Lecture 23: tetrapods, amphibians, amniotes
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What are tetrapods?
– Four footed animals
What groups are tetrapods? (4)
-amphibians
-reptiles
-birds
-mammals
When did vertebrates move onto land?
400 million years ago
What are some traits of early tetrapods?
-freshwater
-Modified fleshy fins to ambulate in the shallow water
-Sometimes went on land
Ancestral tetrapods
– Aquatic as juveniles
– Terrestrial as adults
– Lateral line present
Summary:
Tetrapod (4)
– Limbs, pelvis and pectoral girdle are more ossified
– fusion of bones
– Larger articulations of vertebrae to avoid sagging
– Modern amphibians are an intermediate transition between water and land but highly specialised
What group did modern amphibians arise from?
labyrinthodonts
Transition of the modern and amphibians (5)
-late Devonian., About 365 mya
-radial fin rays supporting a tail
-defined limbs with 8 digits
-weight-bearing girdles
-internal gills
When did the digits of land tetrapod arise?
-before the transition to land
Which two groups of tetrapod lived around the same time?
-Acanthostega
-Coelacanth
When did modern amphibians arise?
– Jurassic
– Roughly 200,000,000 years ago
What are the three extant orders of amphibians?
-order Anura
-order Urodela/Caudata
-order Gymnophiona/Apoda
Order Anura
-amphibians
-include frogs and toads
Order Urodela/Caudata
-include salamanders and newts
Order Gymnophiona/Apoda
-include caecilians
Summary:
caecilians (3)
-legless
-blind
-can be aquatic or subterranean
What amphibian is not found in Australia
-caecilians
(Order Gynophiona/Apoda)
Which modern amphibian most closely resembles ancestral amphibians?
– Salamanders
What are some ancestral characteristics that modern amphibians retained?
– Need for aquatic or habitats
- Need for higher temperatures; tropical and temperate
What happens when aquatic larvae metamorphose into terrestrial adults? (3)
-lose lateral line system
-lungs replace gills
-develop legs
Roughly how many species of amphibians have been discovered?
Around 3000 species
Who did ancestral amphibians evolve from?
-lobe fin fishes → scales (Caecilians retain vestigial scales)
stratum corneum
-modern amphibians have a very thin one
-Limited protection from abrasions and dehydration because of cutaneous respiration
-blood supply is very close to skin surface
Cutaneous respiration
-gas exchange
– Capillary beds are in epidermis (the only known instance in vertebrates)
– Large surface area to body mass ratio
Amphibians:
vertebral adaptations
– Articular processes interlock to provide more rigidity and support due to the lack of water buoyancy
Amphibians:
Pectoral girdle adaptations
– Not joined to the skull
– Development of cervical vertebrae
- Free movement of head
Amphibian
Pelvic girdle adaptations
– Presence of ilium, ischium, and pubis
Part of sacral region articulates with pelvic girdle
How many digits do amphibians have on their hindlimbs?
5
How many digits do amphibians have on their forelimbs?
4
What are four adaptations to the amphibian integument?
– Mucus glands
– Granular glands
– Chromatophores
- Eyelids and tear glands
Integument Adaptations:
Mucus gland
– Continuous secretion
– Prevents dehydration
– Limited role in pathogen entry prevention
Integument Adaptations:
Granular glands
– Poison glands: milky, distasteful secretion
– Toxic: Neuro, toxicity, hallucinations, blood poisoning
Granular glands:
Poison dart frogs
Secrete alkaloids in their poison
– Do not synthesize alkaloids; ingest them from insects and keep them in the glands
Integument Adaptations:
Chromatophores
– Found within the dermis
– May be present within the epidermis
– noxious skin secretions often coupled with striking color
chromatophores:
Poison dart frogs
-aposematic coloration: warning to predators
Integument Adaptations:
Eyelids and tear glands
-developed at metamorphosis
Amphibians:
Reproduction
– Reproduce in or near water
-amplexus (mating posture)
-female releases eggs, male sprays sperm over them
-many species of frogs where males carry tadpoles on their back (some species only carry one, some carry many)
Definition:
Amplexus
– Mating position of frogs where male clasps onto back of female
caecilians:
Reproduction
– Internal fertilization
– Males and females press cloacae together and sperm is transferred into female
Salamander:
Reproduction
– Males produces spermatophore
-females pick up spermatophore with cloaca
Definition:
Spermatophore
-a protein capsule containing a mass of sperm
Amphibians:
Brain
-little development from that fishes
– Lateral line present in aquatic larva, but lost in terrestrial adults
Definition:
Lateral line system (fish and aquatic juvenile amphibians)
-sensory system used to detect water movements and pressure gradients
What are the three amniotic groups?
