A&P 2 Lab - Exam 3
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Label the Nephrons
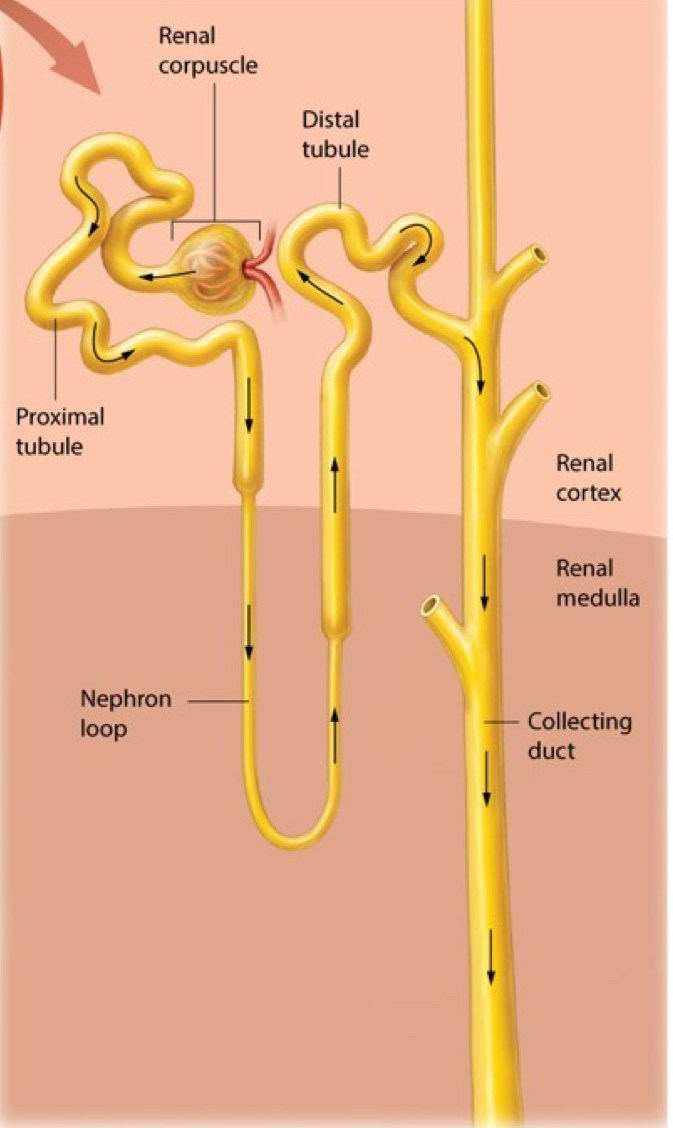
In short, it filters blood and produces urine. Nephrons filter blood to remove waste, reabsorb necessary substances back into the bloodstream, and secrete additional waste products to form urine.
Histology of Kidneys
