Strength Class Chapter 1
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
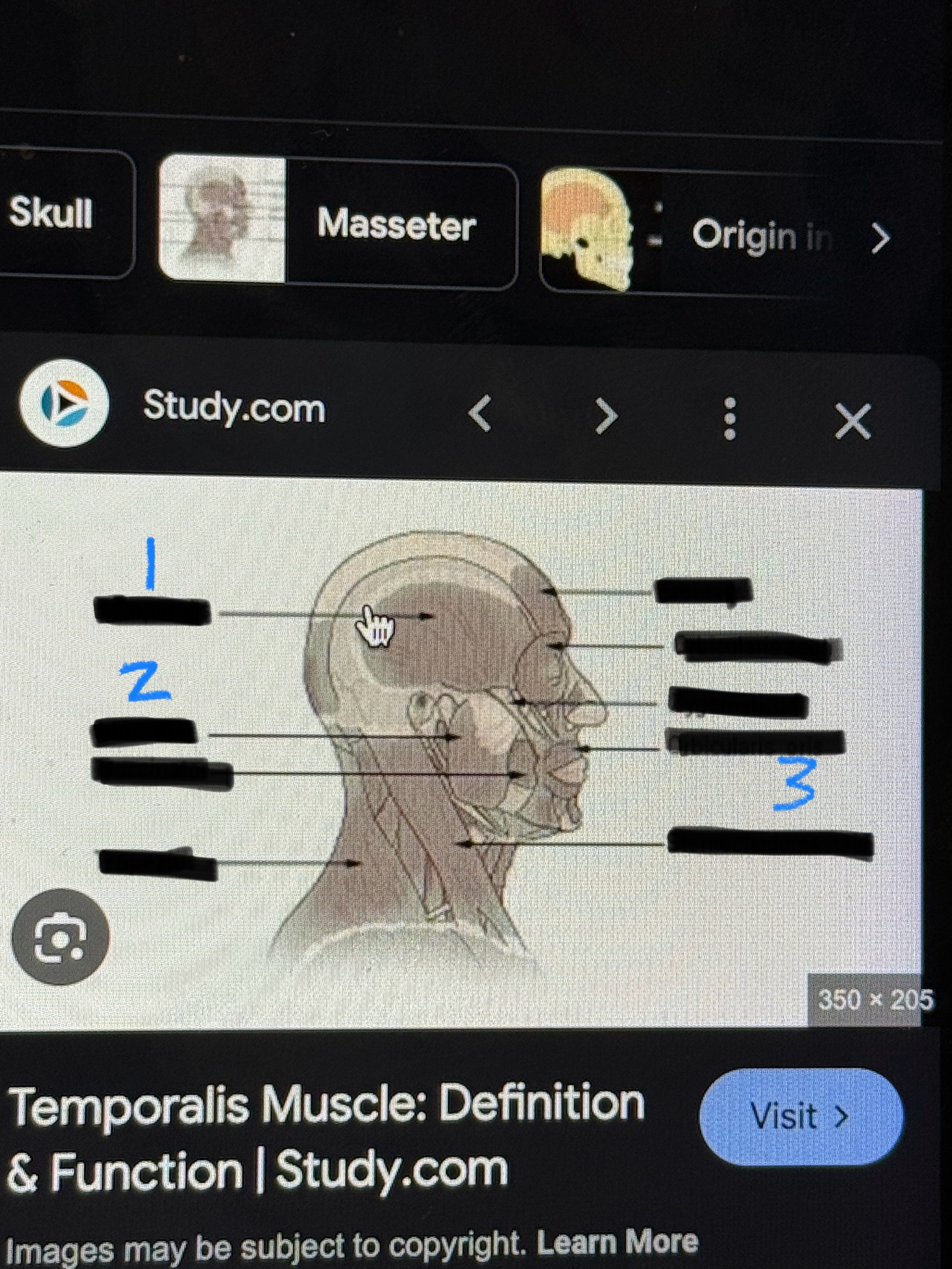
Major Muscles (1)
Temporalis (closes Jaw)
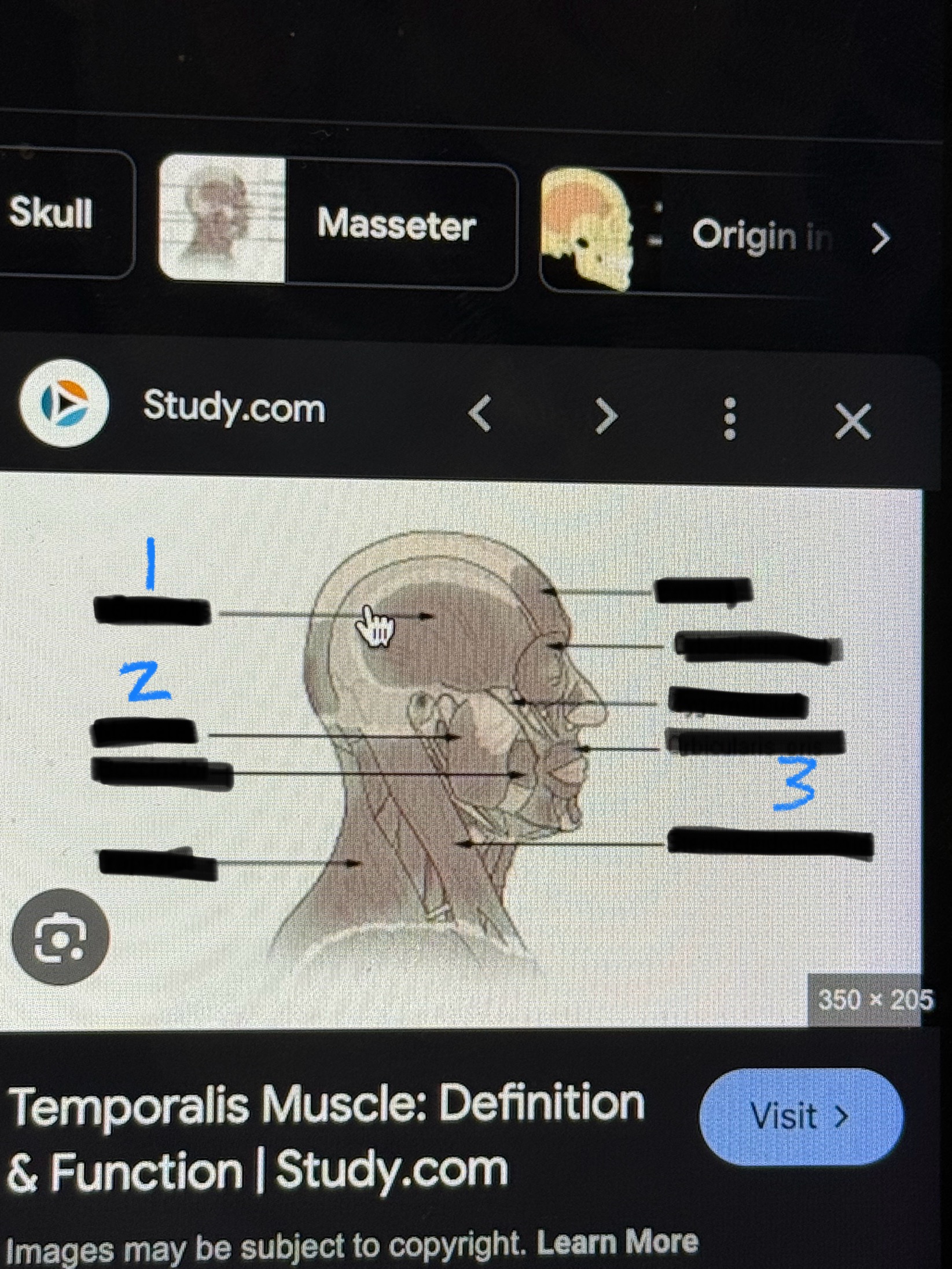
Major Muscles (2)
Masseter (flexes jaw)
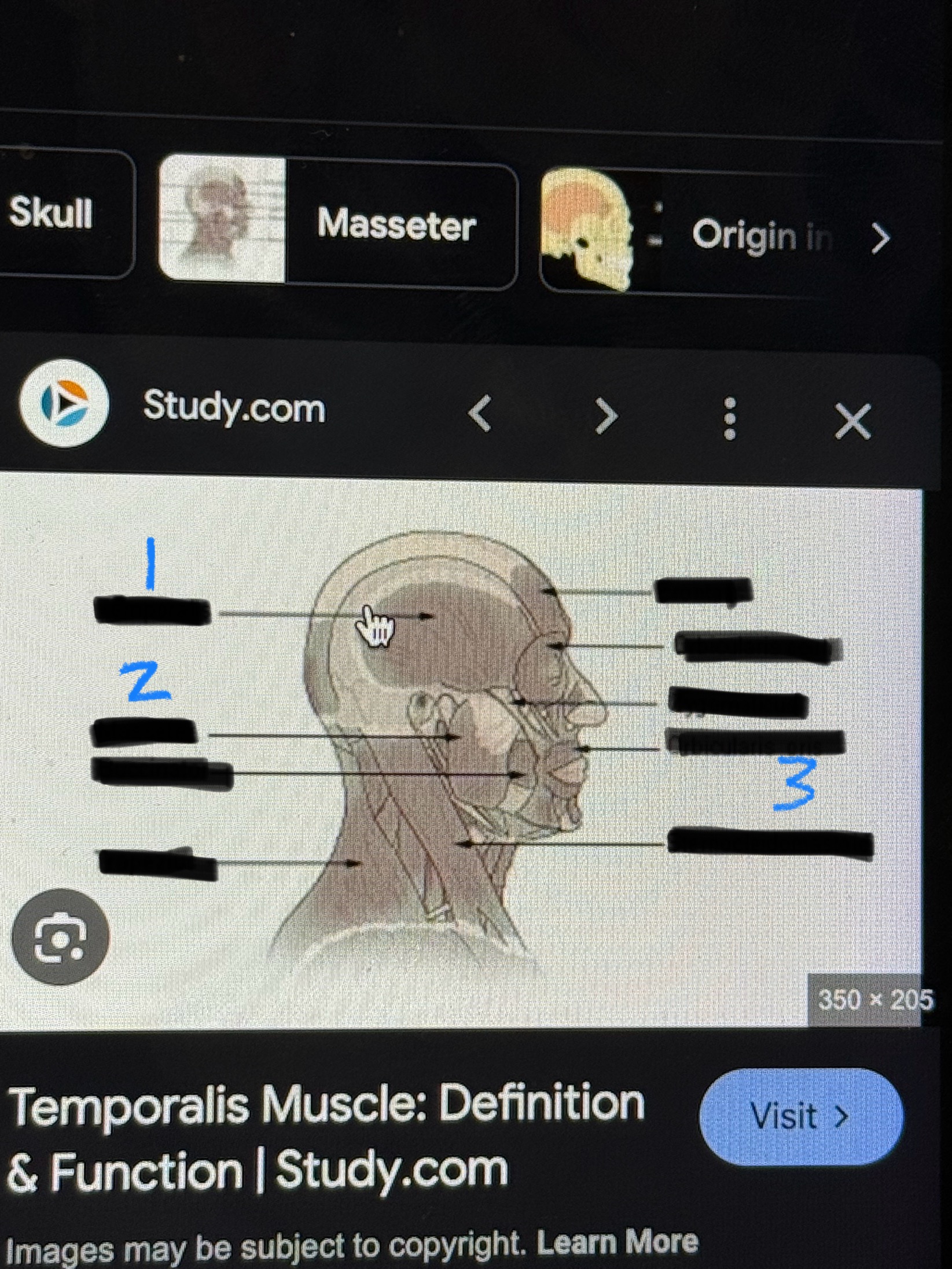
Major Muscles (3)
Sterno-cleido-mastoid (rotates head)
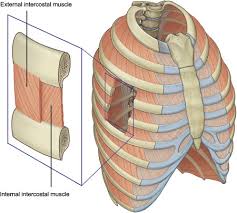
Major Muscles (4)
Intercostals (breathing)
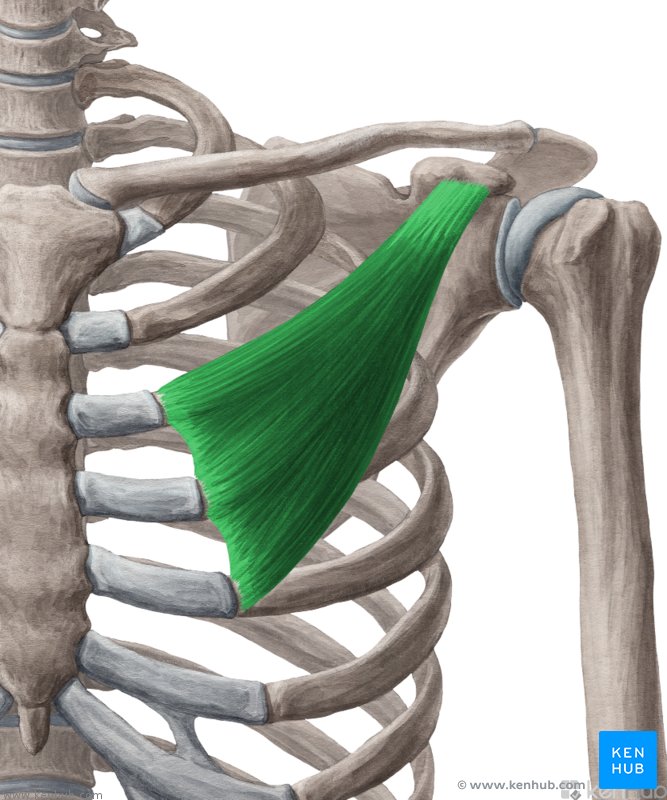
Major Muscles (5)
Pectoralis Minor (abducts ribs)
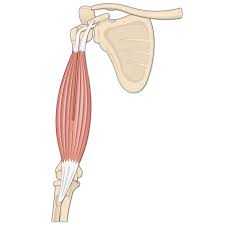
Major Muscles (6)
Biceps Brachii (Flexes elbow)
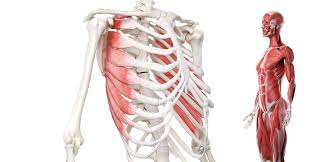
Major Muscles (7)
Serratus (adducts shoulder)
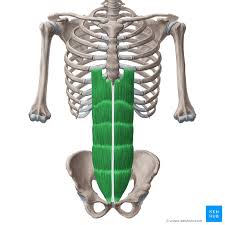
Major Muscles (8)
Rectus abdominus
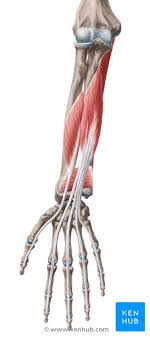
Major Muscles (9)
Deep Flexors (flexes fingers)
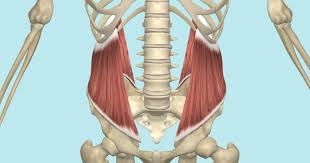
Major Muscles (10)
Internal Oblique (flattens abdomen)
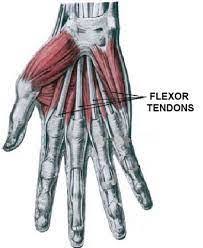
Major Muscles (11)
Tendons from forearm flexors to fingers
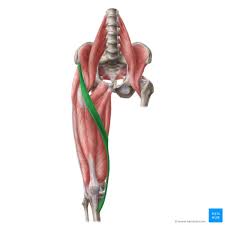
Major Muscles (12)
Sartorius (rotates high)
