[BOTLAB] Seedless Vascular Plants
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Small leaves
Simple Venation
Absent/No leaf gap
Microphyll lineage has:
[BLANK] leaves
[BLANK] venation
[BLANK] leaf gap
larger to reduced leaves
Complex venation
Present/With leaf gap
Megaphyll lineage has:
[BLANK] leaves
[BLANK] venation
[BLANK] leaf gap
Aerial and dichotomously branched, covered with microphylls
Stems of Class Lycopodiopsida
Sessile
Leaves of Class Lycopodiopsida
spiral, in pairs or in whorls
Leaf arrangement of Class Lycopodiopsida
Dichopodial roots
Class Lycopodiopsida has [BLANK] roots that are fibrous or adventitious
False; Class Lycopodiopsida are eusporangiate
T or F: All of Class Lycopodiopsida are leptosporangiate
Strobilus
Specialized cone-like structure at the terminals bearing the sporophylls
True
T or F: Lycopodium is homosporous
False; Both are heterosporous
T or F: Selaginella and Isoetes are homosporous
Aerial stems with megaphyll
Stems of Class Polypodiopsida
siphonostele
Xylem structure of Class Polypodiopsida
monopodial roots
Roots of Class Polypodiopsida
True
T or F: Most species of Class Polypodiopsida are leptosporangiate ferns
Horsetails
Common name of Order Equisetales
True
T or F: Order Equisetales has sporiangiophores
vallecular canals
What is structure number 4
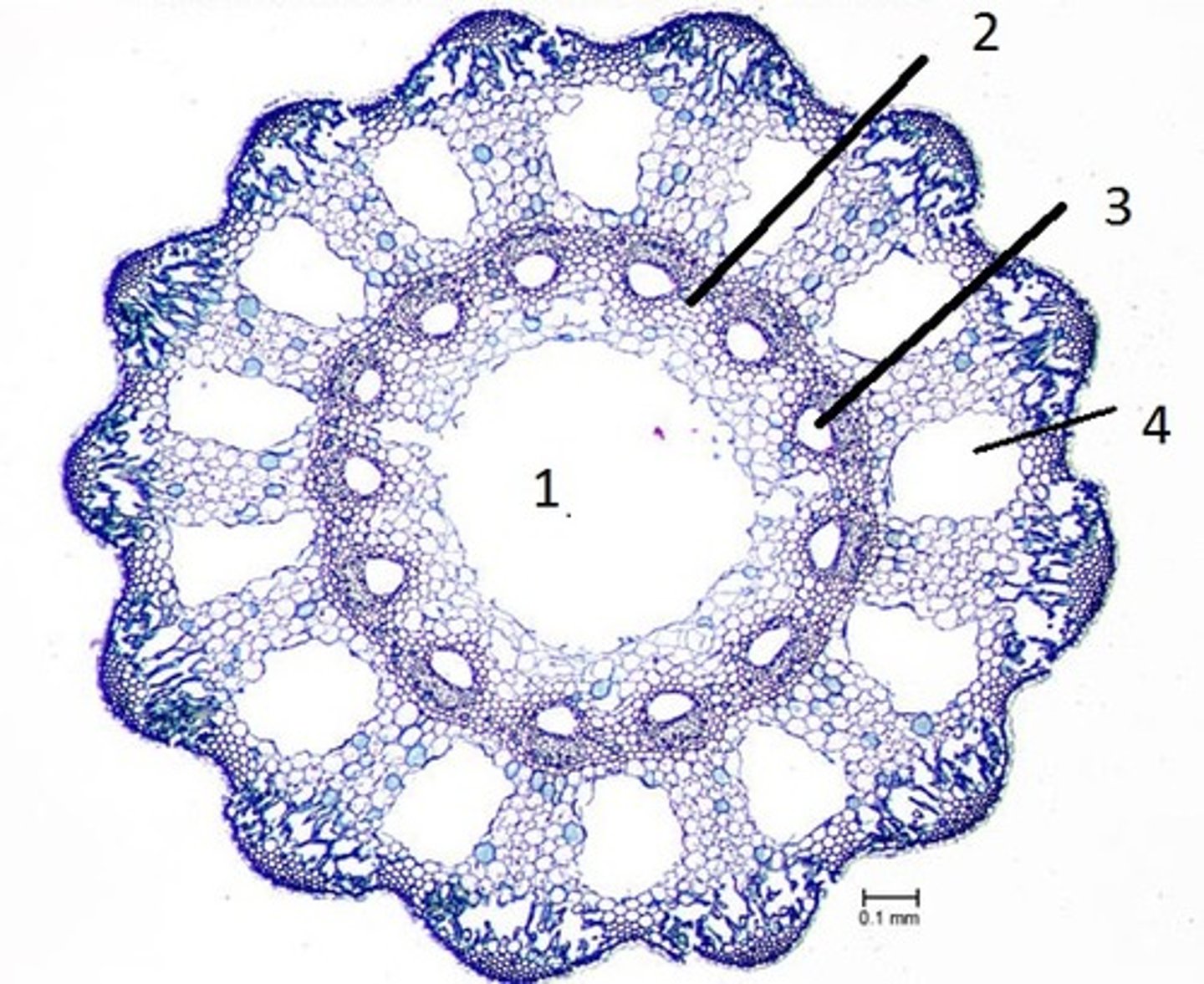
carinal canal
What is structure number 3
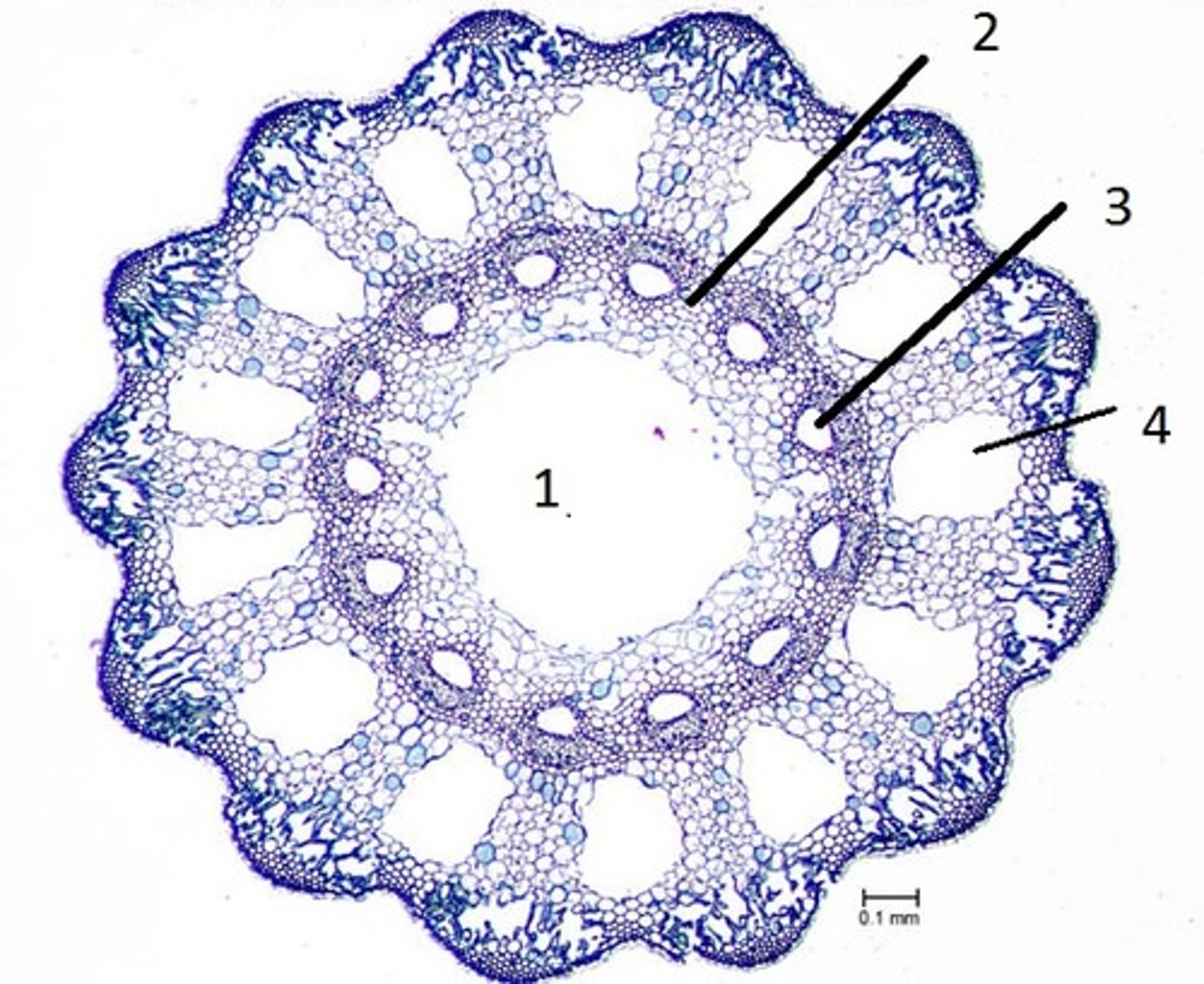
Hollow pith or central canal