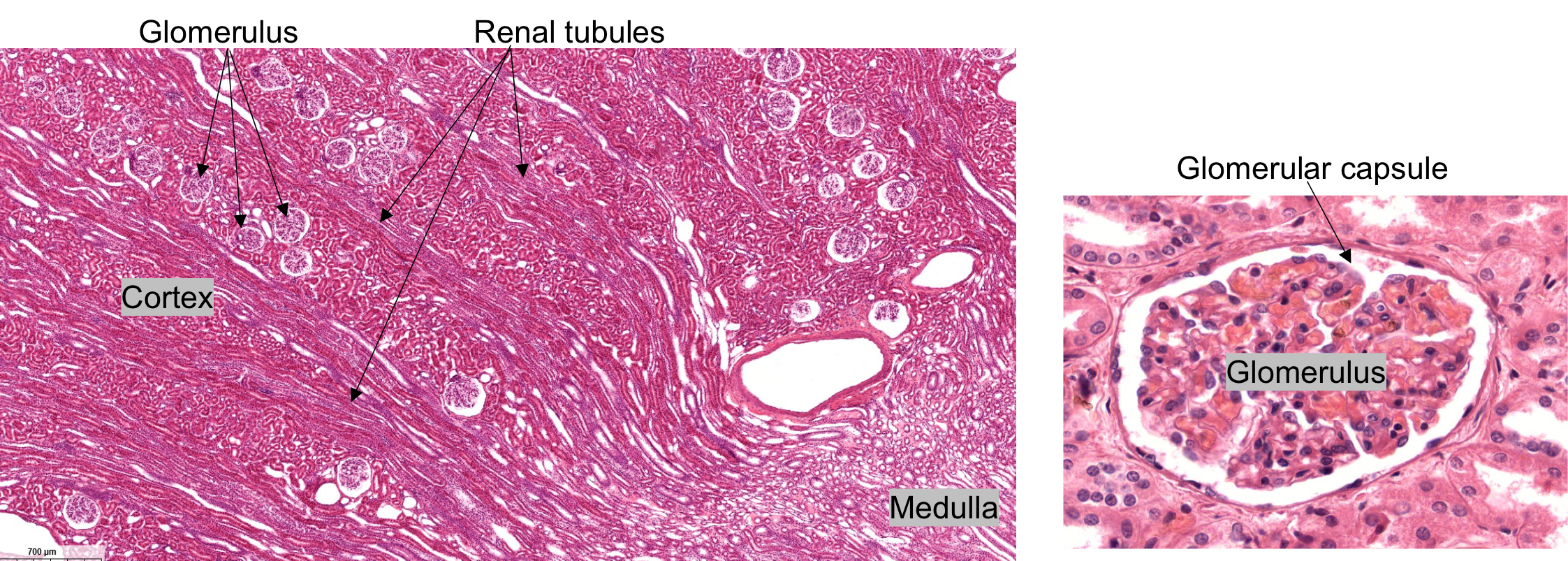
Identify the following histology:
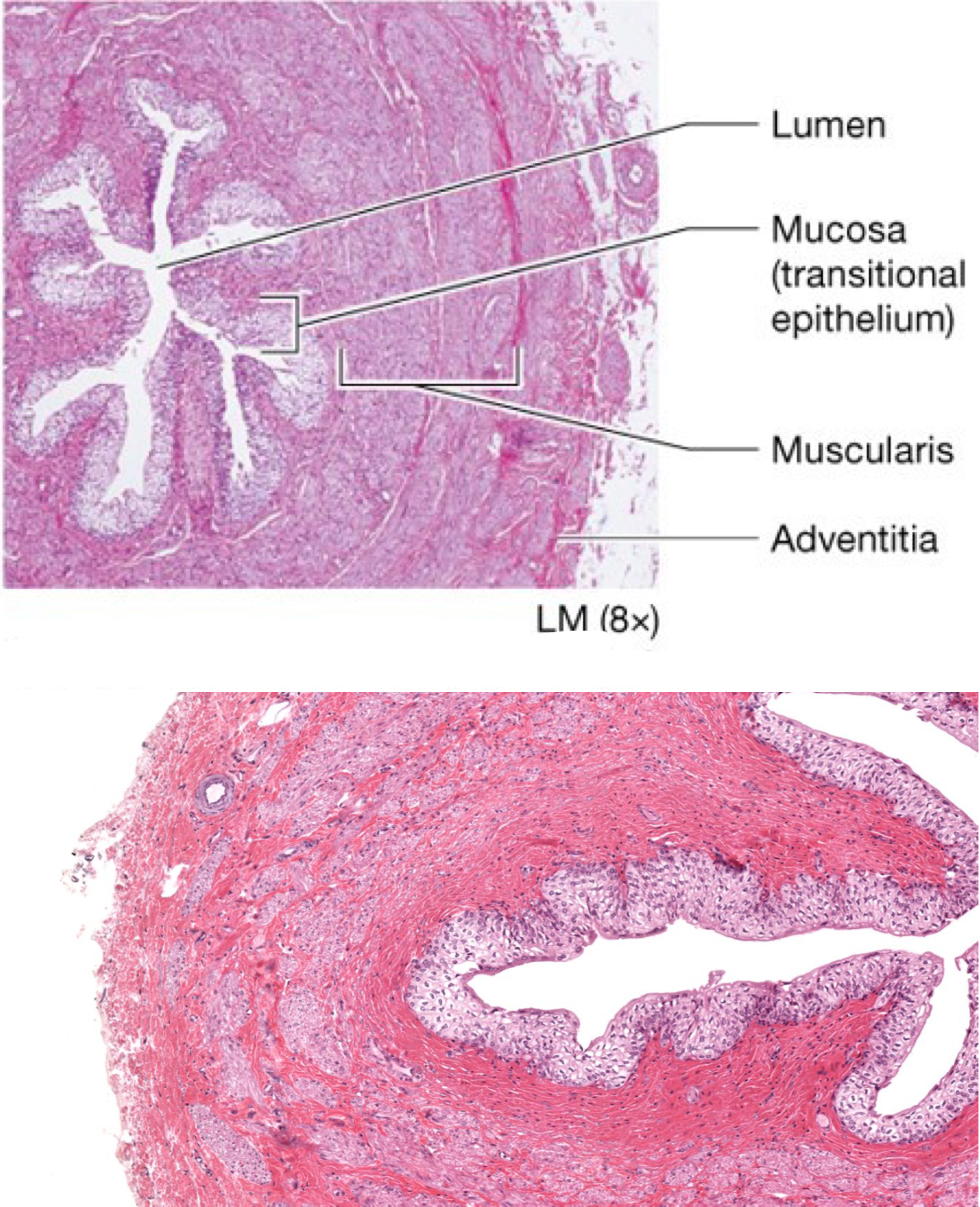
Ureter
Identify the following histology:
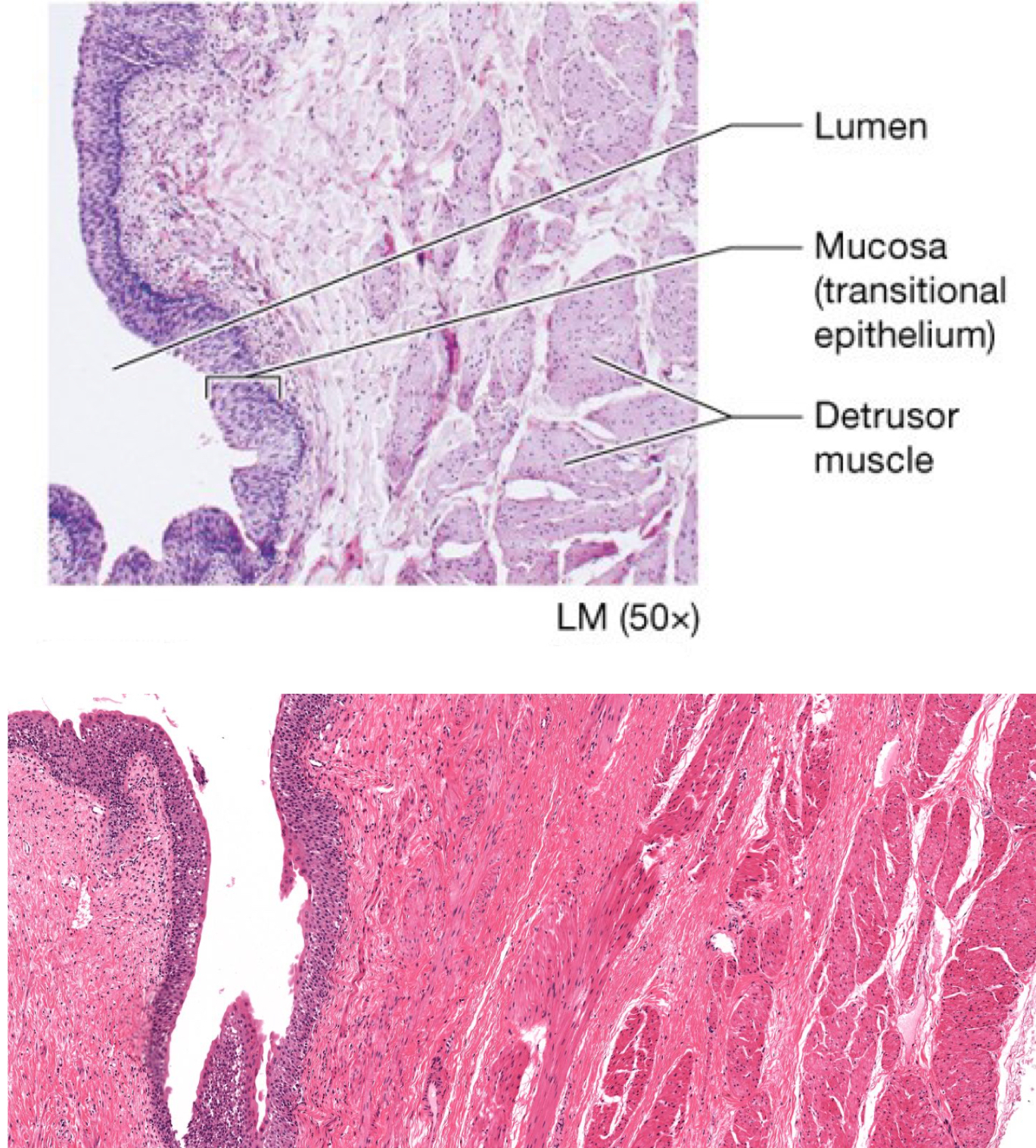
Bladder
What steroid/hormone is synthesized and released by the adrenal cortex
Aldosterone
Give an example of a medical condition for each scenario:
Cloudy urine