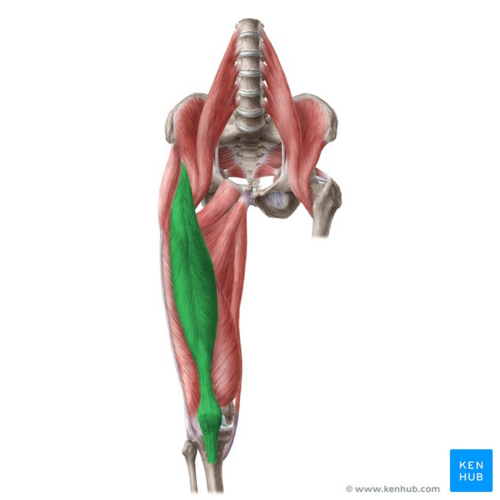
Major Muscles (13)
Rectus Femoris (Extends knee)
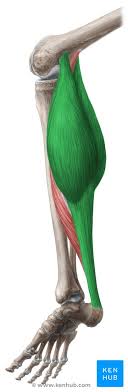
Major Muscles (14)
Gastrocnemius (points toe, flexes knee)
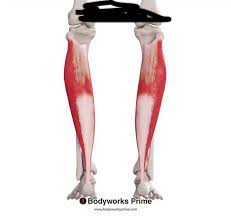
Major Muscles (15)
Soleus (points toe)
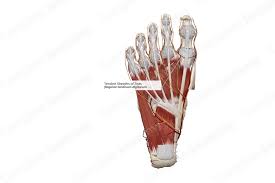
Major Muscles (16)
Tendons of toes
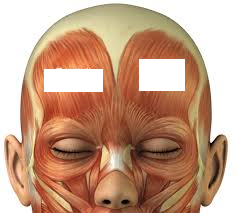
Major Muscles (17)
Frontalis (raises eyebrow)
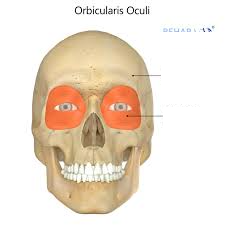
Major Muscles (18)
Orbicularis Oculi (closes eye)
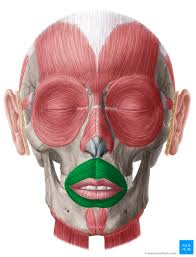
Major Muscles (19)
Orbicularis Oris (purses lips)
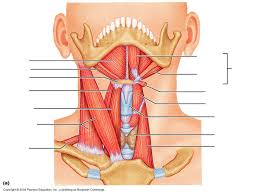
Major Muscles (20)
Throat muscles (aids swallowing)
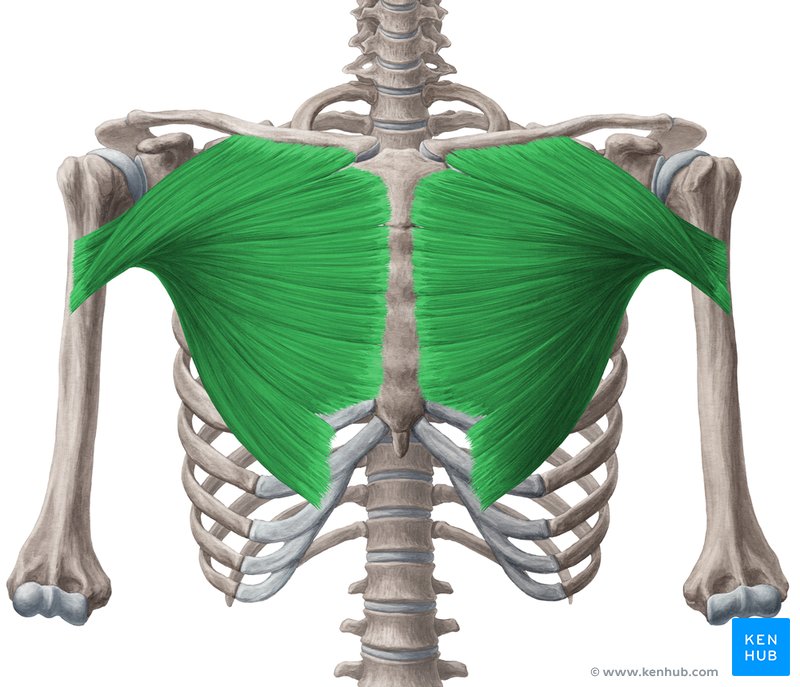
Major Muscles (21)
Pectoralis Major (adducts arm)
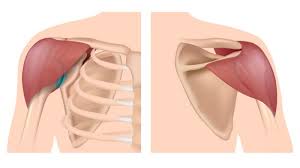
Major Muscles (22)
Deltoid (abducts arm)
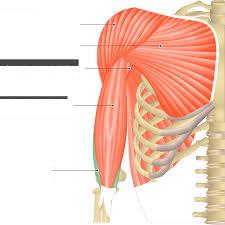
Major Muscles (23)
Brachialis (flexes arm)
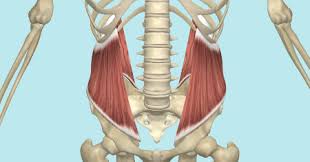
Major Muscles (24)
External Oblique (flattens abdomen)
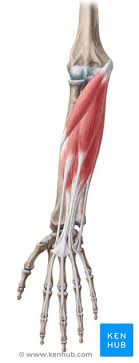
Major Muscles (25)