Reptiles
Birds
Mammals
What was the key to the vertebrates’ success on land?
Evolution of amniotic egg
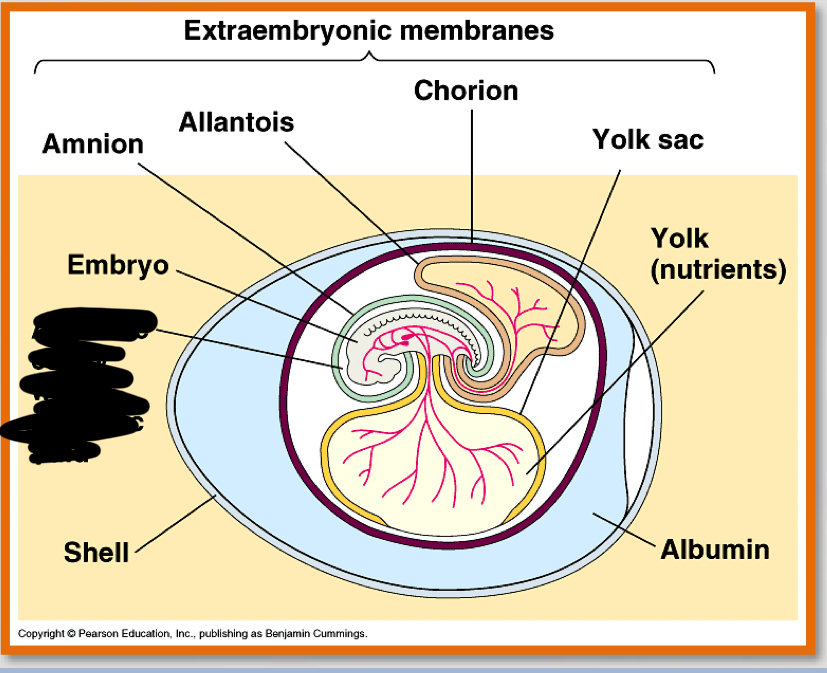
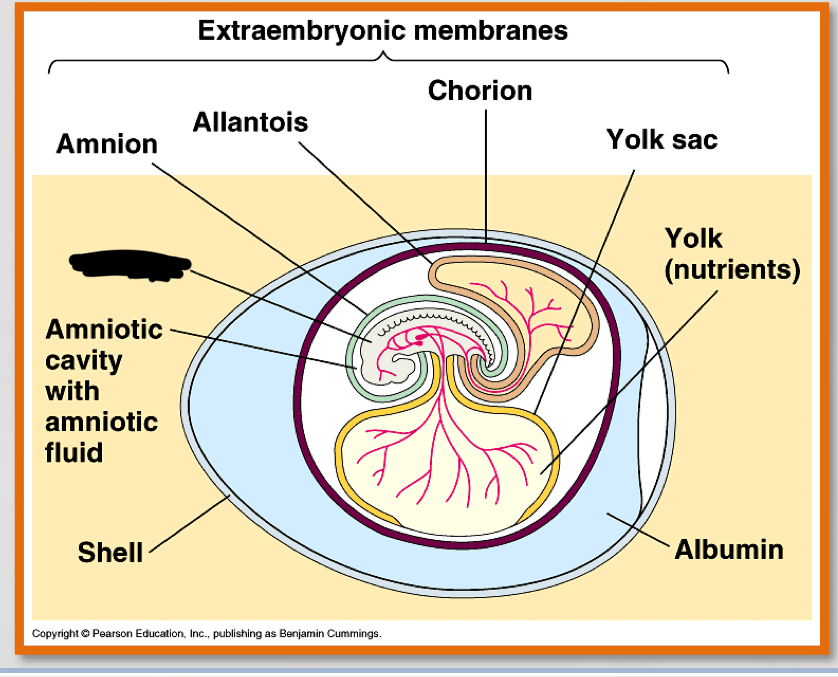
What are the four most important parts of the amniotic egg?
