Lecture 2: Orbital theory, electron configurations and hybridisation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what was john daltons assumption that was proved incorrect?
particle of an atom was indivisible
what are the main types of atomic orbitals?
s, p, d, and f orbitals
lowest energy shells first
the more full the shell the less reactive
how many electrons can be found in each orbital?
s=2 p=6 d=10
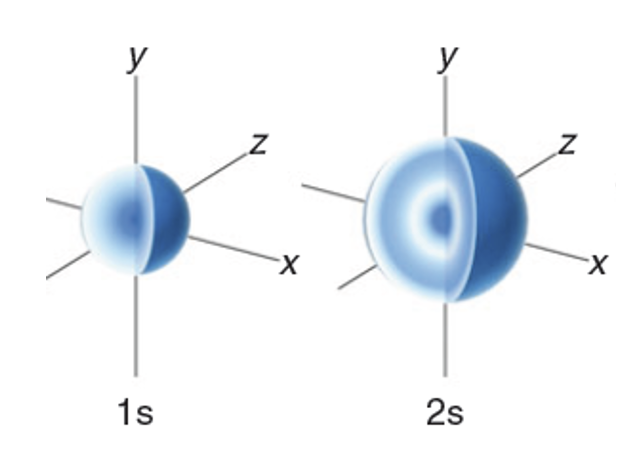
what are S orbitals?
sphere of electron denisty centered on the nucleus
electron can be found anywhere in orbital
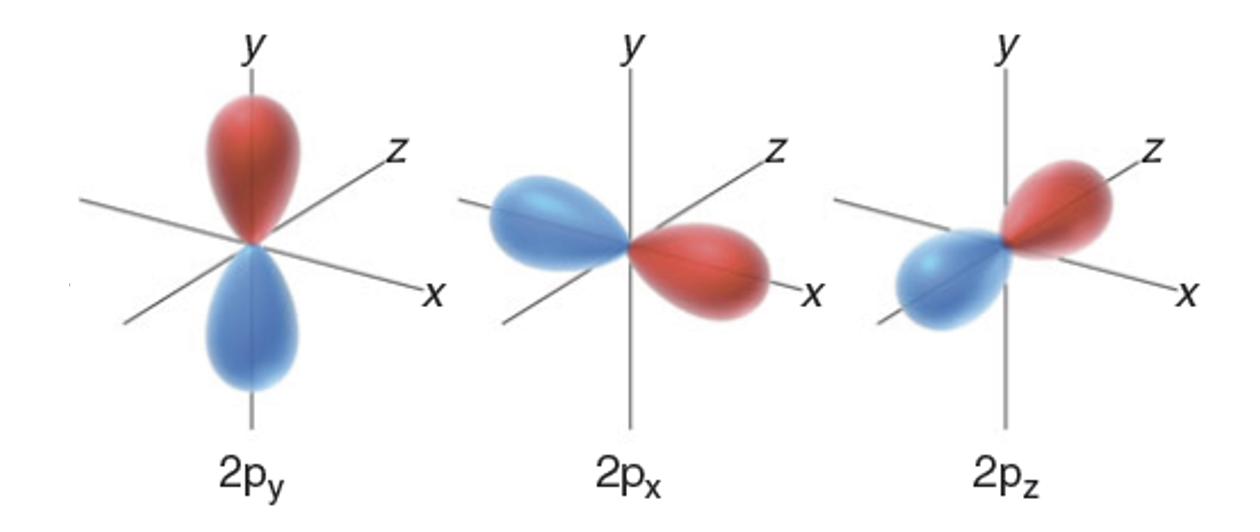
what are P orbitals
dumbell looking
have a node at the centre so no chance of finding e there
what is valency?
the number of bonds needed to complete the outer shell
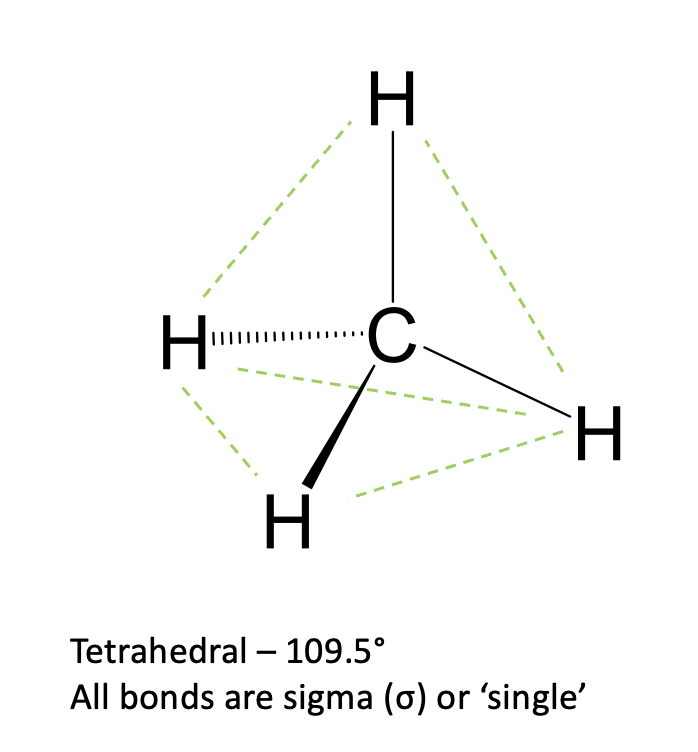
what is Sp3 hybridisation?