Sugar presence inn urine
Protein in the urine
UTI / Dehydration / Kidney Stones
Diabetes
Chronic Kidney Disease
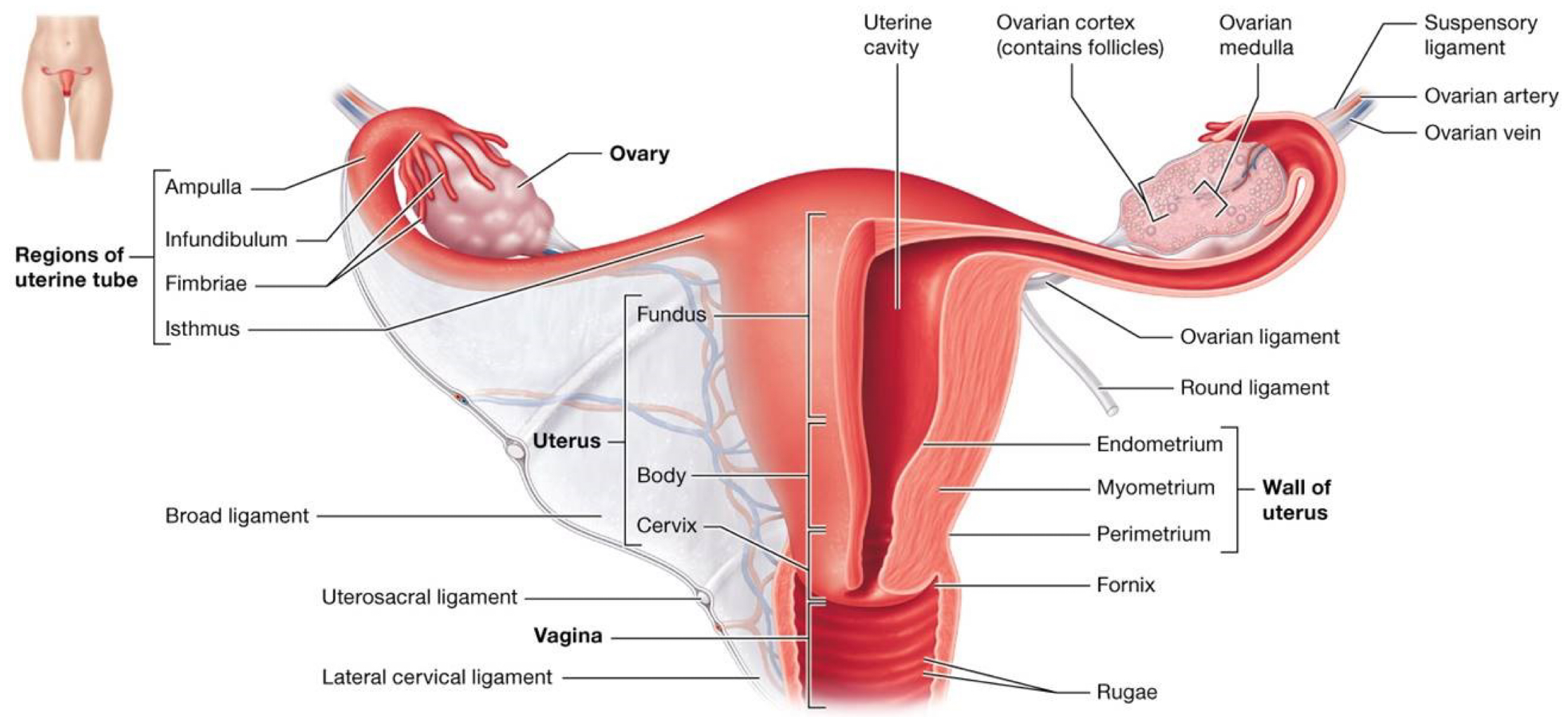
Label the female reproductive organs:
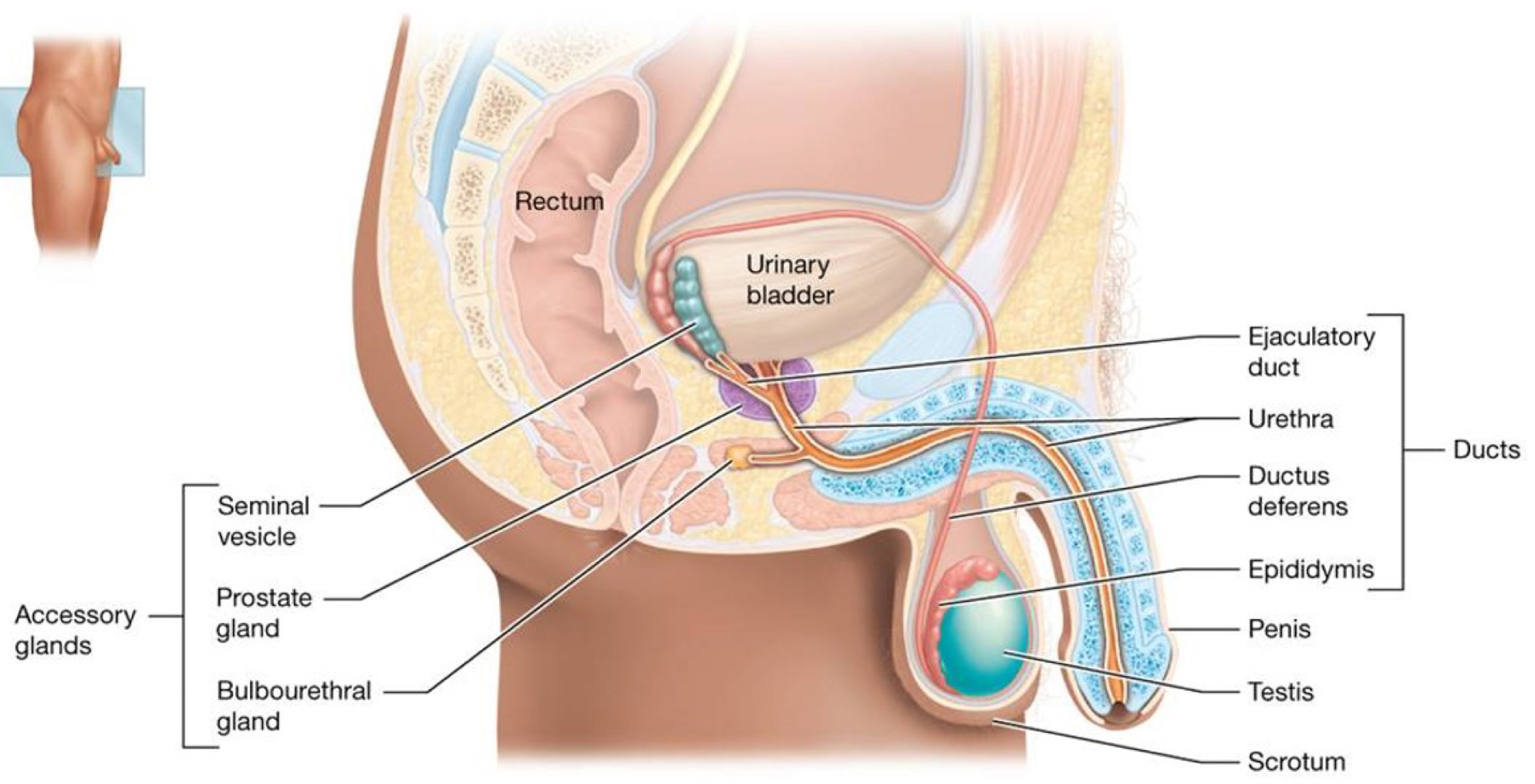
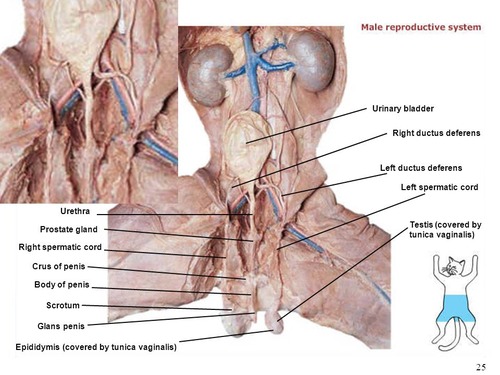
Label the male reproductive organs:
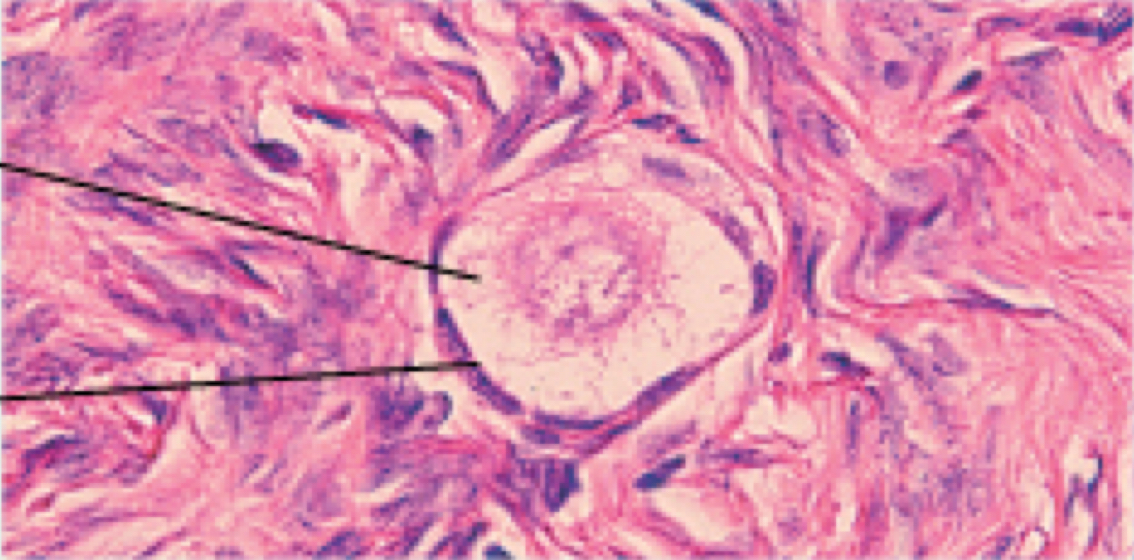
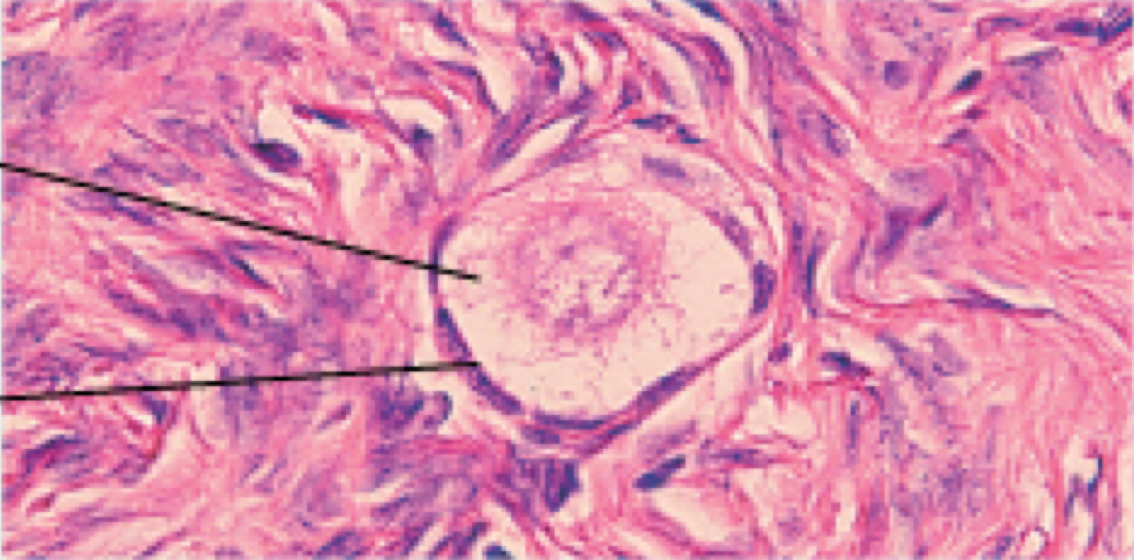