-amnion
-Allantois
-chorion
-yolk sac
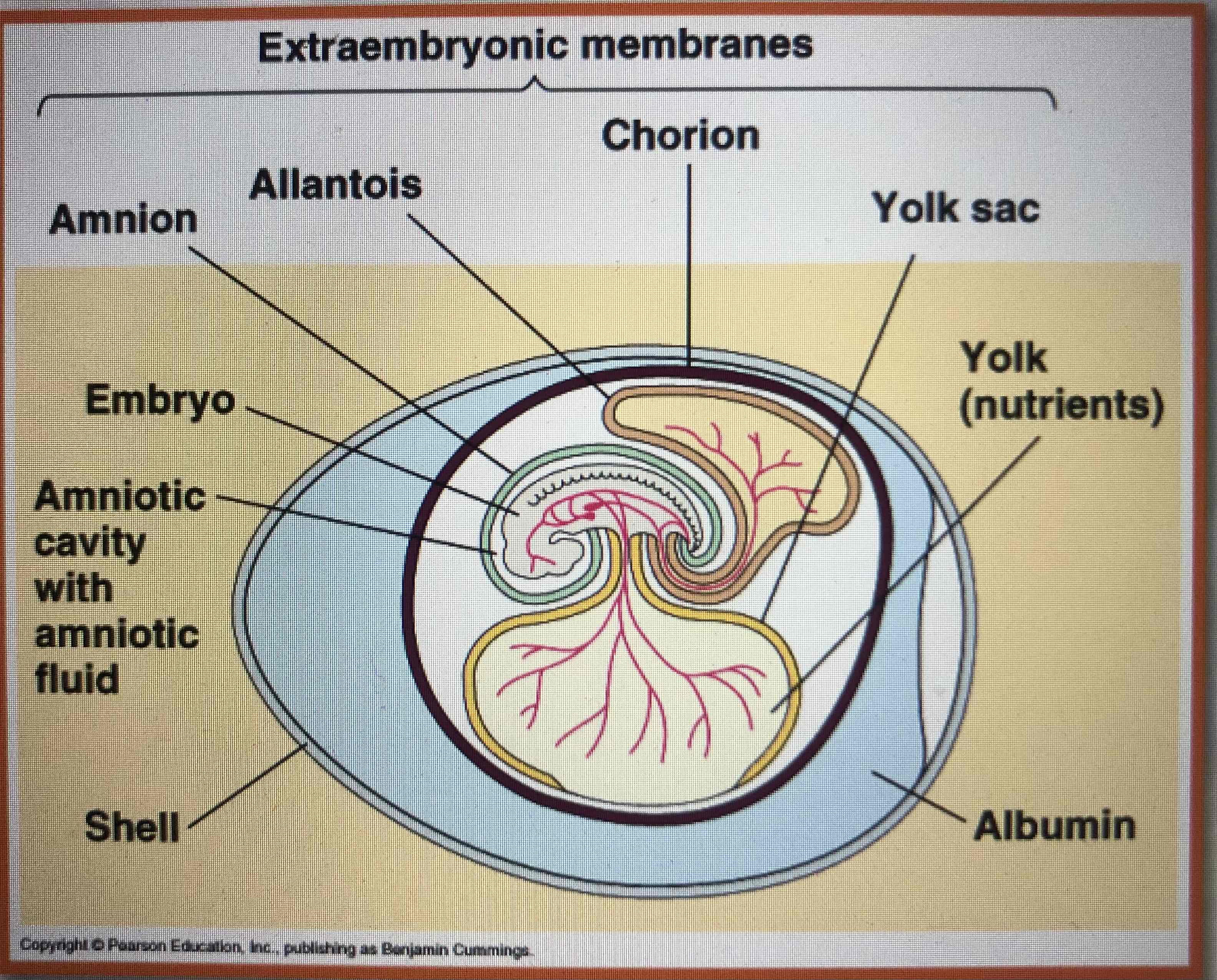
amnion (3)
– Encloses the embryo
– Fluid filled
– Protects the embryo from mechanical shock
allantois (2)
-contains and separates fetal urine from the embryo
-contributes to placenta in eutharian mammals
chorion (2)
-outer envelope
-contributes to placenta in eutharian mammals
Yolk sac
– Source of nutrition for embryo
Amniote egg:
Birds and reptiles
– Embryo and associated membranes are enclosed by a calcareous or leathery shell
-prevents desiccation and allows terrestrial reproduction
Amniotic egg:
eutherian and marsupial mammals
-lost the shell
Eutherians: form a placenta
Marsupials: deliver altricial young
Amniotic egg:
Monotremes (ie. platypus)
-retained egg shell