What is structure number 1

Order Equisetales (Horsetails)
Stems ribbed, with hollow canals
Megaphyll leaf highly reduced, whorled
Homospores with elaters
Presence of silica in the walls of some of the outer cells
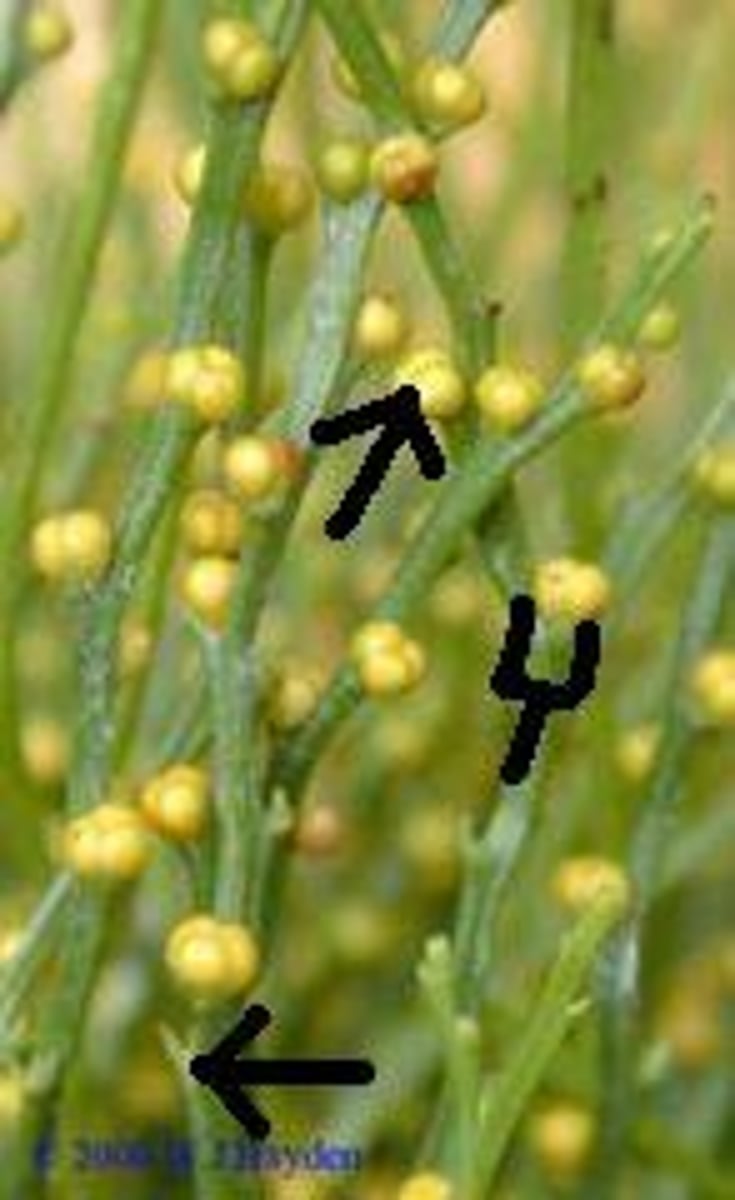
Whisk ferns
Common name of Psilotum
False; Roots and leaves are lost
T or F: Psilotum has the presence of roots and leaves
Synangium
fusion product of two or three lobes of sporangia in whisk ferns that is born on bifid enations

