nephrology
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
14/04/2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
rhabdomyolysis
as skeletal muscles are dying, they release → (3)
common scenarios and hints (5)
it is a common side effect of _______ (drug)
myoglobulin, K, creatine kinase
trapped hours under heavy object, fall → long time lying down, marathon runner, old with frequent falls with AKI, IVDU found not moving, severe crush injury ± reddish brown hematuria (false positive as redness is myoglobulin), hypotension, AKI, very high creatine kinase
statin
myoglobulin is _______ and can lead to ________. initial step → _______.
ECG must be performed to detect ________ (findings?). initial step → _______.
nephrotoxic…AKI…IV fluid
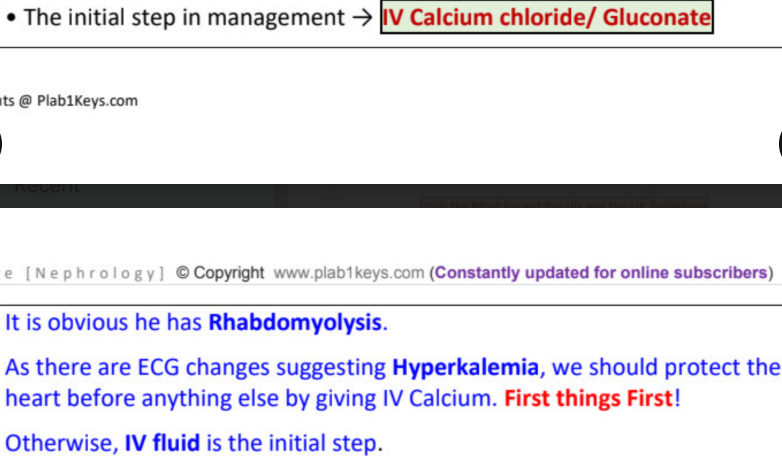
hyperkalemia (tall tented T wave… CaCl/ Ca gluconate (to protect heart)
main complication of rhabdomyolysis → _______ and ________
initial management → ______ (to avoid ____)
initial DX for management → _______
if _______ , initial line → give ______/________
best specific initial test for rhabdomyolysis → ________ (shows _______)
to confirm → _________ (indicates ________)
other lines of TX → ________ and _________
AKI…hyperkalemia
IV fluids…AKI
ecg
hyperkalemia…CaCl/Ca gluconate
urine analysis…red-brown / tea colour (false hematuria)
creatine phosphokinase…muscle necrosis
Sodium bicarbonate…dialysis


most appropriate management →
likely cause of his renal failure →


best investigation to perform →
to confirm →


likely diagnosis →
causing med that needs to be stopped →
rhabdomyolysis
simvastatin

creatine kinase
goodpasture syndrome is ________________ + _____________
expressed as __________ and ____________ + impaired KFT
initial DX →
most accurate DX →
chest x-ray shows →
acute rapid progressive glomerulonephritis + pulmonary alveolar hemorrhage
hematuria + hemoptysis (lung involvement)
anti glomerular basement membrane antibodies
kidney/lung biopsy (cresentic glomerulonephritis)
patchy interstitial infiltration (intra pulmonary bleeding)
goodpasture syndrome → +DX
alport syndrome →
alpha antitrypsin →
churg strauss → +DX
wegener’s granulomatosis → +DX
hemolytic uremic syndrome →
hematuria + hemoptysis (anti GBM antibodies)
hematuria + hemoptysis + can’t see + can’t hear
hemoptysis + jaundice (liver)
eosinophilia + asthma (p-ANCA)
hematuria + upper respiratory syndrome (c-ANCA)
hematuria + diarrhea that turns bloody
“itching after hot shower” +
pale, peripheral edema, skin pigmentation, lethargy → (itching due to _____, lethargy due to ________)
red skin, flushed (due to high ___) ± splenomegaly ± burning fingers and toes ± gout →
linear tracks on skin (burrows) →
yellow skin →
chronic renal failure…uremia…low erythropoietin/anemia
polycythemia rubra vera…high Hb
eczema
liver
normal Na level → _______
hyponatremia can occur after inappropriate _________ such as by _______. this is a _________ cause.
in sepsis either _______ and ______ is allowed (these won’t cause ________)
135-145 mmol/l
IV fluid therapy…dextrose 5%…iatrogenic
ringer lactate…NS (0.5% NaCl)…dilutional hyponatremia