What is the basal group of amniotes?
-Cotylosauria
“stem reptiles”
What are the two major languages of amniotes?
-Sauropsida
-Synapsida
When did Sauropsida & Synapsida diverge?
-Carboniferous period (~300 mya)
Sauropsids
-dinosaur
-modern reptiles
-birds
Synapsids
-mammals
What is one way to identify amniotes?
Skull fenestration
Definition:
Fenestration
-a natural or surgically added opening in a surface
What are the three skull types (based on fenestration)?
-anapsids
-diapsids
-synapsids
Definition:
Anapsid
-no fenestrae
-ancestral amniotes
-modern turtles and tortoises
Definition:
diapsids
-2 fenestrae
-dinosaurs, lizards, snakes, crocodiles, tuatara, birds
Definition:
synapsids
-1 fenestrae
-mammals
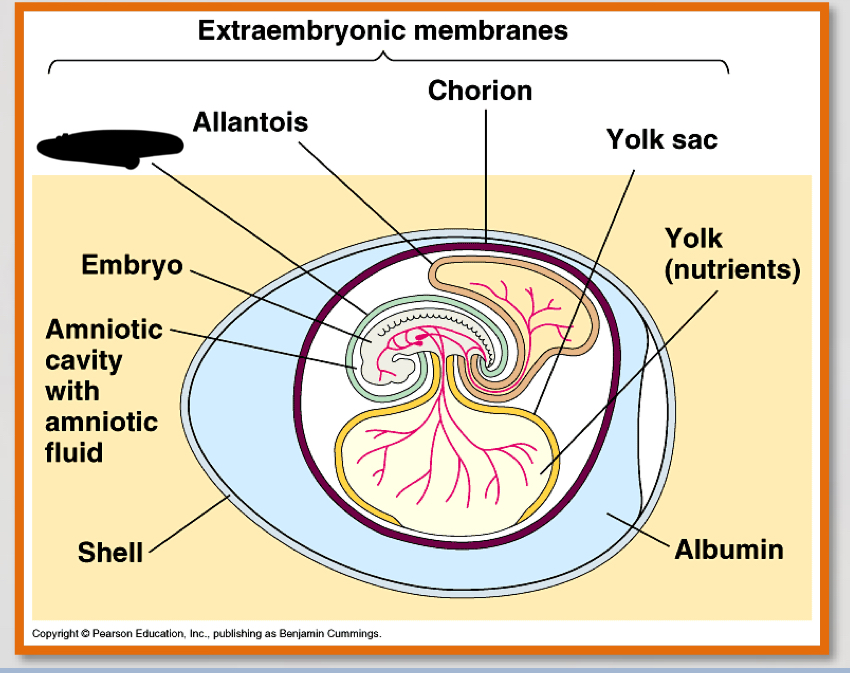
what is the noted structure?