1s orbital + 3 p orbitals
tetrahedral
109.5
all sigma bonds(single)
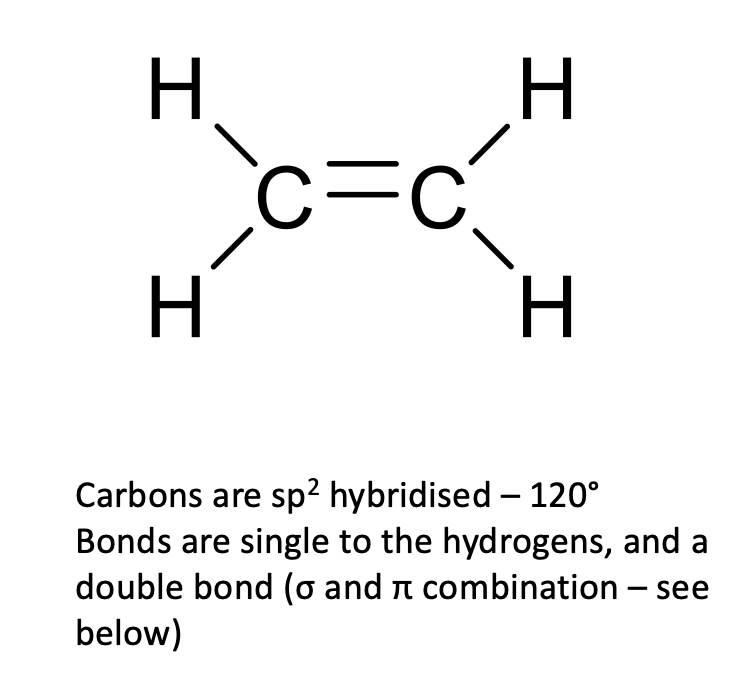
what is Sp2 hybridisation?
1s orbital and 2 p orbitals
trigonal planar
120
sigma and pi bonds
what is Sp hybridisation?
1 s orbital and 1 p orbital
linear
180

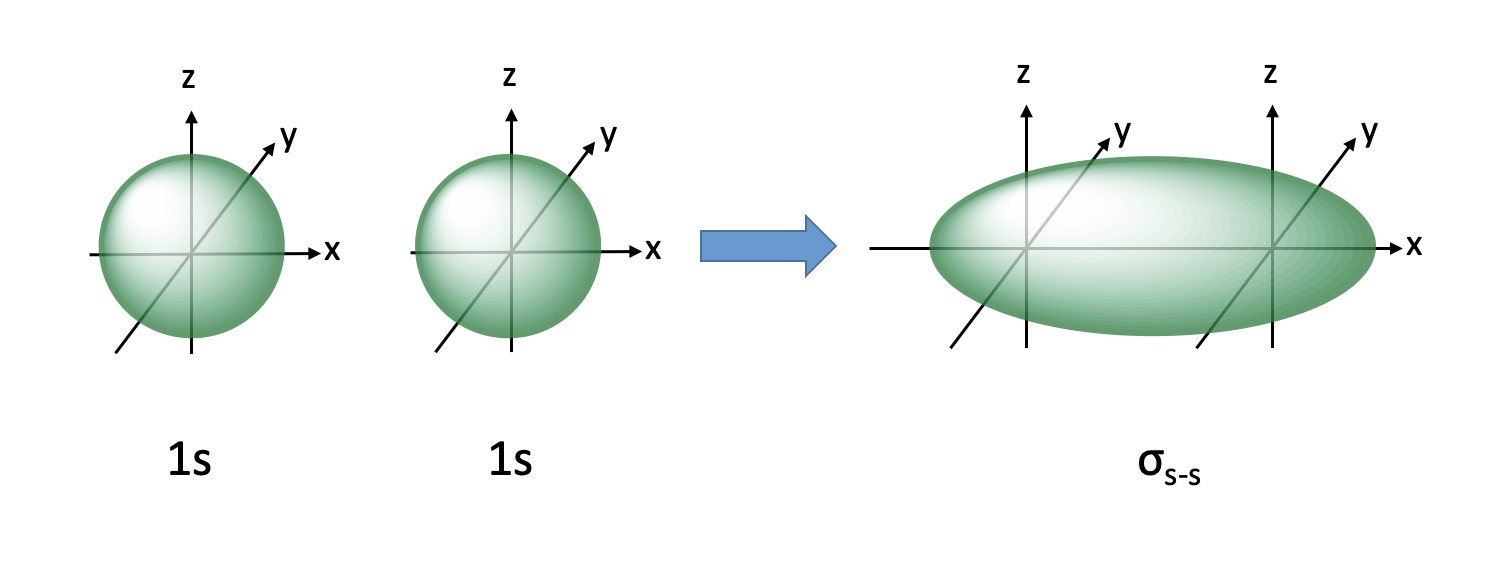
what are sigma bonds?
