Chapter 1 Study Quiz
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
what is the universal energy molecule in living things?
adenosine triphosphate
what three letters are the abbreviation for adenosine triphosphate?
atp
what is the genetic material in all living things?
deoxyribonucleic acid
deoxyribonucleic acid is abbreviated by what three letters
dna
which branch of biology studies fossils to explain life history
paleontology
which domain is prokaryotic?
bacteria/archaea
The diversity of life results from
genetic variation
all life supporting ecosystems on earth make up the
biosphere
all molecules are composed of
two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
what level of biological organization is defined as a large molecule such as DNA?
macromolecule
The smallest unit that still has the property of an element is
an atom
in the living ecosystem, nutrients ((raw materials) are recycled by
decomposers
A single bacterium divides by binary fission into two bacteria that are identical to, but smaller than, the original bacterium
reproduction
You observe a plant on your windowsill that is growing at an angle towards the outside? This is an example of a living thing:
Responding to stimuli
Scientific theory
A general explanation for natural phenomena
The information gathered while performing the experiment is the
Data
A conclusion is
A statement of a possible answer to a problem
The scientific method includes all of the following steps except
testable theory
A change in the DNA sequence of a gene is known as a
mutation
The ultimate source of energy in an ecosystem is the
Sun
all of the following are important to the theory of evolution except
acquired changes in a lifetime
____ is the name of the domain of life that includes all living things that are eukaryotic (their cells contain a nucleus)
eukarya
what are the domains of life?
bacteria, archaea, and eukarya
what is not a domain of life?
plantae
in evolutionary terms, which of the following is considered most primitive?
animals
halophiles
plantar
bacteria
bacteria
which branch of biology studies the biology of the nervous system
neurobiology
what level of biological organization is defined as the smallest unit of life
a cell
what level of biological organization is defined as all the members of a species living in the same area
population
what is the correct sequence of increasing organization?
atom, molecule, organelle, cell
a kitten is born weigh 2 pounds and eventually becomes a 17 pound cat
growth
We use the scientific method every day. Imagine that your car doesn’t start with morning before school. Which of these is a reasonable hypothesis regarding the problem?
change the battery
i’m going to be late
kick the tire
maybe i need gas
add a quart of oil
maybe i need gas
what is the purpose of a control in an experiment?
to provide comparison
what is a variable?
The factor that you are testing in an experiment
The scientist, Alexander Fleming observed that mold inhibited the growth of nearby bacteria. Which of the following was his hypothesis?
The mold produced a substance that killed nearby bacteria
The mold consumed all the nutrients so the bacteria couldn’t grow
The bacteria was dead
The bacteria were dead to begin with
The bacteria changed their DNA when they grew near the mold
The mold produced a substance that killed nearby bacteria
inductive reasoning
drawing general conclusions from specific observations
deductive reasoning
using general principles to reach specific conclusions (a.k.a. logic)
steps of the scientific method
Observation
Question
Hypothesis
Prediction
Experiment
Results
conclusion
Observation
Using the senses to gather information about an object or event
question
Ask a question based off of your observation
Hypothesis
form an educated guess based on your observation
prediction
says what will happen in an experiment if the hypothesis is correct
experiment
A procedure that tests, a hypothesis or theory, or compares models and hypotheses
results
Reports what happened in the experiment
Experimental group
The group in an experiment that receives the treatment or condition being tested
control group
The group in an experiment that does not receive the treatment or condition being tested
basic science
research aimed at understanding fundamental principles and concepts without immediate practical application. It builds a foundation for applied sciences.
applied science
research focused on using scientific knowledge to solve practical problems and create new technologies or products
what are the 8 characteristics of living things?
Cellular organization, metabolism, homeostasis, growth and development, reproduction, response to stimuli, adaptation through evolution, heredity
how is the levels of organization in living organisms arranged?
from the simplest to the most complex
what are each of the levels of organization in living organisms from 1 to 9?
cell
Tissue
Organ
Organ system
organism
population
Community
Ecosystem
biosphere
what is the theory of evolution?
The scientific explanation for how species change overtime through natural selection, genetic variation and adaption
what does the theory of evolution propose about all living organisms?
they all share a common ancestor and that species evolve and diversify as they adapt to their environments over long periods of time
what are the three domains of life?
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
what are examples of organisms in the bacteria domain of life?
E. coli and streptococcus
What are examples of organisms in the archaea domain of life?
halophiles, thermophiles, acidophiles
what are examples of organisms in the eukarya domain of life?
animals, plants, fungi
molecular biology
looks at how molecules like DNA and proteins work together to control biological functions
biochemistry
Studies the chemistry of biological molecules and how they drive the functions of living cells
microbiology
examines tiny organisms that are not visible to the naked eye and how they affect health, the environment, and ecosystems
neurobiology
looks at how the brain and nervous system operate and how they affect behavior and bodily functions
paleontology
investigates fossils to learn about ancient life and earth’s history
zoology
examines animals, and how they live, work, and interact with their surroundings
Botany
focuses on plants and how they grow, work, and their role in the environment
What does the abbreviation "mL" represent in units?
.001 Liter
When water is poured into a graduated cylinder, the curved surface shape of the water is called the:
meniscus
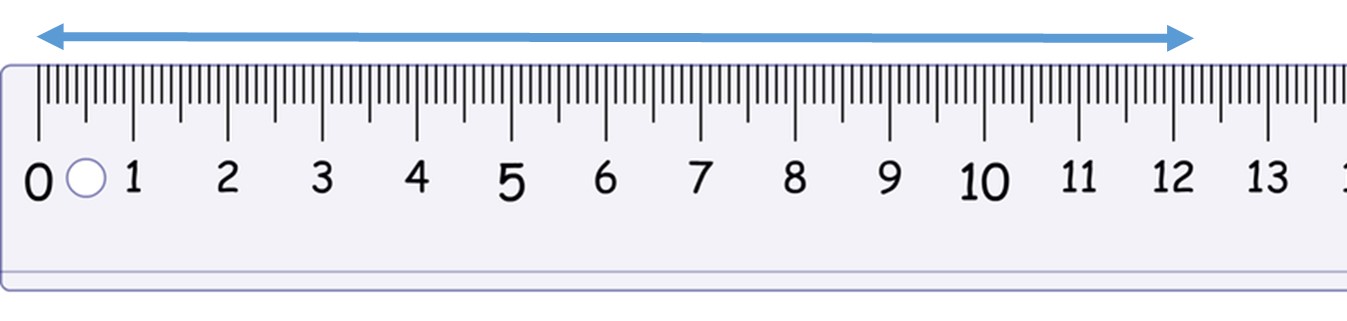
The length of the line below is:
12.2 cm
Formula for density
Density = mass divided by volume (D=m/v)
A piece of metal is placed in a plastic cup. The empty plastic cup weighs 7 grams. The combined mass of the metal and the plastic cup is 200 grams. A graduated cylinder contains 50 mL of water. When the metal is dropped into the graduated cylinder, the water level rises to 60 mL. What is the density of the metal?
19.3 g/mL
The density of water is 1 g/mL. You determine that an irregular shaped object has a volume of 10 mL and a mass of 5 grams. What is the density of the object?
0.5 g/mL
A piece of metal is placed in a plastic cup. The empty plastic cup weighs 7 grams. The combined mass of the metal and the plastic cup is 200 grams. A graduated cylinder contains 50 mL of water. When the metal is dropped into the graduated cylinder, the water level rises to 60 mL. What is the mass of the metal?
193 grams
Convert 8 millimeters to meters
.008 meters
Convert 2.465 m to cm
246.5 cm
Convert .674 kg to grams
674 grams
Convert 100 cm to meters.
1 meter
Convert 250 grams to kilograms
.250 kg