amnion
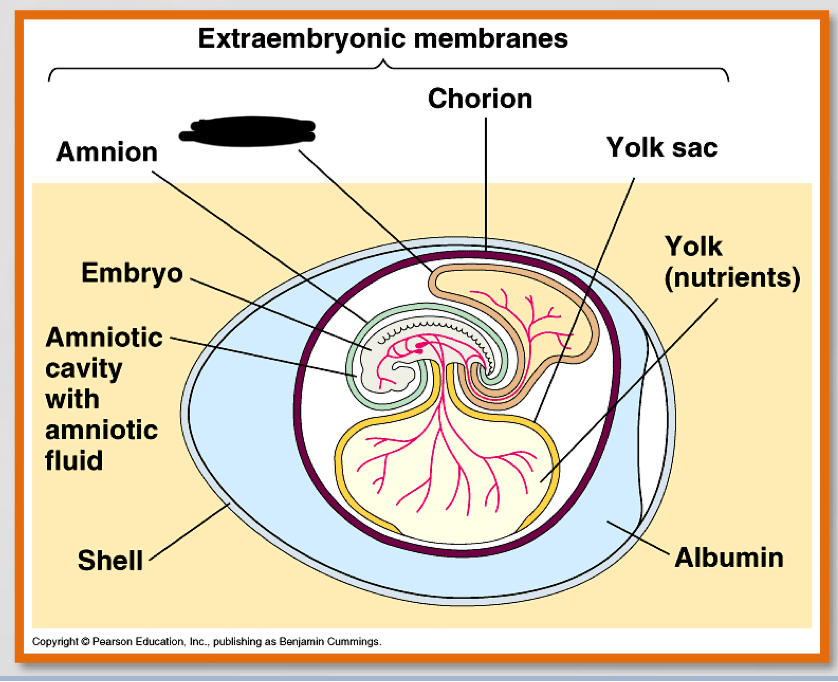
what is the noted structure?
allantois
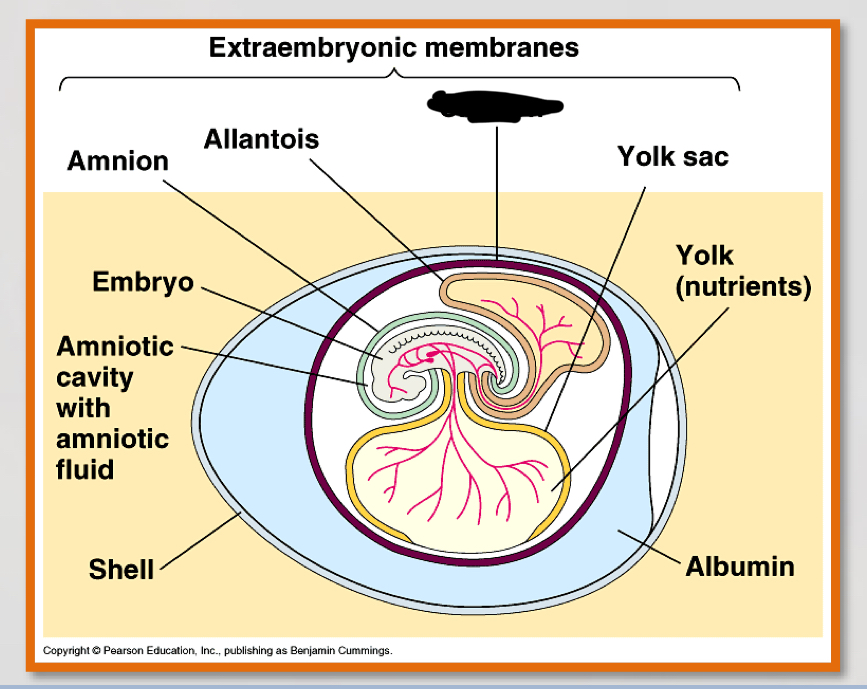
what is the noted structure?
