Chapter 25 - The History of Life on Earth
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
When did Earth form?
~ 4.6 bya
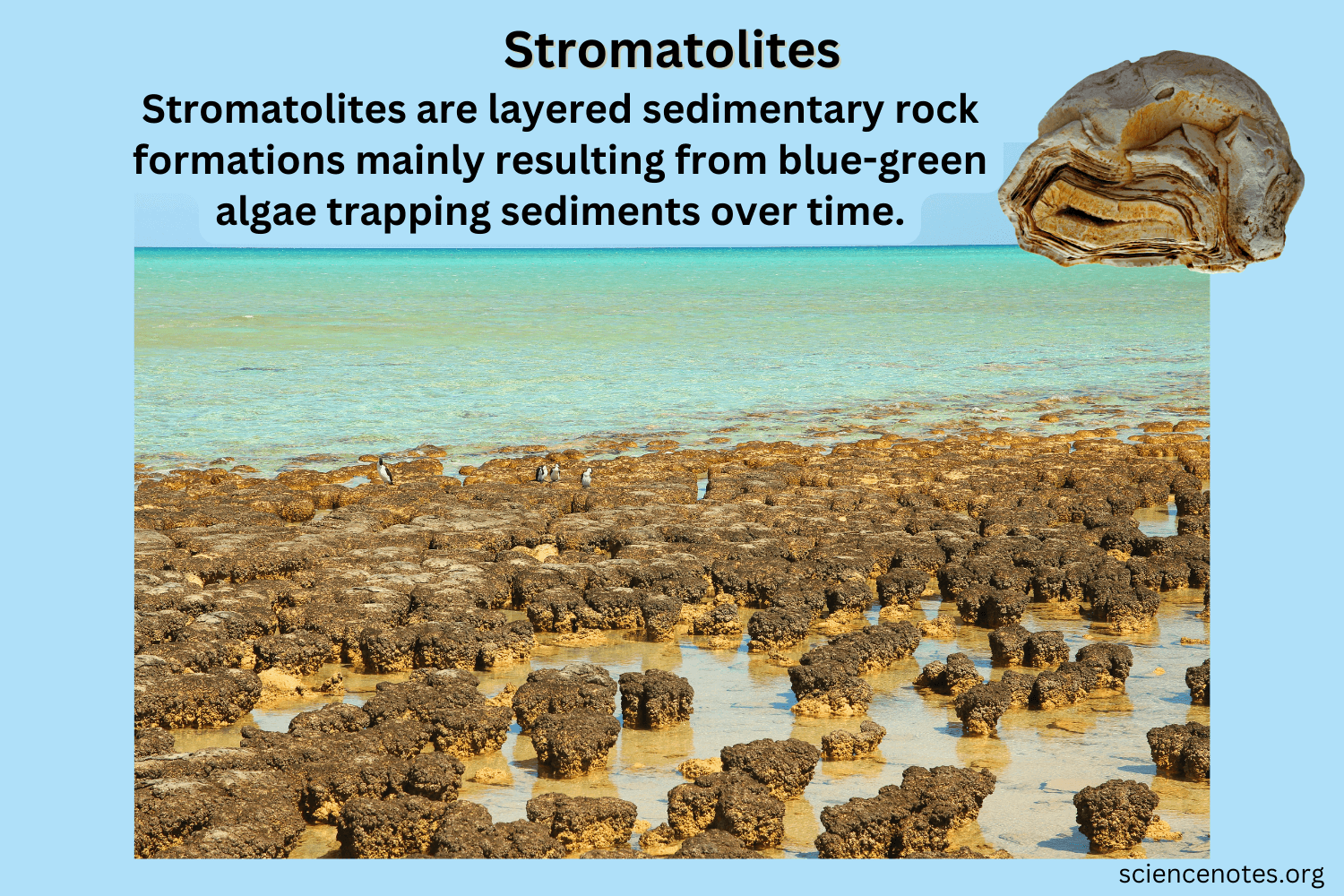
When did life first appear?
~ 3.7-4.0 bya (evidence from stromatolites)
What are the 4 predicted steps in the origin of life?
Abiotic synthesis of small organic molecules, formation of macromolecules, packaging into protocells, origin of self replicating molecules (RNA)
What are protocells?
Membrane bound droplets that can maintain an internal environment and show simple metabolism and reproduction
What is the RNA world hypothesis?
The idea that RNA was the first genetic material, capable of both storing information and causing reactions
What does LUCA stand for?
Last Universal Common Ancestor, the shared ancestor of all living things
Where are most fossils found?
In layers of sedimentary rock called strata
Why is fossil record biased?
Favors species that were widespread, abundant, long lived, and had hard parts
What is radiometric dating used for?
Determining the absolute age of fossils using isotopes
When did the first prokaryotes appear?
~ 3.5 bya
What caused the Oxygen Revolution (~ 2.7 bya)?
Cyanobacteria released O2 (did photosynthesis), which accumulated in the atmosphere
When did the first eukaryotes appear?
~ 2.1 bya
What is the Cambrian explosion?
A period (~ 535 mya) when most major animal phyla appeared in the fossil record
When did organisms colonize land?
~ 500 mya (fungi, plants, animals together)
When did humans diverge from other primates?
~ 6-7 mya
What is plate tectonics?
The theory that Earth’s crust is divided into plates that move slowly over time
How does continental drift affect evolution?
Changes habitats, isolates populations, caused speciation and extinction
What is a mass extinction?
A widespread, rapid loss of many species caused by major environmental changes
What caused the Permian extinction (252 mya)?
Volcanic activity, climate change, ~ 96% marine species extinct
What caused the Cretaceous extinction (66 mya)?
Asteroid impact + volcanic activity, killed dinosaurs (except birds)
Are we in a 6th mass extinction?
Possibly, current rates are 100-1000x higher than the background rate, mostly due to humans
What is adaptive radiation?
When a group of organisms rapidly evolves into many species to fill new ecological niches
What often triggers adaptive radiations?
Mass extinctions, new habitats, or key innovations (like seeds or flight)
Example of a global adaptive radiation?
Mammals expanding after the extinction of dinosaurs
What are exaptations?
Structures that evolved for one function but were later used for another (jaw bones to ear bones)
What does “evolution is not goal oriented” mean?
Evolution works by natural selection on current variation, it doesn’t plan for the future