likely cause →
iatrogenic
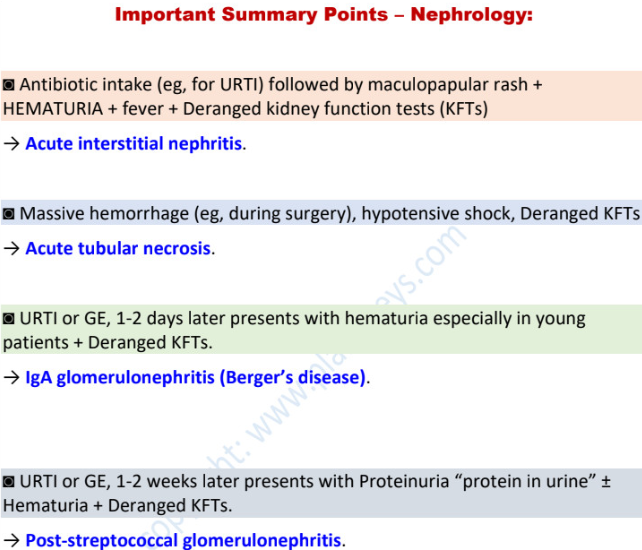
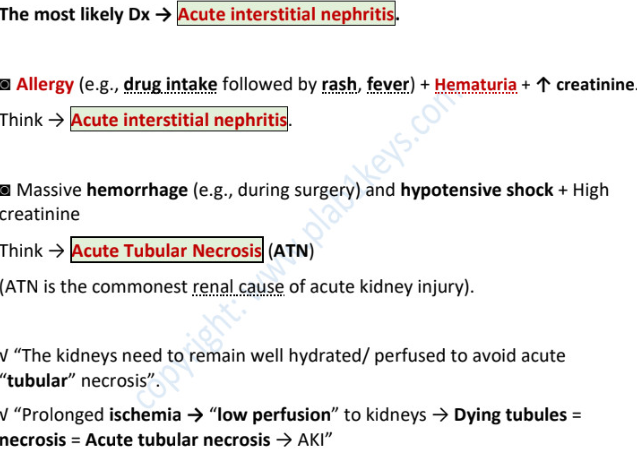
massive hemorrhage + hypotensive shock + high creatinine → _________
kidneys needs to remain _________ to avoid it.
prolonged _______ → low _______ to kidneys → dying ________ = _______ = _______ → ______
acute tubular necrosis
hydrated
ischemia…perfusion…tubules…necrosis…acute tubular necrosis → AKI
allergy (eg drug intake followed by rash/fever) + hematuria + high creatinine →
acute interstitial nephritis
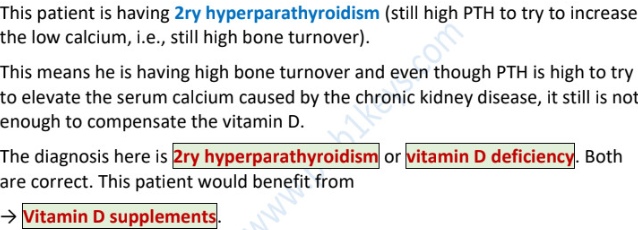
25-alpha-hydroxylation of vit D occurs in →
1-alpha-hydroxylation of vit D occurs in →
25-hydroxyvitamin D is formed in _______ → enzyme called ______ in _______ converts to active form which is _______.
hence, vitamin D deficiency is due to ______________.
liver
kidney
liver…1-alpha-hydroxylase…kidney…1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D
chronic renal failure
hypertension + hx of repeated UTIs →
repeated UTI → _________ → chronic pyelonephritis → __________
loin/back pain + UTI features →
NB! repeated UTI but SUDDEN loin/back pain/fever/rigors ± urinalysis shows blood, nitrites, leucocyte esterase → (why not the other one?)
chronic pyelonephritis
renal scarring…HTN
acute pyelonephritis
acute pyelonephritis (chronic has no active infection such as fever)

