Neuroscience lecture 7
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Protection: the meninges
dura mater - thickest, supplied by nerves
arachnoid mater - spider webby by connective tissue
pia mater - really thin layer delicate tissue
Epidural Hematoma
a collection of blood that forms between the skull and the dura mater
dura mater is injured
middle meningeal artery ruptured
filled with arterial blood
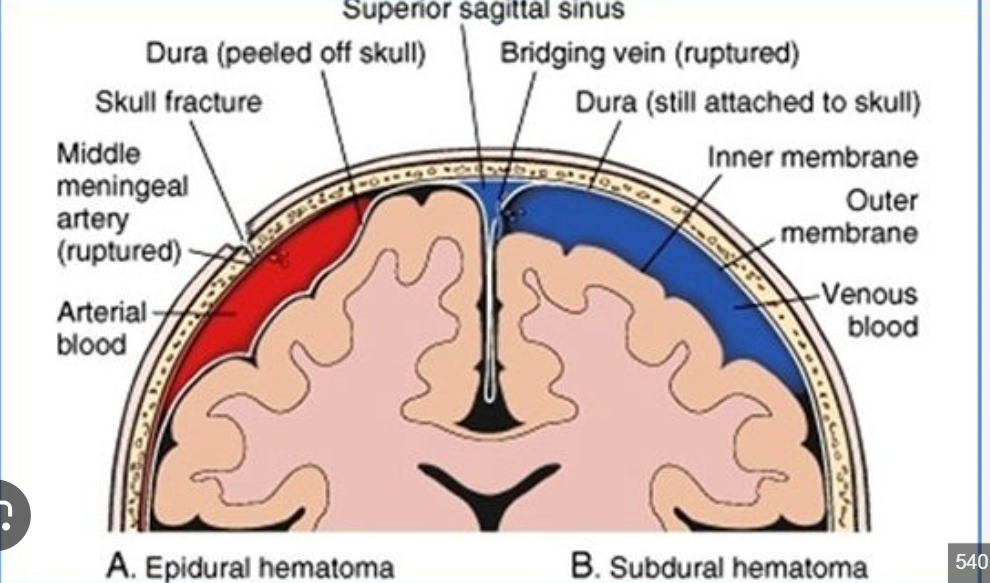
Subdural Hematoma
Dura mater is still attached
layer between dura mater and arachnoid mater is filled with venous blood
Blood brain barrier (BBB)
Functions:
protects against foreign invaders
protects against hormones/ neuro transmitters in rest of body
maintains constant environment of brain
babies in womb don’t have complete blood brain barrier which is why women while pregnant need to avoid drugs and alcohol
Blood brain barrier (BBB) problems
hypertension
developmental problems with BBB
hyperosmolality
microwaves
radiation
infection
trauma, ischemia, inflammation, pressure
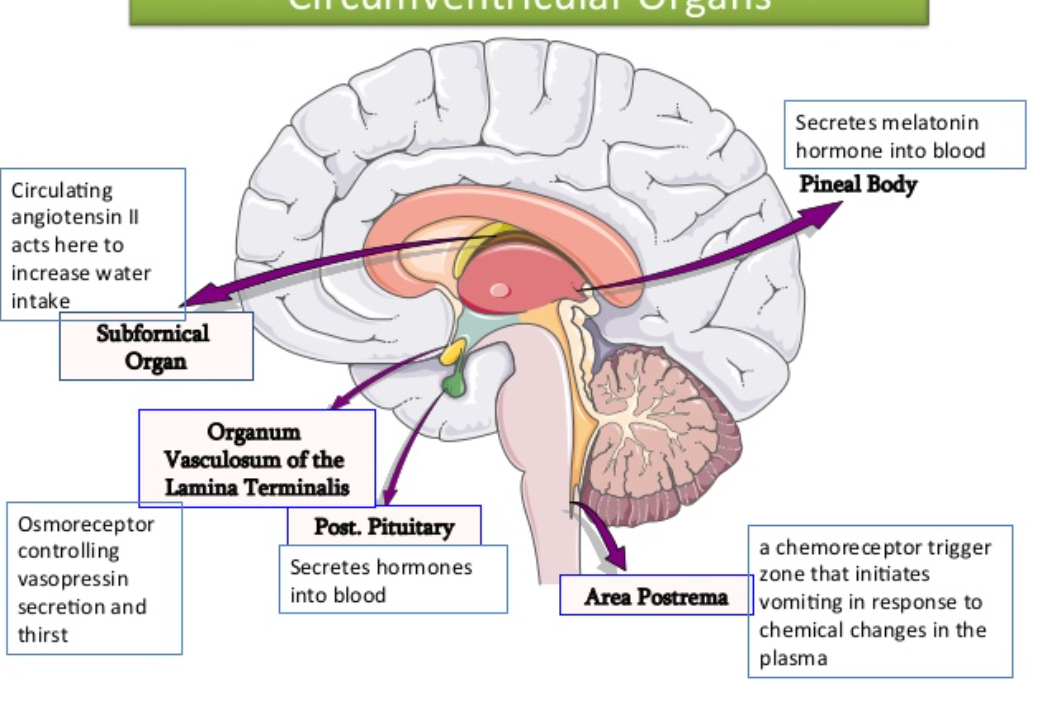
Circumventricular organs
pineal body
neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary)
area postrema
BBB is weak in these areas for receiving melatonin and other neurotransmitters more easily
Circle of Willis
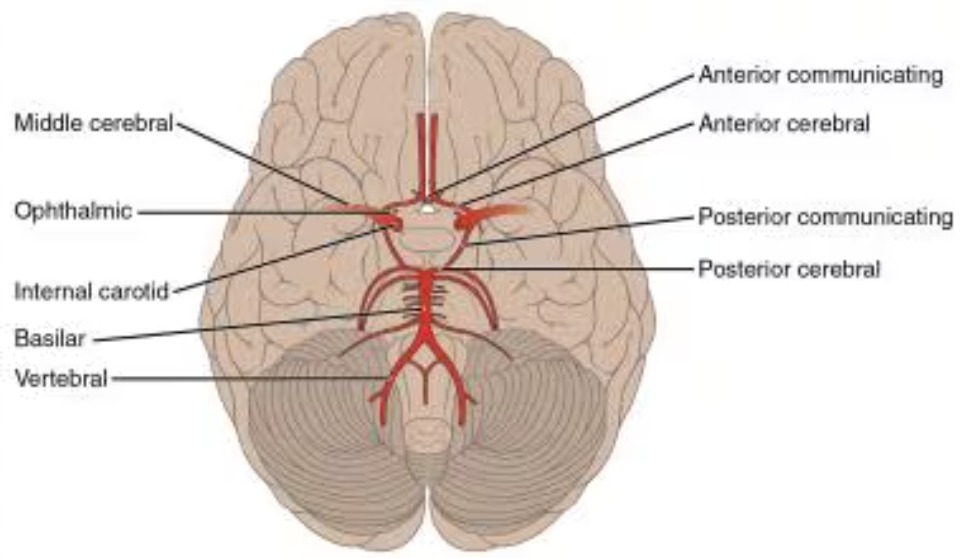