chorion
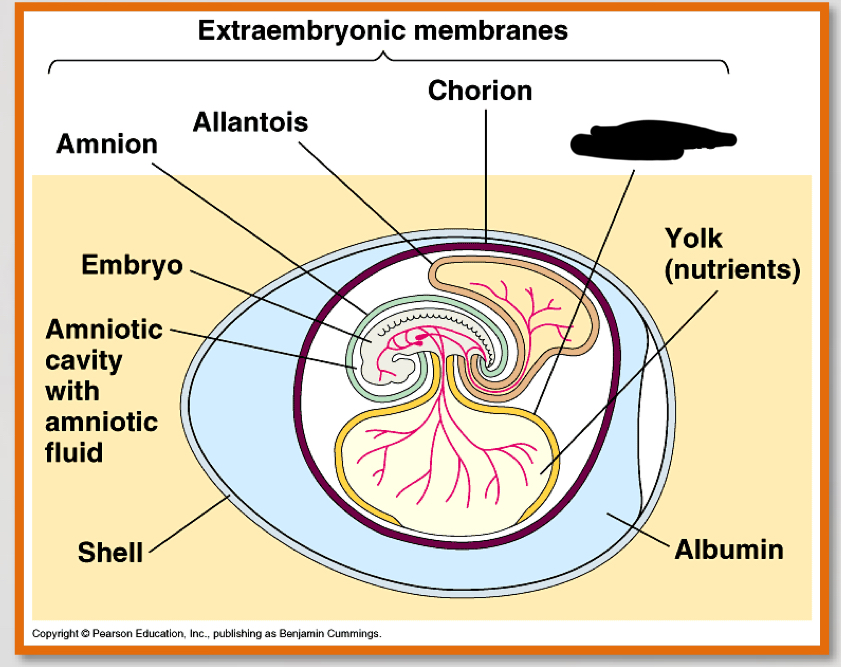
what is the noted structure?
yolk sac
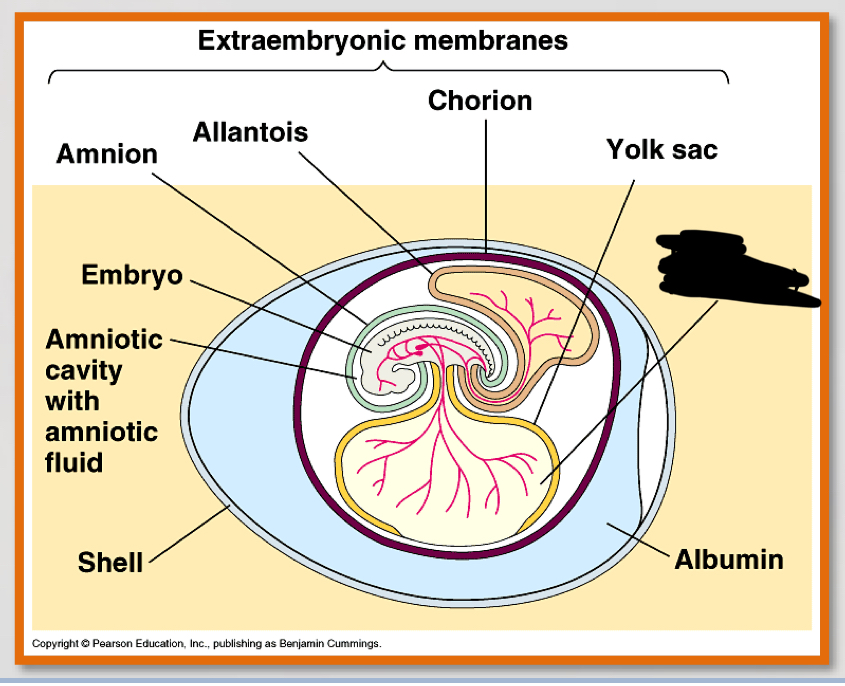
what is the noted structure?