Identify the following histology:
Primordial follicle (ovarian cycle)
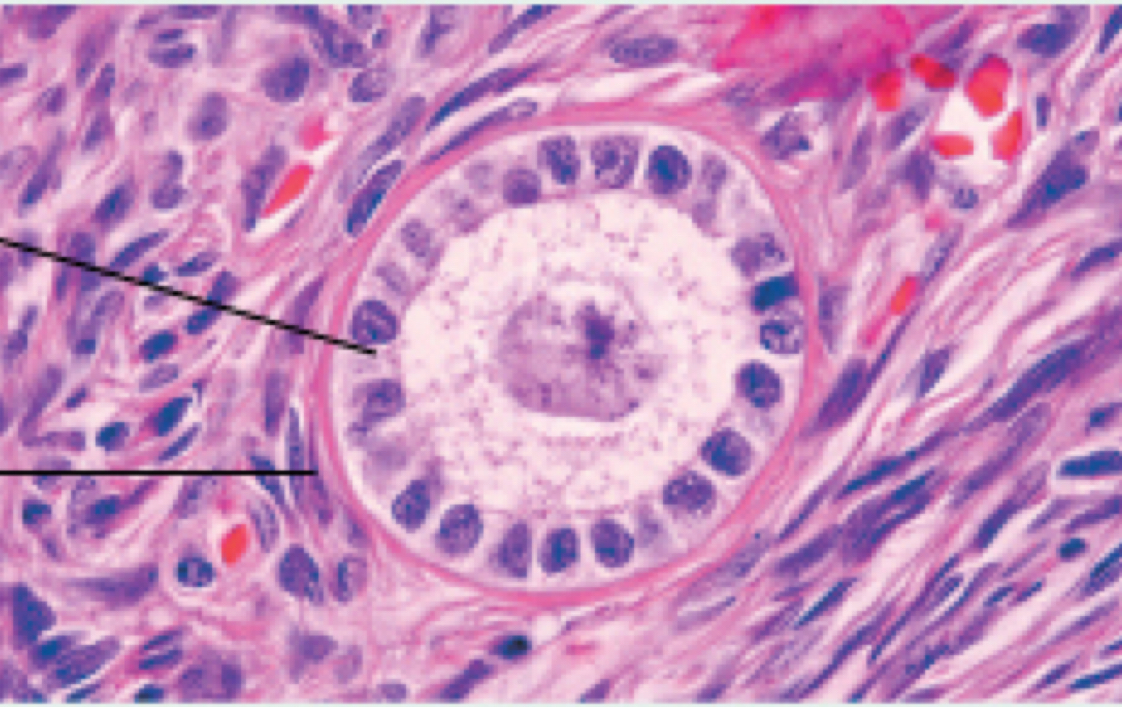
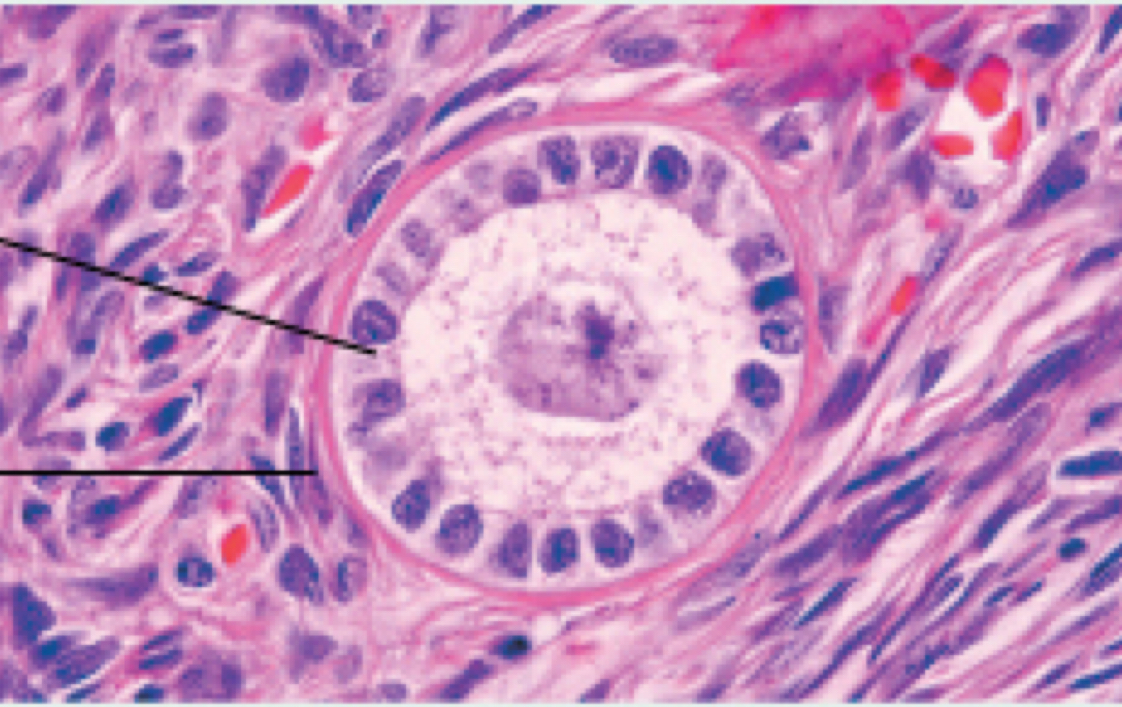
Identify the following hsitology:
Primary follicle (ovarian cycle)
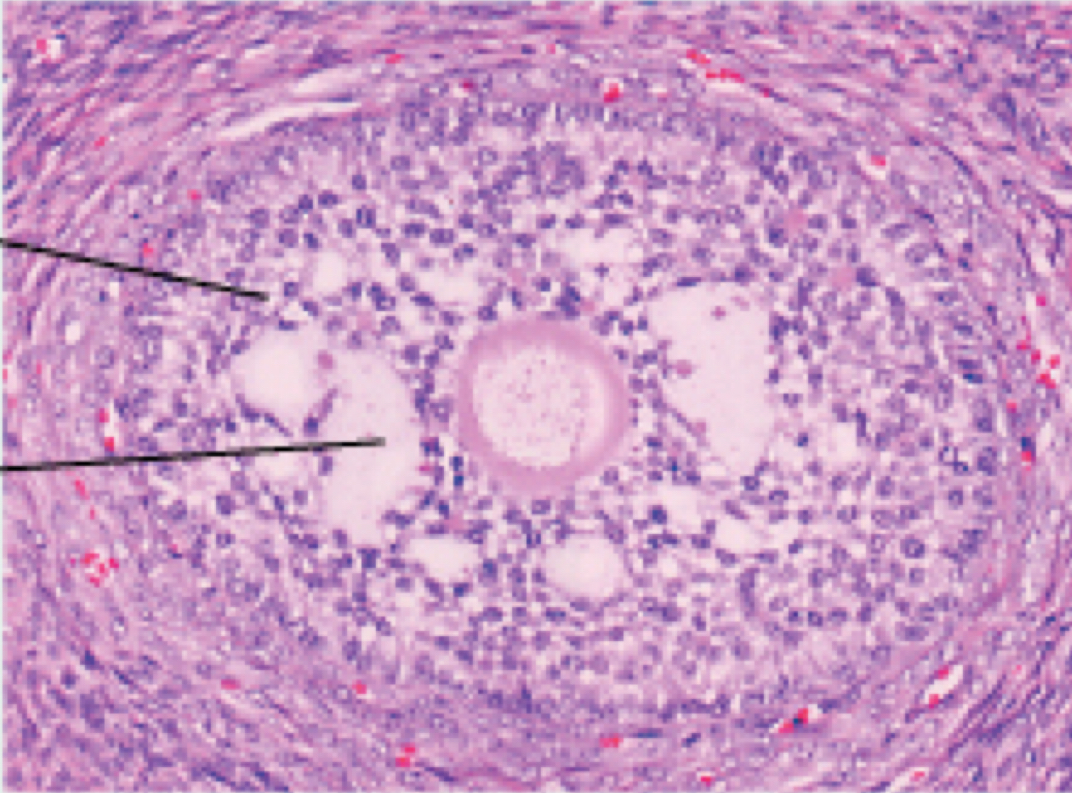
Identify the following histology:
secondary follicle (ovarian cycle)