strongest type of covalent bond(single bond)
formed when atomic orbitals overlap head on
release energy
free rotation
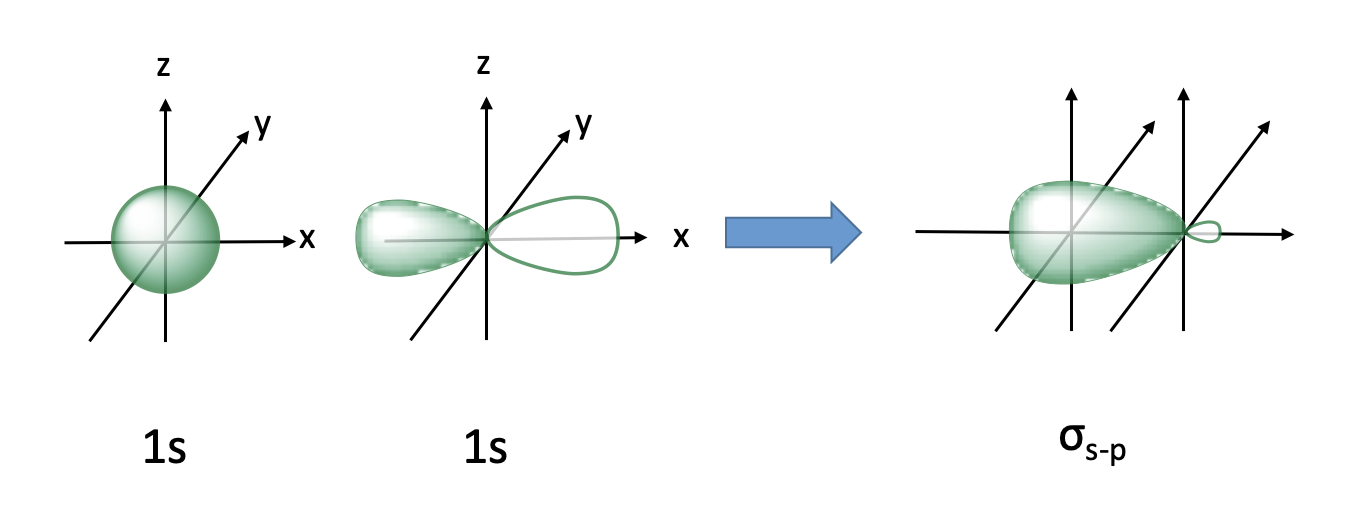
sigma bond with 1s and 1p orbital
lobe opposite new orbital, involved in substitution reactions
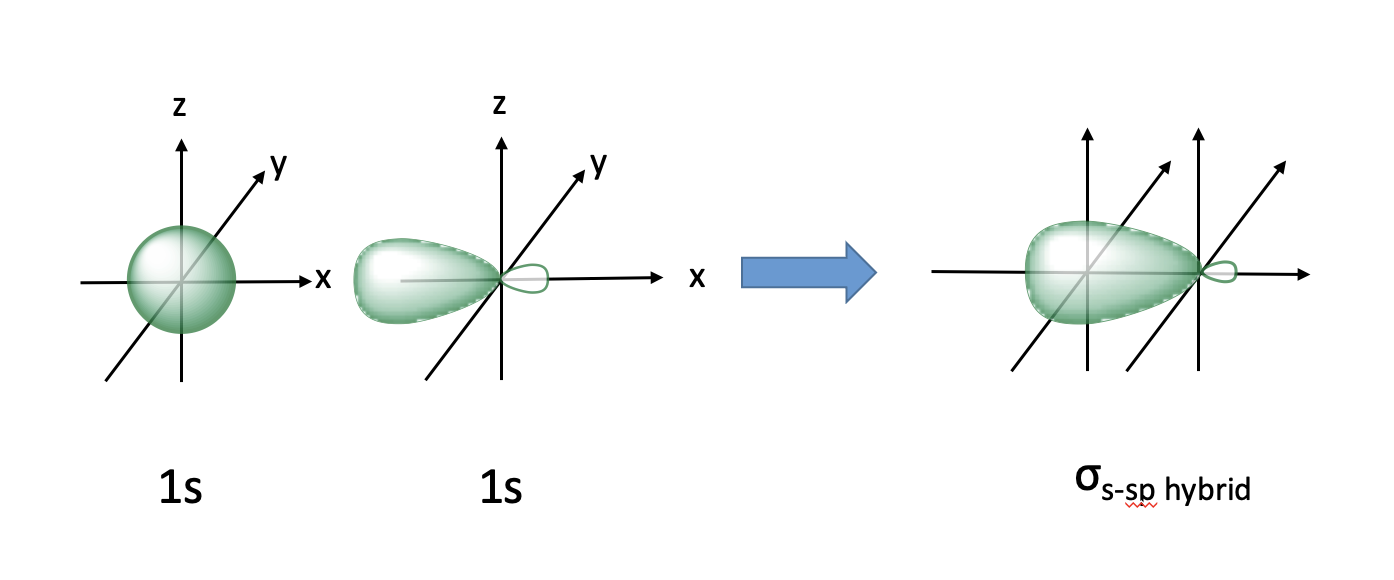
sigma bond with 1s and sp orbital
lobe opposite new orbital, involved in substitution reactions