acute pyelonephritis
pyelonephritis = _______________
RF → (4)
suspect if (4 main) ± (3 in urinalysis)
inflammation of the pelvis of the kidney
stones, pregnancy, VUR, DM
lower UTI features | fever | loin//back pain
± hematuria, nitrites, leucocyte esterase
dysuria, frequency, urgency ± abdominal pain → (+TX)
above + loin/back pain + fever → (+TX)
DX → _______ (to look for ____, ____, ____, ____)
DX → ________ (then start immediately ________!!) (_______ specimen for adults and old children, ________ in young children)
lower UTI || TX - trimethoprim, nitrofurantoin
ascending UTI || TX - co-amoxiclav/ciprofloxacin
urinalysis → blood, nitrate, leucocyte esterase, protein
urine culture and sensitivity…empirical antibiotics
midstream…clean catch/ catheter/ suprapubic aspiration
most common cause of UTI →
TX for non pregnant women, men and patients with indwelling catheters → __________/ ___________
TX for children → 1st line ________, 2nd line __________
TX for pregnant who dont require admission → __________
!! if patient is admitted, these AB are given _____
e.coli (gram negative)
ciprofloxacin 500mg BID 7d / co-amoxiclav 625 mg TID 14d
co-amoxiclav…cefixime
cefalexin 500mg BID 10-14d
IV
small kidneys + HTN → ________/ _______
drug that is CI in ______ → ________