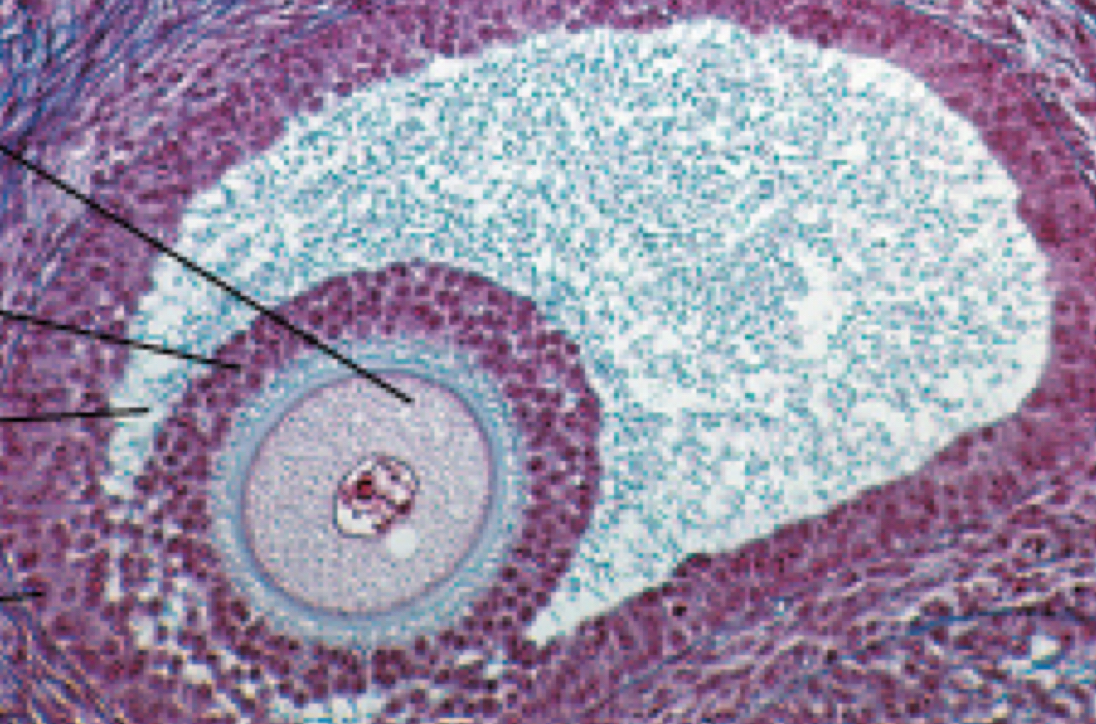
Identify the following histology:
Vesicular follicle


Identify the following histology:
Corpus Luteum (ovarian cycle)
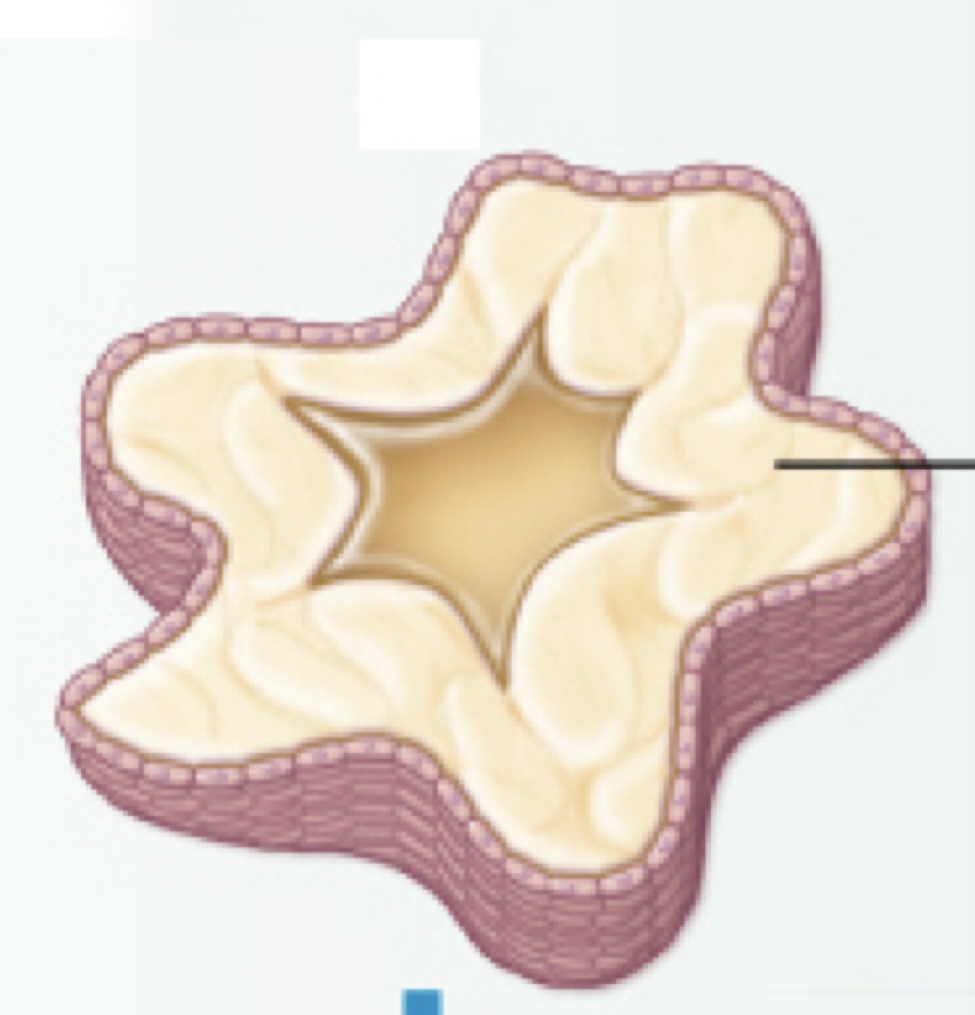
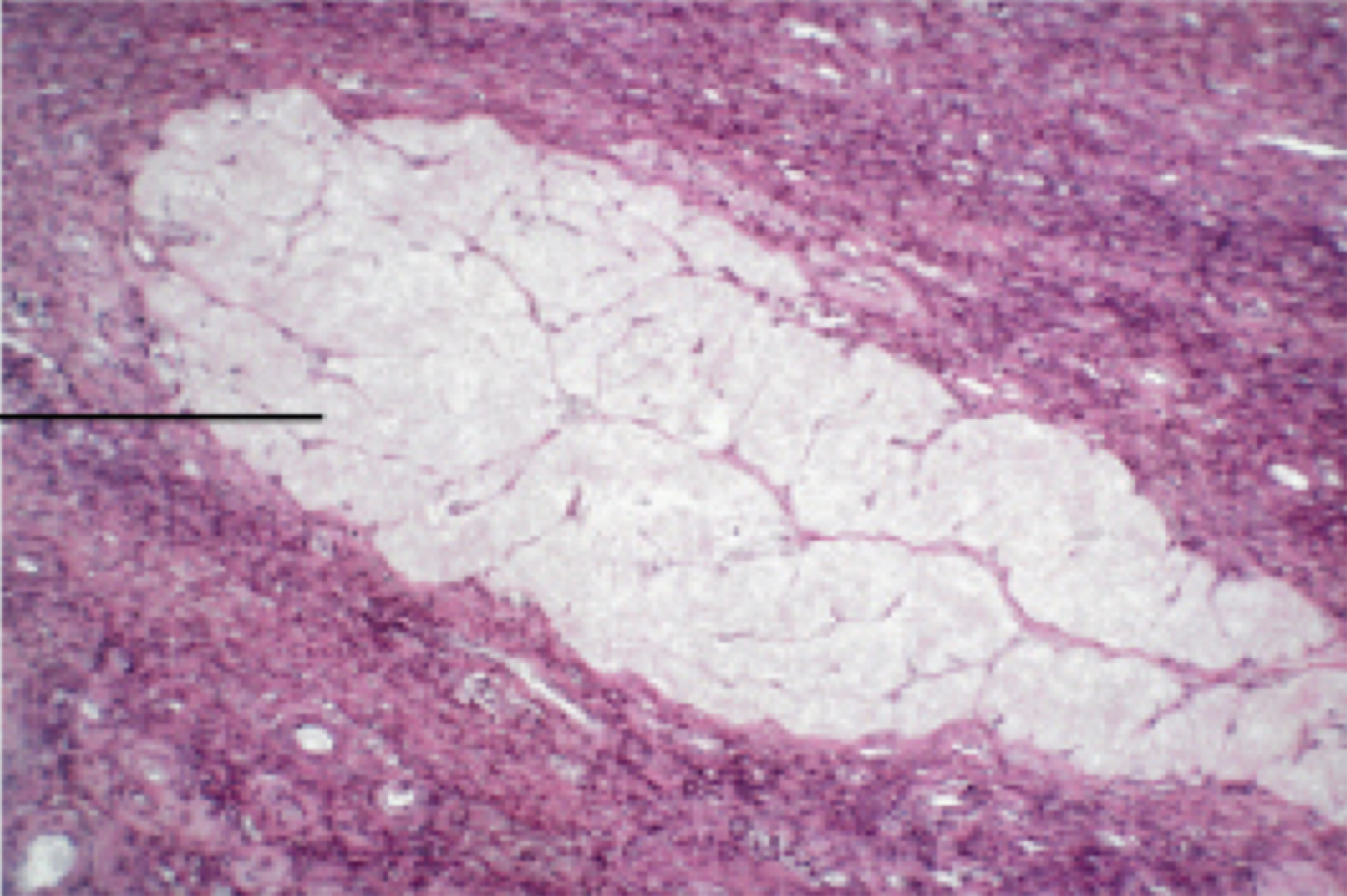
Identify the following histology:
Corpus albicans
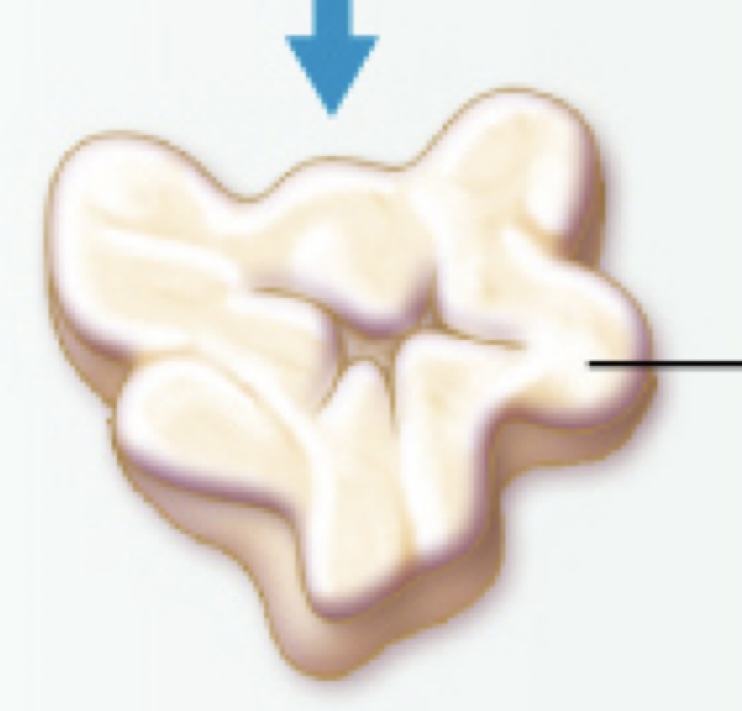
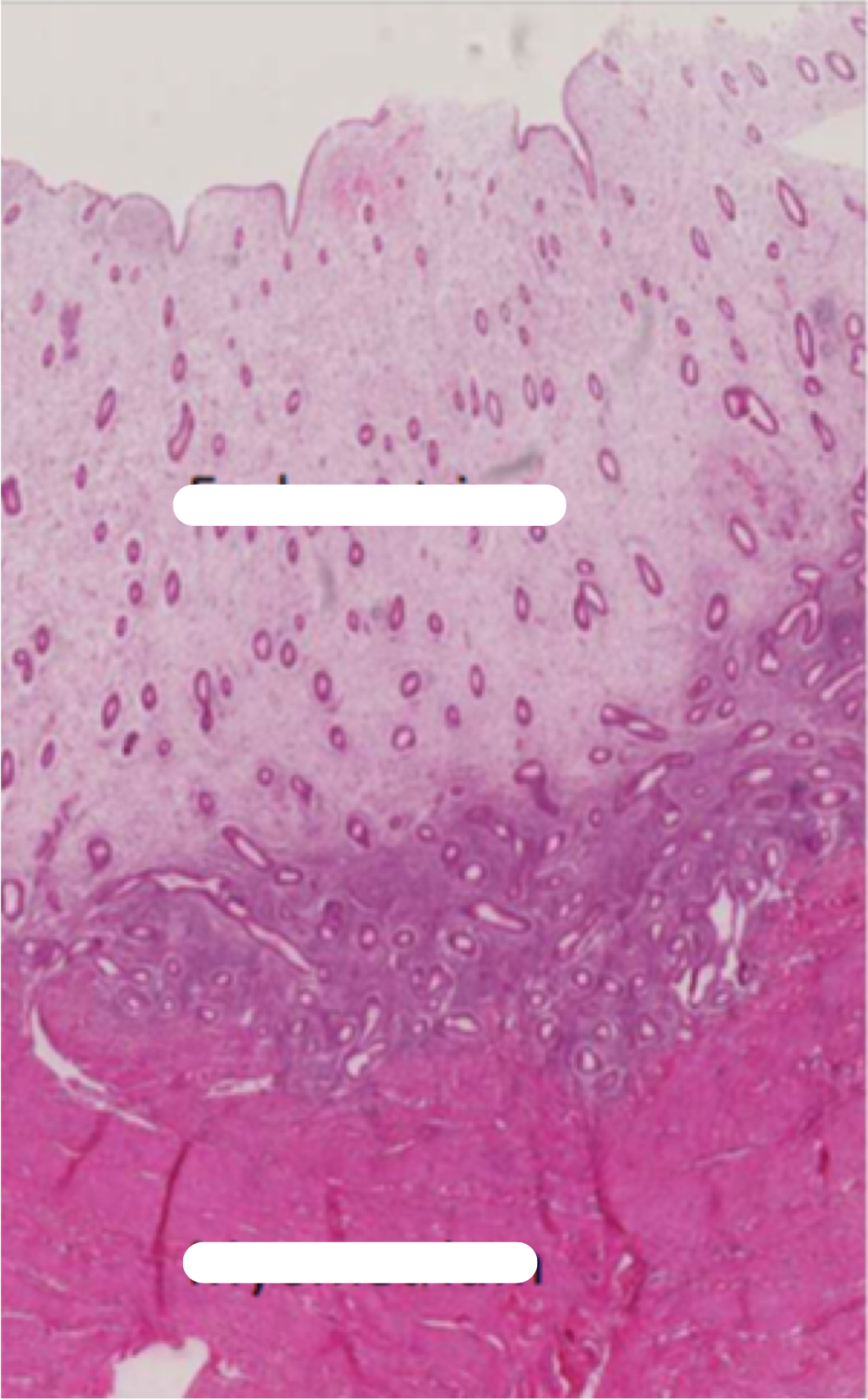