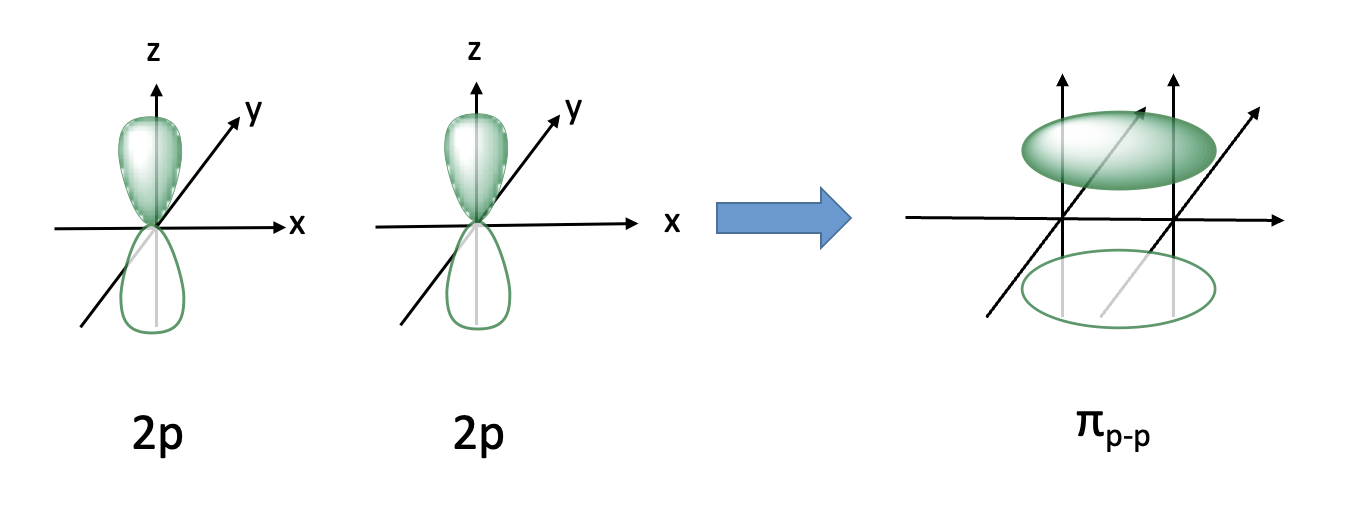
what are pi bonds?
covalent bonds formed from overlap of 2 orbital lobes laterally
the node has no electron density
there is a plane w no electron density
fixed( no free rotation)(leads to isomers)
what is the influence of lone pairs?
lone pairs are held closer to the atom than bonding e- so exert repulsion on other e-
this compreses bond angles, -2.5 for every lp