bilateral renal artery stenosis / chronic pyelonephritis
bilateral renal artery stenosis…ACEi
mild proteinuria on urine dipstick (up to +1) + gymrat →
if no other symptoms →
if still high →
NB! never refer a patient with _______ to renal clinic! always investigate further first.
normal
repeat test
24h urine specimen test / PCR
isolated proteinuria
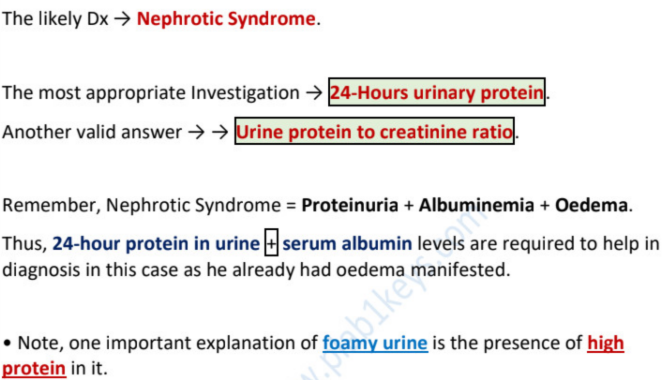
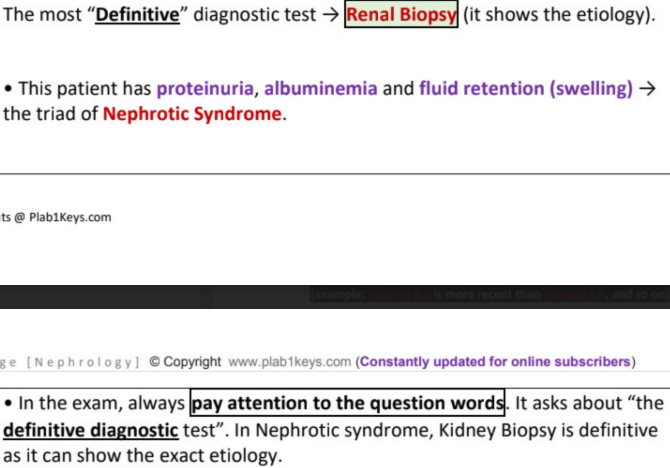
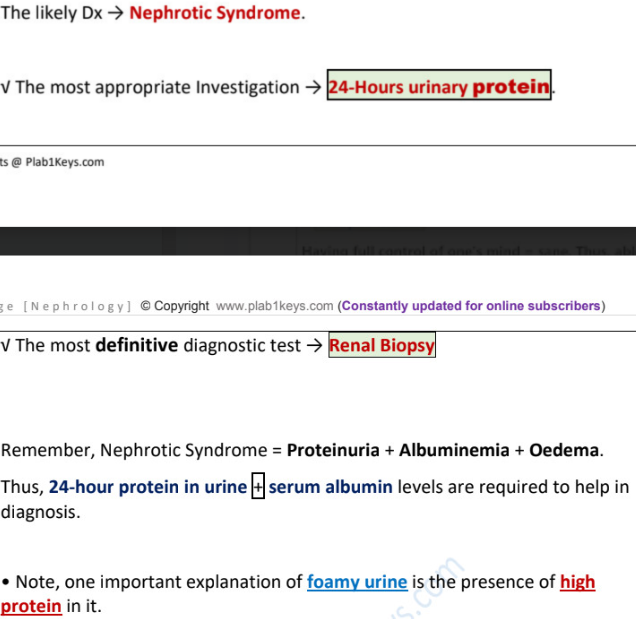
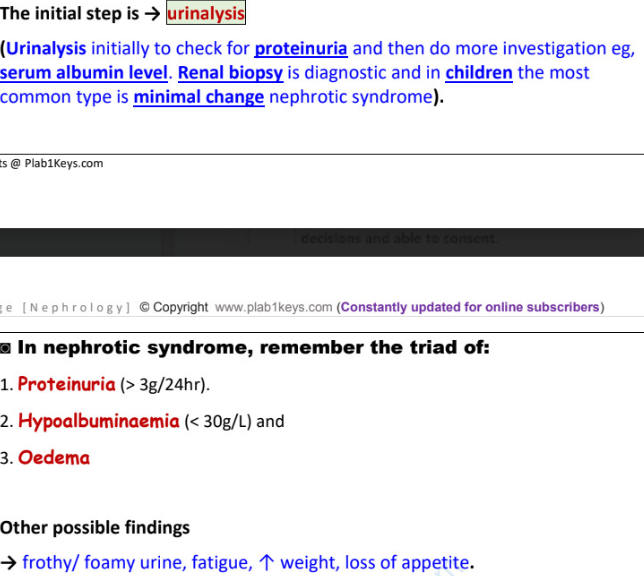
triad of nephrotic syndrome
children peak incidence age ___ to ___ (80% due to MCG)
features of minimal change glomerulonephritis (3)
definitive DX → (+ findings)
proteinuria >3g/24h, hypoalbuminemia <30g/l, edema
2-5 YO
nephrotic syndrome, normotensive, selective proteinuria (mid size protein such as albumin and transferrin can leak through glomeruli)
renal biopsy - fusion of podocytes
_________ always presents as nephrotic syndrome (75% children, 25% adults).
good prognosis with TX ______.
other features (2) due to (2) + (1)
foamy urine indicates →
fluid retention indicates →
minimal change disease
high dose oral steroids
hyperlipidemia, hypercoagulable state (due to loss of antithrombin III), liability of infection (due to loss of Ig)
proteinuria
edema