Case study 1: A patient comes in having right face and arm weakness. He is unable to speak for the most part and can only utter a few barely articulate words. He could follow many simple commands and answer yes/no question. Where do you think the damage is? What blood vessel is likely involved? Which of the lower 4 blood vessels are delivering blood to this area?
diagnoses: left side of brain effected specifically frontal lobe, Broca’s aphasia
middle cerebral artery and left carotid artery problems
Case study 2: . A patient is brought in by his wife. He was sitting at the kitchen table saying meaningless syllables over and over and wouldn't respond to any of her questions. His right arm was hanging down at his side. Where do you think the damage is? What blood vessel is likely involved? Which of the lower 4 blood vessels are delivering blood to this area?
diagnoses theory: left side effected, Wernicke's aphasia, middle cerebral artery and internal carotid problems
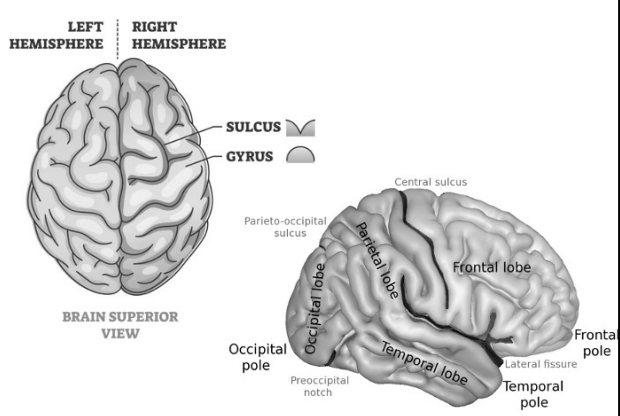
Cerebral cortex features
gyri
sulci
fissures
longitudinal
central
lateral
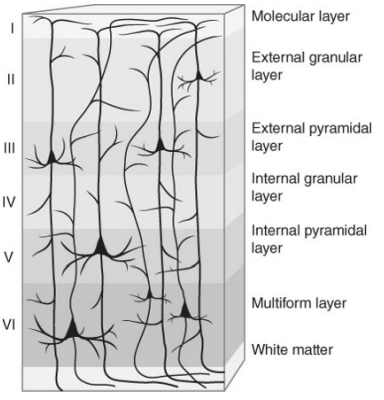
layers of the cerebral cortex
Layer III: large pyramidal cells
layer V: Betz cells
Lobes of the brain: Frontal
executive function
planning
organization
conscious thought
some speech
motor area
etc.
Lobes of the brain: Parietal lobe
sensory area
body awareness
Lobes of the brain: Occipital lobe
vision
Lobes of the brain: temporal lobe
language
auditory
Lobes of the brain: Limbic lobe
houses the hippocampus
memory
emotion
Lobes of the brain: Insular cortex
pain
risk/ reward behavior
language dominance
most people are left hemisphere language dominant:
96% of right handers
85% of ambidextrous (use both hands equally)
73% of left handers
as humans age the less they use their right hemisphere for language
Interhemispheric connections
corpus callosum
white matter tracts
(**fun fact: 200-250 million axons here)
corpus callosum problems
some people are born without a corpus callosum and can have similar characteristics to autism
Cerebral vascular accident: Ischemic
blockage that stops blood flow
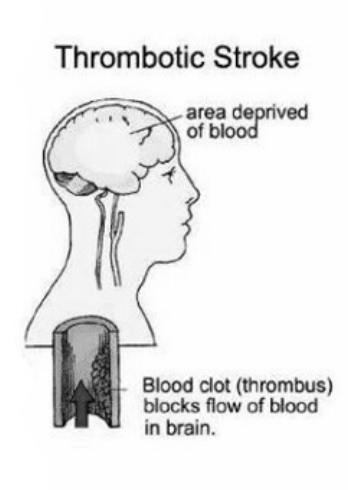
a. thrombotic:
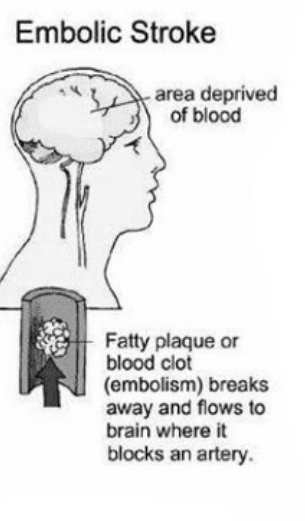
b. Embolic:
c. transient:
Cerebral vascular accident: Hemorrhagic
intracerebral hemorrhage / intra - axial (blood vessel inside brain bursts)
extra - axial: outside brain bleed
subdural bleed
subarachnoid bleed
aneurysms:
AVMS (arteriovenous malformations)
Thrombotic:
walls of the vein is coated in stuff
Embolic:
when the coating on the walls of the vein breaks free and clogs a vein preventing blood from getting through
transient: Ischemic attack
a temporary interruption of blood flow to the brain that causes neurological symptoms that typically resolve within 24 hours
1/3 of people who get this will end up with a hemorrhagic stroke
Aneurysms:
ballooning of weakened blood vessel
AVMS (arteriovenous malformations)
cluster of abnormally formed vessels
main causes of strokes:
high blood pressure
high cholesterol
smoking
obesity
signs of a stroke (FAST)
F: facial drooping
A: arms can’t be controlled
S: Speech slurred
T: time to call 911!!
Traumatic brain injury: closed brain injury
acceleration and deceleration head injury (common in car crashes) - both front and back of brain injured
impact based head injury
Traumatic brain injury: open head injury
when the skull is broken and brain is exposed
example: bullet wounds in the head
Traumatic brain injury: problems
• Coma • Drowsiness
• Headache
• Seizures
• Hydrocephalus
• Plegia/Paresis
• Dyskinesias
• Vision Changes
(they are told to rest and do light physical and mental activity)
TBI problems: cognitive communicative
attention and orientation
memory and learning
reasoning and problem solving
executive functions
speech language issues
dysarthria
aphasia and apraxia
hearing loss
dysphagia
cerebral palsy (CP)
not a genetic dieses
nothing is wrong with the baby until a traumatic accident happen during the birth like lack O2 or brain trauma
spastic CP
damage to the cerebral hemispheres
Dyskinetic CP
damage to basal ganglia
Ataxic CP
damage to cerebellum
Mixed CP
damage to multiple places
stuttering
neurogenic
speech is broken by repetition, prolongation, or stopping
some what genic
some brain differences - the right hemisphere seems to be more active then the left
many kids stutter between ages 2-5 but may not stutter forever.
no cure for stuttering - they learn to manage it but no cure for adults who stutter
neuroplasticity
the idea that the nervous system can change and adapt.
it’s limited when the person is older but not impossible to heal from stokes for example