Identify the following histology:
Endometrium (top), myometrium (bottom)
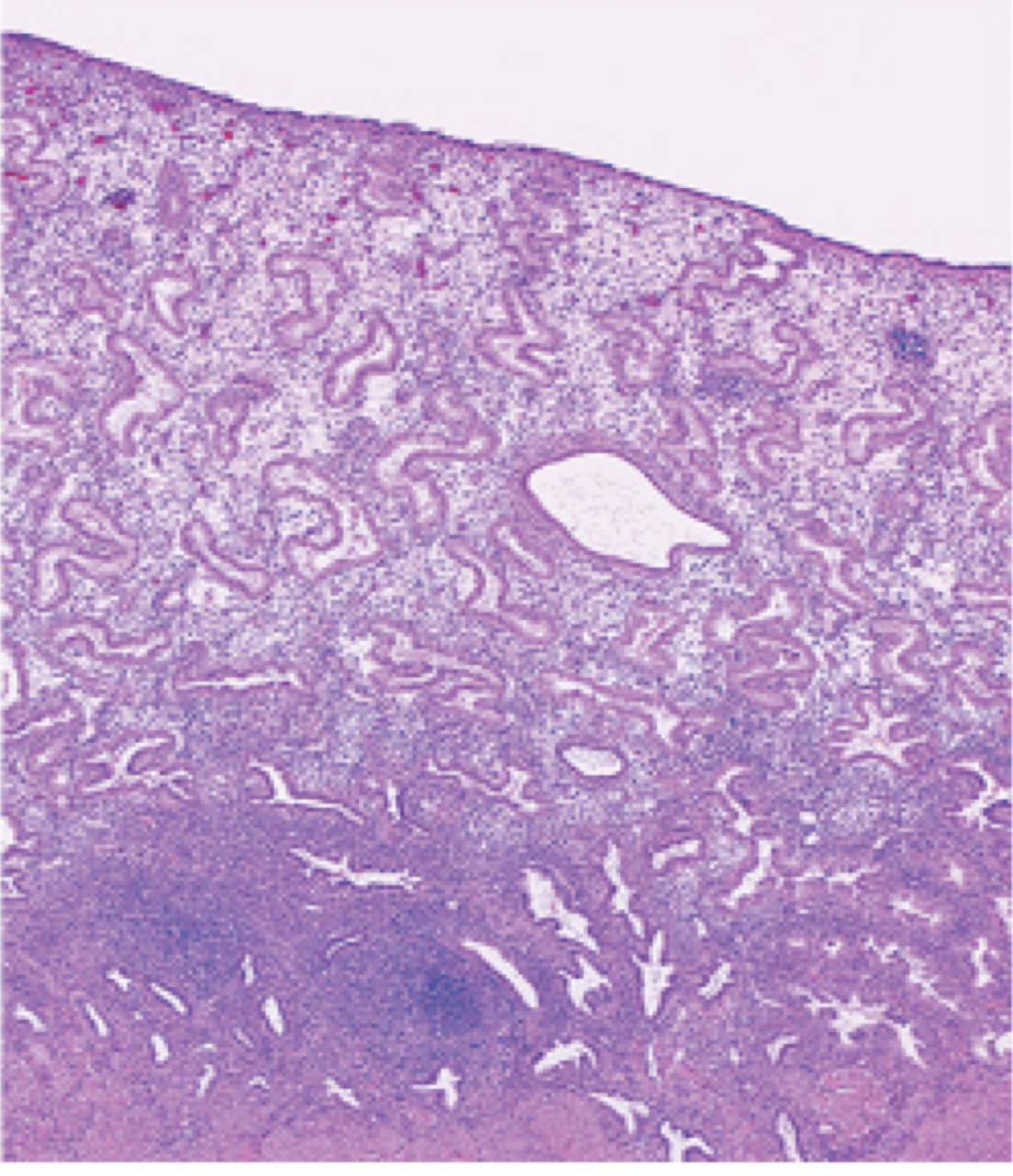
Identify the following histology:
Endometrium
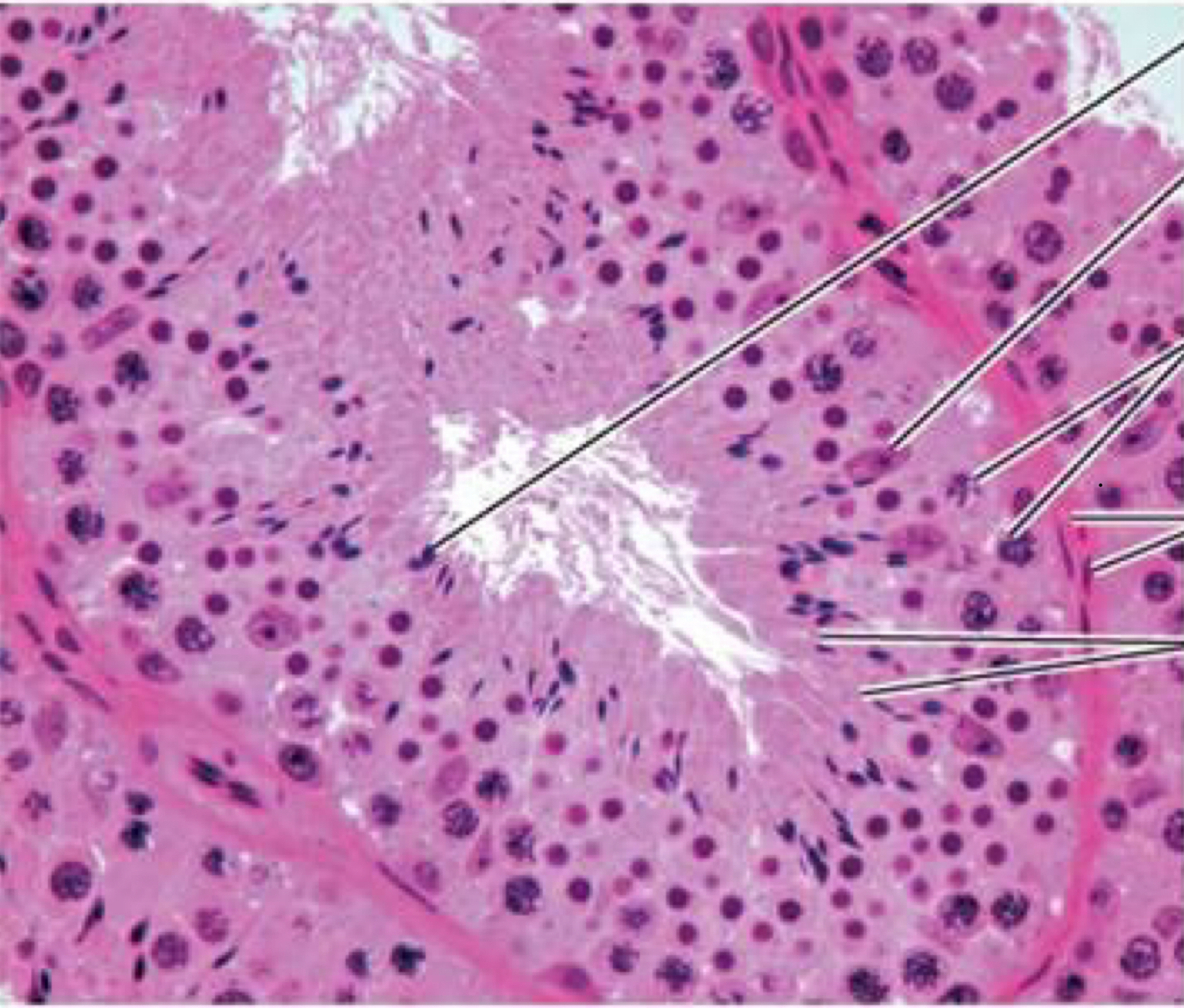
Identify the following histology:
Testes (Seminiferous Tubule)
Label the endocrine organs:
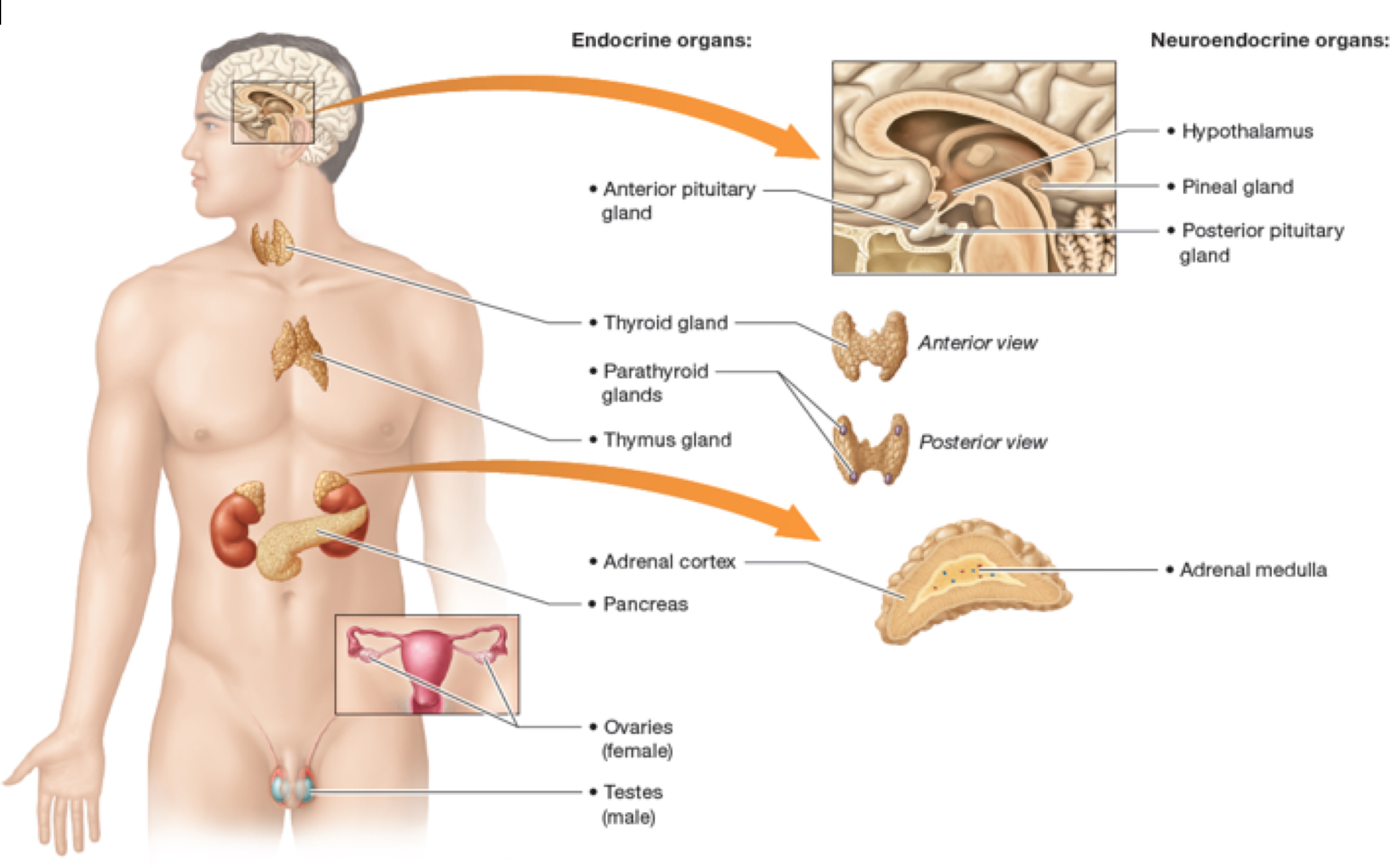
What is growth hormone?