diagnosis →
most appropriate investigation →
another valid answer →

most definitive diagnostic test →

likely diagnosis →
minimal change disease


prolonged vomit and diarrhea can lead to __________ and __________.
most common cause of AKI is ________
AKI → ________ → kidneys unable to excrete K, creatinine, urea → ________, ________, _______.
hypokalemia…dehydration
dehydration “hypovolemia”
decreased eGFR…hyperkalemia, high urea serum, high creatinine
to reduce risk of “contrast induced nephropathy” in CT scan with contrast
→
→
→ ________ (drug) needs to be stopped
drink plenty of water
IV fluid NS (0.9% NaCl)
metformin (nephron harmful)
blood gas norm - abnormality
pH ____ to _____ (> is alkalemia, < is acidemia)
PaCo2 ____ to _____ kPa (< is respiratory alkalosis, > is acidosis)
bicarbonate level _____ to _____mmol/l (< is metabolic acidosis, > is alkalosis)
base level _____ to _____mmol/l (< is metabolic acidosis, > is alkalosis)
*profuse diarrhea also leads to loss of ________ → ________
7.35-7.45
4.7-6
22-26
-2 to +2
hypovolemia “dehydration” → AKI



his blood gas interpretation →

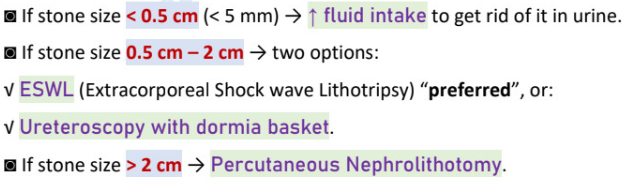
renal stones management
< 0.5cm →
0.5cm-2cm → (2)
> 2cm →
1 functioning kidney + any size stone + dilatation of pelvicalyceal system (PCS) ± anuria, fever
indicates →
initial management is to → (to save remaining kidney)
done by →
2 functioning kidneys, develops AKI, fever, hydronephrosis, stone
indicates →
management →
obstructive uropathy
percutaneous nephrostomy
decompressing the PCS
percutaneous nephrostomy vs percutaneous nephrolithotomy
HTN + CKD + GFR>30 + ACR>30, TX → (2)
if GFR<30 / ACR<30, avoid →
(2) can be used as long as ACR ≥ ____, ACR ≥ ____ (if HTN), ACR ≥ ____ (if DM)
SGLT-2 provides ____, _____, ____ protection
SGLT-2 examples → flozin → ____, _____, _____
percutaneous nephrostomy - stoma catheter to the PCS for decompression (drain fluid)
percutaneous nephrolithotomy - remove stone via scope (if >2cm)
ACEi /ARB
ACEi /ARB
ACEi /ARB…70…30…3
renal…cardio…diabetic
cana, dapa, empa + gliflozin




most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in
children
adults (white/caucasian/unspecified) →
adults (african/black/american/hispanic) →
minimal change glomerulonephritis
membranous GN
focal segmental GN
membranous glomerulonephritis
presentation (3)
cause (4)
prognosis (1/3 for each) → ______, _______, ______
proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome, CKD
idiopathic, infection, rheumatoid drugs, malignancy
remission, partial remission, end stage renal failure
suspect CKD if (4)
reason for hypocalcemia → deficiency of _______ → low vit D and Ca
hypocalcemia SX (4)
anemia + hypocalcemia + hyperphosphatemia + small kidneys (US < 9mm)
1-alpha hydroxylase
tingling, numbness, paresthesia, involuntary spasms/cramps
patient presents with CKD and DM
loss of sensation in fingers and muscle cramps
labs : hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, anemia
likely reason for his symptoms →
other valid answers (2)

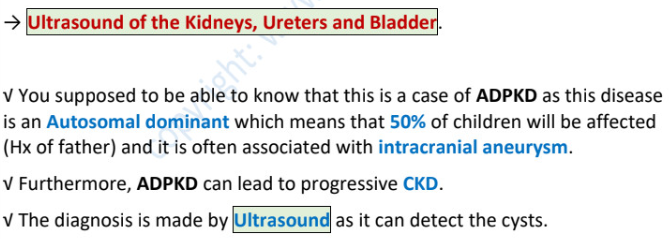
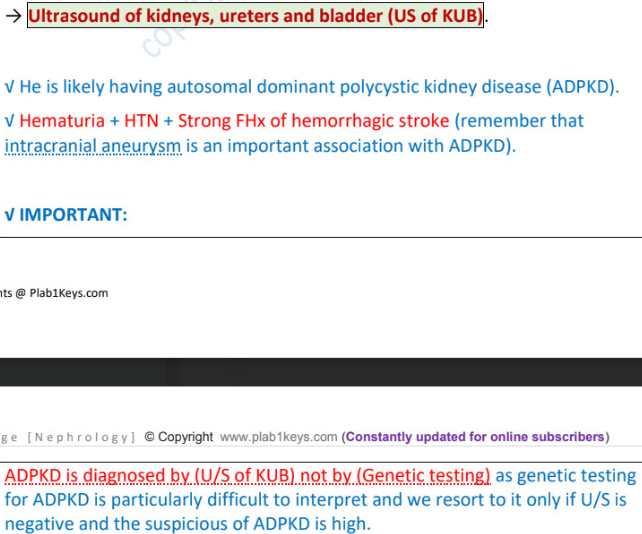
autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) - 50% by fam hx
________ + ________ + _______ → ______PKD
it is associated with ___________
DX (3)
hematuria + HTN + loin/flank pain → adultPKD
intracranial aneurysm
US of kidney, ureter, bladder

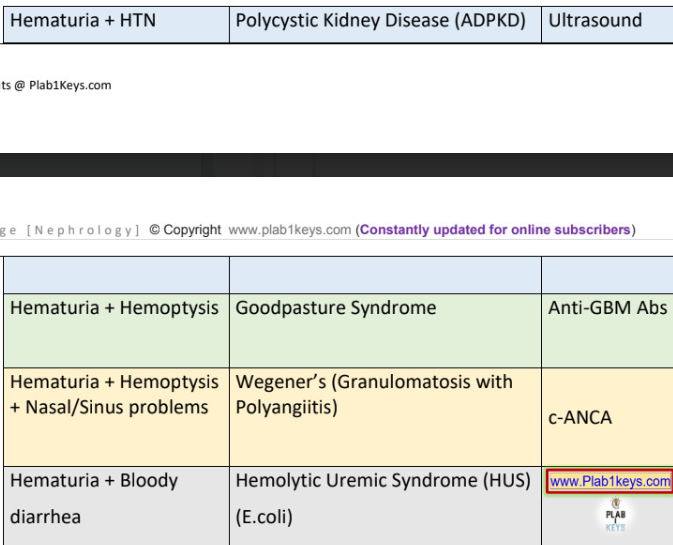
hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) triad
children eat contaminated food → _______ → produce ________ → profuse _______ → turns ______ → (after 2-14d) → ________ “acute renal failure” (________, _______, high _____ and ______)
TX (3), if severe (1), NEVER give (1) because _____________
hemolytic anemia || uremia (acute renal failure) : low urea and creatinine || thrombocytopenia (low platelet)
e.coli 0157…verotoxin…diarrhea…bloody…uremia…(hematuria, proteinuria, high urea and creatinine)
IV fluids, blood transfusion, dialysis || plasma exchange || antibiotics (dead e.coli produce more toxin)
hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) triad + fever + neurological manifestations →
TTP - thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
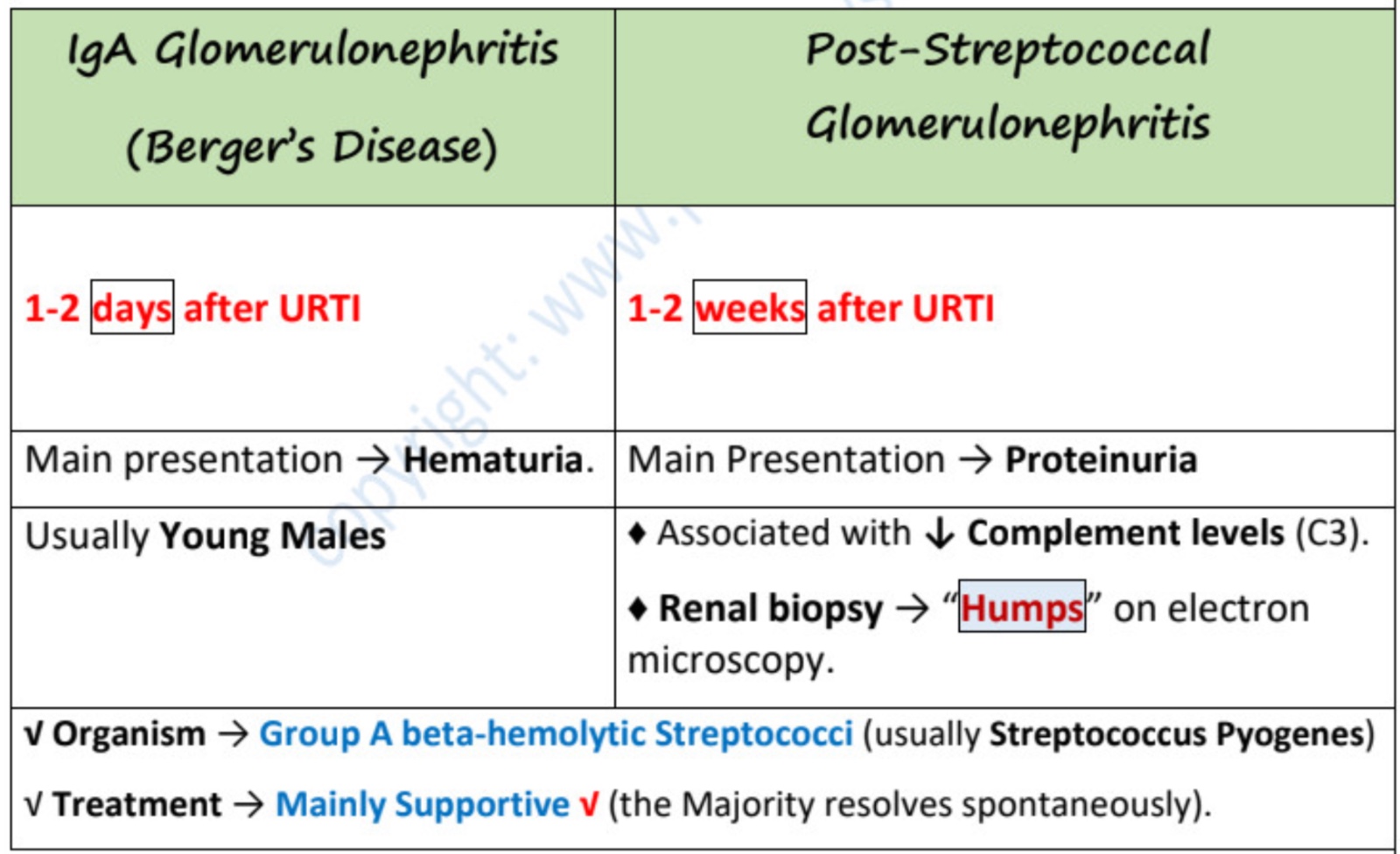
hematuria that develops after a hx of URTI (_______/________) or gastroenteritis is due to
(2) disease
time of exacerbation, main presentation, organisms, TX, ± gender, DX and findings
causes of small kidneys (4) and large kidneys (2)
chronic pyelonephritis || chronic glomerulonephritis || hypertensive renal disease || bilateral renal artery stenosis
ADPKD || obstructive neuropathy (stone/ enlarged prostate → hydronephrosis → large)

simple lower UTI (dysuria,frequency) is treated by
→
→
uncomplicated upper UTI (acute pyelonephritis)
→
→
→ (if pregnant/outpatient)


best management →
likely case of →

indications of hemodialysis (5)
persistently high K ≥ 6.5 (refractory hyperkalemia)
severe metabolic acidosis
fluid overloaded with anuria/non-effective diuretics
uremic pericarditis, pulmonary edema
uremic encephalopathys

most appropriate investigation →

ACEi / statins / BB / diuretics
ACEi (reno protective, delay progress of CKD)

AKI / addison’s/ renal tubular acidosis


MCUG / renal USS / DMSA / urine mcs / ct scan
renal USS
reflux nephropathy (______ → ______ → ______ → ______)
reflux involved
occurs mainly in?
cause
DX initial (2), gold standard, for parenchymal damage(cortical scars)
TX initial (1), failed/parenchymal damage(1)
urine goes back from bladder to ureters and kidneys (vesico-ureteric reflux) → dilated pelvicalyceal system → repeated UTIs → progressive renal failure
young children
congenital abnormality of the insertion of ureters into urinary bladder (can be seen on US)
renal US, urinalysis, urine culture || micturating cystourethrogram || technetium scan (DMSA)
low dose trimethoprim (AB) || surgery/utreters re-implantation



hypertensive neuropathy / bph / prostate car / chronic pyelonephritis / vur
hypertensive neuropathy

diagnosis →
hypertensive renal disease → small and scarred kidneys → renal impairment
HTN + hx of repeated UTIs
think of →
chronic pyelonephritis
repeated UTI → renal scarring → chronic pyelonephritis → HTN

membranous GN / minimal change GN / post strep GN / IgA nephropathy
minimal change GN always presents as nephrotic syndrome

likely reason for hypocalcemia is →
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 deficiency


TFT / x-ray / blood glucose / urinalysis / LFT
urinalysis


abdominal US / blood cultures / serum creatinine phosphokinase / echo / TFT
serum creatinine phosphokinase

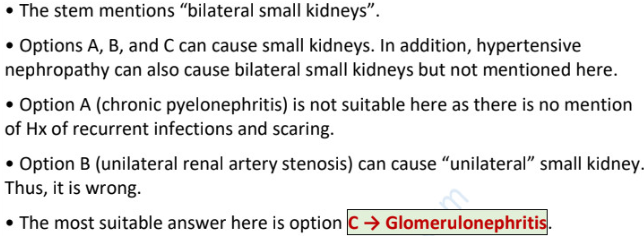
bilaterally small kidneys + HTN
possible diagnosis (2)
bilateral renal artery stenosis
hypertensive renal disease
female presents with dysuria, loin pain and rigors
likely →
initial investigation →
then →
acute pyelonephritis
urinalysis
urine culture

likely diagnosis →
most appropriate investigation →
most definitive diagnostic test →

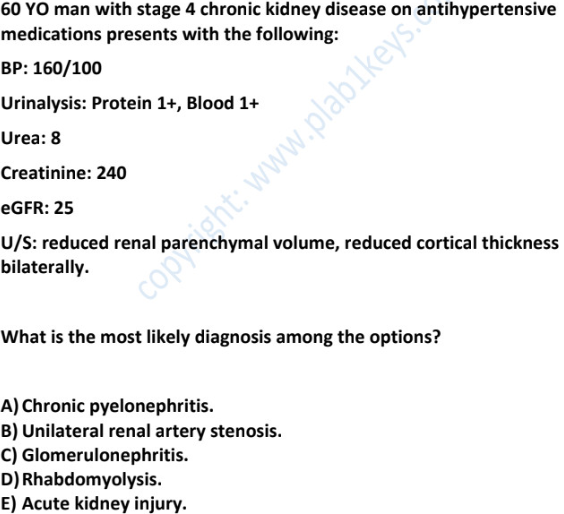
likely cause of renal failure → (+why)
a case of →
myoglobulin (reno toxic)
rhabdomyolysis


D.A.M.N. drugs that need to be stopped if patient presents with diarrhea/vomiting (risk of dehydration and AKI) until symptoms resolve

causes of AKI (6)
rhabdomyolysis
HUS
dehydration : diarrhea/ vomit
sepsis
following major surgery
DAMN drugs


DM + microalbuminuria, start on ________ (even if normotensive)
because DM can lead to _________
ACEi (enalapril, lisinopril)
diabetic nephropathy

BPH / hypertensive nephropathy / prostate car / chronic pyelonephritis / vur
hypertensive nephropathy





initial TX for hypocalcemia (eg tingling, low serum Ca)
calcium gluconate infusion

most likely diagnosis →
most appropriate management →


most likely diagnosis →
most appropriate management →



most likely diagnosis →




common complication of CKD is anemia (eg extreme fatigue, sleepiness, pallor). “due to impaired ________ and ________)
in patients with CKD + anemia but with
normal serum ferritin and iron, give →
low serum ferritin/iron →
iron absorption…erythropoietin


diabetic nephropathy/membranous nephropathy



normal albumin creatine ratio (ACR) is < ____
microalbuminuria (proteinuria) ____ to _____
macroalbuminuria (albumin is a protein) > ___
30
30-300
300
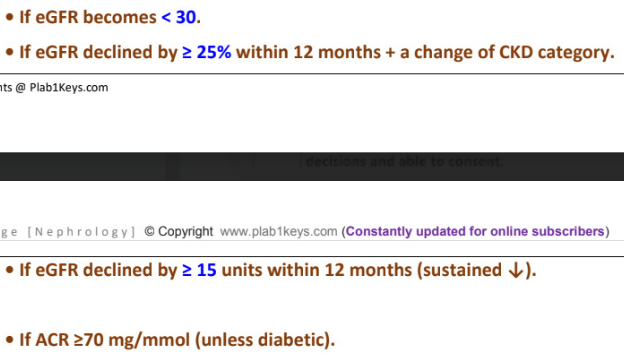
when should GP refer patient to a nephrologist (4)



initial step is →
the anatomical structures affected in nephrotic syndrome are


diagnosis →
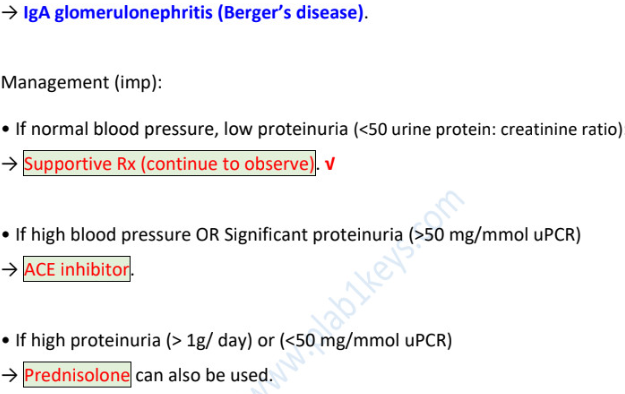
management if
normal bp, low proteinuria (<50 uPCR) →
high bp / high proteinuria (>50 uPCR) →
high proteinuria (>1g/d) or (<50uPCR) →