yolk & nutrients
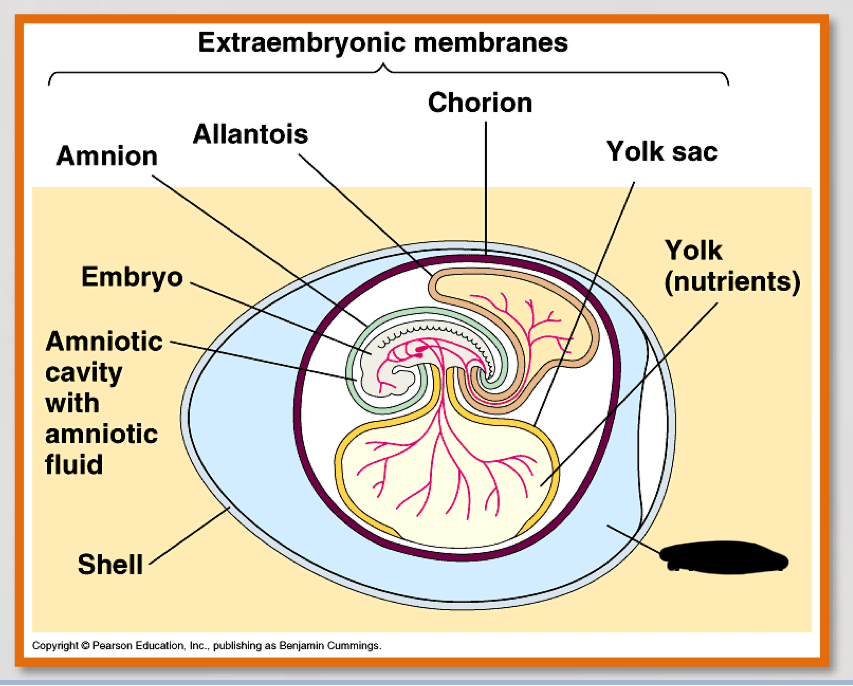
what is the noted structure?
albumin
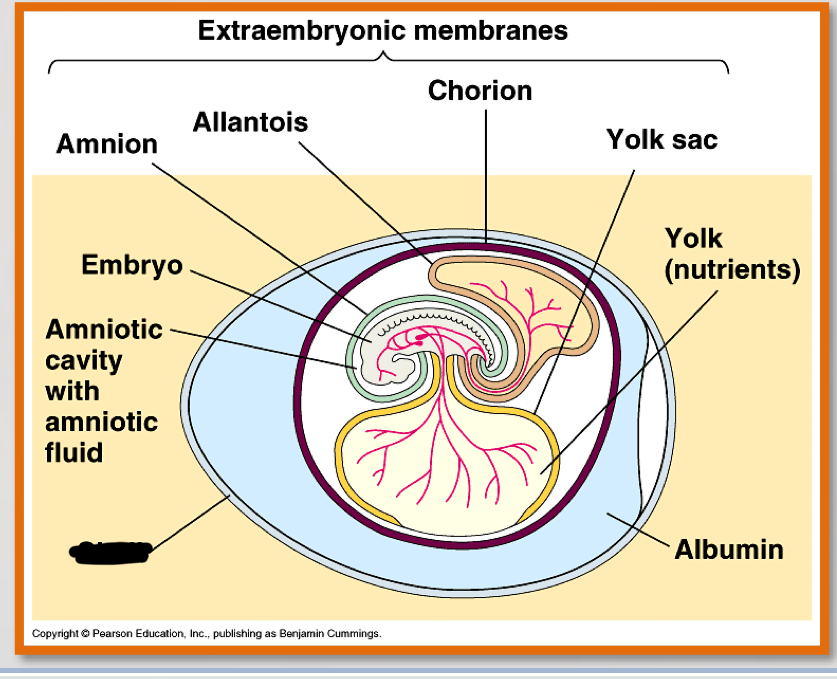
what is the noted structure?
shell
what is the noted structure?
amniotic cavity w amniotic fluid
what is the noted structure?
embryo