Formed by the anterior pituitary gland, its main function is to regulate growth of various target tissues including skeletal and cardiac muscle, adipose, liver, cartilage, and bone. The short-term effects include increased glood glucose and fatty acid levels so they can be used by cells for fuel and raw materials for growth.
What is prolactin?
Produced in the anterior pituitary, it stimulates growth of mammary gland tissue, initiates milk production after childbirth, and maintains milk production during breastfeeding
What is melatonin?
Produced by the pineal gland, main target tissues are sleep-regulation centers in brainstem
What is glucagon?
produced and secreted from alpha cells; promotes reactions that increase blood glucose levels
What is oxytocin?
produced by hypothalamus; stored in axon terminals of posterior pituitary gland
Functions primarily focused on reproduction
Target cells are in mammary glands of breast tissue and smooth muscle of uterus
In nursing mother, breastfeeding stimulates oxytocin release which causes mammary glands to contract resulting in milk ejection
During childbirth, oxytocin stimulates the smooth muscle of the uterus to contract to assist with labor and deliver
What is FSH?
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH; gonadotropin)
▪ in Males—stimulates cells of testes to produce chemicals that bind and concentrate testosterone
▪ in Females—FSH and LH together trigger production of estrogen; FSH also triggers maturation of ovarian follicles into vesicular follicles
What is LH?
Luteinizing hormone (LH; gonadotropin)
▪ Male—stimulates production of testosterone by testes
▪ Female—stimulates production of estrogen and progesterone from ovaries; triggers release of oocyte in ovulation

Identify the following histology:
Thyroid
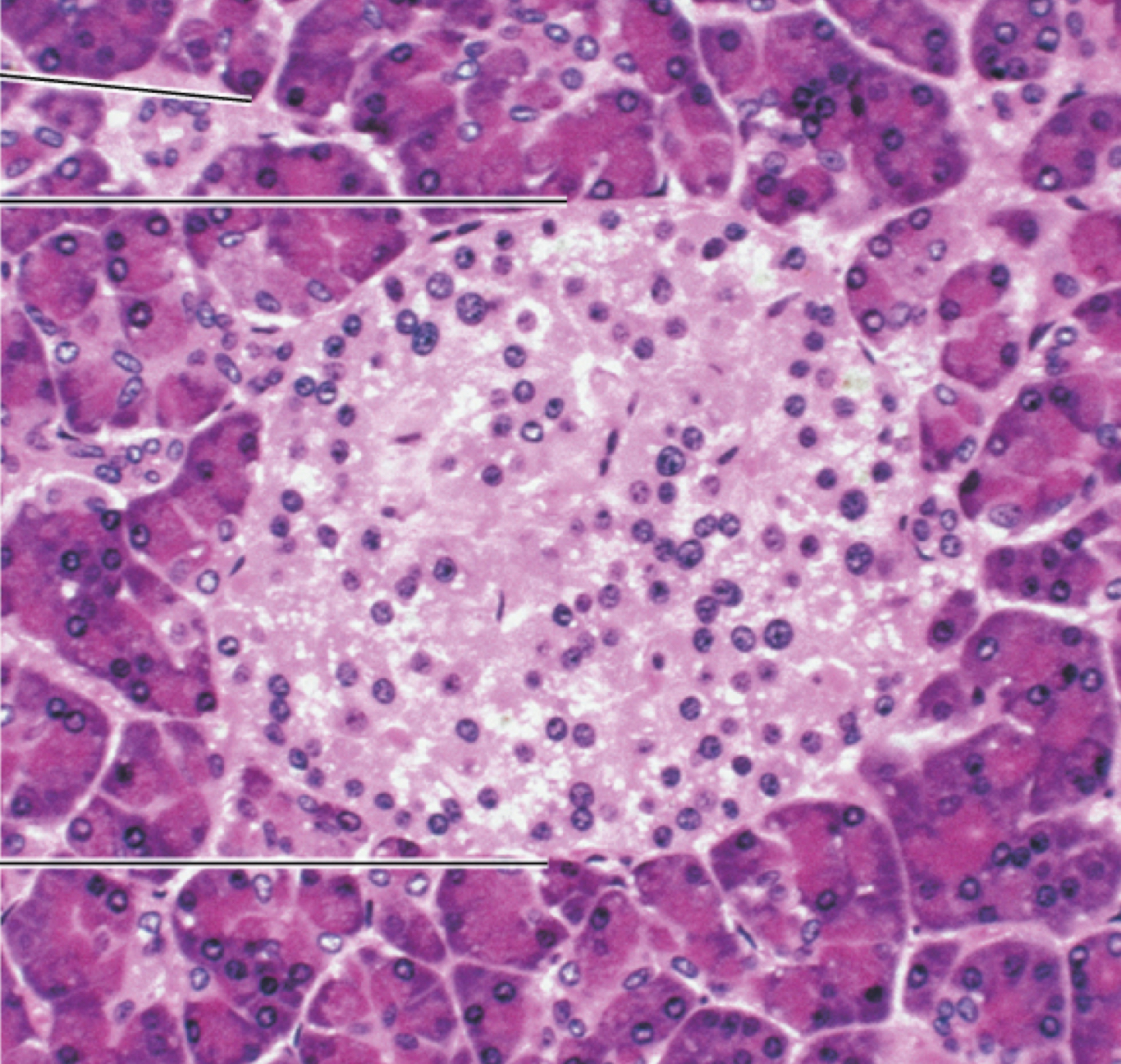
Identify the following histology:
Pancreas
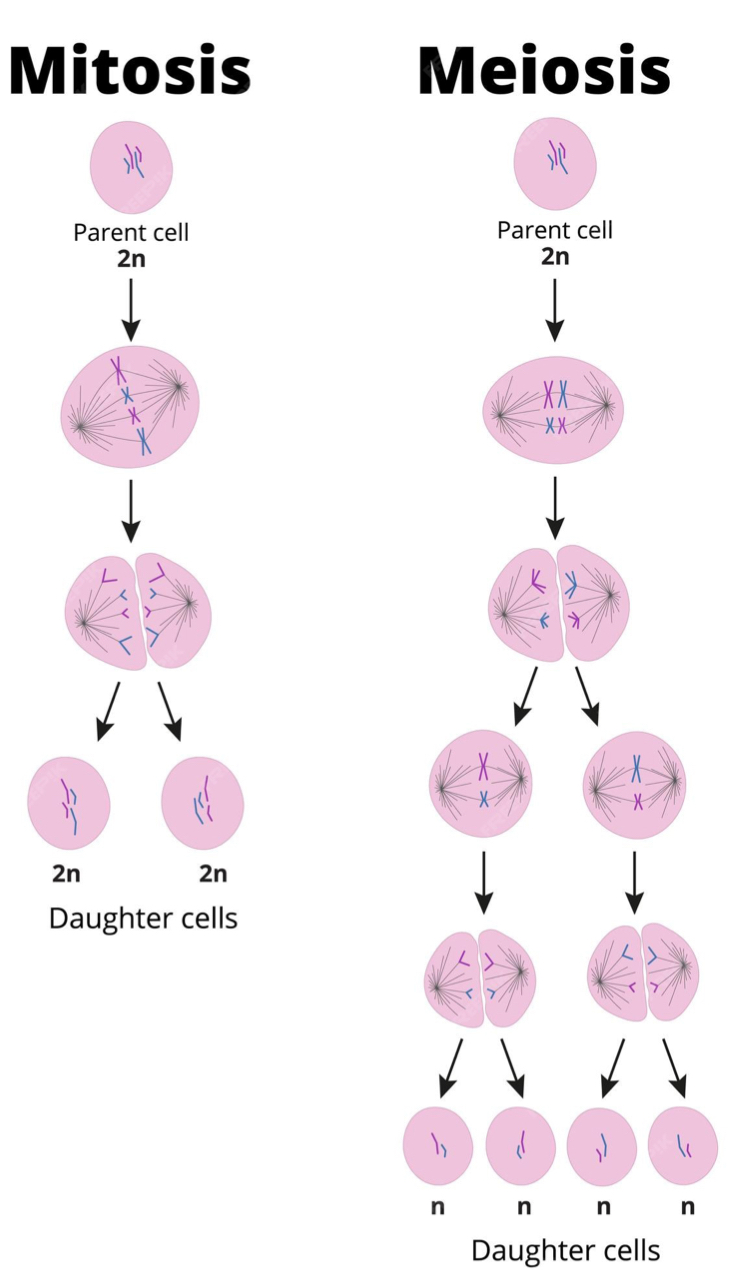
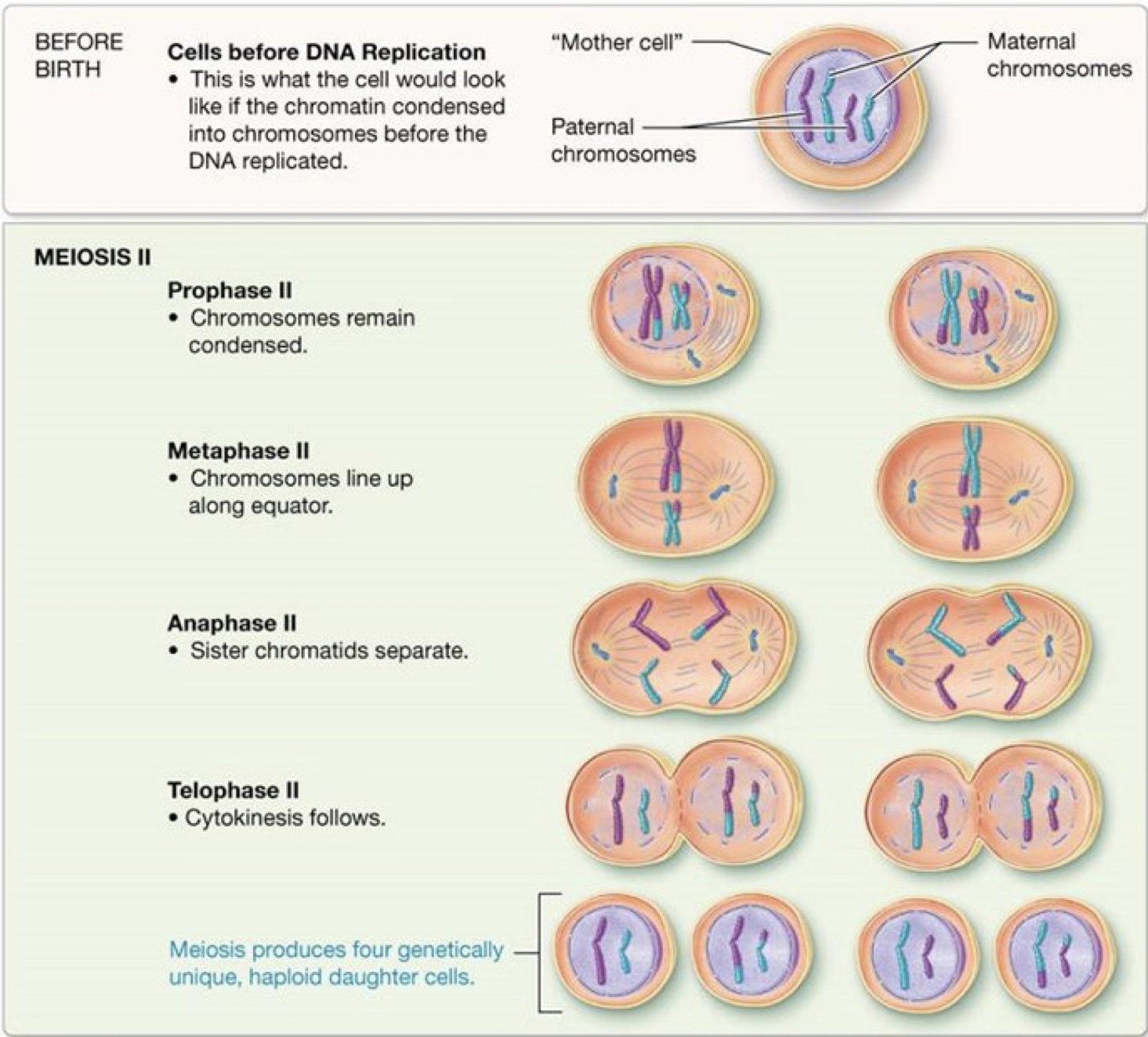
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis results in two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Mitosis is for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction
Meiosis is for sexual reproduction, creating gametes (sperm and egg cells)
Meiosis 1
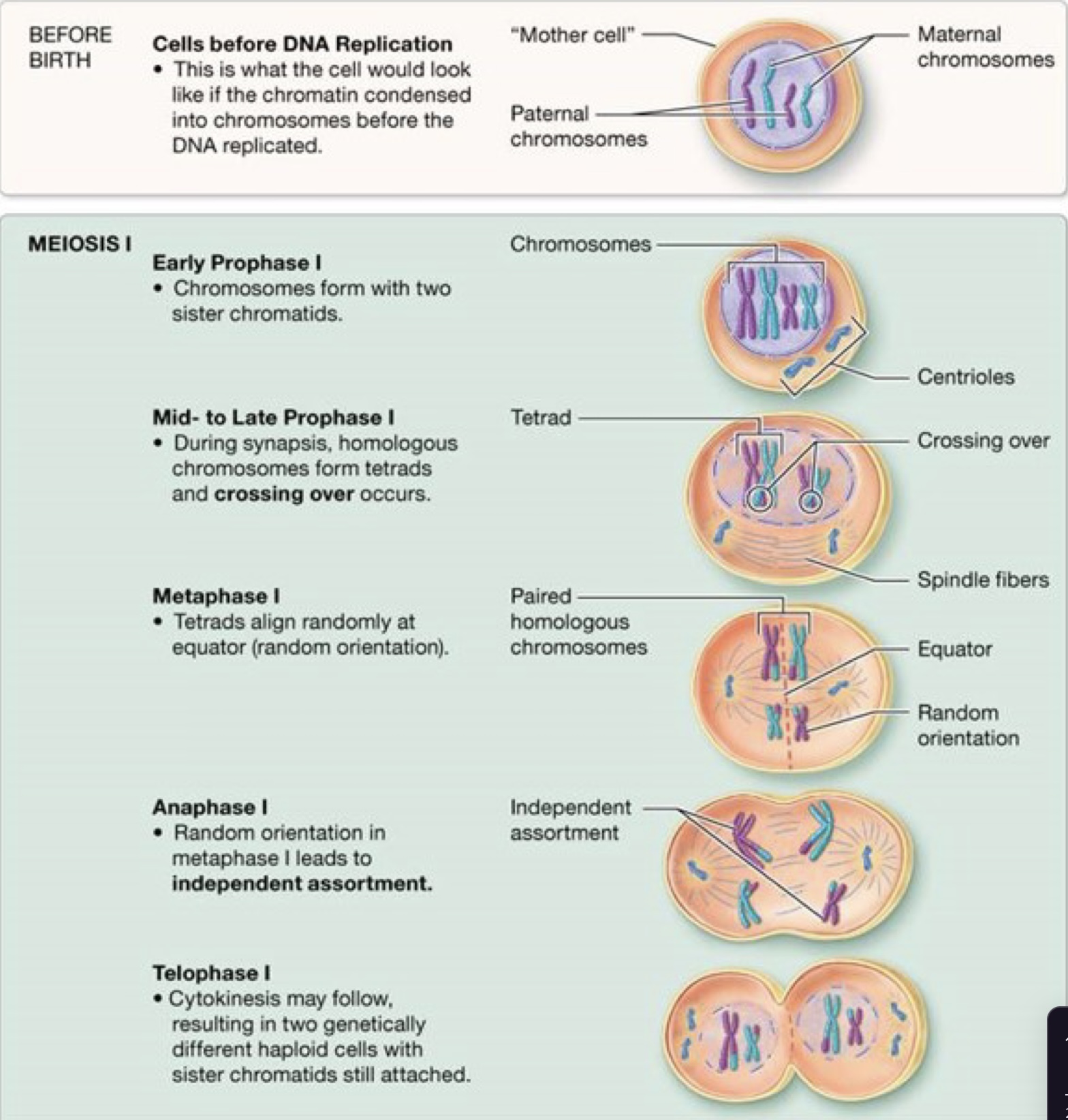
Meiosis 2
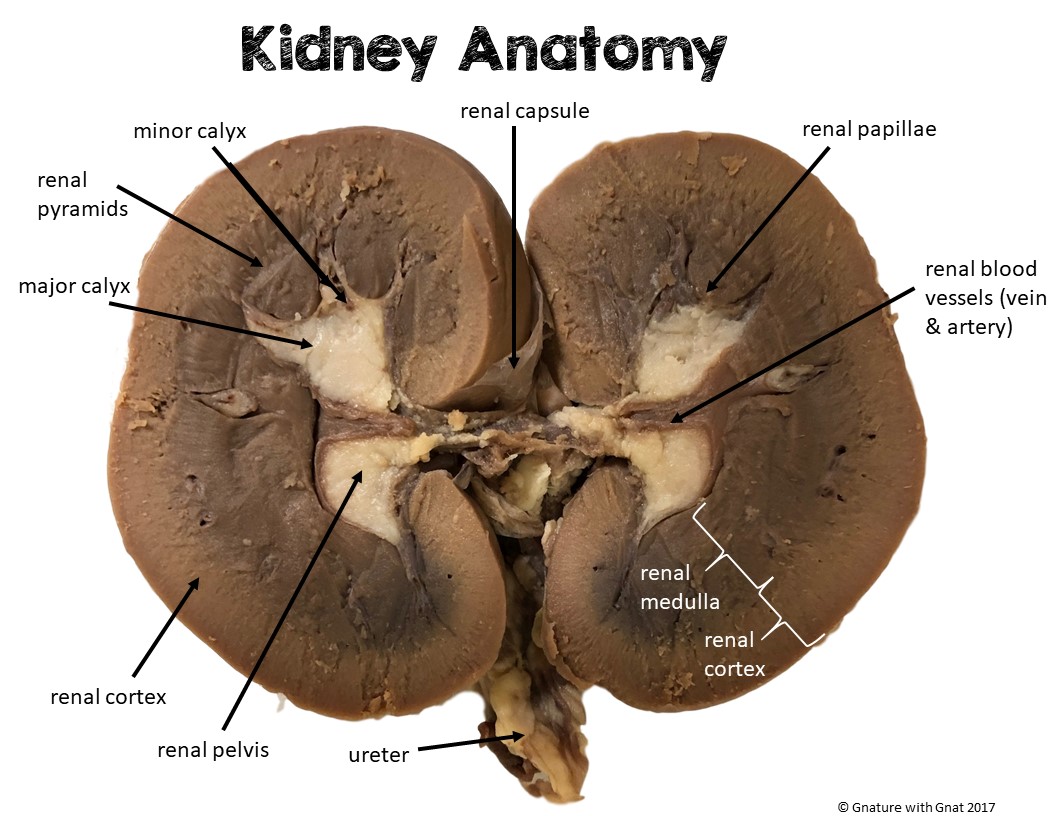
Sheep Kidney Dissection
Male Cat Reprodcutive System
Female Cat Reproductive System:

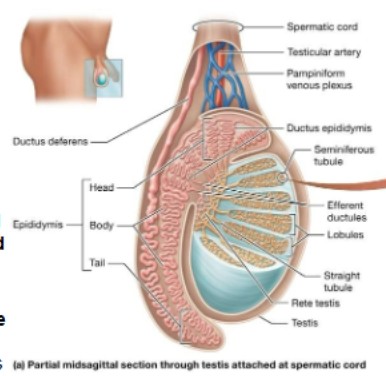
Label the male internal reproductive organ: