Lecture 07 Squid Bioluminescence
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What form of defense do bobtails utilize with their bioluminescent bacteria ?
counterillumination, where the light from their light organs minimizes their shadow and obscures their silhouette
the scientific name for the bobtail squid is »>
Eupyrymna scolopes
How does a bobtail squid acquire symbionts?
Horizontal transmission- from the sand that they burrow in during the day
What is the symbiont of the bobtail squid ?
Gamma proteobacteria - allivibrio fischeri
in the free-living state of vibrio fischeri, they are (flagellated/nonflagellated)
flagellated
vibrio fischeri are flagellated/nonflagellated in the symbiotic state
nonflagellated
where are the gamma-proteobacteria housed ?
in the crypts of the light organ
what benefit does the gamma-proteobacteria gain from the relationship?
food and shelter
the squid-Virbrio system is an example of what kind of mutualism?
defensive
what makes a good model for symbiosis studies?
both partners culturable in a lab
short generation time
partners can be cultured apart from one another
symbiosis can be established in the lab
good genomic resources
(unique to squid-vibrio)- fast light organ development
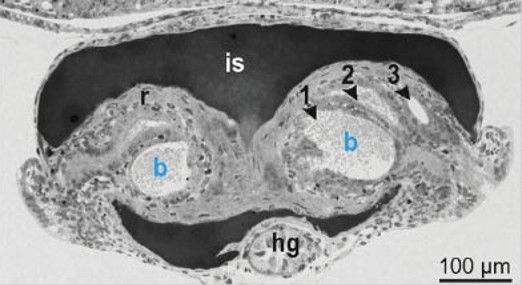
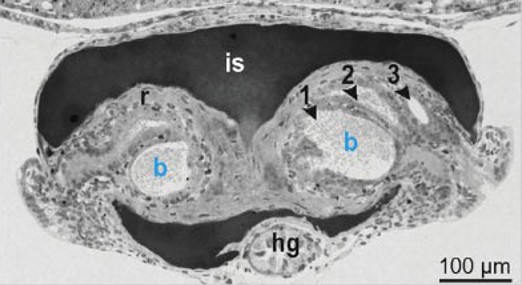
what is the portion labelled r?
reflector that reflects light downward
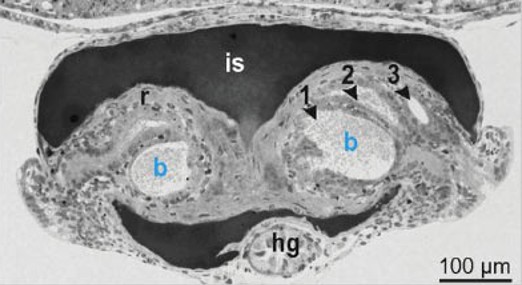
what is the portion labelled is ?
ink sac; it absorbs dorsal light and can be retracted/advanced
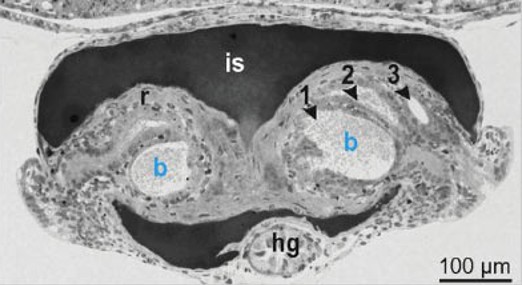
what are the portions labelled 1,2,3
bacterial crypts
extracellular epithelium that opens via pores to mantle cavity
houses 10^9 bacteria per light organ
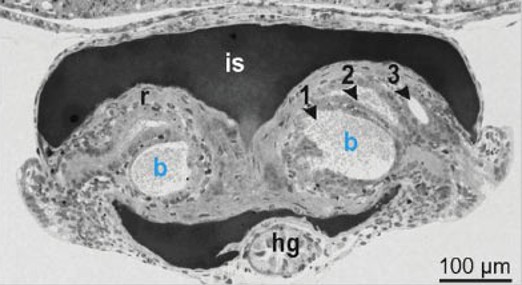
what is the portion labelled hg?
hindgut
What is the light organ made up of?
reflector tissue
a shutter mechanism (ink sack)
transprent lens that covers the light organ
yellow filter that changes color of the emitted light
the organ contains _______ receptors and can be detected by bacterial light
light
how can the squid modify the light output ?
regulating oxygen concentration
at sunrise, the squid will expel ___ % of its symbionts
90
the colonization process is fast/slow and specific
fast
what is the section labelled L ?
lens- made of mostly aldehyde dehydrogenase
is analogous to eye lens and chrysalis
spreads light across the squid body
Describe symbiont transmission
the squid expels 90% of its symbionts by squeezing bacteria out of pores, resulting in large free-living symbiotic populations, and buries itself in sand, where the light organ population regrows during the day.
how is the light organ in a juvenile squid different?
lacks a lens, born with ciliated epithelia and two pairs of arms on nascent light organ
what do the arms on the nascent light organ do on a juvenile ?
create currents to trap bacteria near pores in combination with mucus secretion to aggregate the bacteria
how do the arms aggregate bacteria?
the cilia of juveniles beat and direct particles to 3 pores at the base of the appendages
the light organ of the juvenile squid permits particle entry for roughly how long?
30 min
when the squid detects light from the symbionts, what happens?
the light organ matures, losing the ciliated appendages and prevents any other bacteria from entering, where any non-luminescent V. fischerii do not survive in the crypts of the light organ
What is the bacterial gauntlet?
A series of “obstacles” that weed out non- V. fischerii bacteria:
V. fischerii has chemotaxis toward compound in squid mucous
cilia in ducts beat outward
high nitric oxide concentrations are a V. fischerii attractant
bactericidal acid in crypts kills non-target bacteria
hemocytes patrol and kill non-target bacteria and even offer themselves as additional food for target bacteria
What is the Winnowing?
the process of the bobtail squid becoming selective for V. fischeri to build up a concentration of symbionts in the light organ.