Superficial flexors (flexes Fingers)
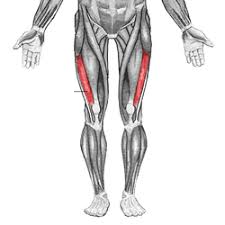
Major Muscles (26)
Vastus Lateralis (extends knee)
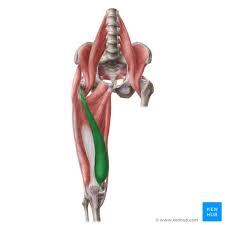
Major Muscles (27)
Vastus Medialis (Extends Knee)
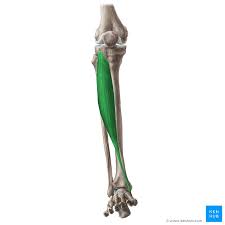
Major Muscles (28)
Tibilais anterior (raises feet
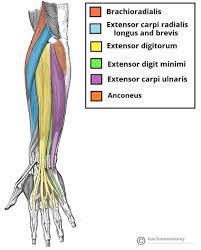
Major Muscles (29)
Extensors of forearm
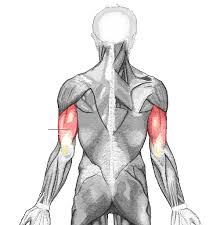
Major Muscles (31)
Triceps
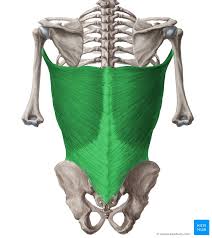
Major Muscles (32)
Latissimus dorsi
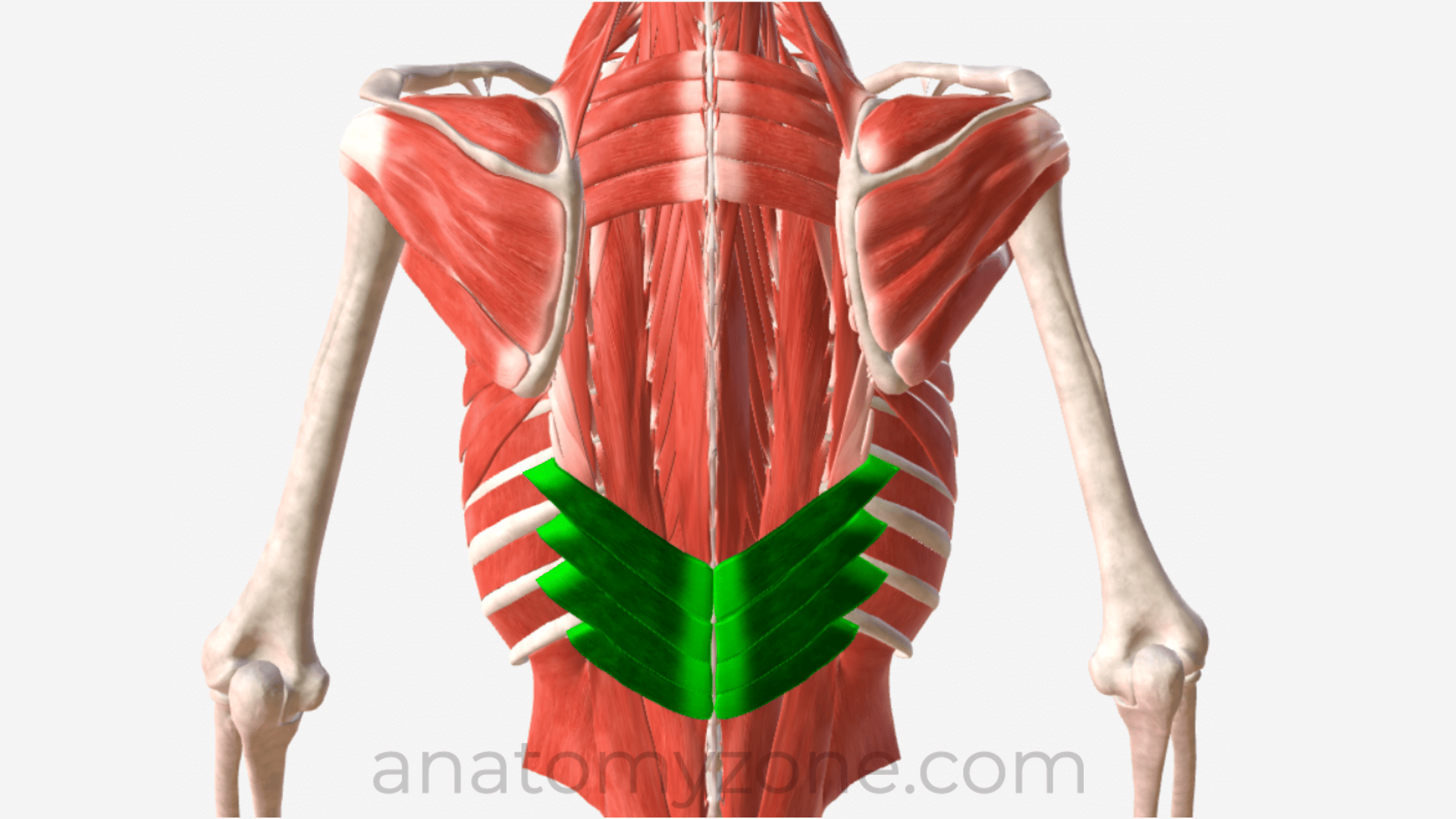
Major Muscles (33)
Serratus posterior inferior
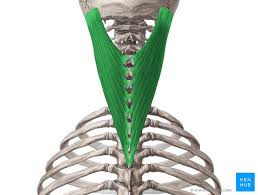
Major Muscles (34)
Splenius Capitus
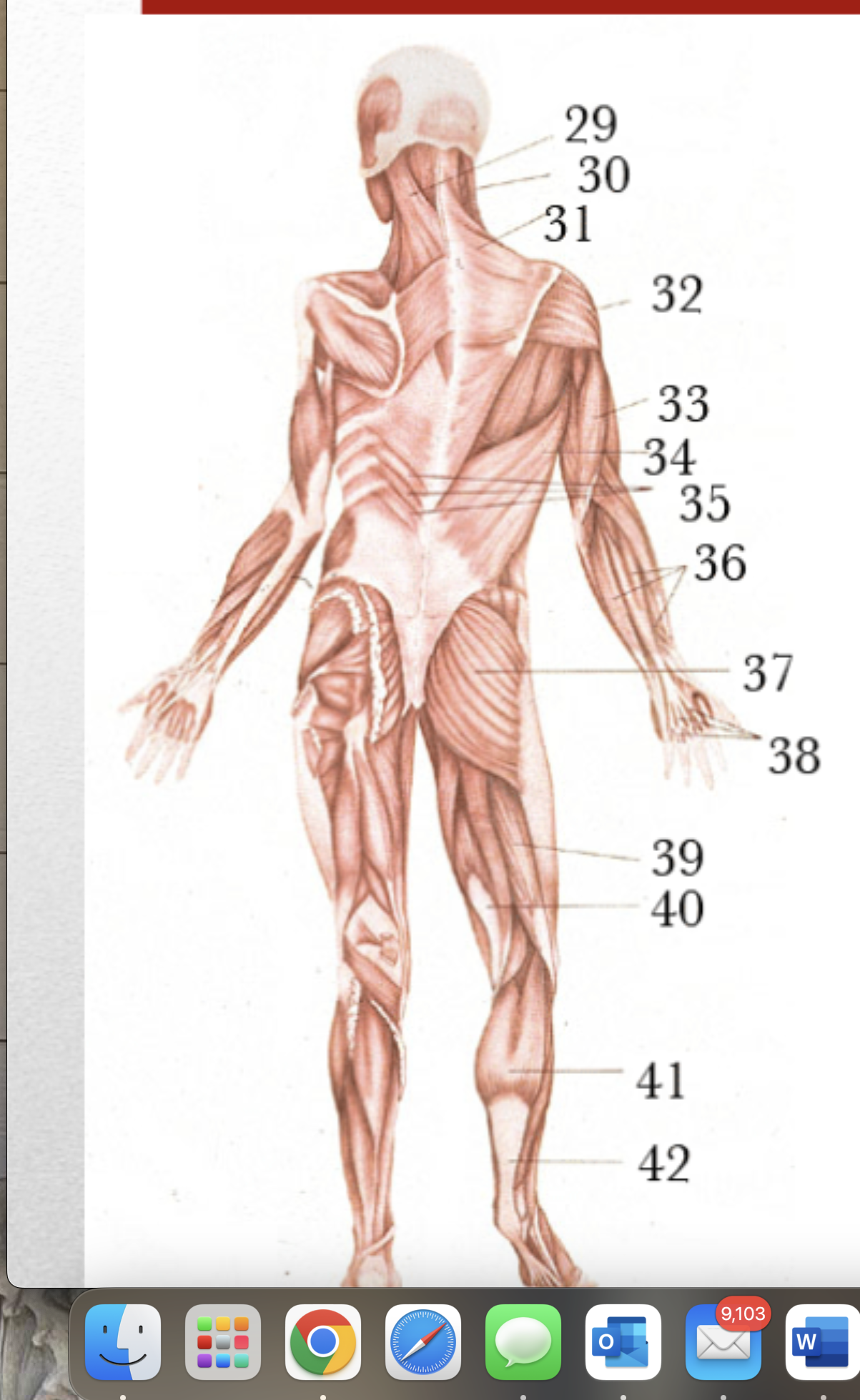
Major Muscles (35)
Serratus Posterior inferior
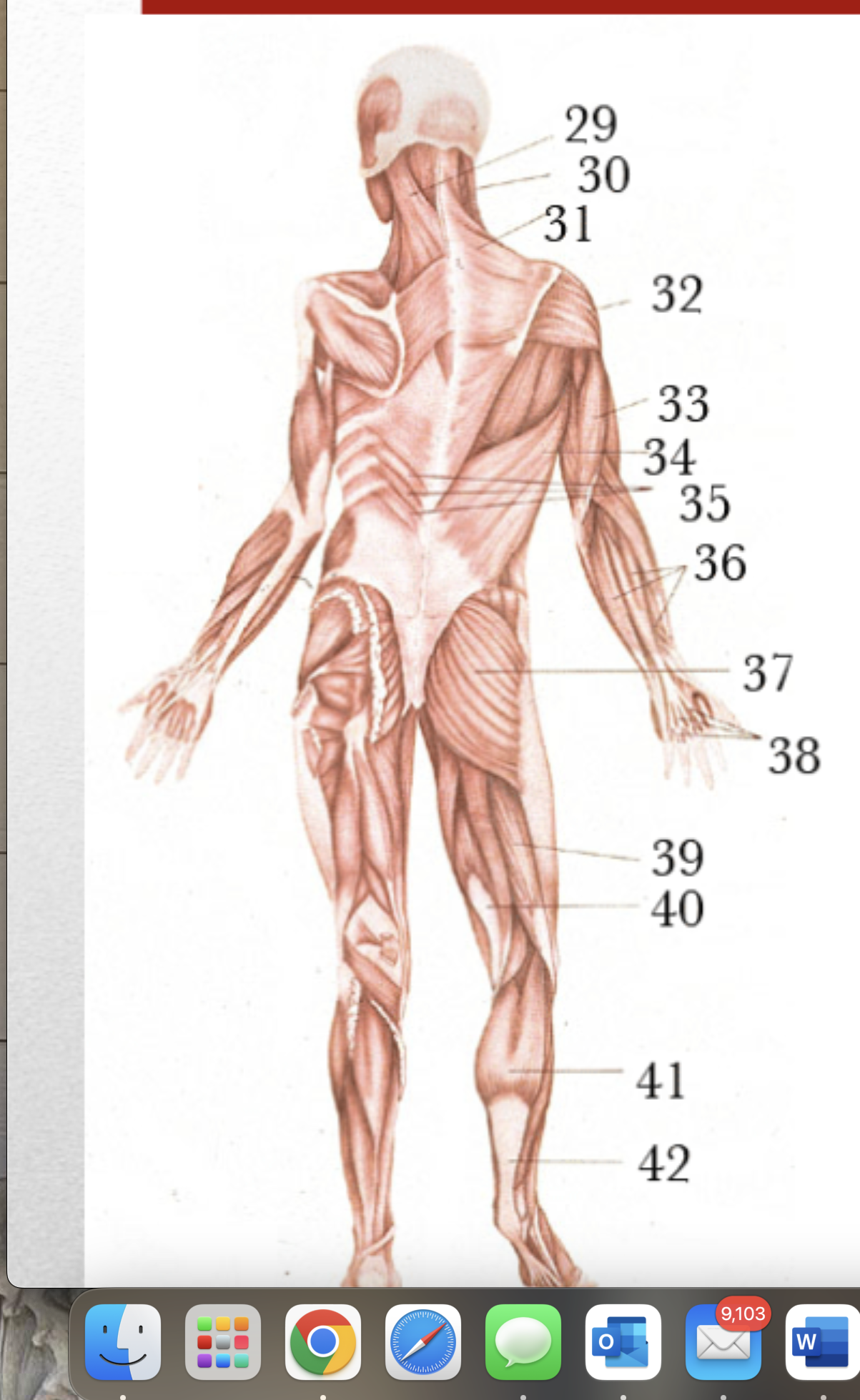
Major Muscles (36)
Sternomastoid
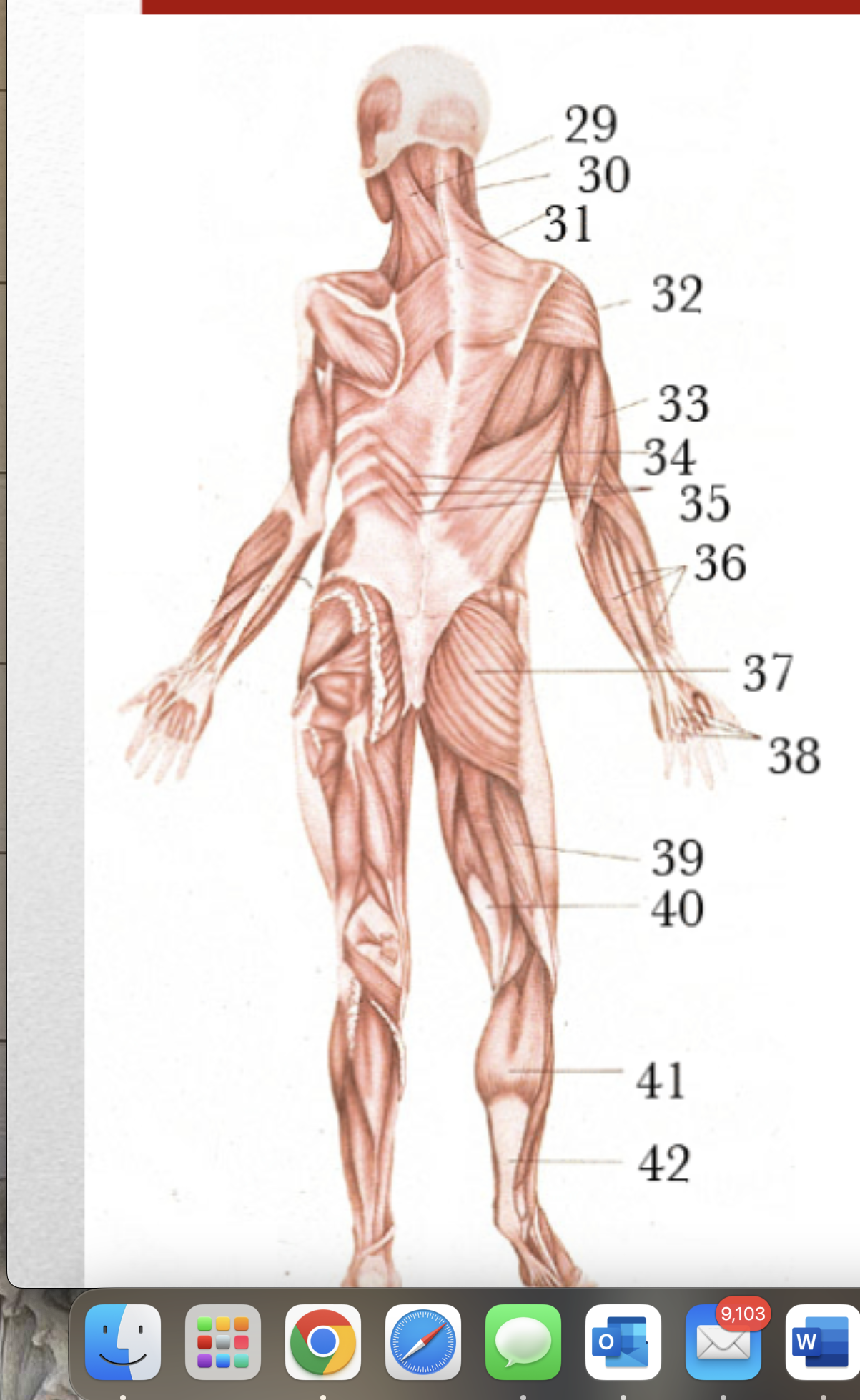
Major Muscles (37)
Gluteus Maximus
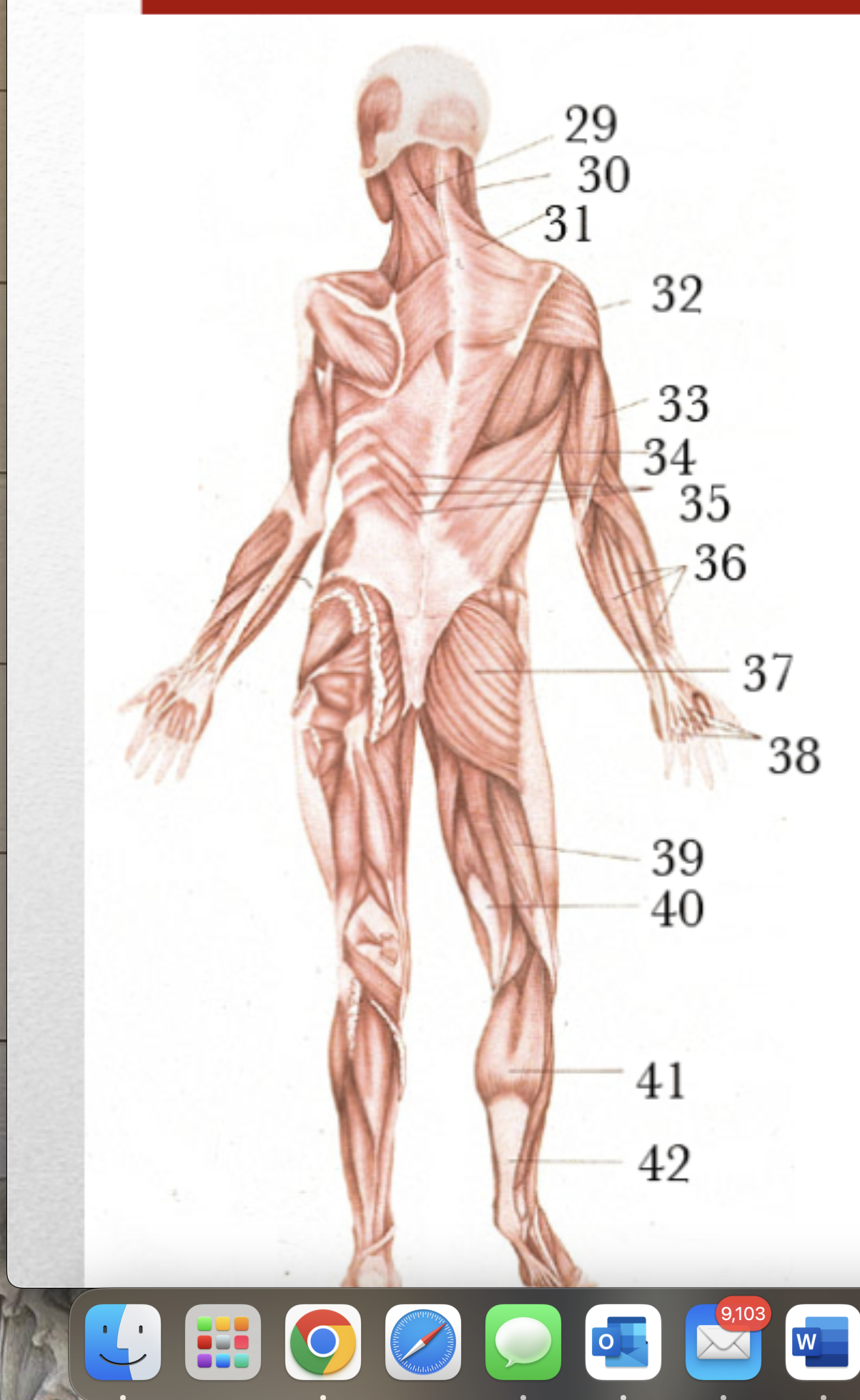
Major Muscles (38)
Tendons from forearm extensors to fingers
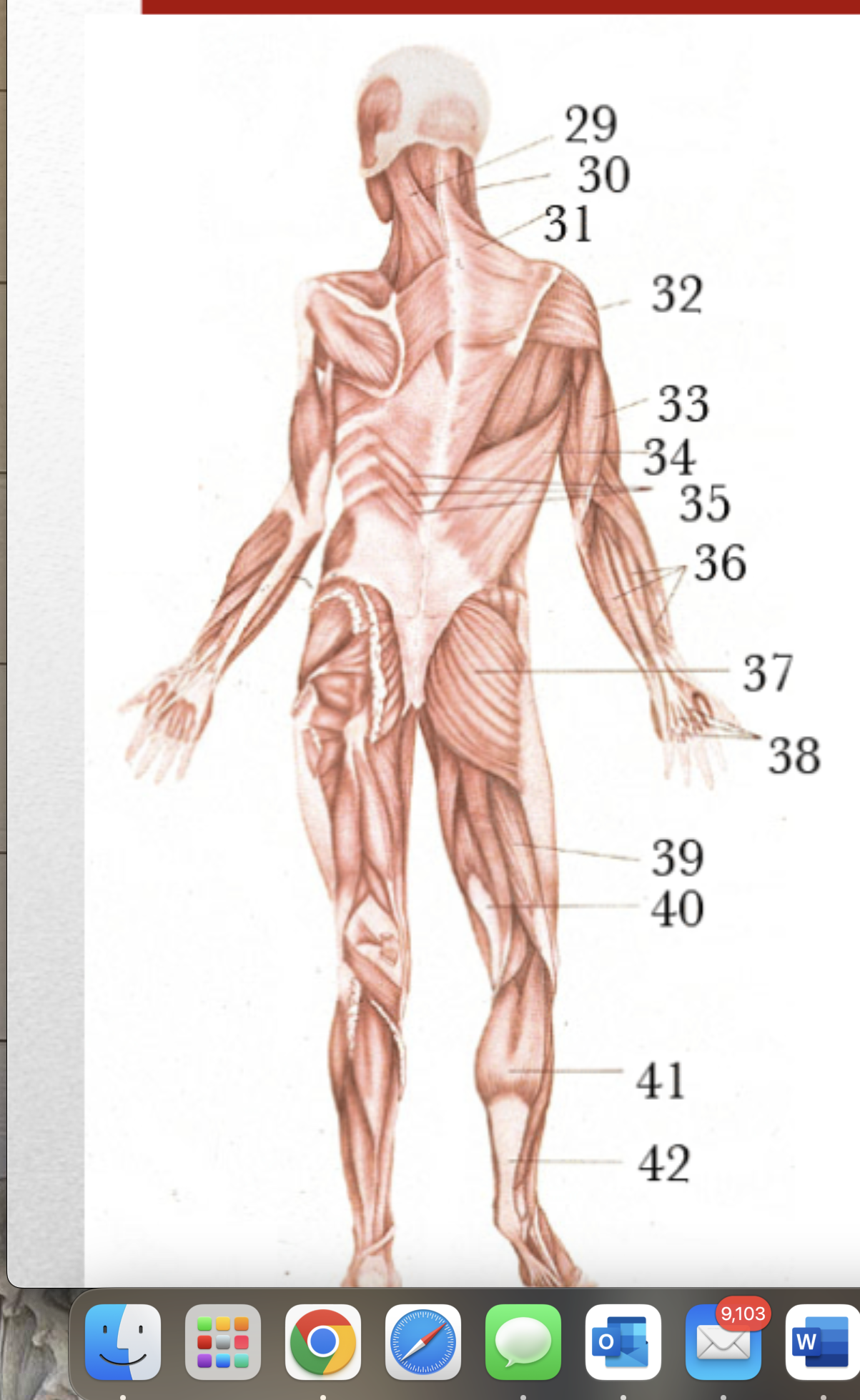
Major Muscles (39)
Biceps Femoris