True Ferns
Perennial, herbaceous
With conspicuous megaphyllous leaves (frond) comprising the blade and stalk (stipe)
endarch siphonostele
what is the structure of stems of true ferns
Present
Absent or Present: Roots on rhizomes in true ferns
Circinate vernation
manner in which a frond emerges in true ferns
Eusporangium
Sporangium arises from several epidermal cells of the sporophyll
Includes fern-allies and marratioid ferns
Leptosporangium
Sporangium arises from a single epidermal cell of the sporophyll
Includes the majority of true ferns
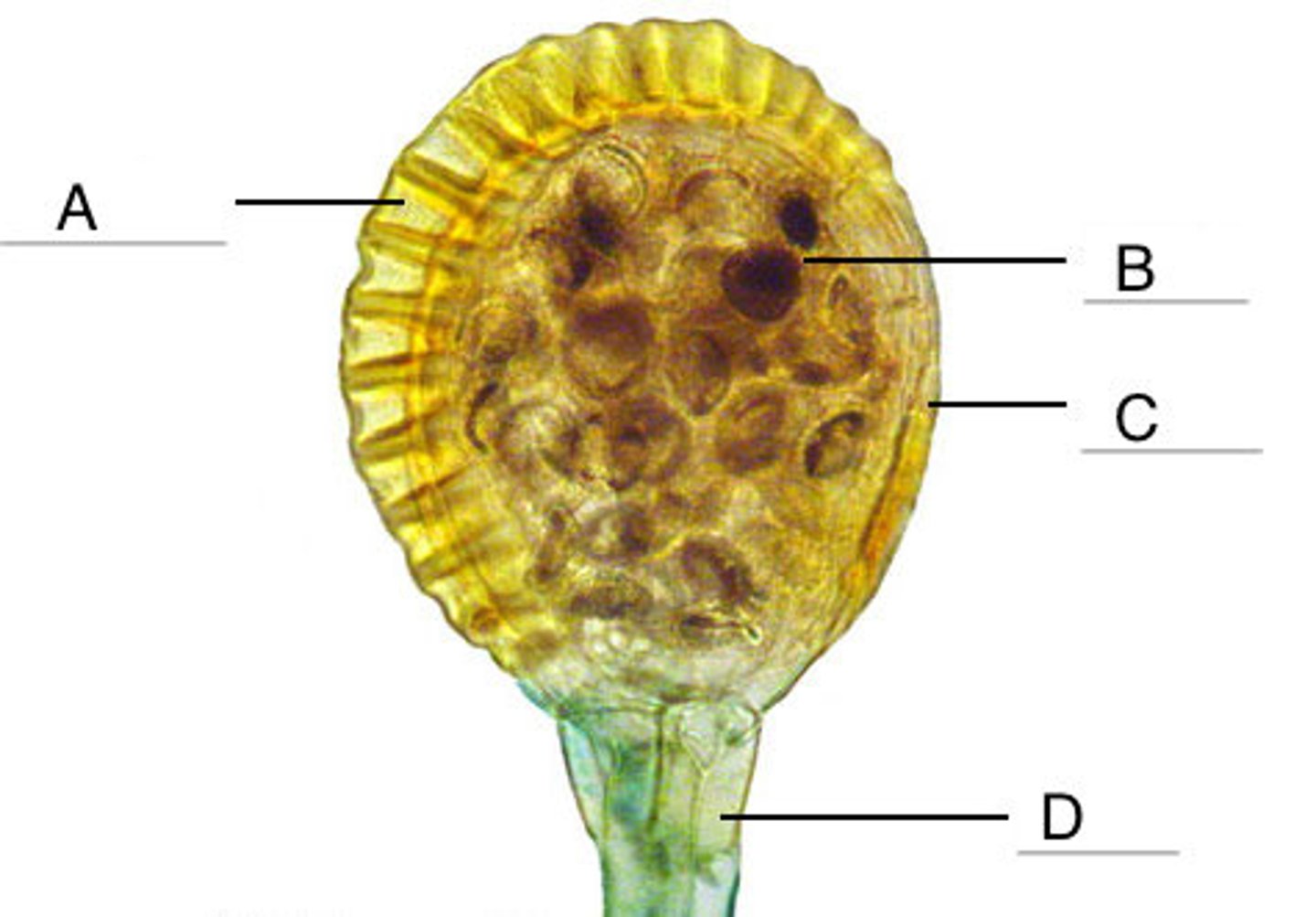
Receptacle
Structure D
sporangial body and stalk in Leptosporangium
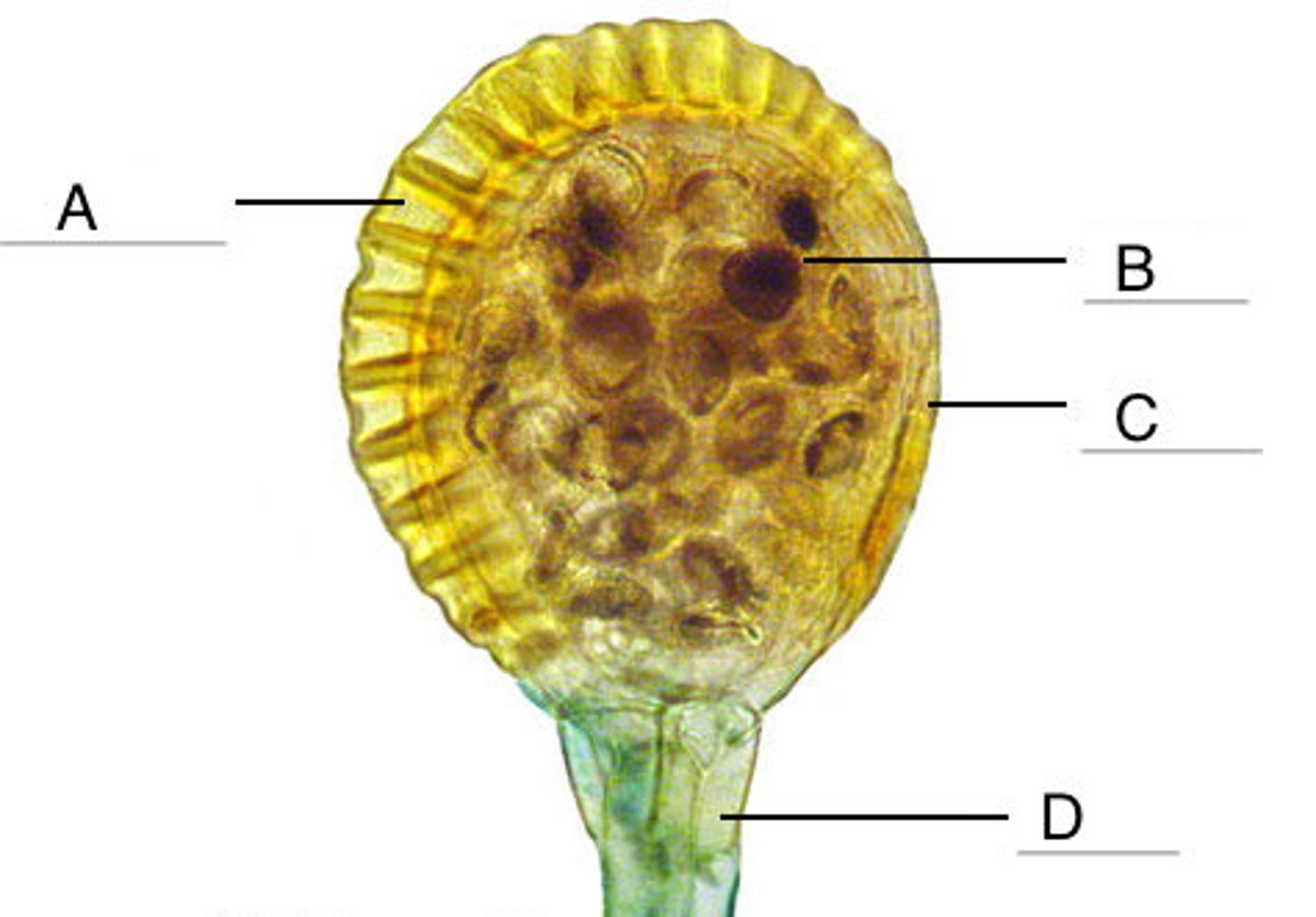
Annulus
Structure A
one cell thick sporangium wall in Leptosporangium
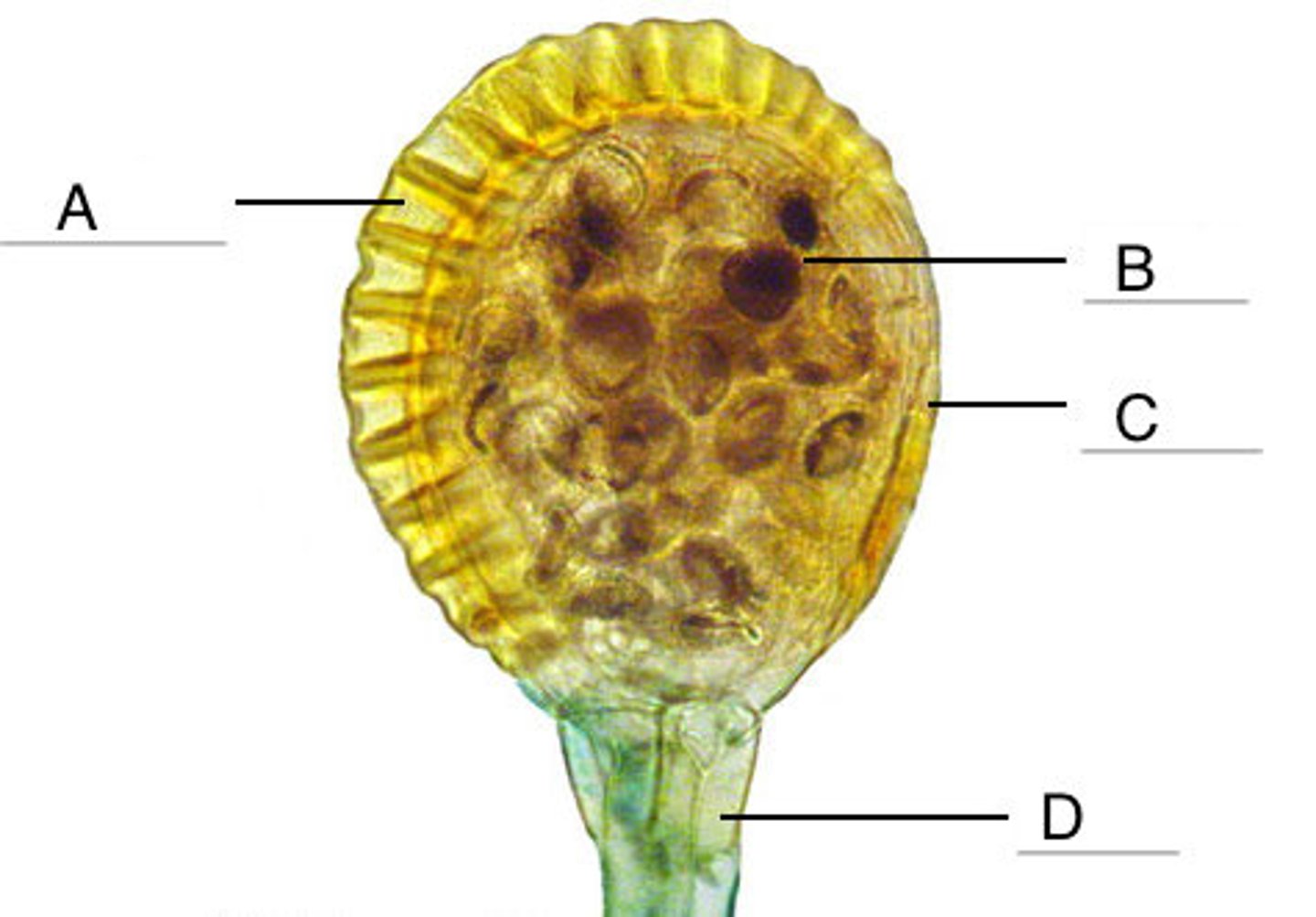
Lip cells
Structure C
the stomium; region of thin-celled walls; structurally weakest, where sporangium splits to eject spores
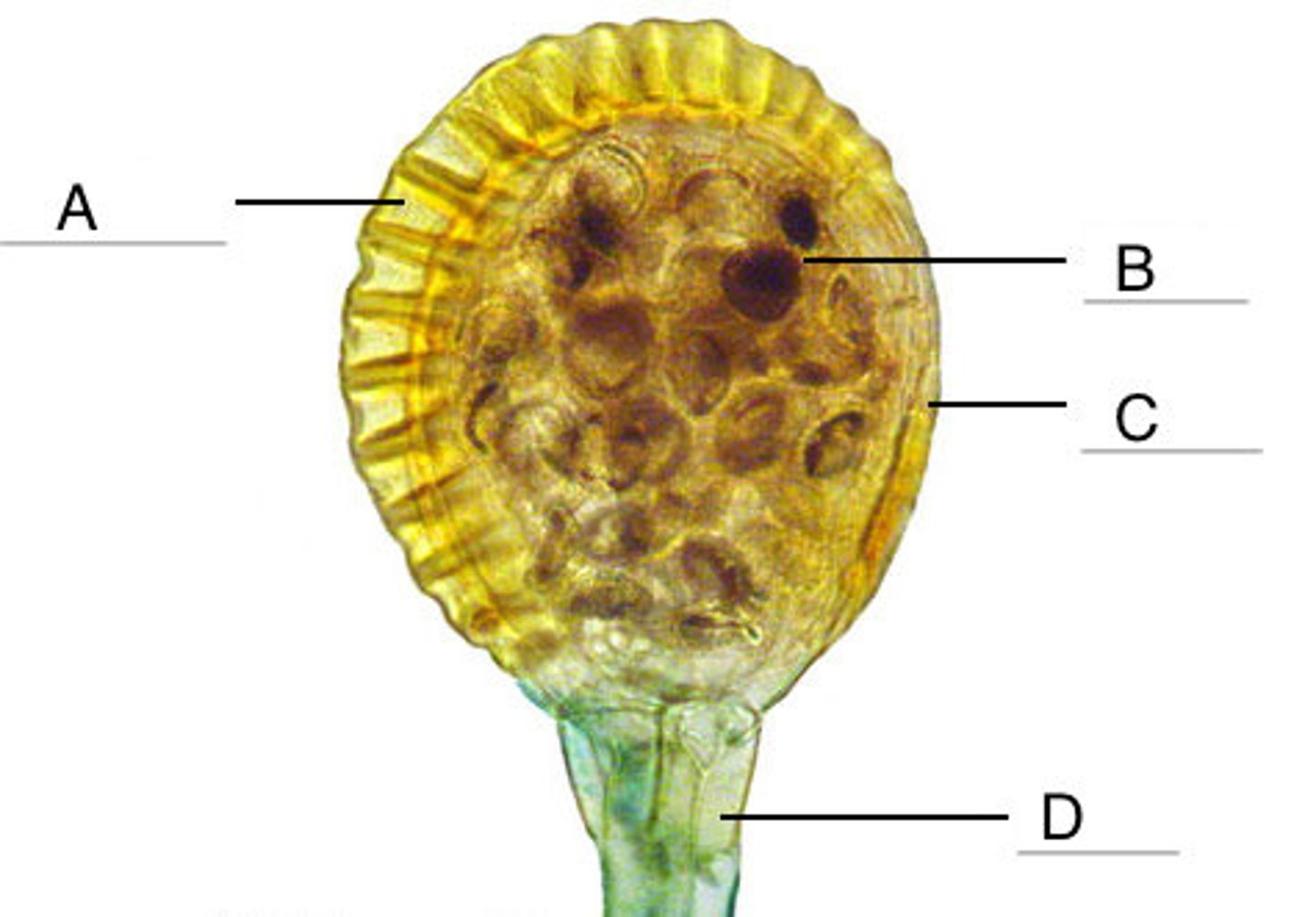
Sorus
clusters of leptosporangium
Spores
What is the structure pointer in Letter B
indusium
flap tissue from the blade surface covers the sorus
Prothallus
photosynthetic, gametophytic body containing the gonia of ferns
Archegonium
what structure of he prothallus is pointed in number 1
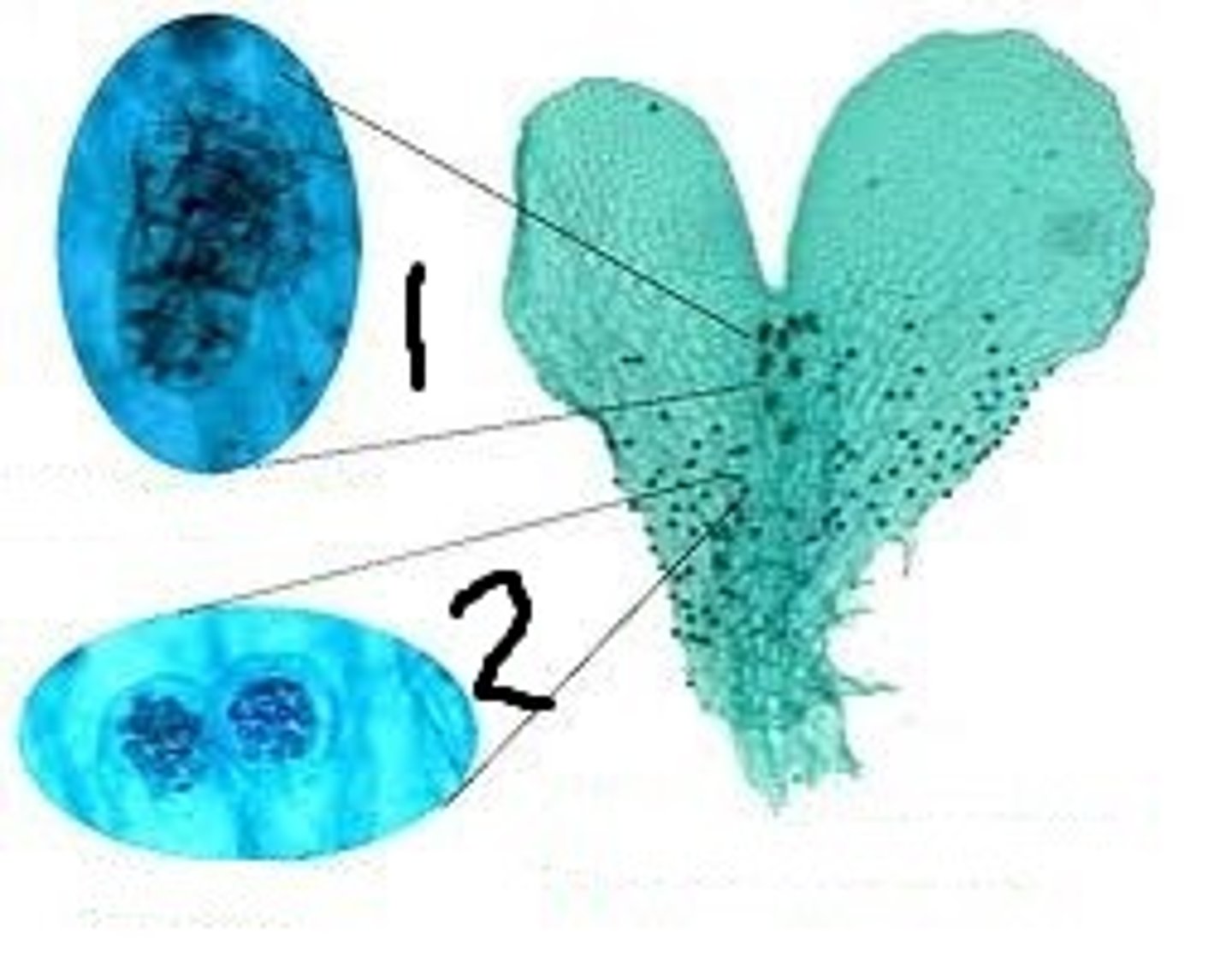
Antheridium
what structure of he prothallus is pointed in number 2
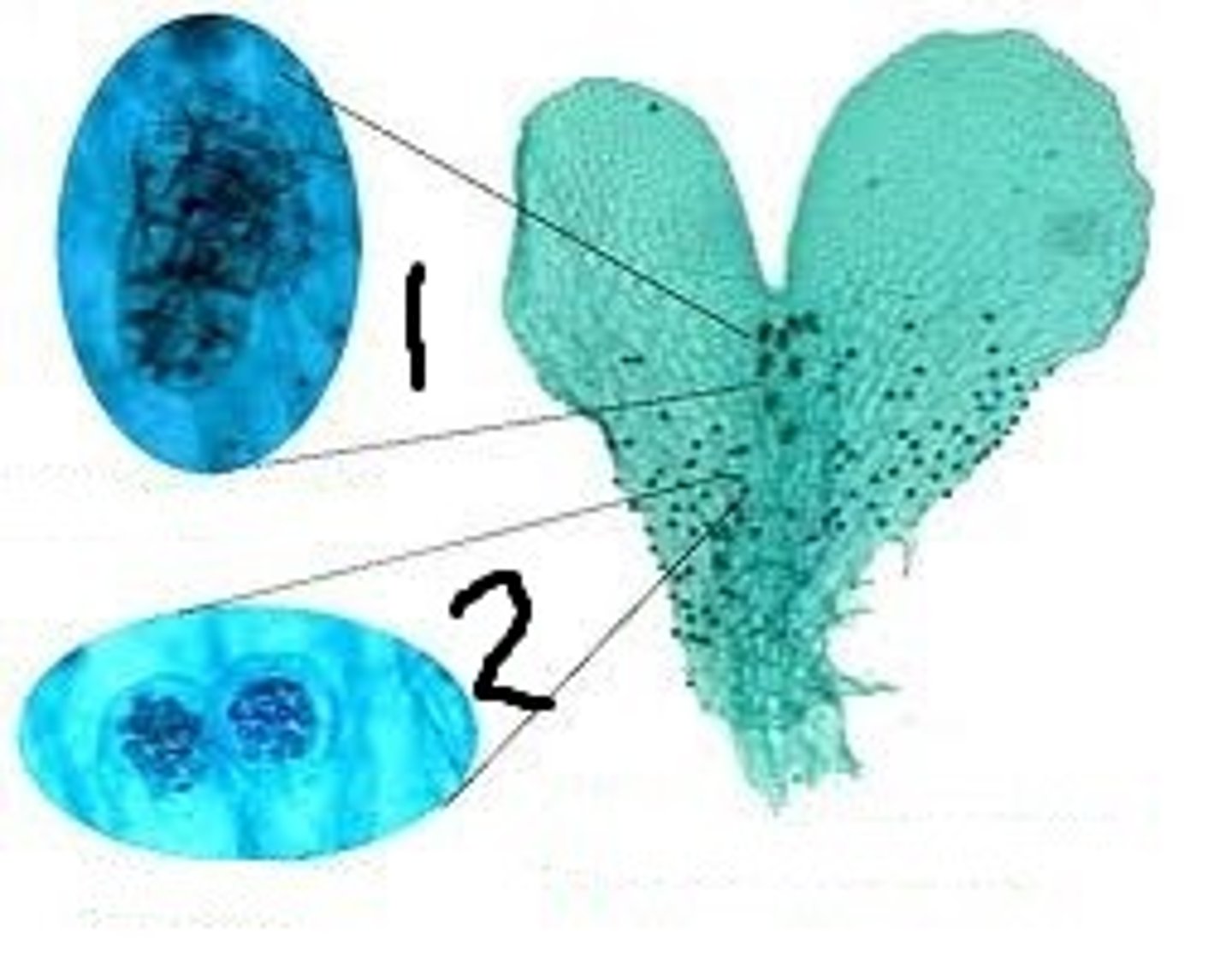
Order Marattiales (Marattoid Ferns)
Bears all features of "true ferns"
Bears the largest fronds in ferns
False; polycyclic siphonostele
T or F: Marattoid Ferns has an endarch siphonostele
True
T or F: Marattoid Ferns is with eusporangium
Order Polypodiales (Common Fern)
Bears all features of "true ferns"
Large species diversity and form
False; leptosporangium
T or F: Order Polypodiales (Common Fern) is with eusporangium
Clubmoss
Common name of Lycopodium
Spikemoss
Common name of Selaginella
Quillwort
Common name of Isoetes