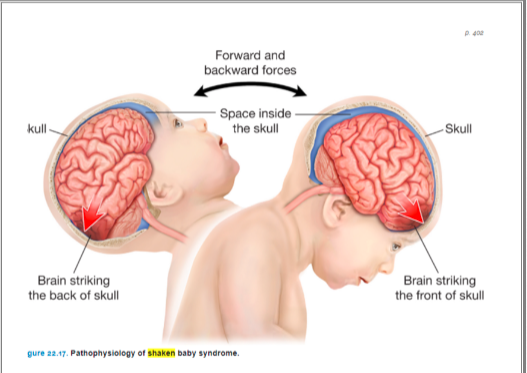
Shaken Baby Syndrome
#1 cause of brain damage in infants
can either be a Suspected Non-Accidental Trauma or deemed intentional or non intention
the force exerted on shaking can cause cerebral edema, hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, and retinal hemorrhage
survivors usually have permanent disabilities
Cues include vomiting, irritability, increased sleeping, seizures and apnea.
cleft lip
Tissues in lip and/or palate do not fuse. Resulting after feeding, ontological, dental, and speech complications.
Primary focus is nutrition and hydration
Prevent aspiration and infection
Surgical repair (lip: 2-6 months; palate: 9-18 months).
Protect suture line post-operatively.
Requires specialized feeding equipment.
Fractures
Fractures in the growth plate have higher risk for deformity and impaired healing
Tx: Immobilize with splints, casts, or traction, Reduce the fracture (put the bone back into place) and immobilize to allow for healing
Provide infection control to avoid osteomyelitis
Mx: swelling, pain, obvious deformities, abnormal positioning, and inability to bear weight or move affected area
Blount Disease
Aka Tibia Vera or Bowed legged
Tibia growth plate grow inward, suspected if still present past the age of 3
Tx: bracing if younger than 4 years old, surgical treatment can be done if bracing is ineffective, may have cast or external frames post-op
Those who receive surgery will have increased risk of compartment syndrome, and DVT post op
Provide Psych support for parents and child
ICP
Developmental (primitive) reflexes present at birth and are replaced by protective reflexes over first year of life.
osteogenesis Imperfecta
Collagen disorder resulting in fragile bones
Collagen: Protein of the body’s connective tissue that bones are formed around.
Tx is palliative in nature
Avoid automatic blood pressure cuffs and rough handling, which can cause fractures.
Provide growth hormones and bisphosphonates for bone growth
Tumor Lysis Syndrome
will result in hyperkalemia (Tx calcium gluconate, followed by insulin & dextrose), hyperphosphatemia (tx phosphate binder), hypocalcemia (will correct when phosphate levels drop), and hyperuricemia (Tx: allopurinol)
Metabolic abnormalities from release of intracellular content offer malignant cells are destroyed. Hydrate pt w/ IV fluids prior to chemo
Treat with allopurinol prophylactically - prevents uric acid from being made, can cause the need for dialysis
S/Sx: hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia (look for tetany), hyperuricemia (can cause kidney stones, HYDRATE!)
Leukemia
2 types: ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA (ALL), ACUTE MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA (AML)
ALL
is the most common form of cancer in US children in which immature, nonfunctioning WBCs (lymphoblast) dominate bone marrow production
Takes alot of different drugs to treat
S/Sx: fatigue, pallor, fever, anorexia, petechiae
Tx: chemo in 3 phases:
Induction - 4 wk course will induce remission
Consolidation - strengthens remission & CNS prophylaxis w/ intrathecal chemo
Petechiae - 2-3 yrs eliminated residual cancer cells w/ intermittent chemo
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
Doesn’t respond to treatment as well ALL, will require shorter more intense treatment. Many require bone marrow or stem cell to survive
Compartment Syndrome
Swelling and pressure inside the muscle can impair circulation and cause necrosis
Assess peripheral pulse, and oxygenation/perfusion to any casted area routinely
A medical emergency, must relieve the pressure in the compartment
Acetaminophen
reduces fever and pain
10-15 mg/kg every 4-6 hours
Do not exceed 4,000 mg/d
Metabolized by liver, can be hepatotoxic
cefepime
Broad spectrum antibiotic
Desmopressin
Intranasal desmopressin is a treatment for hemophilia
Hydroxyurea
Increases the level of fetal hemoglobin and helps to prevent sickle cell crisis
Promotes splenic function
Can cause neutropenia so monitor CBC and fHgb
oxygen
Nasal cannula (0.1-6 L/min (infants are smaller so they may only need 0.1-0.25 L/min of O2)
Simple mask (5-10 L/min)
Non-rebreather mask (10-15 5L/min)
BiPAP, CPA
lead poisoning
Tx: Chelation therapy, poison control