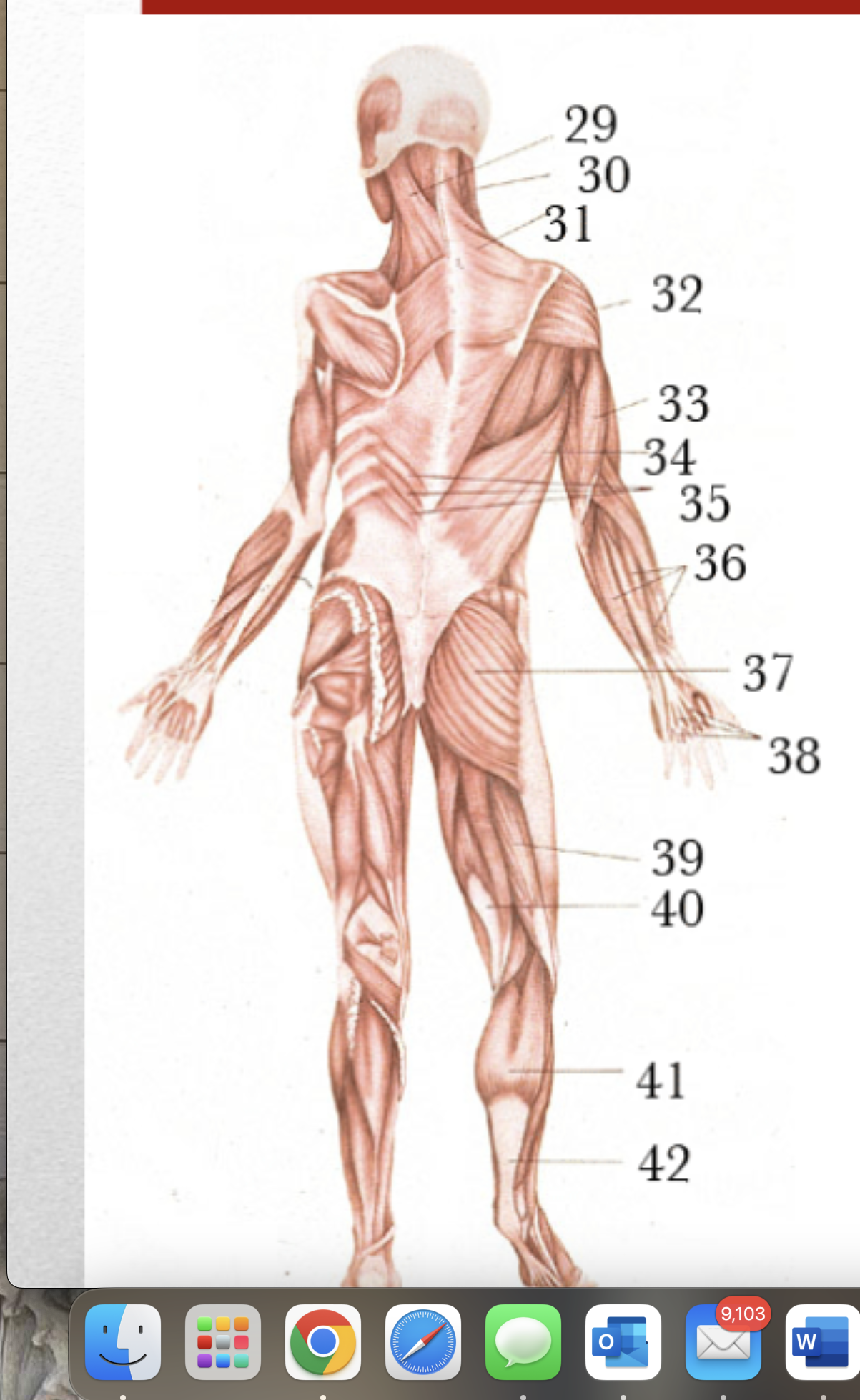
Major Muscles (40)
Semitendonosus
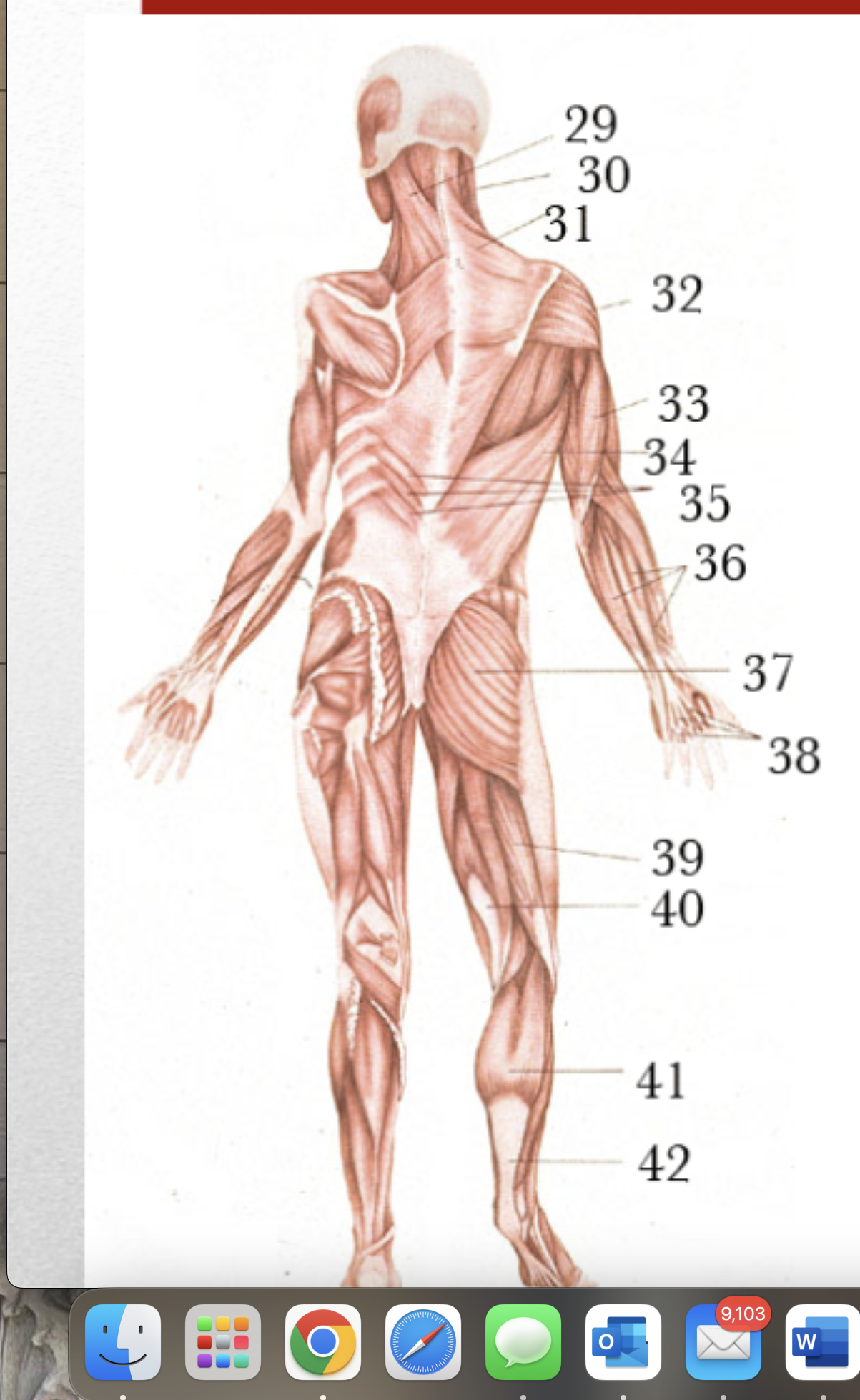
Major Muscles (41)
Gastrocnemius
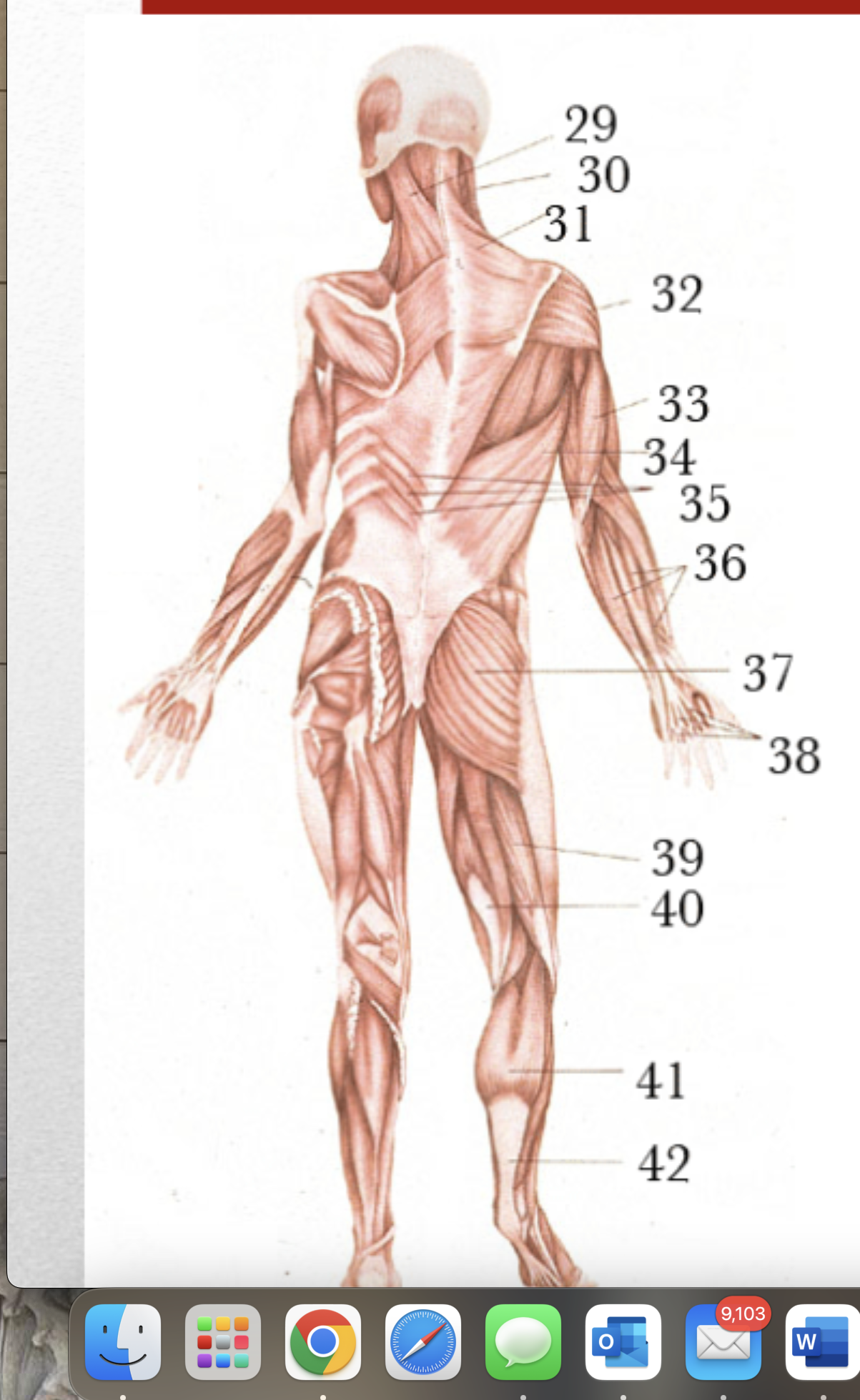
Major Muscles (42)
Tendon of Achilles
How many Skeletal Muscles
640 muscles
Misconceptions of Strength Training (False Statements)
Children should not strength train
Obese people should not strength train
May increase blood pressure
Takes too much time
Benefits of Adequate Strength Levels Part 1
Crucial for daily activities, improves confidence, Helps develop sport skills, promotes joint stability, helps people cope more effectively in emergeny situations, helps increase and maintain muscle
Benefits of Adequate Strength Levels
Promotes psychological well-being, results in higher resting metabolic rate, promotes weight loss and maintenance, lessens the risk for injury, prevents osteoporosis, reduces LBP, arthritic pain, aids in child bearing, improves cholesteral levels, may help lower blood pressure and control blood sugar.
Strenght Training and Bone Health
• Mechanical stress of strength training may stimulate increased bone mineral density
• May decrease the risk of osteoporosis
• Improves size and strength of ligaments and tendons, thereby improving joint stability
Strength and Metabolism
Strength training increases muscle mass
Muscle is metabolically active
Each additional pound of muscle tissue may increase resting metabolism by up to 35 calories per day
Strength training: Exercise Guidelines
Select exercises that involve all major muscle groups, will strenghten the core, never lift weights alone, warm up properly prior to lifting weights, use proper lifting technique for each exercise
Basic Rules of Weight Training
Warm up with static stretching/ raise body temp, large multi-joint movements before iso movements, high technical movements first, work middle out (core → supplemental prioritizing) cool down.
Strength- Training Guidelines for Health Fitness (FITT Principle)
Frequency- Atleast twice a week
Resistance- Enough resistance to perform 8-12 repetitions to near-fatigue (10-15 reps for older and more frail people)
Sets- Minimum of 1 set (3 are recommended)
Mode- 8-10 dynamic strength-training exercises involving major muscle groups
Strength or Endurance Strength Training Principles
Frequency- 2/3 times a week (more often if split body routines are used and up to 12 times per week for body building programs)
Resistance- Muscular Strength: 3-12 reps maximum. Muscular Endurance: More than 12 reps
Sets- 1-6 sets (8 for body building) per exercise
Mode- Isometric, Dynamic (w/o weights, free weights, weight machines, isokinetic)
Muscle Strengthening
• Exercise large muscle groups
• High intensity has the most benefit
• 8-12 reps; should fatigue by last rep
• Rest 2-3 minutes between exercises
• 1 set good, 2 sets better
• Rest day in between
Adaptation (Human Body)
Is capable of adapting to many kinds of stress and even increasing its efficiency as a result of stressful stimuli.
Strength Training
• Strength training is only beneficial as long as it causes the body to adapt to the physical efforts.
• Limited stress – adaptation will not occur
• Too much stress – injury or deterioration will result
Work hard – fitness level will be high
Immediate results for those who begin
*Less intensity – fitness will decrease
Resistance Training (Army men for body)
Activities of specific patterns of motor units in training will determine what tissue and what physiological systems will be affected. Should be specific to goals
Acute Changes
Increase in heart rate and breathing
Chronic Changes
Enlargement of muscles (hypertrophy) ; gradual increases in number and size of myofibrils, increase size of ligaments, and tendons; bones become stronger (These tissues adapt in order to support increased forces)
Who needs Strength Training
Everyone, weight training benefits people of all ages
Why is strength training important
Weight training has both Health and Cosmetic benefits
Health Benefits of strength training include
Increased basal metabolism, strengthened bones, increased joint stability, increased lean body mass. Decreased RBP, improved functioning of the immune system, lowered resting heart rate, improved muscular coordination, improved athletic performance
5 Components of Fitness
Flexibility
Muscular Strength
Muscular Endurance
Cardiovascular Endurance
Body Composition
Flexibility
Increased joint stability
Bodybuilding
Exercise program that utilizes free and stationary weights to change body shape and form.
Conditioning
The development of high levels of muscular strength and endurance and high levels of cardiorespiratory endurance.
Muscle Endurance
The ability of a muscle group to maintain a continuous contraction or repetition over a period of time.
Muscle Endurance
The ability of a muscle group to maintain a continuous contraction or repetition over a period of time.
Muscle Power
The product of strength and speed (force and velocity)
Muscle Strength
The amount of force that can be exerted by a muscle group for one movement or repetition.
Power Lifting
A comprehensive event where the goal is to lift the greatest amount of weight for three different exercise (bench press, dead lift, and squat). Explosive power is important in this event.
Weight Lifting
A competitive event where the goal is to lift the greatest amount of weight for tow exercises (clean/press and snatch). Skill, speed, and strength are important.
Weight Training
Exercise program using free or stationary weights for the purpose of increasing strength, endurance, power, skill, and flexibility.